Master Sourcing Capacitive Touch Sensors for Enhanced
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for capacitive touch sensors
Capacitive touch sensors are revolutionizing the way businesses interact with technology, providing a seamless interface that enhances user experience across a multitude of applications. As these sensors replace traditional mechanical switches, they enable more intuitive controls in devices ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. This guide is designed for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, offering comprehensive insights into the capacitive touch sensor market.
In this guide, we will explore various types of capacitive touch sensors, including projected capacitive sensors and mutual capacitance designs, alongside their material specifications and manufacturing quality control processes. Understanding these elements is crucial for making informed decisions when sourcing components. We will also highlight key suppliers in the industry, providing insights into their capabilities and product offerings.
Additionally, buyers will find a detailed analysis of cost factors, market trends, and potential applications, equipping them with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of global sourcing. The guide will address common FAQs, ensuring that all aspects of capacitive touch technology are covered.
By leveraging the information presented here, B2B buyers will be empowered to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs, driving innovation and efficiency in their respective markets.
Understanding capacitive touch sensors Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Projected Capacitive Sensors | Can detect touch through thick overlays; high sensitivity | Smartphones, tablets, industrial controls | Pros: Versatile, supports multi-touch; Cons: Higher complexity in design. |
| Surface Capacitive Sensors | Requires direct contact; low-cost implementation | ATMs, kiosks, appliances | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective; Cons: Limited to single touch, less sensitive. |
| Self-Capacitance Sensors | Measures changes in capacitance from individual electrodes | Wearables, smart home devices | Pros: Low power consumption; Cons: Sensitive to noise, may require shielding. |
| Mutual Capacitance Sensors | Uses a grid of electrodes; detects multiple touches | Automotive interfaces, gaming devices | Pros: High precision, supports complex gestures; Cons: More expensive, complex calibration. |
| Hybrid Capacitive Sensors | Combines capacitive with other technologies (e.g., resistive) | Industrial machinery, medical devices | Pros: Enhanced durability and functionality; Cons: Increased cost and complexity. |
Projected Capacitive Sensors
Projected capacitive sensors are designed to detect touch through thick overlays, such as glass, making them ideal for high-end consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets. Their ability to support multi-touch functionality allows for innovative user interfaces. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of the design and integration, as well as the costs associated with advanced features.
Surface Capacitive Sensors
Surface capacitive sensors operate by detecting touch directly on the surface, making them a cost-effective solution for applications like ATMs and kiosks. Their straightforward design allows for quick deployment, but they are limited to single-touch detection. Buyers should weigh the benefits of lower costs against the need for more advanced touch capabilities, particularly in environments where multi-user interaction is essential.
Self-Capacitance Sensors
Self-capacitance sensors measure capacitance changes at individual electrodes, making them suitable for low-power applications such as wearables and smart home devices. Their energy efficiency is a significant advantage, especially for battery-operated products. However, buyers must consider potential noise interference and the need for additional shielding, which can complicate design and increase costs.
Mutual Capacitance Sensors
Mutual capacitance sensors utilize a grid of electrodes to detect multiple touches, providing high precision and enabling complex gestures. This technology is commonly used in automotive interfaces and gaming devices, where user experience is paramount. B2B buyers should be aware of the higher costs and the need for careful calibration, which may require specialized expertise.
Hybrid Capacitive Sensors
Hybrid capacitive sensors integrate capacitive technology with other sensing methods, such as resistive touch, to enhance durability and functionality. These sensors are often found in industrial machinery and medical devices, where reliability is crucial. When considering hybrid solutions, buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between increased complexity and the benefits of improved performance in challenging environments.
Related Video: How Touch Sensors Work: Exploring Capacitive Sensors with the TTP223
Key Industrial Applications of capacitive touch sensors
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of capacitive touch sensors | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Touchscreen interfaces for smartphones and tablets | Enhanced user experience through intuitive controls and gestures | Supplier reliability, technology compatibility, and cost-effectiveness |
| Automotive | Touch controls in vehicle dashboards | Improved aesthetics and ease of use, reducing mechanical wear | Environmental durability, compliance with automotive standards |
| Industrial Automation | Control panels for machinery | Increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Robustness against industrial environments, ease of integration |
| Healthcare | Medical devices with touch interfaces | Enhanced hygiene and ease of use, facilitating patient interaction | Regulatory compliance, sensitivity to touch, and ease of cleaning |
| Home Appliances | Touch-sensitive controls for kitchen appliances | Modernized design and user-friendly operation | Compatibility with existing designs and durability against spills |
Consumer Electronics
Capacitive touch sensors are widely used in smartphones and tablets, allowing for seamless touchscreen interfaces. They enable users to interact with devices through intuitive gestures like swiping and tapping, significantly enhancing user experience. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing capacitive sensors that are reliable and cost-effective is crucial. Suppliers must demonstrate technological compatibility with various device models, ensuring a smooth integration process.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, capacitive touch sensors are increasingly replacing traditional mechanical buttons on dashboards. This transition not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also improves user interaction by offering a more responsive interface. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who provide sensors that meet strict automotive standards for durability and environmental resistance, ensuring longevity and reliability in various driving conditions.
Industrial Automation
Capacitive touch sensors are integral to modern control panels used in industrial machinery. They facilitate efficient operation by allowing operators to control machines with simple touch gestures, reducing the need for mechanical switches that can wear out over time. For B2B buyers in Europe and Africa, it’s vital to select suppliers that offer robust sensors capable of withstanding harsh industrial environments, as well as those that can easily integrate into existing systems to minimize downtime.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, capacitive touch sensors are utilized in medical devices, enabling touch interfaces that enhance hygiene and ease of use. These sensors allow healthcare professionals to interact with devices without physical contact, reducing the risk of cross-contamination. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with healthcare regulations and provide sensors that are highly sensitive yet easy to clean, addressing the specific needs of medical environments.
Home Appliances
Capacitive touch sensors are transforming home appliances, allowing for sleek, modern designs with touch-sensitive controls. This technology enhances user-friendliness, making it easier to operate appliances such as ovens and refrigerators. For international buyers, particularly in South America and Africa, sourcing capacitive sensors that are durable and compatible with existing appliance designs is essential to achieving a balance between innovation and practicality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for capacitive touch sensors
When selecting materials for capacitive touch sensors, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in capacitive touch sensor applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Glass
Key Properties:
Glass is a widely used material for capacitive touch sensors due to its high dielectric constant (around 8) and excellent transparency. It can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
Glass offers durability and aesthetic appeal, allowing for sleek designs. However, it can be heavy and may require careful handling during manufacturing to avoid breakage. Additionally, its cost can be higher than alternatives like plastic, which may impact budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application:
Glass is particularly effective in applications where user interaction is frequent, such as consumer electronics and home appliances. Its compatibility with various media, including water and dust, enhances its usability in diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international safety standards, such as ASTM and DIN, particularly in regions with strict regulations. In Europe, REACH compliance is crucial for materials used in consumer products.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a lightweight, impact-resistant plastic with a lower dielectric constant than glass. It is capable of withstanding high temperatures and offers good clarity, although it can be prone to scratching.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polycarbonate is its durability and resistance to impact, making it ideal for rugged applications. However, it may not provide the same level of aesthetic quality as glass and can be more susceptible to environmental degradation over time.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is well-suited for industrial applications where durability is paramount. Its resistance to high-impact forces makes it a preferred choice for devices in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the material’s compliance with local regulations regarding plastics, particularly in the European market. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can also be beneficial for ensuring quality.
Acrylic
Key Properties:
Acrylic is another transparent plastic option with good optical clarity and a moderate dielectric constant. It is lightweight and has better scratch resistance compared to polycarbonate.
Pros & Cons:
Acrylic is cost-effective and easy to fabricate, making it a popular choice for prototypes and low-volume production. However, it is less durable than polycarbonate and can be more prone to yellowing over time.
Impact on Application:
Acrylic is suitable for applications where visual appeal is important, such as in consumer electronics and decorative panels. Its compatibility with various environmental conditions makes it versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards for acrylic materials in different regions. Ensuring compliance with ASTM standards can help mitigate risks associated with material performance.
Silicone
Key Properties:
Silicone is a flexible material that can withstand extreme temperatures and is resistant to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Its dielectric properties can be tailored for specific applications.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone offers excellent durability and flexibility, allowing for innovative designs in touch sensor applications. However, it may have a higher initial cost and can be more complex to manufacture compared to rigid materials.
Impact on Application:
Silicone is particularly effective in applications requiring waterproofing and flexibility, such as medical devices and outdoor electronics. Its ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures makes it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that silicone materials meet relevant international standards, especially in the medical field where compliance with ISO 13485 is critical. Understanding local regulations regarding silicone use in consumer products is also essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for capacitive touch sensors | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | Consumer electronics, home appliances | High durability and aesthetic appeal | Heavy and fragile | High |
| Polycarbonate | Industrial applications | Impact-resistant and lightweight | Prone to scratching | Medium |
| Acrylic | Decorative panels, consumer electronics | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Less durable, can yellow over time | Low |
| Silicone | Medical devices, outdoor electronics | Flexible, waterproof, temperature resistant | Higher initial cost, complex to manufacture | Medium |
This guide serves as a resource for B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding material selection for capacitive touch sensors, considering both performance and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for capacitive touch sensors
Manufacturing Processes for Capacitive Touch Sensors
The manufacturing of capacitive touch sensors involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall functionality and quality of the final product. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable components for their applications.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of manufacturing capacitive touch sensors involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. Key materials include:
- Conductive Materials: These are often metallic layers, such as copper or indium tin oxide (ITO), used to create the capacitive sensing elements.
- Substrate Materials: Common substrates include glass and plastics like polycarbonate, which provide the necessary support and protection for the sensor.
- Adhesives and Coatings: Non-conductive adhesives are used to bond layers, while protective coatings may be applied to enhance durability and environmental resistance.
The quality of materials directly impacts sensor performance, particularly in terms of sensitivity and durability. Buyers should ensure that suppliers utilize high-grade materials compliant with international standards.
2. Forming
Forming processes involve shaping the materials into the desired configurations for capacitive touch sensors. This stage includes:
- Photolithography: A technique used to transfer circuit patterns onto the conductive layers. This process is critical for defining the dimensions of sensor pads and traces.
- Etching: This method removes excess material to create precise conductive paths, ensuring optimal performance of the sensor.
- Deposition: Techniques such as sputtering or chemical vapor deposition are used to apply thin conductive layers uniformly.
Precision during the forming stage is crucial. B2B buyers should inquire about the technologies and machinery used by suppliers, as these directly affect production quality and consistency.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they undergo assembly. This includes:
- Layer Stacking: The conductive layers and substrates are carefully aligned and bonded using adhesives.
- Integration with Electronics: Capacitive sensors often integrate with microcontrollers and other electronic components. This integration is essential for enabling touch detection and communication with other devices.
- Encapsulation: Final assembly may involve encapsulating the sensor in protective housings to prevent damage from environmental factors.
Buyers should assess the assembly processes for automation and manual intervention levels, as these can influence both lead times and the potential for defects.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves finalizing the sensor’s appearance and functionality. This stage includes:
- Surface Treatment: Treatments such as polishing or applying anti-fingerprint coatings enhance the sensor’s usability and aesthetic appeal.
- Quality Control Checks: Before packaging, sensors undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specified performance criteria.
A well-executed finishing process can significantly enhance the product’s marketability. Buyers should ensure that suppliers maintain high standards in this area.
Quality Assurance in Capacitive Touch Sensor Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of manufacturing capacitive touch sensors, ensuring that the final products meet both customer expectations and regulatory standards.
International Standards
Adherence to international quality standards is essential for ensuring product reliability and market acceptance. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS), emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- RoHS Compliance: Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) compliance ensures that the sensors are free from harmful materials.
Buyers should verify that their suppliers are certified in these standards, as this reflects a commitment to quality and compliance.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring processes and conducting tests to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the overall quality of the finished product before shipment, verifying functionality, reliability, and compliance with specifications.
B2B buyers should request detailed QC reports from suppliers to understand their quality management practices.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods for capacitive touch sensors include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that the sensor responds accurately to touch inputs.
- Environmental Testing: Assessing performance under varying conditions, such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to contaminants.
- Durability Testing: Evaluating the sensor’s resistance to wear and tear, including scratch resistance and lifecycle testing.
Understanding these testing methods allows buyers to gauge the reliability of the sensors being sourced.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, buyers should consider the following verification methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports detailing testing results and compliance checks can help assess ongoing supplier performance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer unbiased evaluations of supplier capabilities and product quality.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must consider specific nuances in quality assurance practices. For example:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality perceptions can aid in negotiating terms and expectations.
- Regulatory Requirements: Different regions may have specific regulations affecting product compliance, such as local safety standards or import/export regulations.
- Logistical Challenges: Buyers should consider the logistics of sourcing from international suppliers, including shipping times, costs, and potential delays.
By focusing on these aspects, international buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing capacitive touch sensors, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Related Video: The Most Sophisticated Manufacturing Process In The World Inside The Fab | Intel
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for capacitive touch sensors Sourcing
In the realm of capacitive touch sensors, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section outlines the key cost components, influential pricing factors, and actionable buyer tips to help navigate this complex sourcing landscape.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials for capacitive touch sensors include printed circuit boards (PCBs), glass overlays, and conductive materials. The cost of these materials can vary significantly based on quality and source. For instance, standard glass may be less expensive than specialty materials like Pyrex®.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the region where manufacturing occurs. Countries with lower wage structures may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes compromise quality. Conversely, manufacturing in Europe might incur higher labor costs but could result in superior quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can fluctuate based on the production scale; larger operations often benefit from economies of scale.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and specialized equipment can be substantial, particularly for customized sensor designs. This upfront investment must be factored into the overall pricing, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards. These processes can add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product integrity, particularly in high-stakes applications like automotive or medical devices.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight, customs, and handling fees, can significantly affect total expenses. Buyers should consider the logistics of sourcing from different regions, as these costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and the chosen Incoterms.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. Margins can vary based on market conditions, competition, and supplier relationships.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can dramatically affect pricing. Higher volumes often lead to discounts, whereas smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications can lead to increased costs due to additional engineering and production adjustments. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Premium materials, such as those with enhanced durability or environmental resistance, will command higher prices.
-
Quality/Certifications: Certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can influence costs. Suppliers with verified quality standards may charge more, but this often translates to reduced risk for the buyer.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, but they often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is vital. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the overall cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in proactive negotiation with suppliers. Establishing a strong relationship can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors like lifecycle costs, maintenance, and potential downtimes due to inferior components.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of market trends and pricing fluctuations due to currency exchange rates, especially when dealing with international suppliers. This knowledge can aid in strategic purchasing decisions.
-
Regional Considerations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider regional manufacturing capabilities and supply chain logistics. Local suppliers may reduce lead times and shipping costs.
In conclusion, while the market for capacitive touch sensors presents opportunities for cost savings and efficiency, navigating the complexities of pricing requires a thorough understanding of the associated costs and influential factors. By leveraging these insights, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Disclaimer: The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific order requirements.
Spotlight on Potential capacitive touch sensors Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘capacitive touch sensors’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for capacitive touch sensors
In the world of capacitive touch sensors, understanding essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge aids in making informed purchasing decisions and fosters better communication with manufacturers and suppliers.
Critical Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Capacitive touch sensors are often made from materials such as glass, plastic, or specialized coatings. The choice of material impacts durability, sensitivity, and aesthetic appeal. For instance, glass overlays are preferred for their clarity and robustness, making them suitable for applications in consumer electronics and white goods. Buyers should evaluate material grades to ensure they meet industry standards and application requirements. -
Sensitivity
– Sensitivity refers to the sensor’s ability to detect touch and respond to it. It is influenced by the design, including the size of the sensor pad and the dielectric materials used. High sensitivity is essential for applications requiring precise touch recognition, especially in environments with varying conditions like moisture or dust. Buyers must assess sensitivity specifications to ensure optimal performance in their intended applications. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance indicates the acceptable variation in dimensions and performance of the sensor. It is critical for ensuring compatibility with other components and the overall device design. A tighter tolerance can lead to improved accuracy and reliability, particularly in complex or high-precision applications. Buyers should inquire about tolerance levels to minimize integration issues during manufacturing. -
Operating Temperature Range
– This specification defines the temperatures within which the sensor can operate effectively. Capacitive touch sensors may be exposed to extreme conditions depending on their application, such as in automotive or outdoor settings. Understanding the operating temperature range helps buyers select sensors that can withstand environmental challenges without performance degradation. -
Noise Immunity
– Noise immunity refers to the sensor’s ability to function accurately in the presence of electrical noise, which can lead to false triggering. This property is particularly important in industrial applications where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is common. Buyers should ensure that the sensors they select have robust noise immunity to enhance reliability and user experience.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of capacitive touch sensors, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can meet their specific needs and quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Negotiating MOQs can lead to cost savings, especially for larger orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is essential for initiating procurement processes and ensuring competitive pricing. Buyers should provide detailed specifications in their RFQs to receive accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers manage shipping costs, risks, and obligations effectively. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. This term is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when selecting suppliers to ensure timely delivery and avoid production delays. -
Customization
– Customization involves modifying a product to meet specific buyer requirements. In the capacitive touch sensor market, customization may include changes in size, material, or functionality. Buyers should discuss customization options with suppliers to ensure the product aligns with their needs.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the capacitive touch sensor market more effectively, leading to better product selection and successful procurement strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the capacitive touch sensors Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The capacitive touch sensors market is witnessing a significant transformation driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. As industries increasingly adopt touch interfaces for their user-friendly and intuitive nature, the demand for capacitive touch sensors is projected to grow at a robust pace. Key global drivers include the proliferation of smart devices, the push for automation in manufacturing, and the growing trend of IoT integration across sectors. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing decisions.
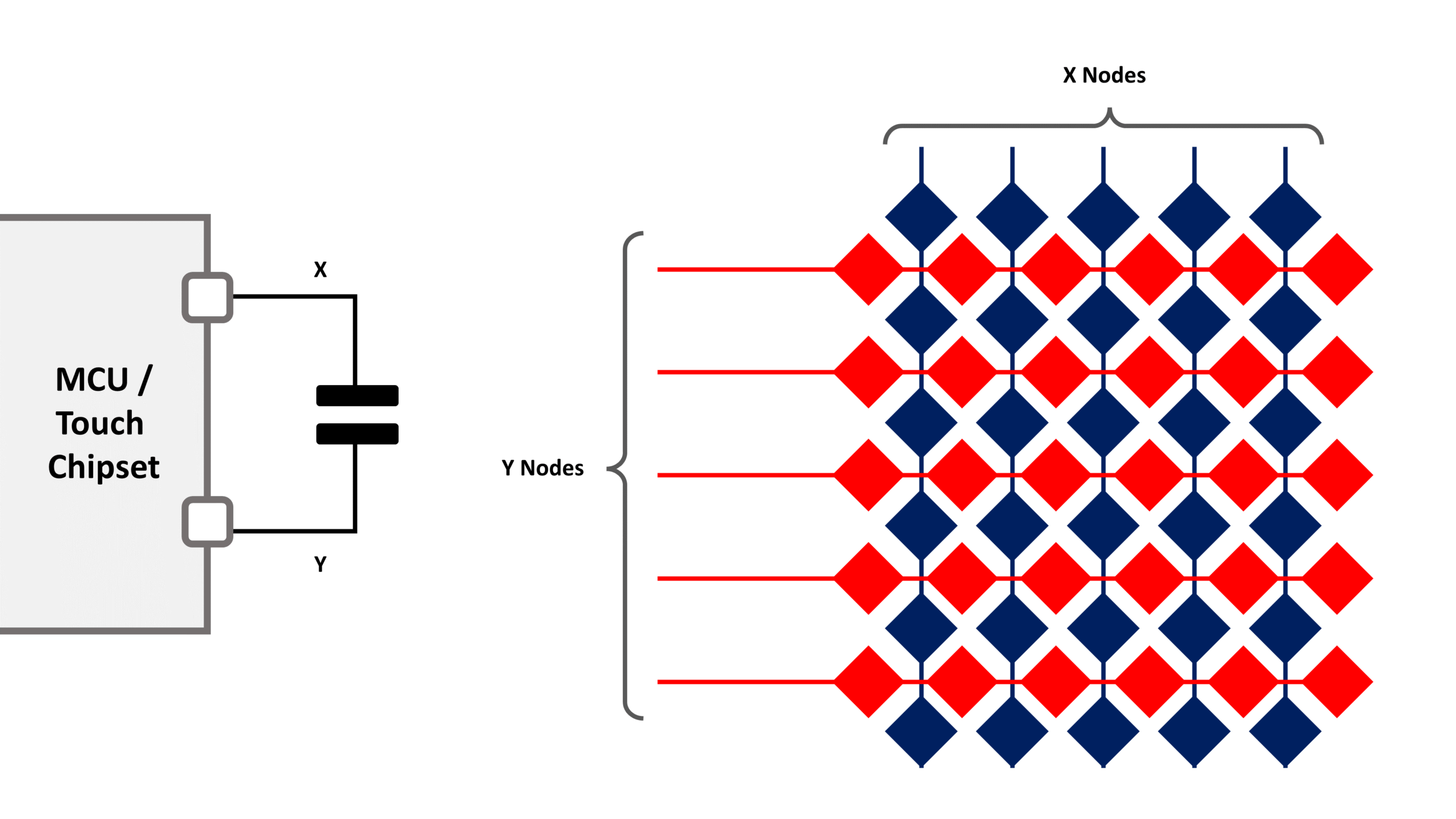
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Emerging trends such as the miniaturization of sensors, the development of multi-touch capabilities, and enhanced environmental resistance are shaping the market landscape. Buyers are encouraged to focus on suppliers offering innovative designs that can seamlessly integrate with modern applications, such as smart home devices, automotive systems, and industrial controls. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms has made it easier for buyers to access a global network of suppliers, facilitating better price comparisons and sourcing opportunities.
In Europe, particularly in countries like France and Poland, there is a notable emphasis on high-quality standards and compliance with regulatory requirements. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international certifications, ensuring product reliability and performance. Meanwhile, in emerging markets across Africa and South America, the focus is shifting towards cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality, making it essential to assess suppliers based on their ability to deliver value at competitive prices.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B sourcing strategies, particularly in the capacitive touch sensors sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in touch sensors is under scrutiny. Buyers must evaluate the lifecycle of products, from sourcing raw materials to end-of-life disposal. This includes a preference for suppliers who utilize recycled or eco-friendly materials in their manufacturing processes.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining importance. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with labor standards and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS for hazardous materials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Moreover, incorporating ‘green’ materials into product design not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the increasing demand from consumers for environmentally responsible products.
By prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing strategies, international buyers can not only mitigate risks associated with environmental compliance but also enhance their competitive edge in a market that increasingly values corporate social responsibility.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of capacitive touch sensors has been marked by significant technological advancements. Initially, these sensors were primarily used in consumer electronics as a replacement for mechanical buttons. Over the years, innovations in mixed-signal devices have expanded their applications to include a broader range of industries, from automotive to industrial automation.
The shift towards capacitive touch technology was driven by the need for more intuitive user interfaces that could support complex operations with simple gestures. As industries continue to innovate, the future of capacitive touch sensors appears promising, with ongoing developments in sensitivity, noise resistance, and environmental resilience, making them an integral part of modern technology solutions.
In summary, international B2B buyers must navigate a rapidly changing landscape characterized by technological advancements and sustainability imperatives to make informed sourcing decisions in the capacitive touch sensors market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of capacitive touch sensors
-
How can I vet suppliers of capacitive touch sensors?
When sourcing capacitive touch sensors, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate quality management systems. Review their client testimonials and case studies to assess their reliability. Consider requesting samples to evaluate product quality firsthand. Additionally, check if they have a track record in international trade, especially in your region, to ensure they understand local regulations and standards. -
Can capacitive touch sensors be customized for my specific application?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for capacitive touch sensors. This can include size, sensitivity, and functionality tailored to your specific needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements to the supplier. Additionally, inquire about their design capabilities and the lead times for custom orders. Ensure that they have a robust process for testing and validating custom designs to meet your quality expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for capacitive touch sensors?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier, often ranging from 100 to several thousand units. It’s essential to discuss your needs upfront to find a supplier that can accommodate your order size. Lead times can also differ based on the complexity of the sensors and the level of customization. Generally, expect lead times of 4-12 weeks for standard products, while custom solutions may take longer. Always confirm these details before placing an order to avoid supply chain disruptions.
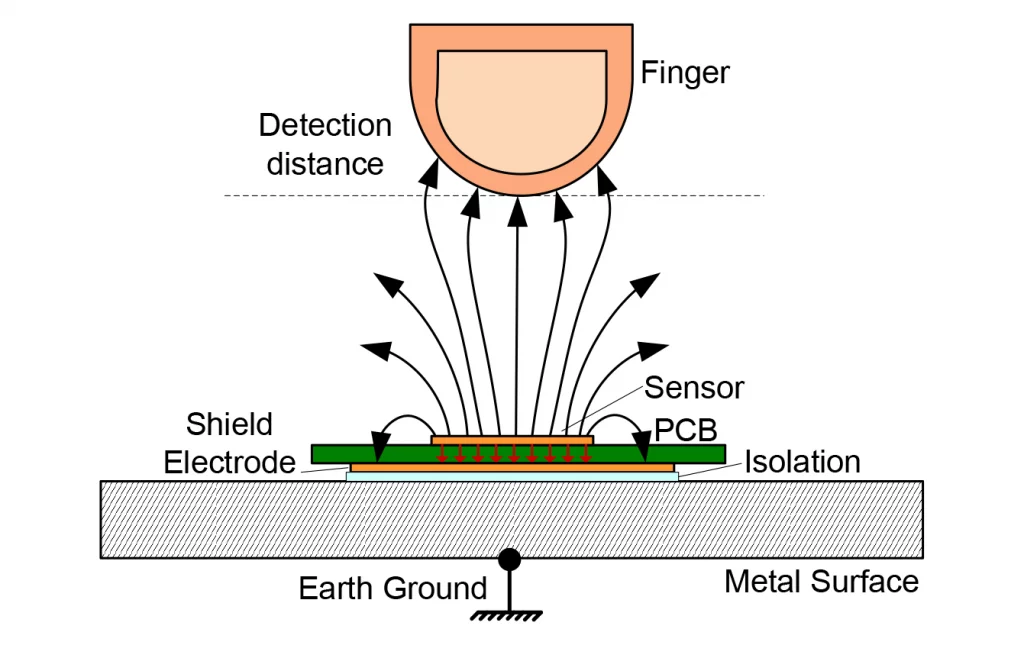
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What payment terms are usually offered for international purchases of capacitive touch sensors?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using escrow services for added security. Negotiate terms that balance your cash flow needs with the supplier’s requirements. It’s also advisable to understand the currency exchange implications and any additional fees associated with international payments to avoid unexpected costs. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reliable suppliers will have stringent quality assurance (QA) processes in place. This includes routine inspections, testing protocols, and certifications such as CE or RoHS compliance. Inquire about their QA procedures, including how they handle defects and returns. Request documentation of test results for the sensors you intend to purchase. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or requesting third-party inspection services to validate their QA practices. -
How can I ensure compliance with international regulations for capacitive touch sensors?
Compliance with international regulations is crucial when sourcing capacitive touch sensors. Suppliers should provide documentation proving compliance with relevant standards, such as CE marking in Europe or FCC certification in the USA. Ensure the sensors meet environmental regulations like RoHS or WEEE. Engage with your supplier to understand their compliance processes and ask for any necessary documentation to facilitate customs clearance and market entry in your region. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing capacitive touch sensors?
Logistics play a vital role in the timely delivery of capacitive touch sensors. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight costs, delivery times, and whether they can handle customs clearance. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping regulations. Factor in potential delays due to customs inspections or documentation issues. It’s also wise to consider insurance for your shipment to mitigate risks during transit. -
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively resolved?
To minimize disputes, establish clear communication and documentation from the outset. Include detailed terms in your contract regarding product specifications, delivery timelines, and payment conditions. In the event of a dispute, approach the supplier directly to discuss the issue amicably. If necessary, refer to the contract for resolution procedures, which may include mediation or arbitration. Consider involving a legal professional with expertise in international trade if the dispute escalates.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for capacitive touch sensors
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of capacitive touch sensors presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. As the demand for user-friendly interfaces continues to rise across diverse industries—from consumer electronics to industrial applications—investing in advanced capacitive touch technology is essential. Key takeaways include understanding the importance of design flexibility, noise resistance, and environmental durability, which are crucial for enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
By leveraging innovative solutions and partnerships with leading manufacturers, buyers can streamline their product development processes while minimizing costs. Moreover, the evaluation systems and development tools offered by various suppliers simplify the integration of capacitive touch technology, reducing time to market.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should proactively seek collaboration with technology providers to stay ahead of industry trends. Embracing these advancements will not only enhance product offerings but also position businesses for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape. Engage with suppliers today to harness the full potential of capacitive touch sensors and drive your innovation forward.