Master RF Shielding Sourcing: A Comprehensive Guide for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rf shielding
In today’s interconnected world, the need for robust RF shielding solutions is more critical than ever. As businesses increasingly rely on wireless communication, the risk of electromagnetic interference and unauthorized data access looms large. RF shielding serves as a vital defense mechanism, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring operational integrity across various sectors, from telecommunications to manufacturing and beyond.
This comprehensive guide is designed specifically for international B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. It offers an in-depth exploration of RF shielding, covering essential topics such as types of shielding materials, manufacturing processes, quality control standards, and supplier evaluations. Additionally, we will delve into cost considerations and market trends, empowering you to make informed sourcing decisions.
As you navigate the complexities of RF shielding, this guide aims to demystify the various options available, providing actionable insights that cater to your unique business needs. Whether you are looking to enhance security protocols, improve data accuracy, or comply with industry regulations, understanding RF shielding is crucial. By leveraging the knowledge contained within this guide, you will be better equipped to select the right solutions that not only protect your assets but also drive your business forward in a competitive global market.
Understanding rf shielding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive Shielding | Utilizes conductive materials like copper or aluminum; effective against a wide range of frequencies. | Telecommunications, electronics manufacturing, and military applications. | Pros: High effectiveness; Cons: Can be expensive and heavy. |
| Magnetic Shielding | Employs materials that absorb magnetic fields, typically using mu-metal or similar alloys. | MRI facilities, sensitive electronics, and industrial applications. | Pros: Excellent for low-frequency interference; Cons: Limited to magnetic fields only. |
| RF Absorber Materials | Designed to absorb RF energy rather than reflect it; often made of foam or composite materials. | Automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. | Pros: Lightweight and versatile; Cons: May not provide full shielding in all scenarios. |
| Faraday Cages | Enclosures made of conductive materials that block external electromagnetic fields. | Secure data facilities, laboratories, and military installations. | Pros: Highly effective for complete shielding; Cons: Requires careful design and installation. |
| Shielded Enclosures | Complete rooms or cabinets designed to prevent RF leakage, often incorporating multiple shielding types. | Data centers, research labs, and sensitive manufacturing. | Pros: Comprehensive protection; Cons: High initial investment and space requirements. |
Conductive Shielding
Conductive shielding is characterized by the use of materials such as copper or aluminum to block electromagnetic interference (EMI). This type of shielding is highly effective across a broad frequency range, making it suitable for various applications in telecommunications and electronics manufacturing. When considering purchasing conductive shielding, buyers should evaluate the material’s conductivity, weight, and cost-effectiveness, as these factors can significantly impact the overall project budget and performance.
Magnetic Shielding
Magnetic shielding focuses on reducing magnetic field interference using materials like mu-metal, which are specifically designed to absorb magnetic fields. This type is particularly beneficial in environments like MRI facilities or industrial settings where low-frequency magnetic interference can disrupt operations. B2B buyers should consider the specific magnetic frequency ranges they need to shield against and the physical space available for installation, as magnetic shielding can be bulky.
RF Absorber Materials
RF absorber materials are engineered to absorb RF energy rather than reflect it, typically comprising lightweight foams or composite materials. This type of shielding is ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries, where weight is a critical factor. Buyers should assess the specific RF absorption characteristics of these materials and their compliance with industry standards, ensuring they meet the necessary performance requirements without adding excessive weight.
Faraday Cages
Faraday cages are enclosures crafted from conductive materials that block external electromagnetic fields, providing a high level of protection. These structures are commonly used in secure data facilities and military installations. For B2B buyers, the design and installation of Faraday cages are crucial considerations, as they require careful planning to ensure effective shielding while maintaining accessibility and functionality.
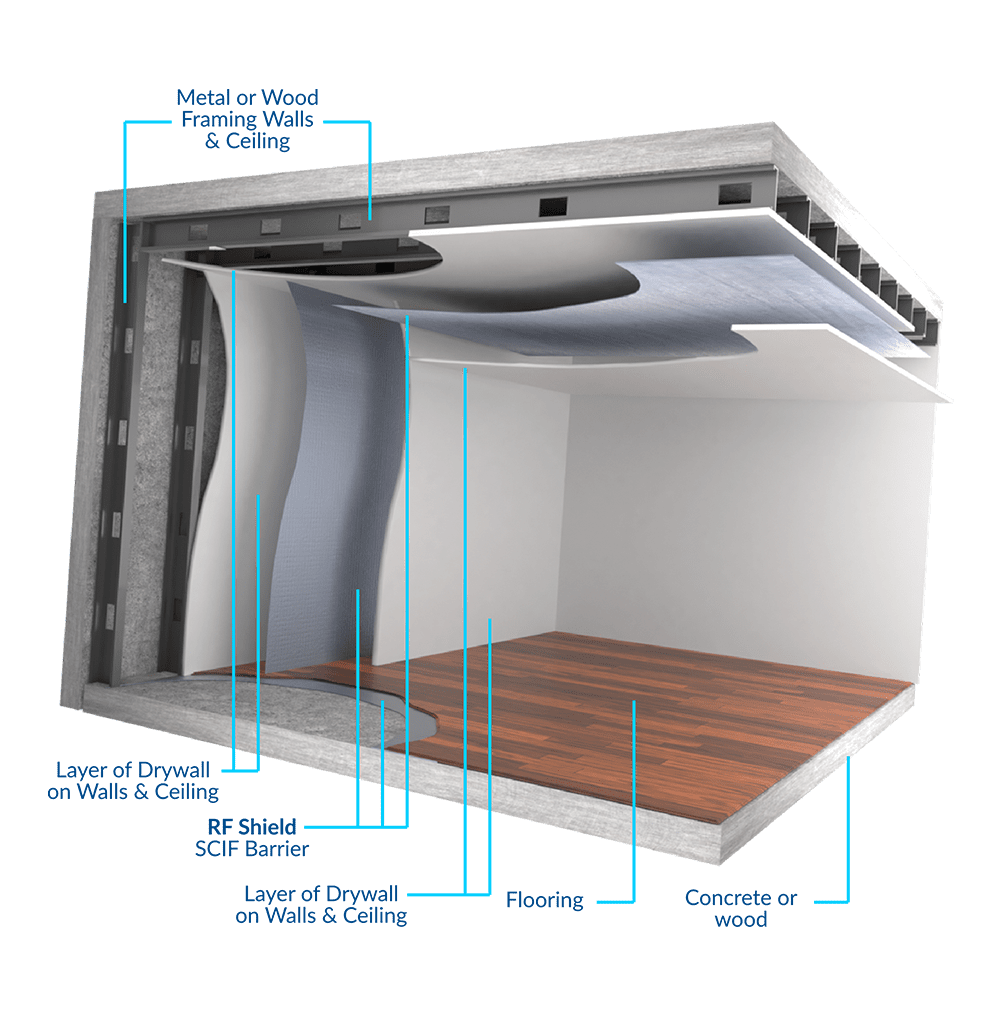
Shielded Enclosures
Shielded enclosures, which can be complete rooms or cabinets, are designed to prevent RF leakage by integrating various shielding types. They are essential in data centers and research labs where sensitive information needs protection from external interference. Buyers must evaluate the overall cost of implementation versus the level of protection required, as these enclosures often represent a significant investment but provide comprehensive shielding capabilities.
Related Video: MRI scanner room RF shielding
Key Industrial Applications of rf shielding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rf shielding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | RF shielding in cell towers | Enhances signal quality and protects sensitive data | Evaluate materials for durability and compliance with local regulations. |
| Healthcare | RF shielding in medical imaging equipment | Prevents interference, ensuring accurate diagnostics | Ensure materials are compliant with healthcare standards and regulations. |
| Defense and Security | RF shielding in military communication systems | Secures sensitive information against electronic eavesdropping | Look for specialized materials that meet military standards for RF shielding. |
| Automotive | RF shielding in vehicle electronic systems | Reduces interference from external signals, improving performance | Assess compatibility with existing vehicle designs and safety standards. |
| Manufacturing | RF shielding in automated production lines | Minimizes operational disruptions, enhancing efficiency | Consider sourcing from suppliers with experience in industrial applications. |
Telecommunications
In the telecommunications sector, RF shielding is critical for cell towers and communication devices. It ensures that sensitive data transmitted through these systems is protected from unauthorized interception and interference. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, it is essential to source materials that comply with local telecommunications regulations and standards. Buyers should also prioritize durability and resistance to environmental factors, such as humidity and temperature fluctuations.
Healthcare
In healthcare, RF shielding is essential for medical imaging equipment, such as MRI machines. It prevents electromagnetic interference that could compromise diagnostic accuracy, thereby safeguarding patient outcomes. Buyers in the healthcare sector must ensure that shielding materials comply with stringent healthcare regulations and standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Additionally, sourcing from reputable manufacturers who can provide certifications for their products is crucial to maintain operational integrity.
Defense and Security
The defense and security industry relies heavily on RF shielding to protect sensitive communication systems from electronic eavesdropping. This application is vital for military operations where the confidentiality of information is paramount. For B2B buyers in this sector, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, it is important to source shielding materials that meet rigorous military specifications. Understanding the specific requirements for secure communications will help buyers make informed decisions about their RF shielding needs.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, RF shielding is used to enhance the performance of electronic systems within vehicles. It minimizes interference from external signals, which is crucial for the operation of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment systems. Buyers in this sector should consider the compatibility of shielding materials with existing vehicle designs and ensure that they meet safety standards. This is especially relevant for international buyers looking to integrate RF shielding into new vehicle models.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities increasingly incorporate RF shielding into automated production lines to reduce electromagnetic interference that can disrupt operations. This application enhances overall efficiency and minimizes downtime caused by signal disruptions. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, it is essential to work with suppliers who have experience in industrial RF shielding applications. Ensuring that sourcing decisions align with operational requirements and production capabilities will lead to better integration and performance.
Related Video: RF Shielding Installation Procedures National Shielding
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rf shielding
When selecting materials for RF shielding, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations, particularly for international B2B buyers. The right choice can significantly impact the effectiveness of shielding solutions, compliance with local standards, and overall project costs. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in RF shielding, tailored to the needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a popular choice for RF shielding. It typically has a high-temperature rating, withstanding up to 200°C, and offers good corrosion resistance when treated properly.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which allows for effective shielding against a wide range of frequencies. However, it can be more expensive than alternative materials, and its weight can complicate manufacturing and installation processes. Additionally, copper is susceptible to oxidation, which can reduce its effectiveness over time if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application:
Copper is particularly effective in environments where high-frequency signals are prevalent, such as telecommunications and aerospace applications. However, its weight may limit its use in portable devices.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Copper RF shielding products must comply with standards such as ASTM B193 for electrical conductivity. Buyers should also consider the availability and cost fluctuations of copper in their local markets.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good electrical conductivity, with a temperature rating typically around 150°C. It also exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum’s lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and install, reducing labor costs. However, its conductivity is lower than copper, which may necessitate thicker layers for effective shielding. Additionally, while aluminum is generally less expensive than copper, its performance can vary based on alloy composition.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for a variety of applications, including consumer electronics and automotive industries, where weight is a critical factor. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Aluminum products should meet standards such as ASTM B209 for sheet and plate. Buyers must also be aware of local regulations regarding recycling and environmental impact.
Steel
Key Properties:
Steel, particularly stainless steel, offers good mechanical strength and durability, with a temperature rating exceeding 300°C. However, its electrical conductivity is lower than that of copper and aluminum.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of steel is its robustness and resistance to physical damage, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, its heavier weight can increase shipping and installation costs. Additionally, the lower conductivity may require thicker materials to achieve the desired shielding effectiveness.
Impact on Application:
Steel is commonly used in industrial applications, such as manufacturing plants and military facilities, where durability is paramount. It is also effective in shielding against lower frequency signals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Steel RF shielding must comply with standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Buyers should also consider the implications of corrosion resistance in their specific environments, particularly in humid or coastal areas.
Conductive Fabrics
Key Properties:
Conductive fabrics are made from materials like polyester or nylon blended with conductive metals such as silver or copper. They offer flexibility and can be tailored to various temperature ratings depending on the base material.
Pros & Cons:
The flexibility of conductive fabrics allows for easy integration into a variety of products, including wearable technology. However, they may not provide the same level of shielding effectiveness as solid materials and can be more expensive due to the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application:
These fabrics are ideal for applications requiring lightweight and flexible shielding solutions, such as in medical devices and consumer electronics. Their adaptability makes them suitable for various shapes and sizes.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that conductive fabrics meet relevant standards such as ASTM D4935 for measuring shielding effectiveness. Additionally, sourcing may be more complex due to the specialized nature of these materials.
| Material | Typical Use Case for rf shielding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Telecommunications, aerospace | Superior conductivity | High cost, oxidation issues | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer electronics, automotive | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial, military facilities | High durability, physical strength | Heavier, lower conductivity | Medium |
| Conductive Fabrics | Wearable technology, medical devices | Flexibility, easy integration | Potentially lower shielding effectiveness | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into RF shielding materials, helping them make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rf shielding
The manufacturing processes for RF shielding encompass several critical stages, each of which demands precision and expertise. Understanding these processes will help B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, evaluate suppliers effectively.
Manufacturing Processes for RF Shielding
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing RF shielding involves selecting appropriate materials. Common materials include conductive metals like copper, aluminum, and specialized conductive polymers. Key considerations in material selection include:
- Conductivity: Higher conductivity ensures better shielding effectiveness.
- Weight: Lightweight materials are often preferred for ease of installation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Materials must withstand environmental factors, particularly in humid or corrosive atmospheres.
Once selected, materials undergo preparation processes such as cutting, shearing, or rolling to achieve desired dimensions and forms.
Forming
Forming is where materials are shaped into the required configurations. Techniques include:
- Stamping: Used for producing components like RF shielding enclosures, ensuring precise dimensions and consistency.
- Molding: In the case of conductive polymers, injection molding allows for complex shapes that are both lightweight and effective.
- Welding: For metal components, welding techniques such as TIG or MIG ensure strong joints that maintain shielding effectiveness.
Each technique should be optimized for the specific requirements of the final product, balancing quality and production efficiency.
Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled. This stage may involve:
- Mechanical Assembly: Components are joined using screws, rivets, or adhesive bonding. The choice of method depends on the application and environmental conditions.
- Integration of Gaskets and Seals: To enhance shielding effectiveness, RF shielding products often incorporate gaskets made from conductive materials to seal joints and openings.
Proper assembly is critical, as gaps or misalignments can significantly reduce shielding performance.
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the durability and appearance of RF shielding products. Techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear, especially in outdoor applications.
- Surface Treatments: Processes like anodizing or plating can improve conductivity and surface integrity.
- Quality Checks: Visual inspections and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods ensure that the finished products meet specifications.
Quality Assurance in RF Shielding Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the RF shielding industry, given the critical role that effective shielding plays in protecting sensitive information and equipment. Adhering to international standards ensures consistent quality and reliability.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that comply with recognized international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and ensures that suppliers maintain consistent quality in their processes.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant in Europe, this indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential for products used in sensitive environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) should occur at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process help identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it meets all specifications and standards.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods for RF shielding products include:
- Shielding Effectiveness Testing: Measures the ability of materials to block electromagnetic interference (EMI) using specialized equipment.
- Environmental Testing: Assesses performance under various environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature).
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluates the durability and strength of the shielding products.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must implement strategies to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Key actions include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s quality management systems and manufacturing processes directly.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control measures, including test results and compliance certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality processes and products.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers from diverse regions, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital. Here are some considerations:
- Local Standards Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are familiar with and compliant with local regulations and standards in your region, which may differ from international norms.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Different cultures may have varying perceptions of quality and compliance. Building relationships and establishing trust can facilitate better communication and understanding.
- Logistical Considerations: Shipping and handling practices can impact product quality. Ensure that suppliers have robust processes in place for packaging and transport to mitigate damage.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards is essential for B2B buyers in the RF shielding industry. By focusing on the details outlined in this section, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source products that meet their operational needs while adhering to the highest quality standards.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rf shielding Sourcing
In the realm of RF shielding sourcing, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis focuses on the various components that contribute to the overall cost, factors that influence pricing, and practical tips for buyers operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in RF shielding is the type of materials used. Common materials include metals (like copper and aluminum), conductive fabrics, and specialized polymers. Prices can vary significantly based on the material’s conductivity, durability, and environmental resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses associated with skilled personnel required for production and installation. The labor market varies greatly by region, with some areas having lower labor costs, which can influence overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specific RF shielding solutions. This one-time cost can be significant, especially for complex designs, but it is amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that RF shielding products meet industry standards involves rigorous testing and inspection. QC costs can vary depending on the complexity of the product and regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling expenses are crucial, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, transportation mode, and customs duties can significantly affect logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing structure. This margin can vary based on market competition, supplier reputation, and perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders usually attract better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their budget.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific requirements often come at a premium. Buyers should balance the need for customization with cost implications.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with industry certifications (e.g., ISO, MIL standards) tend to be more expensive but may offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a solid reputation may charge higher prices, reflecting their reliability and service quality. Newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share but may come with higher risks.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect pricing and risk management. Understanding the implications of different terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for cost-effective sourcing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate prices and terms. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals and flexibility.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider long-term costs, including maintenance, durability, and potential operational savings.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that pricing can fluctuate based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors. Regularly review contracts and be prepared to adapt to changing circumstances.
-
Regional Considerations: Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider local market conditions, trade regulations, and logistics challenges that may impact sourcing strategies.
Disclaimer
The prices associated with RF shielding solutions can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing information relevant to their specific needs and circumstances.
Spotlight on Potential rf shielding Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘rf shielding’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rf shielding
Key Technical Properties of RF Shielding
When considering RF shielding solutions, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications that play a significant role in the effectiveness and applicability of RF shielding materials:
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the quality and composition of the materials used in RF shielding, such as copper, aluminum, or specialized polymers.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials generally offer better conductivity and attenuation, ensuring that unwanted RF signals are effectively blocked. This is vital for industries requiring stringent data protection, such as finance and defense. -
Shielding Effectiveness (SE)
– Definition: This measures the ability of a shielding material to attenuate electromagnetic fields, typically expressed in decibels (dB).
– Importance: A higher SE value indicates better performance in preventing RF interference. B2B buyers should assess SE to ensure that the shielding solution meets specific operational requirements, especially in environments with high electromagnetic interference. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the shielding material or assembly.
– Importance: Precise tolerances are crucial in ensuring proper installation and effectiveness of the shielding. Inaccurate dimensions can lead to gaps that may allow RF signals to penetrate, compromising security. -
Frequency Range
– Definition: This specifies the range of frequencies that the shielding material is designed to block effectively, often categorized in kilohertz (kHz) to gigahertz (GHz).
– Importance: Different applications require shielding against specific frequency ranges. Understanding this property allows buyers to select materials that are appropriate for their unique operational environment, whether it’s for consumer electronics or sensitive military communications. -
Durability and Environmental Resistance
– Definition: This property assesses how well shielding materials withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and physical wear.
– Importance: For B2B buyers, especially those in harsh environments, selecting durable materials ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs. This is critical in sectors like telecommunications and aerospace, where equipment is often exposed to extreme conditions. -
Ease of Installation
– Definition: Refers to how straightforward it is to apply or integrate the RF shielding into existing systems or structures.
– Importance: Solutions that offer easier installation can save time and labor costs. This is particularly beneficial for industries requiring rapid deployment, such as emergency response and temporary setups.
Common Trade Terminology in RF Shielding
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are several common terms relevant to RF shielding:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Buyers often source RF shielding from OEMs to ensure compatibility with their existing products, enhancing performance and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps B2B buyers manage their budgets and inventory effectively, particularly when sourcing specialized RF shielding products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they receive the best deal for their RF shielding needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risk, and delivery responsibilities, which is essential when sourcing RF shielding solutions from international suppliers. -
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference)
– Definition: Disruption that electromagnetic fields can cause to electronic devices.
– Relevance: Recognizing EMI is crucial for buyers as effective RF shielding must mitigate this interference to ensure operational integrity.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their RF shielding solutions effectively meet their operational needs while also optimizing costs and compliance.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the rf shielding Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The RF shielding sector is witnessing robust growth driven by increasing demands for data security and privacy across various industries. As wireless communication technologies proliferate, concerns over electromagnetic interference (EMI) and unauthorized data interception have surged, prompting businesses to invest in effective shielding solutions. Key drivers include the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), the rise of smart cities, and heightened regulations around data protection, particularly in regions like Europe, where GDPR has set stringent compliance standards.
Emerging trends in sourcing for RF shielding materials highlight a shift towards advanced materials that offer enhanced performance while being lightweight and cost-effective. Innovations such as conductive polymers and nanomaterials are gaining traction, allowing manufacturers to produce more effective shielding solutions that can be integrated into smaller devices. Moreover, there is a growing trend towards modular shielding solutions, particularly for sectors like telecommunications and defense, where adaptability and scalability are crucial.
International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should note the shift towards local sourcing to mitigate supply chain disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting companies to seek suppliers closer to their operational bases. This move not only reduces lead times but also enhances the ability to meet local regulatory requirements effectively.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the RF shielding sector. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. The production of shielding materials can contribute to significant waste and pollution; thus, companies are urged to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes utilizing recycled materials and minimizing the carbon footprint throughout the manufacturing process.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses strive to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitation and environmental degradation. Buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to recognized sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to effective environmental management systems. Additionally, the use of “green” materials, such as bio-based or recyclable shielding products, can provide a competitive edge while addressing environmental concerns.
Choosing suppliers who prioritize sustainability not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also appeals to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers. By integrating sustainability into their procurement strategies, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and foster long-term loyalty among customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of RF shielding technology has been shaped by the increasing complexity of electromagnetic environments. Initially, RF shielding was primarily focused on military applications, where secure communications were paramount. Over the decades, as consumer electronics and wireless technologies emerged, the need for effective shielding solutions expanded into commercial sectors.
With the advent of regulations such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) guidelines in the United States, the standards for RF shielding became more stringent, leading to innovations in materials and design. Today, RF shielding not only encompasses traditional applications but also addresses modern challenges posed by IoT devices and smart infrastructure, making it a vital component of contemporary technology strategies across various industries.
In summary, international B2B buyers should focus on the dynamic market landscape for RF shielding, prioritize sustainable and ethical sourcing practices, and remain informed about the historical context that shapes current innovations in the sector.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rf shielding
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for RF shielding?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, certifications, and client testimonials. Verify their compliance with international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, technology used, and ability to customize products based on your needs. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their previous projects, particularly in your industry, and to request samples of their RF shielding materials to ensure they meet your specifications. -
Can RF shielding solutions be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for RF shielding solutions to cater to unique application requirements. This may include tailored dimensions, specific shielding materials, or added features like enhanced durability or flexibility. When discussing customization, clearly outline your project needs, and consider requesting prototypes to validate that the final product meets your expectations before full production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for RF shielding products?
MOQs for RF shielding products can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the customizations. Standard products may have lower MOQs, while specialized solutions could require larger orders. Lead times typically range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the supplier’s capacity and your order size. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid delays in your project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing RF shielding internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always ensure that the payment terms are clearly outlined in your contract, including any penalties for late payments. -
How can I ensure the quality of RF shielding products?
To ensure quality, request certifications from the supplier that validate their compliance with industry standards, such as ASTM or IEC. Ask for test reports that demonstrate the shielding effectiveness of their products. Implement a quality assurance process that includes inspections upon delivery and consider third-party audits if you are making a significant investment. Establishing clear quality expectations in your contract is also vital. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing RF shielding?
Logistical considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Discuss with your supplier about their logistics capabilities and whether they can handle shipping to your location. Be aware of potential import tariffs or duties in your country, and ensure you have a reliable logistics partner to manage transportation and delivery efficiently. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding RF shielding products?
In the event of a dispute, refer to the terms outlined in your contract, which should include clauses on dispute resolution. Open communication is key; discuss the issues directly with your supplier to seek a resolution. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods. Document all correspondence and agreements to protect your interests throughout the process.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What are the best practices for long-term partnerships with RF shielding suppliers?
Establishing a long-term partnership involves regular communication and feedback on product performance. Share your future project needs and involve suppliers in your planning process to foster collaboration. Conduct periodic evaluations of their performance in terms of quality, delivery, and responsiveness. Building a strategic relationship can lead to better pricing, priority service, and innovations tailored to your business needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rf shielding
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of RF shielding solutions offers substantial advantages for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing high-quality materials and innovative designs, companies can effectively mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access and signal interference. This ensures not only the security of sensitive data but also operational integrity in environments where multiple RFID technologies are in use.
Key takeaways include the importance of selecting suppliers who understand the nuances of RF shielding, including compliance with industry standards like ICD 705 for secure facilities. Additionally, investing in advanced shielding solutions can lead to enhanced asset protection and improved data management practices.
As the demand for secure communication and data protection continues to grow globally, it is vital for businesses to remain proactive in their sourcing strategies. International B2B buyers should engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive support and innovative products tailored to their specific needs.
Looking ahead, the evolution of RF shielding technologies will play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information. Embrace these advancements and secure your competitive edge by investing in robust RF shielding solutions today.