Master Sourcing Fractional Horsepower Motors for Optimal
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fractional horsepower motor
In today’s competitive landscape, fractional horsepower motors (FHPMs) are crucial components that enable businesses to innovate and enhance operational efficiency. Operating at less than one horsepower, these motors are versatile and integral to a wide array of applications, from household appliances to advanced robotics. Their compact size and reliability make them a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to optimize energy consumption while maintaining high performance.
This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Mexico and Germany. Within these pages, you will explore the various types of fractional horsepower motors, including brushed and brushless options, as well as their design specifications and material considerations.
Moreover, we delve into manufacturing practices and quality control measures that ensure product reliability, guiding buyers in selecting the right suppliers. A thorough analysis of cost factors and market trends will empower your purchasing decisions, ensuring you maximize value while minimizing risk.
Lastly, our FAQs section addresses common queries, offering insights that facilitate informed sourcing strategies. By leveraging this guide, you will enhance your understanding of fractional horsepower motors, enabling you to make strategic decisions that drive your business forward in the global marketplace.
Understanding fractional horsepower motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brush Series Motor | Simple design, cost-effective, uses brushes for commutation | Power tools, household appliances, automotive systems | Pros: Low cost, easy speed control. Cons: Higher maintenance due to brush wear. |
| Brushless Motor | No brushes, uses electronic controllers for commutation | Robotics, HVAC systems, medical devices | Pros: Low maintenance, higher efficiency. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Stepper Motor | Precise control of angular position, used in open-loop systems | 3D printers, CNC machines, automated equipment | Pros: Excellent precision, easy to control. Cons: Limited torque at high speeds. |
| Permanent Magnet Motor | Utilizes permanent magnets for efficiency and compactness | Electric vehicles, consumer electronics | Pros: High efficiency, compact design. Cons: Sensitive to temperature changes. |
| Synchronous Motor | Operates at synchronous speed, ideal for constant speed applications | Industrial machinery, conveyor systems | Pros: High efficiency, reliable operation. Cons: Requires precise frequency control. |
Brush Series Motor
Brush series motors are among the oldest types of fractional horsepower motors, characterized by their straightforward design involving brushes that make contact with a rotating commutator. These motors are particularly suitable for applications where variable speed and moderate torque are required, such as power tools and household appliances. When considering a brush series motor, buyers should assess the balance between initial cost and maintenance needs, as the brushes require periodic replacement, impacting long-term operational costs.
Brushless Motor
Brushless motors stand out for their efficiency and low maintenance requirements, as they eliminate the need for brushes. Instead, they rely on electronic controllers to manage commutation. This type of motor is ideal for applications requiring high reliability and performance, such as robotics and HVAC systems. B2B buyers should consider the higher upfront investment against the long-term benefits of lower maintenance and improved energy efficiency, making them a preferred choice for high-performance applications.
Stepper Motor
Stepper motors offer exceptional precision, making them ideal for applications that require accurate positioning, such as 3D printers and CNC machines. They operate in discrete steps, allowing for precise control over angular position. Buyers should evaluate the torque requirements and speed capabilities when selecting stepper motors, as they can experience limitations in torque at higher speeds. Their ease of control and precision make them valuable in automation and robotics sectors.
Permanent Magnet Motor
Permanent magnet motors utilize permanent magnets to create a magnetic field, resulting in a compact and efficient design. They are commonly found in electric vehicles and consumer electronics due to their high efficiency and power density. For B2B buyers, it is essential to consider the operating environment, as these motors can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Their compact size and efficiency often justify the investment, particularly in applications where space and energy consumption are critical factors.
Synchronous Motor
Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed synchronized with the frequency of the power supply, making them suitable for industrial machinery and conveyor systems that require steady operation. These motors are known for their high efficiency and reliability. Buyers should be aware that synchronous motors require precise control of frequency to maintain performance, which may necessitate additional investment in control systems. Their robustness and efficiency can result in significant operational savings over time, making them an attractive option for many industrial applications.
Related Video: Motorcycle Types for Beginners – How to Choose at RevZilla.com
Key Industrial Applications of fractional horsepower motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Fractional Horsepower Motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| HVAC Systems | Fan and blower systems | Enhanced energy efficiency and reduced operational costs | Evaluate motor efficiency ratings and noise levels. |
| Medical Equipment | Surgical tools and devices | Precision control and reliability in critical operations | Ensure compliance with medical standards and certifications. |
| Agriculture | Irrigation pumps | Improved water management and crop yield | Assess durability against environmental conditions. |
| Consumer Appliances | Washing machines and kitchen devices | Cost-effective solutions with compact design | Consider voltage compatibility and service availability. |
| Robotics | Actuators in robotic arms | High precision and control for automation tasks | Focus on torque requirements and integration capabilities. |
HVAC Systems
In HVAC applications, fractional horsepower motors are integral to fan and blower systems, providing the necessary airflow for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. These motors enhance energy efficiency, translating to lower operational costs for businesses. For international buyers, particularly in regions with varying electrical standards, it is crucial to evaluate the motor’s efficiency ratings and noise levels, ensuring compliance with local regulations and operational requirements.
Medical Equipment
Fractional horsepower motors play a pivotal role in powering surgical tools and medical devices, where precision and reliability are paramount. These motors ensure that equipment operates smoothly during critical procedures, thereby enhancing patient safety and operational efficiency. Buyers in the medical sector should prioritize sourcing motors that comply with stringent medical standards and certifications to guarantee safety and efficacy in their applications.
Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, fractional horsepower motors are commonly used in irrigation pumps, enabling efficient water management and contributing to improved crop yields. These motors provide the necessary power to move water from sources to fields, optimizing irrigation processes. Buyers should assess the durability of these motors against environmental conditions, particularly in regions prone to extreme weather, to ensure longevity and reliability.
Consumer Appliances
Fractional horsepower motors are essential in household appliances, such as washing machines and kitchen devices, where they provide cost-effective solutions with a compact design. These motors enable efficient operation, improving user experience and energy consumption. When sourcing motors for consumer appliances, it is important to consider voltage compatibility and the availability of local service support to address maintenance needs.
Robotics
In the field of robotics, fractional horsepower motors are utilized as actuators in robotic arms, offering high precision and control for automation tasks. These motors facilitate accurate movements, making them ideal for applications in manufacturing and assembly lines. Buyers should focus on the torque requirements and integration capabilities of these motors to ensure they meet the specific demands of their robotic systems.
Related Video: What is a Servo Motor and How it Works?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fractional horsepower motor
When selecting materials for fractional horsepower motors, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. The choice of material can significantly affect the motor’s performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in fractional horsepower motors.
1. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity, and offers good corrosion resistance. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150°C (302°F) and is suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for motor housings and components. However, it may not be as strong as steel, which can limit its use in heavy-duty applications. The manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, but the material can be more expensive than some alternatives.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as portable tools and small appliances. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments with moisture or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Europe and Germany, aluminum components must meet stringent environmental regulations regarding recyclability and energy efficiency.
2. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high strength and durability, with a temperature rating of up to 250°C (482°F). It is resistant to wear and can handle high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its robustness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which can be a drawback for portable devices. Steel can also be prone to corrosion if not properly treated, leading to increased maintenance costs.
Impact on Application:
Steel is commonly used in applications requiring high torque and load-bearing capabilities, such as industrial machinery and HVAC systems. Its strength makes it ideal for motors that operate in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings to prevent corrosion, especially in humid regions like parts of Africa and South America. Compliance with standards such as JIS for steel quality may also be necessary.
3. Plastic
Key Properties:
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, offer lightweight properties and good electrical insulation. They can typically withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and are resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of plastics makes them suitable for compact designs. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals and can be affected by UV exposure over time. Manufacturing processes can vary in complexity, impacting cost.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are often used in consumer electronics and household appliances where weight reduction is essential. Their insulating properties make them suitable for electrical components.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with international standards for electrical safety and environmental impact, particularly in Europe where regulations on plastic use are stringent.
4. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties, with a melting point of around 1,085°C (1,985°F). It is also resistant to corrosion, especially when properly treated.
Pros & Cons:
Copper is essential for windings and electrical connections in motors due to its conductivity. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can add significant weight to the motor. The manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precise winding.
Impact on Application:
Copper is crucial in applications where efficient electrical performance is necessary, such as in servo motors and high-performance fractional horsepower motors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the fluctuating costs of copper and the implications for budget constraints. Compliance with standards regarding electrical components is vital, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for fractional horsepower motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable tools, small appliances | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less strong than steel | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial machinery, HVAC systems | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics, household appliances | Lightweight and good insulation | Less durable and UV sensitive | Low |
| Copper | Servo motors, high-performance applications | Excellent electrical conductivity | Expensive and heavy | High |
This guide provides insights for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting materials for fractional horsepower motors, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fractional horsepower motor
The manufacturing of fractional horsepower motors involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is a detailed overview of the typical manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures relevant to fractional horsepower motors.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The initial phase of manufacturing involves sourcing and preparing high-quality raw materials. Common materials used in fractional horsepower motors include:
- Copper Wire: Essential for winding coils.
- Silicon Steel: Used for the stator and rotor cores, chosen for its magnetic properties.
- Insulating Materials: Such as varnishes and plastics to prevent electrical shorting.
Key Techniques:
– Material Testing: Conducting tests on incoming materials (IQC – Incoming Quality Control) to ensure they meet specified standards.
– Inventory Management: Efficient tracking of materials to reduce waste and ensure timely availability.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will make up the motor. Key activities include:
- Winding Coils: Copper wire is wound around a core to create the motor’s electromagnetic coils. This process can be automated to enhance precision and reduce labor costs.
- Stator and Rotor Fabrication: Stator and rotor components are stamped and shaped from silicon steel sheets. High precision is crucial to minimize air gaps, which affect efficiency.
Key Techniques:
– CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are often used for precise cutting and shaping.
– Laser Cutting: Employed for high-precision parts that require intricate designs.
3. Assembly
The assembly process involves integrating all components to create a functional motor. This includes:
- Mounting the Stator and Rotor: Ensuring proper alignment for optimal performance.
- Installing Bearings and Other Components: Bearings reduce friction and wear, crucial for motor longevity.
Key Techniques:
– Automated Assembly Lines: Use of robots and automated systems to enhance speed and accuracy.
– Manual Assembly: In some cases, skilled technicians perform assembly to ensure quality in complex parts.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing focuses on enhancing the motor’s durability and performance. This includes:
- Coating and Painting: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and wear.
- Final Assembly Checks: All components are double-checked for proper fit and functionality.
Key Techniques:
– Quality Control Inspections: Visual and functional checks to ensure that all parts meet specifications.
– Testing for Vibration and Noise Levels: Ensures the motor operates smoothly and within acceptable limits.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of fractional horsepower motors. It ensures that products meet international standards and specific customer requirements.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This quality management system standard is essential for ensuring consistent quality across processes. Suppliers should have certification to demonstrate adherence to these standards.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, crucial for B2B buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for motors used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring reliability under harsh conditions.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that motors operate within specified voltage and current limits.
- Performance Testing: Assesses torque, speed, and efficiency under load conditions.
- Endurance Testing: Simulates long-term use to identify potential failure points.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
- Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can reveal their commitment to quality and adherence to standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and inspection records.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can provide unbiased assessments of product quality.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification that may vary by region:
- Local Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in their manufacturing countries, as this can affect product quality and safety.
- Language Barriers: Documentation and reports may be in different languages; ensure that all quality reports are clearly understood to avoid misinterpretation.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding different cultural approaches to quality can help in negotiating and establishing effective supplier relationships.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for fractional horsepower motors are intricate and critical for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes and implementing rigorous quality checks, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing motors from international suppliers. This knowledge not only enhances procurement efficiency but also contributes to the overall success of their operations.
Related Video: BMW 5 Series (2024) PRODUCTION 🇩🇪 Car Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fractional horsepower motor Sourcing
To effectively navigate the sourcing of fractional horsepower motors, understanding the cost structure and pricing factors is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, including copper for windings, steel for frames, and magnets for brushless motors, constitutes a significant portion of the total cost. Prices can fluctuate based on global market trends, impacting overall expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the final price significantly. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, the overall manufacturing expense will be greater compared to regions with lower labor costs, like some parts of Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient operations can help minimize overheads, but buyers should be aware that these costs are often passed on in pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling for motor production can be substantial. Custom tooling is often required for specific designs, which can increase the upfront costs for buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential for ensuring reliability and performance. The cost associated with QC can vary depending on the complexity of the motor and the certifications required.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are significant, especially for international transactions. These costs can be influenced by distance, shipping mode, and volume.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary greatly depending on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized motors may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected expenses during production.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials and certifications can lead to increased prices. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term costs related to maintenance and replacement.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and capacity can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but their reliability can lead to lower total costs over time.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the overall landed cost of the motors.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly if you can commit to larger volumes. Establishing a long-term relationship may also lead to better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes acquisition, operational, and maintenance costs. Sometimes a higher upfront cost can lead to lower operational expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Consider hedging strategies or locking in prices where feasible.
-
Supplier Diversity: Don’t rely solely on one supplier. Explore multiple sources, including local and international options, to compare pricing and service levels.
-
Certification Importance: Ensure that the motors meet relevant international standards and certifications, as this can impact both safety and performance.
In conclusion, careful analysis of the cost structure, price influencers, and strategic purchasing tips will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing fractional horsepower motors. Always consider the broader implications of pricing and supplier selection to optimize both cost and operational efficiency.
Spotlight on Potential fractional horsepower motor Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘fractional horsepower motor’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fractional horsepower motor
In the international B2B landscape, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the technical properties and trade terminology related to fractional horsepower motors is essential for informed purchasing decisions. Below, we explore critical specifications and key industry terms that are crucial for navigating the market effectively.
Key Technical Properties
-
Power Rating
The power rating of a fractional horsepower motor typically ranges from 1/20 to 1 horsepower (746 watts). Understanding this specification is vital as it directly correlates to the motor’s performance in various applications. Buyers must ensure the selected motor meets the specific power requirements of their equipment to achieve optimal efficiency and reliability. -
Efficiency Class
Efficiency is a critical metric that measures how effectively a motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Motors are often classified according to efficiency standards, such as IE1, IE2, IE3, and IE4. Higher efficiency classes result in lower energy consumption and operational costs, making them particularly appealing in regions where energy costs are high. -
Voltage Rating
Fractional horsepower motors are available in various voltage ratings, including 120V, 230V, and 400V. The voltage rating must match the electrical supply available in the buyer’s region to prevent operational issues. This is especially important in international transactions, where voltage standards can vary significantly. -
Torque Characteristics
Starting torque and running torque are critical specifications that define how well the motor performs under load. Starting torque is particularly important in applications requiring the motor to overcome inertia, while running torque is crucial for maintaining performance during operation. Buyers should assess the torque requirements of their application to select a suitable motor. -
Duty Cycle
The duty cycle indicates how long a motor can operate under specific conditions before it needs to rest. This specification is vital for applications requiring continuous operation. Understanding duty cycles helps buyers select motors that can handle their operational demands without overheating or failing prematurely. -
Mounting Configuration
The mounting configuration refers to how the motor is attached to its application. Common configurations include foot-mounted, flange-mounted, and face-mounted designs. Selecting the correct mounting configuration ensures proper integration into existing systems, minimizing installation challenges.
Common Trade Terminology
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they receive quality products that meet industry standards.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory management and capital allocation. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing needs to avoid excess inventory costs.
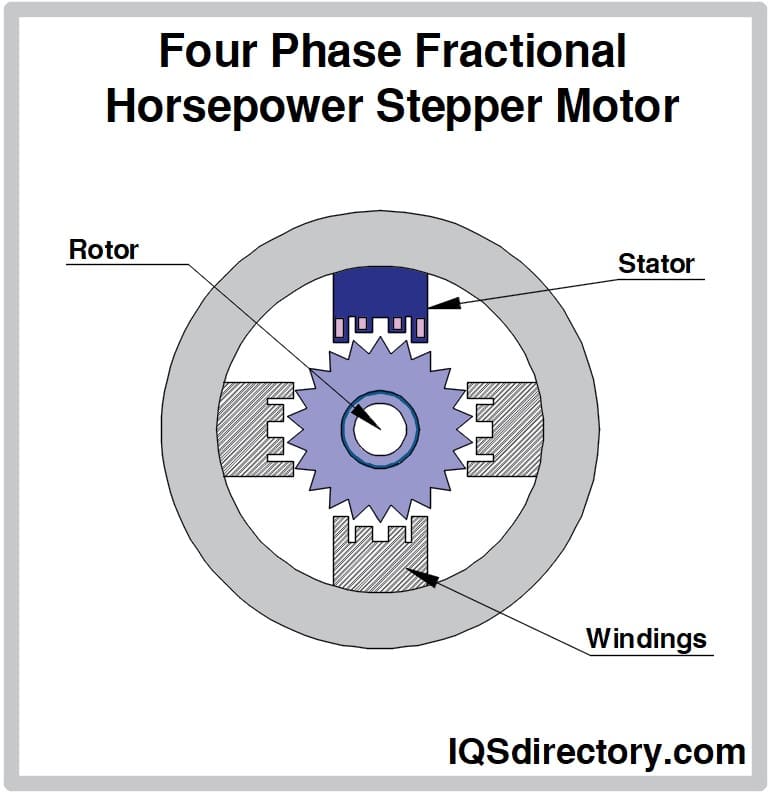
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. An effective RFQ should include detailed specifications and quantities. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities, cost implications, and risk management. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who need to plan their production schedules. Understanding lead times helps in managing expectations and minimizing delays. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or CE marking, indicate that a product meets specific safety and quality criteria. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to recognized certification standards to ensure compliance and reduce liability risks.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their fractional horsepower motors meet their operational requirements while optimizing their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the fractional horsepower motor Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The fractional horsepower motor (FHP motor) market is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. Increased demand for energy-efficient solutions, the proliferation of automation in manufacturing, and the surge in electric vehicle (EV) technology are pivotal drivers. In regions like Africa and South America, the push for sustainable energy solutions is fostering innovation in the FHP sector, particularly in applications such as irrigation and renewable energy systems. European markets, particularly Germany, are also emphasizing energy efficiency, leading to a heightened focus on advanced motor technologies.
Emerging trends in sourcing for international B2B buyers include the adoption of smart technologies and IoT integration within FHP motors. This tech-enhanced approach allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can significantly reduce operational costs and improve reliability. Additionally, buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer customization options, aligning motor specifications with specific application needs, which is particularly relevant in sectors like robotics and medical devices.
Another key dynamic is the shift toward local sourcing in response to supply chain vulnerabilities exposed by recent global events. Buyers from regions like the Middle East are seeking to establish partnerships with local manufacturers to mitigate risks associated with international shipping and tariffs. This trend not only ensures quicker turnaround times but also fosters regional economic development.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of procurement strategies for fractional horsepower motors. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint through innovative manufacturing practices and the use of renewable energy sources.
Ethical supply chains are critical in this sector, particularly for international buyers who must navigate varying regulations and standards across different regions. The importance of transparency in sourcing materials, especially for components like copper and rare earth magnets, cannot be overstated. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other relevant green certifications that ensure sustainable practices.
The use of eco-friendly materials and sustainable manufacturing processes not only enhances product appeal but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products. By partnering with suppliers who emphasize sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the increasing demand for green products in the market.
Brief Evolution/History
Fractional horsepower motors have evolved significantly since their inception in the early 20th century. Initially, brushed motors dominated the market due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, the introduction of brushless motors in the late 20th century marked a pivotal shift, offering enhanced efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements.
Today, the FHP motor landscape is characterized by a diverse range of technologies, including stepper and servo motors, that cater to a variety of applications. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to the increasing demand for precision, energy efficiency, and adaptability in modern devices. As international markets continue to expand, the evolution of fractional horsepower motors will play a crucial role in supporting technological advancements across various sectors.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fractional horsepower motor
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of fractional horsepower motors?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a proven track record in the fractional horsepower motor sector. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region. Assess their production capabilities and technology to ensure they can meet your specifications. Engaging in a direct conversation or site visit can also provide insights into their operations and reliability. -
Are customization options available for fractional horsepower motors?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific application needs. Customizations can include modifications in size, voltage, torque, and speed control features. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements, including performance specifications and environmental conditions. Confirm the supplier’s capacity to produce custom motors, as well as any additional lead times or costs associated with these modifications. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for fractional horsepower motors?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and region, typically ranging from 50 to several hundred units. Lead times also fluctuate based on order size, customization, and supplier location, often ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. When negotiating, discuss potential flexibility in MOQs and inquire about expedited options if urgent delivery is required. Always clarify these terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
What payment options are commonly accepted by suppliers?
Most suppliers accept a variety of payment methods, including wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. For larger orders, letters of credit may provide additional security for both parties. Discuss payment terms upfront, including deposits and payment schedules, to ensure clarity. Consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow needs while maintaining a good relationship with the supplier. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in a supplier?
Ensure that your supplier has robust quality assurance (QA) processes in place. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards that indicate a commitment to quality. Request information about their testing procedures, including electrical performance and durability tests. Also, inquire if they provide warranties or guarantees for their products, which can be a good indicator of their confidence in quality. -
Are there any certifications or standards that fractional horsepower motors must meet?
Yes, fractional horsepower motors may need to comply with various international standards depending on the application and region. Common certifications include CE marking in Europe, UL certification in North America, and others relevant to specific industries. Verify that the supplier’s products meet the necessary standards for your market to avoid compliance issues and ensure product safety and reliability. -
How should I approach logistics and shipping for international orders?
When planning logistics, consider the total cost of shipping, including duties and taxes. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to streamline the process. Discuss incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to clarify responsibility for shipping costs and risks. It’s also advisable to use a reliable freight forwarder to manage customs clearance and delivery, ensuring your fractional horsepower motors arrive on time and in good condition. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, start by reviewing your contract to understand the agreed-upon terms. Communicate openly with the supplier to resolve the issue amicably, and document all correspondence. If direct negotiation fails, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation. Ensure your contract includes a clause detailing the dispute resolution process, which can save time and costs should issues arise.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fractional horsepower motor
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of fractional horsepower motors offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse types of fractional horsepower motors—such as brushed, brushless, and servo motors—allows companies to select the optimal solutions tailored to their specific applications. By focusing on efficiency, performance, and adaptability, organizations can enhance their operational capabilities and reduce long-term costs.
Key Takeaways:
- Diverse Applications: Fractional horsepower motors are integral to various industries, from household appliances to robotics, enabling precise control and energy efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Leveraging these motors can lead to significant savings in both energy consumption and maintenance costs, enhancing overall profitability.
- Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with reputable manufacturers ensures access to high-quality products, timely delivery, and ongoing support.
As the market continues to evolve, buyers should remain proactive in exploring innovative motor technologies and sustainable sourcing strategies. Engaging with global suppliers and participating in industry forums will provide invaluable insights into emerging trends. By embracing these opportunities, companies can position themselves for future growth and success in an increasingly competitive landscape.