Master Sourcing Electrical Actuators: A Complete B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrical actuators
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, electrical actuators play a pivotal role in automating processes across various sectors, from manufacturing to energy management. These devices convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, enabling precise control over machinery and systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of electrical actuators is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower decision-makers by exploring the diverse types of electrical actuators, the materials used in their construction, and the manufacturing and quality control standards that ensure reliability. Buyers will gain insights into the landscape of suppliers, including key players in different regions, and learn how to navigate pricing structures to find the best value.
Furthermore, the guide addresses common FAQs to clarify misconceptions and provide essential information for informed sourcing decisions. By equipping international buyers with the knowledge needed to select the right electrical actuators, this guide not only enhances procurement strategies but also drives innovation and competitiveness in global markets. As industries increasingly lean towards automation, understanding electrical actuators is not just beneficial; it is imperative for sustained growth and success.
Understanding electrical actuators Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Linear Actuators | Converts electrical energy into linear motion; can be screw-driven or belt-driven. | Manufacturing automation, robotics, packaging. | Pros: High precision, low maintenance. Cons: Limited stroke length. |
| Electric Rotary Actuators | Provides rotational movement; often used in conjunction with gears. | Robotics, aerospace, automotive. | Pros: High torque, versatile. Cons: More complex installation. |
| Servo Actuators | Highly accurate positioning and speed control; typically closed-loop systems. | CNC machines, robotics, aerospace. | Pros: Excellent control, feedback capabilities. Cons: Higher cost. |
| Stepper Motors | Moves in discrete steps; ideal for precise positioning. | 3D printers, CNC equipment, medical devices. | Pros: Simple control, cost-effective. Cons: Can lose steps under load. |
| Smart Electric Actuators | Integrates IoT technology for remote monitoring and control; often programmable. | Smart factories, energy management, HVAC. | Pros: Enhanced control, data analytics. Cons: Requires robust cybersecurity measures. |
Electric Linear Actuators
Electric linear actuators are essential for converting electrical energy into linear motion, making them ideal for applications requiring precise positioning. Commonly found in manufacturing automation and robotics, these actuators can be either screw-driven or belt-driven. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the required stroke length and load capacity, as these factors can significantly impact performance and suitability for specific applications.
Electric Rotary Actuators
Electric rotary actuators provide rotational movement and are often paired with gears to enhance torque output. These actuators are widely used in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where precise motion control is critical. Buyers should assess the torque requirements and installation complexity when selecting rotary actuators, as these considerations can influence both performance and overall project timelines.
Servo Actuators
Servo actuators are known for their high accuracy in positioning and speed control, typically employing closed-loop systems for feedback. They are widely utilized in CNC machines and robotics, where precision is paramount. While servo actuators offer exceptional control capabilities, they come at a higher cost. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of precision against budget constraints when exploring servo options.
Stepper Motors
Stepper motors operate by moving in discrete steps, making them suitable for applications that require precise positioning, such as 3D printers and CNC equipment. They are relatively simple to control and cost-effective, which makes them appealing to budget-conscious businesses. However, buyers must consider the potential for losing steps under heavy loads, which can impact accuracy and reliability.
Smart Electric Actuators
Smart electric actuators are the latest innovation in actuator technology, incorporating IoT capabilities for remote monitoring and programmable features. These actuators are particularly beneficial in smart factories and energy management systems, where data analytics can enhance operational efficiency. While the integration of smart technology provides significant advantages, buyers must also prioritize cybersecurity to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of their systems.
Related Video: Actuator introduction and types of actuators in IOT
Key Industrial Applications of electrical actuators
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electrical Actuators | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines and robotic arms | Increases efficiency and precision in production | Reliability, load capacity, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Oil and Gas | Valve control in drilling and extraction processes | Enhances safety and operational efficiency | Environmental ratings, remote operation capabilities, and maintenance support |
| Automotive | Electric vehicle (EV) battery management systems | Improves energy efficiency and vehicle performance | Thermal management, integration with EV systems, and scalability |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and bottling processes | Ensures consistent quality and reduces waste | Hygiene standards, speed of operation, and regulatory compliance |
| Water Treatment | Flow control in treatment plants | Optimizes resource management and reduces downtime | Corrosion resistance, adaptability to varying conditions, and energy consumption |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, electrical actuators are integral to automated assembly lines and robotic arms. These systems enhance production efficiency by enabling precise movements and actions that surpass human capabilities. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing actuators that are reliable and compatible with existing machinery is crucial. Considerations such as load capacity and environmental conditions also play a significant role in ensuring seamless integration and operational efficiency.
Oil and Gas
Electrical actuators are critical in the oil and gas industry for controlling valves during drilling and extraction processes. They significantly enhance safety by allowing remote operation, which is essential in hazardous environments. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize actuators with high environmental ratings and robust maintenance support to ensure longevity and reliability in demanding conditions. The ability to operate under extreme temperatures and pressures is a vital consideration for sourcing.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), electrical actuators are used in battery management systems to optimize energy use and enhance vehicle performance. Buyers should focus on actuators that offer thermal management capabilities and seamless integration with EV systems. As the automotive market continues to evolve, scalability and adaptability to new technologies will be key for businesses looking to stay competitive in Europe and beyond.
Food and Beverage
In food and beverage manufacturing, electrical actuators play a crucial role in packaging and bottling processes. They ensure consistent quality and help reduce waste, which is vital for maintaining profitability. Buyers must consider hygiene standards and speed of operation when sourcing these actuators. Additionally, compliance with food safety regulations is paramount, especially for international companies looking to expand into new markets.
Water Treatment
Electrical actuators are essential for flow control in water treatment plants. They optimize resource management and minimize downtime, which is critical for maintaining operational efficiency. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, sourcing actuators that are corrosion-resistant and adaptable to varying environmental conditions is important. Energy consumption is another key factor, as businesses strive to implement sustainable practices while managing operational costs effectively.
Related Video: Basics of Electric Valve Actuators
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrical actuators
When selecting materials for electrical actuators, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The choice of material can significantly impact the actuator’s efficiency, durability, and compatibility with various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of electrical actuators, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand moderate temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating up to 150°C and can handle pressures around 10 bar.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which makes it ideal for applications requiring mobility. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture. However, aluminum may not be suitable for high-pressure applications and can be less durable than other metals in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for corrosive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with regional standards such as ASTM or DIN for aluminum components. In markets like Africa and South America, where environmental factors may be harsher, additional coatings or treatments may be necessary.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and a temperature rating of up to 300°C. It can withstand pressures exceeding 50 bar, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability and strength of stainless steel make it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine, leading to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals, making it a versatile choice for various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A276 or JIS G4303 is crucial. Buyers in regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures and humidity are common, should prioritize stainless steel for its resilience.
Plastic Composites
Key Properties: Plastic composites, often reinforced with fibers, provide good chemical resistance and can operate effectively in temperatures up to 120°C. They are lightweight and can handle moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for various applications. However, they may not offer the same strength or durability as metals, and their performance can degrade under extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for applications involving corrosive substances, but they may not be suitable for high-load scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for plastics. In regions like Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent, selecting recyclable composites can be advantageous.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments, and has a temperature rating of up to 200°C. It can withstand pressures around 30 bar.
Pros & Cons: Brass is easy to machine and offers good conductivity, making it suitable for electrical applications. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be less durable in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with various media, including water and gases, but may not be suitable for highly corrosive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 is important. Buyers from regions like South America should consider the local availability and cost of brass, as it can be more expensive due to import tariffs.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electrical actuators | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications, general use | Low weight and cost | Not suitable for high-pressure | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty, corrosive environments | High strength and durability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic Composites | Corrosive media applications | Excellent chemical resistance | Lower strength compared to metals | Medium |
| Brass | Electrical components, marine applications | Good conductivity and corrosion resistance | More expensive than aluminum | Medium |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, assisting them in making informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrical actuators
Manufacturing Processes for Electrical Actuators
Electrical actuators are critical components in various industrial applications, providing precise control over movement and position. Understanding the manufacturing processes involved can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. The typical manufacturing process for electrical actuators consists of several key stages:
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of electrical actuators involves selecting and preparing the raw materials. Common materials include metals like aluminum or steel for structural components, along with plastics or composites for housings and insulations.
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on mechanical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Preprocessing: Materials are often cut, machined, or treated to meet specific design requirements before moving to the next stage.
Forming
The forming stage shapes the raw materials into components that will be assembled into the actuator. This stage may involve several techniques:
- Machining: Processes like CNC milling and turning are used to achieve precise dimensions.
- Casting or Molding: For complex shapes, materials may be cast into molds or formed through injection molding.
- Stamping: Sheet metal components are often produced through stamping, ensuring efficiency and uniformity.
Assembly
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into the final actuator. This stage requires careful attention to detail to ensure functionality and reliability.
- Sub-Assembly: Individual components, such as motors, gears, and electronic controls, are first assembled into sub-assemblies.
- Final Assembly: The sub-assemblies are then integrated into the actuator, which may include installing sensors and wiring.
- Quality Checks: At various points during assembly, quality checks should be conducted to ensure components fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing includes finishing processes that enhance the actuator’s durability and performance.
- Surface Treatment: Coatings or treatments (e.g., anodizing, painting) protect against corrosion and wear.
- Testing and Calibration: Each actuator undergoes functional testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This may involve dynamic testing under various loads and conditions.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of electrical actuators, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of the following QA practices and standards:
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For actuators used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To maintain quality throughout the manufacturing process, several checkpoints should be established:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspect raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conduct checks at various stages of the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Perform thorough inspections and testing of the finished product before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are vital to ensure the reliability and performance of electrical actuators. Common tests include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying the actuator operates as intended under different loads and conditions.
- Environmental Testing: Assessing performance in extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors.
- Endurance Testing: Evaluating how well the actuator withstands repeated use over time.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing results, compliance with standards, and corrective actions taken for any identified issues.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent assessments of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes.
Quality Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing electrical actuators internationally, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider specific nuances:
- Local Regulations: Be aware of local certifications and regulations that may differ from international standards.
- Cultural Differences: Understand the cultural context that may affect manufacturing practices and quality perceptions.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ensure transparency in the supply chain, as this can impact quality assurance and delivery timelines.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing electrical actuators and make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Related Video: Cell Production | Battery Manufacturing Automation
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrical actuators Sourcing
When sourcing electrical actuators, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of cost structures and pricing dynamics. Understanding these elements can significantly impact procurement decisions, especially for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
A comprehensive cost structure for electrical actuators includes several key components:
- Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as metals and plastics, can fluctuate based on global supply chains and market demand. Specialty materials for high-performance actuators can further increase costs.
- Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. Countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but this may come with trade-offs in quality and service levels.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs associated with running production facilities, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory management. Efficient operations can lead to lower overhead, which can positively influence pricing.
- Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized actuator designs can be a substantial upfront investment. Buyers should consider this when evaluating quotes, as tooling costs are often amortized over large production runs.
- Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards, which can add to overall costs but is essential for long-term operational success.
- Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and regional logistics capabilities. Buyers should factor in both domestic and international shipping expenses.
- Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market positioning and competition. Understanding a supplier’s margin can provide insights into pricing flexibility during negotiations.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of electrical actuators:
- Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should evaluate their needs against potential savings from bulk purchasing.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom designs and specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should assess whether standard products meet their needs or if customization is essential.
- Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) can drive up prices but may be necessary for specific applications. Buyers must weigh the importance of these factors against their budget constraints.
- Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge a premium but offer greater peace of mind.
- Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect the total landed cost, including shipping responsibilities and risk levels. Buyers should carefully select terms that align with their logistical capabilities.
Buyer Tips
To optimize the sourcing process for electrical actuators, consider the following strategies:
- Negotiation: Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms with suppliers. Understanding the cost components can empower buyers during discussions.
- Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to overall savings.
- Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, suppliers in emerging markets may offer lower prices but could have longer lead times or less robust support services.
- Local Regulations: Understand any import tariffs or regulations that may affect the final pricing. This is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where trade policies can vary significantly.
Disclaimer
Prices for electrical actuators can fluctuate due to market conditions and specific buyer requirements. The information provided here is intended as a general guide and should be supplemented with detailed quotes and supplier discussions to achieve the best procurement outcomes.
Spotlight on Potential electrical actuators Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electrical actuators’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrical actuators
Critical Technical Properties of Electrical Actuators
Understanding the essential technical properties of electrical actuators is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the quality of materials used in actuator construction, such as aluminum, stainless steel, or composite materials.
– Importance: Material choice affects the actuator’s durability, weight, and resistance to environmental factors. For example, stainless steel is preferred in corrosive environments, while aluminum is lighter and may offer cost advantages. -
Torque Rating
– Definition: The maximum torque an actuator can produce, usually measured in Newton-meters (Nm).
– Importance: This specification is critical for ensuring that the actuator can handle the load requirements of your application. Inadequate torque can lead to system failure or inefficiencies. -
Speed Rating
– Definition: Indicates the speed at which the actuator can operate, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM) or millimeters per second (mm/s).
– Importance: Understanding speed is essential for applications requiring precise timing and coordination. Buyers need to ensure that the actuator can meet the speed demands of their specific processes. -
Stroke Length
– Definition: The maximum distance an actuator can travel when fully extended, measured in millimeters or inches.
– Importance: Stroke length determines the range of motion available for applications. Buyers must align stroke length with their equipment’s design to ensure compatibility. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
– Definition: A classification that indicates how well the actuator is protected against solids and liquids, such as dust and water.
– Importance: A higher IP rating means better protection, which is vital in industries like food processing or outdoor applications where exposure to harsh conditions is common. -
Power Supply Voltage
– Definition: The voltage required to operate the actuator, commonly 24V, 110V, or 230V.
– Importance: Compatibility with existing electrical systems is essential. Buyers should ensure that the actuator’s voltage matches the power supply available in their facilities to avoid operational issues.
Common Trade Terminology in Electrical Actuators
Navigating the purchasing process requires familiarity with specific industry jargon. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure the compatibility of components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Buyers must be aware of MOQ to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. This is particularly relevant for small to medium-sized enterprises looking to minimize excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs facilitate competitive pricing and help buyers gauge market rates, ensuring they get the best possible deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law.
– Importance: Incoterms clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements, helping to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping costs, risks, and delivery points. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management. Buyers need to consider lead time when aligning actuator availability with production schedules. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The duration for which the manufacturer guarantees the actuator against defects in materials and workmanship.
– Importance: A longer warranty period often indicates higher product quality and can provide buyers with peace of mind regarding their investment.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure successful integration of electrical actuators into their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electrical actuators Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electrical actuators market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace. As global industries pivot towards smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, the demand for precision motion control solutions is escalating. Key drivers include technological advancements in actuator design, such as the integration of IoT and AI, which enhance operational efficiency and data analytics capabilities.
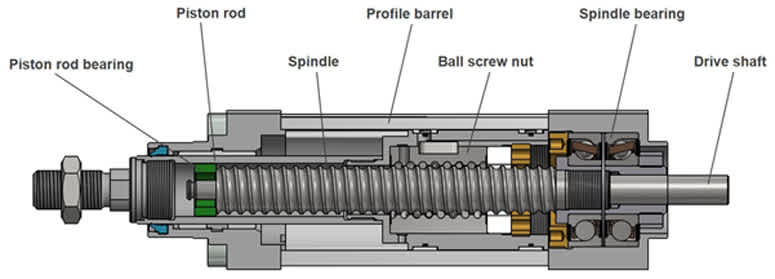
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Emerging trends include a shift towards modular actuator systems that allow for easier integration and scalability. Additionally, the rise of electric actuators over traditional pneumatic and hydraulic systems is notable, primarily due to their energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
Another critical aspect is the focus on local sourcing and supplier diversification to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. B2B buyers should consider collaborating with manufacturers that offer customization options, ensuring that solutions are tailored to specific operational needs. Furthermore, integrating digital tools for procurement and inventory management can streamline sourcing processes, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of electrical actuators cannot be overstated. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, the sustainability of sourcing practices is becoming a key consideration. For B2B buyers, partnering with manufacturers that prioritize sustainable materials and production methods is essential. This includes sourcing components that comply with environmental regulations and certifications, such as ISO 14001, which signifies a commitment to effective environmental management systems.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important as consumers and businesses alike demand transparency. Buyers should seek suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices, including fair labor standards and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wood-based components and the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) for recycled materials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability.
Investing in “green” technologies not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance brand reputation. As the market moves towards electric and hybrid actuators, buyers should evaluate the lifecycle impacts of their purchases, aiming for products that offer durability and recyclability at the end of their operational life.
Brief Evolution/History
The electrical actuator sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by hydraulic and pneumatic systems, the industry began transitioning to electric solutions in the late 20th century as technology improved. The advent of solid-state electronics and microcontrollers allowed for more precise control and automation capabilities, leading to widespread adoption in various sectors.
Today, electrical actuators are at the forefront of innovation, incorporating advanced features such as smart sensors and connectivity options that facilitate real-time monitoring and diagnostics. As industries continue to embrace automation and sustainable practices, the evolution of electrical actuators is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing and process control. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can inform strategic sourcing decisions and investments in cutting-edge technologies.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrical actuators
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for electrical actuators?
To vet suppliers, start by assessing their industry experience and reputation. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate quality management systems. Request references and conduct background checks on previous clients. Additionally, review their production capabilities and technology used in manufacturing. Attending trade shows or visiting their facilities can also provide valuable insights into their operations and reliability. -
Can electrical actuators be customized to meet specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electrical actuators. Buyers can specify requirements such as size, force, stroke length, and control options. Before proceeding, communicate your needs clearly and request prototypes or samples to evaluate performance. Ensure that the supplier has a robust engineering team to support your customization requests, as this can impact lead times and costs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
MOQs for electrical actuators can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, standard products may have lower MOQs, while customized solutions could require higher volumes. Lead times can range from a few weeks for standard items to several months for custom designs. Always confirm these details upfront and consider discussing flexible arrangements if your project requires it. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electrical actuators?
Payment terms typically vary by supplier and can include options such as upfront payments, net 30/60/90 days, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate these terms early in the relationship. Consider using letters of credit for larger orders to mitigate risks. Always review the supplier’s payment policies and any associated fees, especially if dealing with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for electrical actuators?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation that verifies compliance with international standards such as CE, RoHS, or UL certifications. A supplier should be willing to provide test reports and quality control processes. Additionally, consider implementing regular audits or inspections during production, especially for large orders, to confirm that products meet your specifications and standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing from international suppliers?
When dealing with international suppliers, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Evaluate the supplier’s experience with logistics and their ability to handle international shipping. It may be beneficial to work with freight forwarders who can navigate complex logistics and provide insurance options. Lastly, ensure that the delivery timeline aligns with your project schedule to avoid disruptions. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication with the supplier. Document all correspondence and agreements. If necessary, escalate the matter to a formal dispute resolution process outlined in your contract, such as mediation or arbitration. Familiarize yourself with the legal framework governing international trade in your contract to understand your rights and options. -
How can I effectively manage the supply chain for electrical actuators?
Managing the supply chain involves maintaining clear communication with suppliers and regularly monitoring inventory levels. Implement inventory management systems to track usage and anticipate needs. Building strong relationships with multiple suppliers can provide flexibility and mitigate risks. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and potential disruptions can help you make proactive decisions to maintain a steady supply of electrical actuators.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrical actuators
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of electrical actuators is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By prioritizing suppliers who offer advanced technology and robust after-sales support, businesses can ensure longevity and reliability in their automation processes. It is essential to evaluate potential partners based on their ability to meet regional compliance standards, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory landscapes can vary significantly.
Key Takeaways:
- Assess Supplier Capabilities: Look for suppliers that provide comprehensive technical support and customization options to cater to specific industry needs.
- Leverage Local Partnerships: Engaging with local distributors can facilitate quicker response times and better understanding of market dynamics.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime when evaluating actuator solutions.
As the demand for automation continues to rise, now is the time for international B2B buyers to invest in reliable electrical actuator solutions. Embrace the future of automation and partner with trusted suppliers to drive your business forward.