Master Metal Plating Sourcing: Essential Insights for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal plating
In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, metal plating serves as a cornerstone for enhancing the durability, performance, and aesthetic appeal of a vast array of products. From automotive components to electronic devices, the right plating can significantly influence product longevity and customer satisfaction. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and established sectors in Europe—understanding the nuances of metal plating is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricate landscape of metal plating by providing actionable insights into various plating methods such as electroplating, electroless plating, and immersion techniques. It covers a range of essential metals and alloys, including nickel, chrome, and gold, alongside their specific applications and selection criteria. Furthermore, it delves into manufacturing and quality control practices to ensure compliance and consistency, while offering strategic advice on supplier selection, sourcing strategies, and cost optimization.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to navigate these complexities, this guide empowers them to make informed sourcing decisions. Whether optimizing for regulatory compliance in Europe, addressing logistical challenges in Africa, or leveraging high-volume production in South America and the Middle East, buyers will find valuable insights that foster supply chain resilience and drive sustainable growth in the competitive field of metal plating.
Understanding metal plating Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel Plating | Durable, corrosion-resistant, bright or matte finish | Automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery | Excellent wear/corrosion resistance; moderate cost; brittle over time |
| Chromium (Chrome) Plating | High-gloss, hard, excellent corrosion resistance | Automotive parts, appliances, decorative fittings | Superior aesthetics, durability; environmental/safety concerns |
| Zinc Plating | Economical, sacrificial corrosion protection, matte/bright | Construction hardware, fasteners, electronics | Cost-effective rust prevention; limited lifespan in harsh environments |
| Gold Plating | Outstanding conductivity, non-tarnishing, aesthetic appeal | Electronics, connectors, luxury goods, aerospace | Top-tier conductivity/aesthetics; high cost; soft, prone to wear |
| Tin Plating | Solderable, non-toxic, matte/silvery finish | Food processing equipment, electronics, wires | Good for food-safe/PCB use; limited wear resistance; can whisker |
Nickel Plating
Nickel plating is highly regarded for its durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries. Its ability to provide either a bright or matte finish allows for versatility in design. For B2B buyers, especially those in humid or coastal regions, nickel plating offers significant benefits in terms of extending the lifespan of components. However, buyers should be aware of the potential brittleness over time, which may impact long-term performance.
Chromium (Chrome) Plating
Chrome plating is synonymous with high-gloss finishes and exceptional resistance to corrosion and wear. It is primarily used in automotive parts and decorative fixtures, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality. While the visual appeal can drive consumer demand, B2B buyers must navigate regulatory concerns related to environmental and safety standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. The long-term value can be considerable, but higher production costs and compliance requirements should be factored into procurement strategies.
Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is favored for its cost-effectiveness and sacrificial protection against corrosion, making it a go-to option for construction hardware and fasteners. Its application is particularly beneficial in environments prone to moisture, although its lifespan may be limited under harsh conditions. B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America can leverage zinc plating for short-to-medium term protection, but should plan for regular maintenance and inspections to maximize durability.
Gold Plating
Gold plating stands out for its superior electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal, making it essential in electronics and luxury goods. Its non-tarnishing nature enhances reliability in electronic connectors, crucial for high-performance applications. However, the high cost and softness of gold plating pose challenges, particularly in high-wear environments. Buyers must ensure secure logistics and certified sourcing to protect their investment, while weighing the benefits of performance against the financial implications.
Tin Plating
Tin plating is widely recognized for its non-toxic properties and excellent solderability, making it a standard choice in electronics and food processing applications. Its matte or silvery finish is safe for direct food contact, which is critical in the food industry. However, while tin plating is effective for certain applications, its limited wear resistance may necessitate careful consideration for components subject to frequent handling or environmental stress. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications to determine the best use of tin plating.
Related Video: Metal Plating Process | A Complete Guide To Its Types And Technique.
Key Industrial Applications of metal plating
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Metal Plating | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Corrosion-resistant coatings for components | Extended lifespan of parts, reduced maintenance costs | Supplier compliance with environmental regulations |
| Electronics | Gold plating for connectors and circuit boards | Enhanced electrical performance and reliability | Quality assurance and certification of materials |
| Aerospace | Nickel plating for engine components | Improved durability and resistance to extreme conditions | Proven track record of supplier in aerospace standards |
| Construction | Zinc plating for fasteners and hardware | Cost-effective rust protection in harsh environments | Availability of local suppliers for logistics efficiency |
| Food Processing | Tin plating for food contact equipment | Non-toxic, safe for direct food contact | Compliance with food safety standards |
Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, metal plating is primarily used to apply corrosion-resistant coatings to components such as engine parts and body panels. This process significantly extends the lifespan of these parts, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacements. For international buyers, especially in regions with high humidity or coastal environments, sourcing suppliers that adhere to stringent environmental regulations and provide consistent quality is essential to ensure long-term performance and compliance.
Electronics Applications
Gold plating is widely utilized in the electronics sector for connectors and circuit boards due to its exceptional conductivity and resistance to tarnish. This application enhances the reliability and performance of electronic devices, critical for manufacturers aiming to deliver high-quality products. Buyers must prioritize sourcing from certified suppliers who can guarantee the quality and purity of gold, as well as adherence to international standards, to ensure the integrity of their electronic components.
Aerospace Applications
Nickel plating is employed in aerospace for engine components and other critical parts that require exceptional durability and resistance to extreme conditions. This application not only improves the lifespan of components but also contributes to overall aircraft safety. B2B buyers in the aerospace sector should focus on suppliers with a proven track record in meeting aerospace industry standards and certifications, ensuring that all products withstand rigorous testing and performance evaluations.
Construction Applications
Zinc plating is commonly applied to fasteners and hardware used in construction, providing cost-effective protection against rust and corrosion. This is particularly valuable in regions with harsh environmental conditions, where metal components are exposed to moisture and corrosive elements. Buyers should consider local suppliers to optimize logistics and reduce lead times, while also assessing the quality and thickness of zinc coatings to ensure adequate protection for their specific applications.
Food Processing Applications
In the food processing industry, tin plating is used for equipment that comes into direct contact with food, offering a non-toxic and safe option for manufacturers. This application is crucial for ensuring compliance with food safety standards while maintaining functionality. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous food safety regulations and provide certified materials, as any compromise in quality can lead to significant legal and health implications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal plating
When selecting materials for metal plating, B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors that directly impact product performance, cost, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common plating materials: Nickel, Chromium, Zinc, and Gold. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can influence the decision-making process for international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Nickel Plating
Key Properties: Nickel plating is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications in automotive and aerospace sectors.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantages of nickel plating include its wear resistance and ability to provide a bright or matte finish. However, it can be more expensive than other options and may become brittle over time, particularly in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Nickel’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, such as coastal areas in Africa or humid climates in South America. However, buyers should be aware of the potential for brittleness, which may necessitate additional engineering considerations.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider the environmental regulations surrounding nickel plating, particularly in Europe, where stricter guidelines are in place.
Chromium Plating
Key Properties: Chromium plating offers exceptional hardness and a high-gloss finish. It is highly resistant to corrosion and wear, making it suitable for decorative applications and components that require aesthetic appeal.
Pros & Cons: The aesthetic qualities of chrome plating are a significant advantage, along with its durability. However, the environmental impact of chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium, raises concerns. Regulatory compliance can be a challenge, especially in Europe and the Middle East, where strict environmental laws apply.
Impact on Application: Chromium is often used in automotive parts and household appliances. Its resistance to tarnishing makes it suitable for decorative items, but buyers must ensure that suppliers adhere to safety and environmental regulations.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who comply with local and international environmental standards. The cost of chrome plating can also vary significantly based on regulatory compliance, so procurement strategies must account for potential price fluctuations.
Zinc Plating
Key Properties: Zinc plating is primarily valued for its sacrificial corrosion protection. It is economical and provides a matte or bright finish, making it a popular choice for mass-produced items.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of zinc plating is its cost-effectiveness and ability to protect against rust. However, its lifespan can be limited in harsh environments, and it may not be suitable for components exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Impact on Application: Zinc plating is commonly used in construction hardware and fasteners, especially in areas with moderate corrosion risks. Buyers in Africa and South America can benefit from its affordability, but regular maintenance is essential to maximize service life.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the local climate and environmental conditions when selecting zinc plating. Compliance with standards such as ISO and ASTM can also influence sourcing decisions.
Gold Plating
Key Properties: Gold plating is renowned for its outstanding electrical conductivity and resistance to tarnishing. It is often used in high-performance electronic applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of gold plating is its superior conductivity and aesthetic appeal. However, it comes at a high cost, and its softness makes it prone to wear, which can limit its applications.
Impact on Application: Gold plating is essential in electronics and aerospace industries, where reliability and performance are critical. Buyers must weigh the benefits of gold’s conductivity against its cost and potential for abrasion.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Secure logistics and certified sourcing are crucial due to gold’s high value. Buyers should also be aware of compliance with international standards and the potential for fluctuations in gold prices.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal plating | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel | Automotive, aerospace components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Can become brittle over time | Medium |
| Chromium | Automotive parts, decorative items | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Environmental compliance issues | Medium to High |
| Zinc | Construction hardware, fasteners | Cost-effective rust protection | Limited lifespan in harsh conditions | Low |
| Gold | Electronics, aerospace applications | Outstanding conductivity | High cost and wear susceptibility | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights to make informed decisions in the metal plating landscape. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is critical for optimizing product performance and ensuring compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal plating
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for metal plating are critical components that B2B buyers must understand to ensure they are sourcing high-quality products. This section delves into the typical stages of metal plating manufacturing and the essential quality control measures that should be in place to meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Manufacturing Processes for Metal Plating
The metal plating process consists of several distinct stages, each playing a vital role in ensuring the final product meets the required specifications. The main stages of the manufacturing process include:
1. Material Preparation
Substrate Cleaning
The initial step involves meticulous cleaning of the substrate, which is the base material that will be plated. This cleaning is crucial as any surface contaminants can interfere with the adhesion of the plating material. Techniques such as abrasive cleaning, ultrasonic cleaning, and acid washing are commonly employed to achieve a pristine surface.
Surface Treatment
After cleaning, the substrate may undergo additional treatments, such as etching or activation, to enhance its surface properties. This step may involve the application of a primer or a conductive layer to promote better adhesion of the plating material.
2. Plating Process
Electroplating
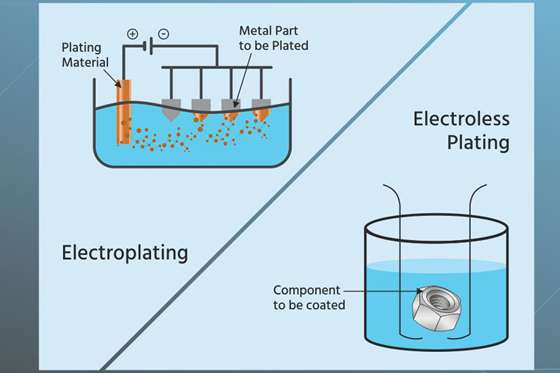
This is one of the most prevalent methods, wherein the substrate is submerged in an electrolyte solution containing metal ions. An electric current is applied, causing the metal ions to deposit onto the substrate, forming a uniform layer. This method is favored for its precision and ability to produce thin coatings.
Electroless Plating
Unlike electroplating, electroless plating does not require an electric current. Instead, a chemical reaction reduces metal ions in the solution, allowing for an even deposition over complex geometries. This technique is beneficial for achieving a consistent coating thickness across irregular surfaces.
Immersion Plating
In this method, the substrate is dipped into a solution containing metal ions, where the substrate metal displaces the ions, resulting in a layer of the new metal. This technique is often used for applications requiring a quick turnaround.
Rapid Plating
For high-volume production, rapid plating techniques are employed, allowing for faster processing times. However, this speed can sometimes compromise the quality of the coating, necessitating a careful balance between efficiency and quality.
3. Finishing
Once the plating process is complete, the plated components undergo finishing operations, which may include polishing, buffing, or passivation. These steps enhance the aesthetic appeal and performance of the plated surface, such as improving corrosion resistance or achieving a specific finish.
4. Assembly
In some cases, plated components will proceed to assembly, where they are integrated into larger systems or products. Proper handling and storage during this phase are essential to prevent damage to the plated surfaces.
Quality Assurance in Metal Plating
Quality assurance is paramount in metal plating to ensure that the final products meet both customer specifications and regulatory requirements. Several international standards and industry-specific guidelines govern quality assurance processes.
Relevant International Standards
-
ISO 9001
This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to organizations of any size. Companies involved in metal plating should implement ISO 9001 to demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. -
CE Marking
For products sold in Europe, compliance with CE marking is crucial. This certification indicates that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. -
API Standards
For applications in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential. These standards ensure that materials and processes used in metal plating meet the rigorous demands of this sector.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in metal plating involves several critical checkpoints to monitor and ensure product quality throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the plating process, regular monitoring is conducted to assess parameters such as plating thickness, adhesion quality, and uniformity of the coating. This ongoing inspection helps identify any issues early in the process. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
After the plating and finishing stages, final inspections are carried out to verify that the products meet all relevant specifications. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance testing.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of plated products:
-
Adhesion Testing
Methods such as the tape test and cross-cut test evaluate how well the plating adheres to the substrate. -
Thickness Measurement
Techniques like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and magnetic induction are used to measure the thickness of the plating layer, ensuring it meets required specifications. -
Corrosion Testing
Salt spray tests and other accelerated corrosion tests are conducted to assess the durability of the plating under various environmental conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance. Here are some strategies to effectively assess supplier QC:
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards firsthand. This can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request documentation of quality control processes, including inspection reports, testing results, and certifications. This transparency can help verify the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product compliance. This is particularly useful for international buyers who may not be able to conduct on-site audits.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances:
-
Regulatory Compliance
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that impact product quality. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that suppliers comply with these standards. -
Cultural Differences
Understanding cultural differences in business practices can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers. This can enhance the quality assurance process and foster stronger partnerships. -
Supply Chain Considerations
Buyers should assess the entire supply chain, including logistics and transportation factors, that could affect product quality. Ensuring that products are handled and stored appropriately throughout the supply chain is vital for maintaining quality.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for metal plating is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal plating Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of metal plating is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies. Here, we break down the key components of cost, the factors influencing pricing, and actionable tips for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Metal Plating
-
Materials
The cost of materials varies significantly based on the type of plating used. For instance, gold and nickel plating are generally more expensive due to the high cost of raw materials. Additionally, the choice of substrate (e.g., steel, aluminum) also impacts overall material costs. -
Labor
Labor costs depend on the complexity of the plating process and the region of manufacturing. Skilled labor is often required for processes like electroless plating, which can drive up costs. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America and Africa, buyers may find more competitive pricing. -
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes expenses related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. The overhead can vary by region and the efficiency of the manufacturing process. Buyers should consider suppliers with optimized operations to minimize these costs. -
Tooling
Tooling costs involve the equipment and tools needed for the plating process. Custom tooling for specific applications can add significant expense. It’s crucial for buyers to discuss tooling costs upfront, especially for specialized plating jobs. -
Quality Control (QC)
Investing in robust QC processes ensures consistent quality and compliance with industry standards. While this adds to the upfront costs, it can prevent costly rework or product failures in the long run. -
Logistics
Transporting plated components can be costly, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect logistics costs. Buyers should evaluate logistics strategies to optimize shipping expenses. -
Margin
The supplier’s profit margin can vary greatly based on their operational model and market position. Understanding the typical margins in the region can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Establishing long-term contracts can also lead to favorable pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom plating solutions or specific finishes can increase costs. Clear communication of requirements helps avoid surprises in pricing.
-
Materials: Fluctuations in raw material prices can impact overall costs. Buyers should stay informed about market trends affecting material availability and pricing.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications (e.g., ISO) can lead to increased costs but often justify the investment through enhanced product performance.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, experience, and reputation can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services but provide greater assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can significantly affect overall costs, particularly regarding responsibility for shipping and customs duties. Understanding these terms is essential for budget planning.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to negotiate better terms. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can also encourage favorable pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the initial cost but also maintenance and longevity. Higher upfront costs may be justified by lower operational costs over time.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing dynamics. For instance, buyers in Europe may face higher regulatory compliance costs compared to those in less regulated markets in Africa or South America.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly monitor market trends and material prices to anticipate cost changes. This proactive approach allows for better budgeting and procurement planning.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence before making procurement decisions.
Spotlight on Potential metal plating Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘metal plating’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal plating
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with metal plating is essential for international B2B buyers. These insights help facilitate informed decision-making and ensure that procurement processes align with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal used in plating, which indicates its quality and suitability for particular applications.
– B2B Importance: Different grades exhibit varying levels of durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Buyers should choose the appropriate grade to ensure product longevity and performance in their intended environment. -
Thickness of Coating
– Definition: This property measures the depth of the metal layer applied during the plating process, typically expressed in micrometers (µm).
– B2B Importance: The thickness directly impacts the effectiveness of corrosion resistance and wear protection. Buyers must specify the required thickness to meet industry standards and ensure product reliability. -
Adhesion Strength
– Definition: Adhesion strength indicates how well the plated layer bonds to the substrate material.
– B2B Importance: Strong adhesion prevents flaking and peeling, which can lead to premature failure of components. Ensuring adequate adhesion is crucial for maintaining product integrity, especially in harsh operational conditions. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: This property measures the ability of the plated metal to withstand corrosive environments without deteriorating.
– B2B Importance: Understanding corrosion resistance is vital for applications in industries like automotive and aerospace, where components are exposed to challenging environments. Buyers should assess this property to prevent costly maintenance and replacements. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: Surface finish describes the texture and appearance of the plated surface, which can be glossy, matte, or textured.
– B2B Importance: The finish impacts both aesthetic appeal and functional performance, such as friction reduction. Buyers in sectors like consumer electronics should prioritize surface finish to enhance product attractiveness and usability.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensures that sourced components meet specific quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Buyers must consider MOQ to manage inventory levels and ensure cost-effectiveness. It also influences procurement strategies, especially for startups and smaller companies.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ enables buyers to compare prices and terms across different suppliers, fostering competitive bidding and better procurement decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, as they clarify costs, risks, and responsibilities, helping buyers avoid misunderstandings and potential disputes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time refers to the total time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory management and project planning. Buyers should factor lead times into their procurement strategies to avoid delays in production schedules. -
Plating Bath Composition
– Definition: This term describes the chemical makeup of the solution used in the plating process, which can influence the properties of the final product.
– Importance: Buyers should be aware of the plating bath composition as it affects the quality, consistency, and environmental impact of the plating process. Ensuring proper composition aligns with regulatory compliance and product standards.
Incorporating these technical properties and trade terms into procurement discussions will enhance communication with suppliers, streamline sourcing processes, and ultimately lead to better purchasing outcomes in the metal plating industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the metal plating Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global metal plating market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Factors such as urbanization, industrialization, and the rising need for corrosion-resistant materials are propelling this growth, particularly in emerging markets in Africa and South America. For international B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing.
Key trends influencing the market include the adoption of advanced technologies such as automation and digitalization in plating processes. Techniques like electroless plating and rapid plating are gaining traction due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles—like IoT and data analytics—enables better monitoring of plating quality and process optimization, which is vital for maintaining competitive advantage.
Moreover, buyers are increasingly focusing on supply chain resilience and flexibility. This is particularly relevant for regions like the Middle East and Europe, where geopolitical factors can impact sourcing strategies. For example, buyers in Spain and South Africa should prioritize suppliers with diversified sourcing options and robust logistics capabilities to mitigate risks associated with raw material fluctuations and transportation challenges.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As environmental concerns escalate, sustainability has emerged as a significant factor in the metal plating industry. The environmental impact of traditional plating processes—particularly concerning waste generation and the use of hazardous chemicals—has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adopt eco-friendly plating techniques, such as non-toxic alternatives and closed-loop systems that minimize waste.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains for compliance with environmental and social standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) standards are becoming essential for establishing credibility. By choosing suppliers who meet these certifications, buyers can ensure their operations align with global sustainability goals.
Furthermore, the adoption of green materials in plating processes—such as biopolymers and water-based solutions—can significantly reduce the environmental footprint. This focus not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally-conscious consumers, thereby enhancing brand reputation.
Brief Evolution/History
The practice of metal plating has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century. Initially used for aesthetic purposes, advancements in technology have transformed plating into a crucial industrial process aimed at enhancing durability and functionality. The introduction of electroplating in the early 20th century marked a significant milestone, allowing for more efficient and uniform coatings. Over the decades, the sector has witnessed innovations such as electroless plating and immersion plating, broadening its applications across industries.
Today, metal plating is not only a means of protection but also an essential component in the manufacturing of high-performance products. As industries continue to innovate, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing is reshaping the landscape, making it imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed and agile in their sourcing strategies.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal plating
-
How do I vet suppliers for metal plating services?
When vetting suppliers, start by assessing their industry reputation through online reviews and client testimonials. Request samples of their previous work to evaluate quality and finish. Ensure they hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) that demonstrate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, check their experience with specific metals and processes pertinent to your needs. Establish communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your requirements, which is crucial for building a reliable partnership. -
Can I customize the metal plating process for my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for metal plating processes to meet specific requirements. You can discuss your desired thickness, finish, and type of metal with potential suppliers. It’s essential to provide detailed specifications, including environmental conditions the plated item will face, to ensure optimal results. Some suppliers may also offer specialized treatments or coatings for enhanced durability or aesthetics. Be sure to confirm their capabilities before finalizing your order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for metal plating?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly by supplier and the complexity of the plating process. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times also depend on factors like order volume, customization, and the supplier’s current workload. On average, expect lead times from 2 to 6 weeks. To avoid production delays, clarify these details during negotiations and consider suppliers who can accommodate your project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing metal plating?
Payment terms can vary between suppliers, but common practices include partial payments upfront (20-50%) and the remainder upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms or discounts for larger orders. Be sure to discuss payment options early in the negotiation process, and consider using secure payment methods that provide buyer protection. Additionally, ensure that you clearly understand the total costs, including shipping and any potential customs duties, to avoid surprises. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in metal plating suppliers?
Quality assurance is critical in metal plating. Look for suppliers who implement rigorous quality control processes, including inspections at various stages of production. Request documentation of their quality management systems and certifications like ISO 9001. Inquire about their testing methods, such as adhesion tests, thickness measurements, and corrosion resistance assessments. A supplier committed to quality will have a clear process for addressing defects and ensuring consistency in their plating services.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What certifications should my metal plating supplier have?
Your metal plating supplier should ideally have certifications that reflect industry standards and quality management practices. Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. For specific industries, additional certifications may be necessary, such as AS9100 for aerospace or TS16949 for automotive applications. Verifying these certifications helps ensure that the supplier adheres to best practices and meets regulatory requirements relevant to your business. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping when sourcing metal plating internationally?
Managing logistics involves coordinating with your supplier on shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Discuss whether they can handle logistics or if you’ll need to work with a freight forwarder. Ensure that you understand customs regulations in your country and any documentation required for importing plated materials. It’s advisable to establish a clear communication channel with your supplier regarding shipping updates and potential delays to mitigate risks and ensure a smooth delivery process. -
What steps should I take if I encounter a dispute with my metal plating supplier?
If a dispute arises, start by addressing the issue directly with your supplier to seek resolution. Document all communications and agreements for reference. If informal negotiations fail, refer to your contract for dispute resolution procedures, which may include mediation or arbitration. Consider involving a legal advisor with experience in international trade to understand your options. Maintaining a professional demeanor throughout the process can often lead to a more favorable outcome for both parties.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal plating
As the global landscape of metal plating continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains paramount for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse types of plating methods, from nickel and chrome to gold and zinc, allows buyers to select the most suitable options tailored to their specific applications. By prioritizing quality control, compliance with local regulations, and supplier reliability, companies can enhance product performance, reduce costs, and ensure long-term durability.
In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to navigate complex supply chains and fluctuating material prices is critical. Buyers should leverage technological advancements in plating processes and consider partnerships that align with their strategic goals.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable and innovative plating solutions will only increase. Now is the time for businesses to engage with suppliers who prioritize environmental stewardship and quality assurance. By investing in informed sourcing strategies today, B2B buyers can secure a competitive edge in tomorrow’s market, driving growth and resilience in their operations. Embrace the future of metal plating—your strategic choices today will shape your success in the years to come.