Master Molding Metal for Competitive Advantage: A B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for molding metal
Navigating the global market for molding metal is essential for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their manufacturing capabilities and product offerings. As industries evolve, the demand for high-performance, intricately designed metal components continues to rise, driven by sectors such as automotive, healthcare, electronics, and industrial tools. Molding metal, particularly through techniques like Metal Injection Molding (MIM), allows businesses to achieve remarkable precision and scalability, making it a pivotal process in modern manufacturing.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Egypt. It covers a variety of critical topics: the different types of molding processes available, the materials and their specific applications, best practices in manufacturing and quality control, as well as strategies for supplier evaluation and sourcing. Additionally, it delves into cost structures and market dynamics, providing valuable insights that can help streamline procurement decisions.
By leveraging the knowledge presented in this guide, B2B buyers can make informed choices that not only enhance their operational efficiency but also foster stronger supplier relationships. With a clear understanding of the molding metal landscape, businesses can position themselves competitively in the global market, ensuring they meet the ever-evolving demands of their customers.
Understanding molding metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard MIM (Conventional MIM) | Utilizes fine metal powders with polymer binders; ideal for high volumes | Automotive, medical devices, electronics, defense | Excellent for complex, high-strength parts; moderate tooling costs; limited to small-medium sizes |
| High-Performance Alloy MIM | Incorporates advanced alloys like titanium and tungsten; exceptional properties | Aerospace, medical implants, high-wear parts | Superior mechanical properties; higher costs; ideal for demanding environments |
| Micro-MIM | Capable of ultra-fine features (<1 mm); micron-scale precision | Micro-electronics, medical instruments | Produces intricate parts with tight tolerances; requires advanced tooling |
| Two-Component MIM | Co-injects two metals or metal/ceramic blends; functional integration | Cutting tools, dental devices, smart electronics | Reduces assembly steps; complex process; requires strict quality control |
| Large-Part or Structural MIM | Modified for thicker walls and larger components (up to 150 mm) | Industrial machinery, robust connectors | Enables larger components; longer cycles; potential for shrinkage issues |
Standard MIM (Conventional MIM)
Standard MIM is the most widely used method for producing small to medium-sized intricate metal parts. This technique is particularly valuable for B2B buyers in industries such as automotive and electronics, where high-volume production is essential. Key purchasing considerations include the minimum order quantity, tooling costs, and the complexity of part designs. This method balances mechanical performance with cost, making it an attractive option for consistent, high-quality output.
High-Performance Alloy MIM
High-Performance Alloy MIM leverages advanced materials like titanium and cobalt-chromium to meet stringent mechanical and chemical requirements. This variation is particularly suited for aerospace and medical sectors where performance is critical. B2B buyers should consider the higher costs associated with these materials against the benefits of enhanced durability and compliance with industry standards. Proper vendor qualification is crucial, especially when dealing with regulatory compliance and certification.
Micro-MIM
Micro-MIM specializes in producing parts with intricate details at a sub-millimeter scale, making it essential for microelectronics and advanced medical devices. B2B buyers must evaluate suppliers based on their micro-molding capabilities, quality assurance processes, and experience in handling delicate components. While the initial tooling costs can be high, the precision and capability for tight tolerances can lead to significant advantages in product performance and functionality.
Two-Component MIM
The Two-Component MIM process allows for the integration of different materials within a single component, enhancing functionality and reducing assembly needs. This method is particularly beneficial for applications in cutting tools and smart electronics. Buyers should be aware of the complexities involved in quality control and the necessity for advanced manufacturing capabilities. The potential for innovative product features can justify the investment in this sophisticated molding technique.
Large-Part or Structural MIM
Large-Part MIM is tailored for producing larger components with thicker walls, suitable for industrial machinery and robust connectors. This method can accommodate dimensions up to 150 mm, making it a valuable option for sectors that require durability and strength. B2B buyers should consider the longer production cycles and potential challenges related to shrinkage and density variations. Understanding the specific requirements of large-part applications is essential for optimizing manufacturing outcomes.
Related Video: Types of Injection Mold Explained | Crescent Industries inc.
Key Industrial Applications of molding metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Molding Metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision Engine Components | Enhanced performance and durability of vehicles | Supplier reliability, material certifications, and lead times |
| Medical Devices | Surgical Instruments | High precision and biocompatibility for safety | Regulatory compliance, quality control standards, and supplier expertise |
| Electronics | Connectors and Circuit Components | Improved efficiency and reliability in devices | Cost competitiveness, material properties, and production scalability |
| Aerospace | Structural Components | Lightweight and high-strength parts for safety | Advanced material options, certifications, and supplier capabilities |
| Industrial Equipment | Tooling and Machinery Parts | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Tooling costs, production volume, and lead times |
Automotive
In the automotive sector, molding metal is crucial for producing precision engine components such as fuel injectors, valve bodies, and transmission parts. These components require high durability and performance under stress. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that can demonstrate consistent quality, adherence to material certifications, and the capability to meet stringent lead times. As the automotive industry evolves with electric and hybrid vehicles, understanding the changing specifications and materials will be vital.
Medical Devices
The medical device industry relies heavily on molding metal for surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. These products must meet high standards of precision and biocompatibility to ensure patient safety. Buyers must focus on suppliers with robust quality control processes and certifications like ISO 13485, which indicate compliance with medical device regulations. Sourcing from regions with established medical manufacturing capabilities, such as Europe and the Middle East, can also mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance.
Electronics
In electronics, molding metal is essential for producing connectors, housings, and circuit components that require high reliability and efficiency. The demand for miniaturized and high-performance electronic devices makes precision in molding critical. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that can provide competitive pricing while ensuring high-quality materials that can withstand thermal and electrical demands. Additionally, assessing a supplier’s production scalability is crucial for meeting fluctuating market demands.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry utilizes molding metal for creating lightweight, high-strength structural components that meet rigorous safety standards. Applications include brackets, housings, and complex assemblies that must endure extreme conditions. Buyers must seek suppliers with expertise in advanced materials and compliance with aerospace certifications such as AS9100. Understanding the nuances of aerospace material properties and supplier capabilities can significantly impact project success and safety.
Industrial Equipment
In the realm of industrial equipment, molding metal is applied to produce tooling and machinery parts that enhance operational efficiency. This includes gears, housings, and fixtures that require durability and precision. B2B buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including tooling costs and production volume, to ensure a favorable return on investment. Moreover, understanding lead times is essential, as delays can lead to production bottlenecks and increased operational costs.
Related Video: An Overview of Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for molding metal
When selecting materials for molding metal, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, manufacturing complexity, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in metal molding, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and can handle pressures exceeding 1000 psi, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is one of its greatest advantages, as it can withstand harsh environments without degrading. However, it is more expensive than other materials like carbon steel, and its manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precise machining and finishing.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is ideal for applications in the medical and food industries, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount. Its compatibility with various media, including acids and alkalis, further enhances its utility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088. In regions like Europe, the preference for stainless steel in food-grade applications is strong due to stringent regulations.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, with a high strength-to-weight ratio, and offers good corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and is often used in applications requiring thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace applications where reducing weight is critical. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be more prone to deformation under high stress.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is particularly effective in applications requiring good thermal and electrical conductivity, such as heat exchangers and electrical components. Its compatibility with various coatings allows for enhanced performance in specific environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should be aware of the differences in aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, which have varying mechanical properties. Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 is essential, especially in regions like South America, where local regulations may dictate specific alloy usage.
Tool Steel
Key Properties:
Tool steel is designed for high hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for tooling applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, typically rated up to 400°C.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of tool steel is its durability and ability to maintain sharp edges, which is essential in cutting applications. However, it is more expensive than standard carbon steels and requires specialized heat treatment processes, adding to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Tool steel is commonly used in molds and dies for injection molding, where precision and durability are critical. Its resistance to wear makes it ideal for high-volume production runs.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the specific grades of tool steel, such as D2 or S7, which may be required for different applications. Compliance with standards like ASTM A681 is crucial, particularly in the Middle East, where industrial standards are strictly enforced.
Titanium Alloys
Key Properties:
Titanium alloys are known for their high strength, low density, and excellent corrosion resistance, with temperature ratings exceeding 600°C. They are particularly effective in high-stress environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of titanium is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. However, it is one of the most expensive materials to mold, and its machining can be challenging due to its hardness.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is favored in applications requiring biocompatibility, such as surgical implants, as well as in aerospace for components that must withstand extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers must be aware of the stringent certification requirements for titanium products, especially in the medical field. Compliance with standards like ASTM F136 is critical, particularly in Europe and North America, where regulatory scrutiny is high.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for molding metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex machining | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive parts, heat exchangers | Lightweight and good conductivity | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
| Tool Steel | Molds and dies for injection molding | High wear resistance and durability | Expensive and requires heat treatment | High |
| Titanium Alloys | Aerospace components, surgical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Very high cost and challenging machining | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for molding metal, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for molding metal
Manufacturing Processes for Molding Metal
Molding metal is a multifaceted process that encompasses various stages, each critical for producing high-quality components. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers aiming to ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous standards. Below are the main manufacturing stages involved in metal molding:
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the molding process involves selecting and preparing the metal materials. This can include:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right alloy or metal type based on the desired properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Common choices include stainless steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys like titanium or cobalt-chromium.
- Powder Preparation: In processes like Metal Injection Molding (MIM), fine metal powders are mixed with polymer binders to create a feedstock. This mixture must be homogenous to ensure consistent quality in the final product.
- Quality Checks: Conducting initial quality assessments of raw materials to ensure they meet industry specifications and standards. This includes visual inspections and laboratory tests for composition and purity.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the prepared materials are shaped into the desired components. Key techniques include:
- Casting: This involves pouring molten metal into a mold. Techniques such as sand casting and die casting are common, with the choice depending on the complexity and size of the parts.
- Injection Molding: In the case of MIM, the feedstock is heated and injected into a mold under pressure, allowing for intricate designs and high precision.
- Forging and Machining: For larger or more robust components, forging (shaping metal using localized compressive forces) and machining (cutting away material to achieve final shapes) are essential techniques that enhance strength and durability.
3. Assembly
After forming, components may require assembly to create final products. This stage can involve:
- Joining Techniques: Methods such as welding, brazing, or mechanical fastening are used to assemble parts. Selection depends on the application and materials involved.
- Integration of Components: In multi-material applications, ensuring that different materials bond effectively without compromising functionality is critical.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional properties of the molded parts. It includes:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like polishing, anodizing, or coating to improve corrosion resistance and surface finish.
- Inspection and Testing: Final products undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet all specifications. This can include visual inspections, dimensional checks, and functional testing.
Quality Assurance in Molding Metal
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the metal molding industry, ensuring that products meet international standards and specific industry requirements. Here are key aspects of QA for B2B buyers:
International Standards
B2B buyers should be familiar with the relevant international quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard emphasizes quality management systems and continuous improvement. Suppliers certified under ISO 9001 are more likely to provide consistent quality.
- CE Marking: Common in Europe, this certification indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries like oil and gas, the American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for quality assurance in manufacturing.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control should include several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process in real-time to detect and rectify issues as they arise.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough inspections and tests on finished products before they are shipped. This includes dimensional checks and performance tests.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods can vary based on the industry and product type but commonly include:
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection help assess internal defects without damaging the components.
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluating properties such as tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance.
- Chemical Analysis: Ensuring that the composition of the metal meets required specifications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can reveal their commitment to quality and adherence to standards. Consider third-party audits for unbiased assessments.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing methods, results, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection services to verify that products meet the agreed specifications before shipment.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
Navigating quality control in international markets can present unique challenges:
- Cultural Differences: Understand that quality perceptions may vary by region. What is considered acceptable in one culture may not be in another.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that products meet local regulations in their countries, which may differ from the supplier’s country.
- Communication Barriers: Clear communication about quality expectations is vital. Utilize detailed specifications and quality agreements to bridge potential gaps.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards in metal molding, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their rigorous quality requirements.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for molding metal Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of molding metal is essential for B2B buyers, particularly for those sourcing internationally from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A thorough analysis of the cost components, price influencers, and actionable buyer tips can significantly enhance decision-making and procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials
The choice of raw materials directly impacts the cost of molding metal. Common materials include various metal alloys, which vary in price based on market demand, purity, and availability. For instance, high-performance alloys like titanium or cobalt-chromium are typically more expensive than standard ferrous alloys. -
Labor
Labor costs fluctuate depending on geographic location and the complexity of the molding process. Regions with skilled labor shortages may experience higher costs. Additionally, labor-intensive processes, such as micro-MIM, can elevate overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Buyers should consider suppliers with efficient operations that can minimize overhead costs without compromising quality. -
Tooling
Tooling costs are significant in molding metal, particularly for custom designs. Initial investments can be high, but they are amortized over production runs. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) required to justify tooling costs is critical for B2B buyers. -
Quality Control (QC)
Implementing robust quality control measures adds to the overall cost but is essential for ensuring that products meet required standards and specifications. This includes regular inspections and certifications, which can be particularly relevant in regulated industries such as medical devices. -
Logistics
The cost of shipping materials and finished products varies significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. Buyers must account for these logistics costs when evaluating supplier quotes. -
Margin
Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can vary widely based on market competition and the supplier’s position in the value chain.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ
Purchasing in larger quantities usually results in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities that align with their production needs. -
Specifications/Customization
Custom designs and specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized tooling and manufacturing processes. Clear communication of requirements can help mitigate unexpected expenses. -
Materials
The type of materials selected plays a crucial role in pricing. High-performance or specialty materials typically incur higher costs. -
Quality and Certifications
Products requiring specific industry certifications may be priced higher due to the additional quality assurance processes involved. -
Supplier Factors
Supplier reliability, experience, and geographical location can influence pricing. Established suppliers often provide better value through efficiency and consistency. -
Incoterms
Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should clarify which party is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation
Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Leverage volume commitments and long-term relationships to negotiate better terms. -
Cost-Efficiency
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial costs, maintenance, and logistics. This holistic view helps in selecting suppliers that provide the best long-term value. -
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may face additional tariffs or trade barriers. Understanding local regulations and trade agreements can lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
Pricing for molding metal can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and geographic factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential molding metal Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘molding metal’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for molding metal
Metal molding is a sophisticated process that requires a solid understanding of technical specifications and industry terminology. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, grasping these elements is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the metal based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include stainless steel, aluminum alloys, and tool steels. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is essential for ensuring product performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. -
Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a part. It is critical in ensuring that components fit together correctly and function as intended. In industries such as automotive and aerospace, tight tolerances are often required, making it imperative for buyers to communicate their specifications clearly to suppliers to avoid costly rework or defects. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and quality of a part’s surface after manufacturing. Different applications may require specific finishes for aesthetic or functional reasons, such as corrosion resistance or friction reduction. Understanding surface finish specifications helps B2B buyers ensure that their products meet both performance criteria and regulatory requirements. -
Dimensional Stability
This property indicates how well a material maintains its dimensions under varying temperature and humidity conditions. For buyers, especially in sectors like electronics or medical devices, ensuring dimensional stability is vital to guarantee the long-term functionality of components in diverse environments. -
Mechanical Properties
These include strength, hardness, ductility, and toughness of the material. Each property plays a significant role in how the molded part will perform under load and stress. Buyers must specify the required mechanical properties to ensure the components can withstand their intended applications.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers as it often dictates the quality and compatibility of parts in larger assemblies. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, being aware of MOQs helps in budgeting and inventory planning, ensuring that procurement aligns with production schedules without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. It is a fundamental tool for B2B buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost implications, which is particularly important in cross-border trade. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. For B2B buyers, knowing the lead time is critical for effective supply chain management and project planning, as it impacts production schedules and delivery commitments.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their negotiation capabilities and supplier selection processes, ultimately driving efficiency and value in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the molding metal Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The molding metal sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by advancements in technology and changing market demands. Globalization has enabled international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to access diverse suppliers and innovative manufacturing techniques such as Metal Injection Molding (MIM). This method stands out for its ability to produce complex geometries with high precision at scale, making it essential for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
A notable trend is the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which incorporate automation, data exchange, and IoT in manufacturing processes. These technologies enhance efficiency, reduce lead times, and improve product quality, making it crucial for buyers to partner with suppliers who are aligned with these advancements. Additionally, as the demand for customization increases, suppliers that offer flexible production capabilities will gain a competitive edge.
Emerging markets are increasingly investing in infrastructure, which is expected to boost the demand for metal components. For instance, Brazil’s automotive sector is expanding, while Egypt’s industrial landscape is modernizing. Buyers in these regions should monitor local regulations and incentives that may affect sourcing strategies, such as tariffs or trade agreements. Understanding these dynamics will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions and optimize their supply chains effectively.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the molding metal sector, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer expectations. The environmental impact of metal production is significant, with energy-intensive processes and waste generation posing challenges. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who implement sustainable practices, such as recycling materials and utilizing energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should seek suppliers with transparent supply chains, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and labor practices comply with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the rise of “green” materials—such as recycled metals or bio-based binders in MIM—offers opportunities for buyers to enhance their sustainability profiles. Choosing suppliers that offer environmentally friendly materials not only helps in meeting regulatory requirements but also resonates with end consumers who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of molding metal techniques has roots dating back centuries, but the modern era has seen rapid advancements. Traditional methods like sand casting and forging laid the groundwork for more sophisticated processes. The introduction of Metal Injection Molding in the late 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for the production of intricate parts with high precision and reduced costs.
In recent years, the focus has shifted toward integrating advanced technologies and sustainable practices into the manufacturing process. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to global market demands and the need for efficiency, quality, and environmental responsibility. As B2B buyers navigate this landscape, understanding the historical context of these techniques can provide valuable insights into future trends and innovations in molding metal.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of molding metal
-
What criteria should I use to vet potential suppliers for metal molding?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in the industry, technology capabilities, and production capacity. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your industry, to gauge reliability. Evaluate their certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific accreditations, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Additionally, assess their ability to provide customization and flexibility in order volumes, as well as their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery. -
Can I customize metal components according to my specifications?
Yes, most reputable metal molding suppliers offer customization options. You can collaborate with them to design parts that meet your specific requirements, including size, shape, and material properties. It’s important to communicate your needs clearly and provide detailed specifications. Some suppliers may also offer design assistance to optimize manufacturability, which can enhance product performance and reduce costs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for metal molding?
MOQs can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units, depending on the complexity of the part and the molding process used. Lead times generally range from a few weeks to several months, influenced by factors such as order size, material availability, and production schedules. It’s advisable to discuss these details upfront to align expectations and plan your inventory accordingly. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s location and policies. Common options include upfront deposits (often 30-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. For larger orders or established relationships, some suppliers may offer credit terms. Ensure you clarify payment methods (e.g., wire transfers, letters of credit) and consider using escrow services for added security in international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with certifications?
To ensure quality, inquire about the supplier’s quality management systems and processes. Request documentation for relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality control. You can also ask for sample parts to evaluate their quality before placing a larger order. Regular communication and establishing a clear inspection process can further ensure that the final products meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing metal components?
Logistics are crucial in international sourcing. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight costs, delivery timelines, and responsibilities for customs clearance. Consider the total landed cost, which includes production, shipping, and import duties. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can help streamline the process and mitigate risks associated with delays or damages during transit. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers in international transactions?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing. Include clauses in contracts that outline dispute resolution processes, such as mediation or arbitration, to avoid lengthy legal battles. If disputes arise, approach the supplier professionally to discuss concerns and seek a resolution. Having a local legal advisor familiar with international trade laws can also be beneficial in navigating complex situations. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with metal molding suppliers?
Building a successful long-term relationship with suppliers involves consistent communication, transparency, and mutual respect. Provide feedback on product quality and delivery times, and engage in regular reviews of performance metrics. Consider collaborating on new projects or sharing forecasts to help suppliers plan their production. Recognizing their efforts and successes can foster loyalty and may lead to better pricing and service in the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for molding metal
In summary, the strategic sourcing of metal injection molding (MIM) offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging the precision and scalability of MIM, businesses can achieve high-quality, complex metal components that meet the demands of diverse industries such as automotive, medical, and electronics. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right MIM variant based on specific application needs, ensuring rigorous quality control, and fostering strong supplier relationships to mitigate risks associated with global sourcing.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
As markets continue to evolve and competition intensifies, strategic sourcing is not merely a procurement function; it is a crucial driver of innovation and efficiency. B2B buyers are encouraged to actively engage with suppliers, explore new material options, and stay informed about market trends and technological advancements.
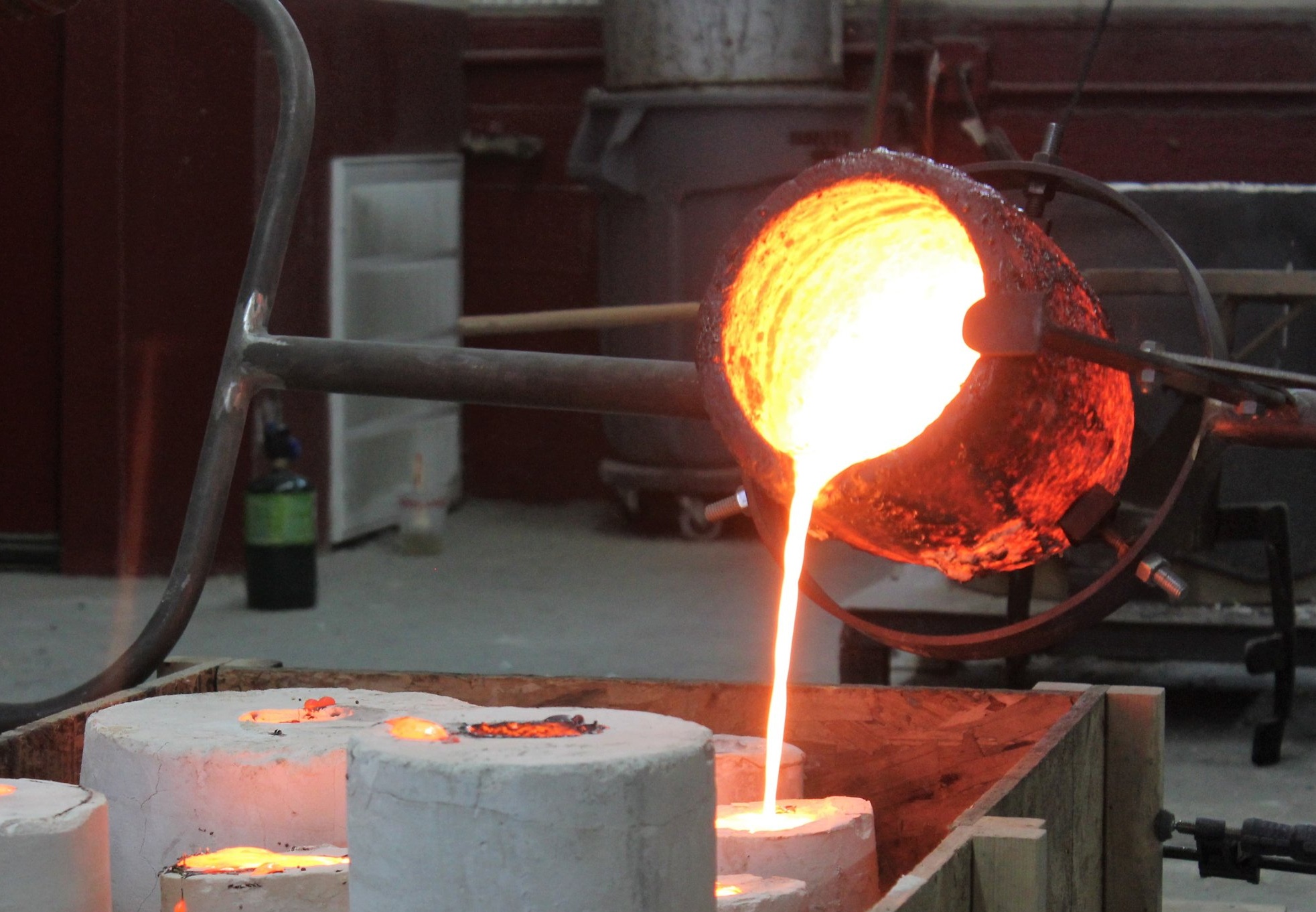

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies such as automation and AI in metal molding processes will further enhance productivity and cost-effectiveness. Now is the time for international buyers to embrace these changes, ensuring they are well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in the global landscape.