Master Sourcing Gasket Materials: Strategies for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gasket materials
In today’s interconnected industrial landscape, gasket materials serve as the unsung heroes of operational integrity across various sectors. From the oil and gas pipelines that power economies in the Middle East to the sophisticated manufacturing systems in Europe, these materials ensure airtight seals and prevent costly leaks that can disrupt production and compliance. For B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, and Europe, selecting the right gasket materials is not merely a purchasing decision; it is a strategic imperative that can influence overall operational resilience and regulatory adherence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This guide provides a comprehensive framework for navigating the intricate global market for gasket materials. It covers a diverse range of gasket types—including natural rubber, EPDM, neoprene, silicone, and advanced metallic options—offering insights into their properties, applications, and performance characteristics. Additionally, buyers will find detailed information on manufacturing practices, quality control standards, and supplier vetting strategies tailored to their specific regional contexts.
Moreover, the guide explores critical elements such as cost analysis, market trends, and compliance requirements, empowering procurement professionals with the knowledge needed to make informed sourcing decisions. By demystifying the complexities of gasket material selection, this resource equips international B2B buyers with actionable insights to enhance their supply chain efficiency and operational success, ensuring that they secure the best sealing solutions for their unique industrial demands.
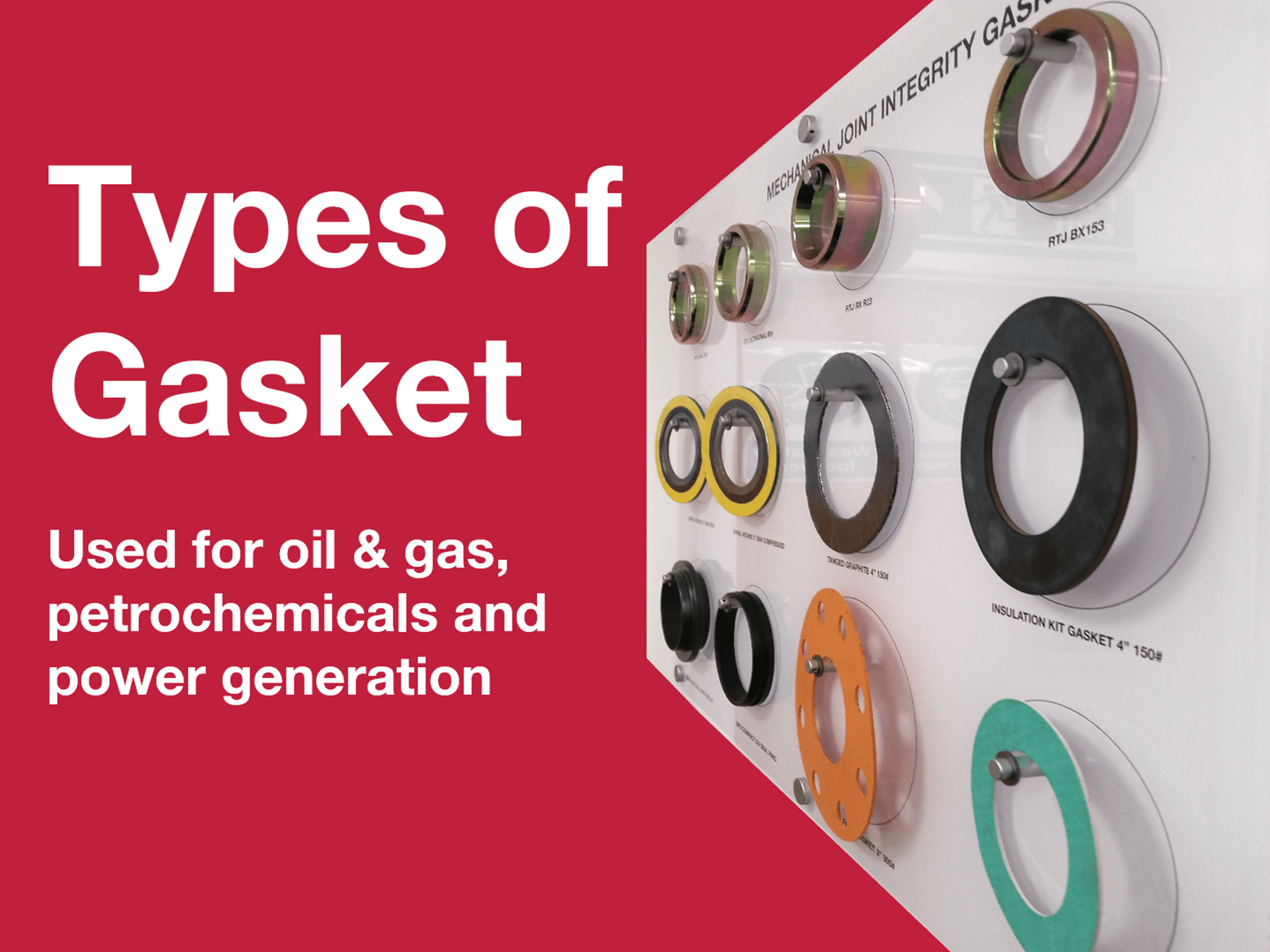
Understanding gasket materials Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber (NR) | High elasticity, abrasion resistance, low cost | Water systems, automotive vibration dampening | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible, resilient in mild conditions. Cons: Poor chemical and temperature resistance. |
| EPDM | Excellent weather, ozone, steam, and chemical resistance | Water treatment, HVAC, outdoor piping | Pros: UV and ozone resistant, ideal for outdoor applications. Cons: Not compatible with oils and fuels. |
| Neoprene (CR) | Good oil and chemical resistance, flame retardant | Oil & gas, refrigeration, marine, HVAC | Pros: Versatile and reliable, performs well in varied temperatures. Cons: Limited in extreme temperature applications. |
| Silicone Rubber | Wide temperature tolerance, chemically inert | Food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics | Pros: High purity and safety, performs well under extreme conditions. Cons: Higher cost, less tear resistance. |
| Ring-Type Joint (RTJ, Metal) | Precision-machined, withstands extreme pressure/heat | Oil & gas pipelines, petrochemical, power plants | Pros: Exceptional sealing in high-pressure environments. Cons: Single-use, higher lifecycle costs. |
Natural Rubber (NR) Washers & Gaskets
Natural rubber is an economically viable choice for many industrial applications due to its elasticity and abrasion resistance. It is particularly effective in environments where exposure to oils, fuels, or extreme temperatures is minimal, making it suitable for water supply systems and automotive applications. B2B buyers should consider its cost-effectiveness and flexibility, but be cautious of its limitations regarding chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, which may necessitate more frequent replacements in harsher environments.
EPDM Gaskets
EPDM gaskets are highly regarded for their resilience against environmental factors such as UV rays, ozone, and steam, making them ideal for outdoor and aqueous applications like water treatment and HVAC systems. This material’s ability to withstand a wide range of chemicals, especially in water-based solutions, enhances its appeal for municipal and industrial buyers seeking durability. However, EPDM is not suitable for applications involving oils and fuels, so buyers must evaluate their specific operational conditions before selection.
Neoprene (CR) Washers & Gaskets
Neoprene offers a balanced performance profile, providing good resistance to oil and chemicals while maintaining stability across a range of temperatures. This versatility makes it a popular choice in sectors like oil and gas, refrigeration, and HVAC. B2B buyers appreciate its flame retardant properties, which enhance safety in critical applications. However, while neoprene is reliable, it may not be the best fit for extreme temperature environments, requiring buyers to assess their specific needs carefully.
Silicone Rubber Gaskets
Silicone rubber is a premier choice for applications demanding high purity and safety, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. It boasts excellent temperature tolerance and chemical inertness, making it suitable for extreme conditions. However, this material typically comes at a higher cost and may not offer the same tear resistance as other options. Buyers should weigh the benefits of compliance with health and safety regulations against the increased expenditure when considering silicone gaskets.
Ring-Type Joint (RTJ, Metal)
RTJ gaskets are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, often found in oil and gas pipelines and petrochemical industries. Their precision machining allows for exceptional sealing capabilities, crucial for safety and regulatory compliance in hazardous environments. However, these gaskets are typically single-use, leading to higher lifecycle costs. B2B buyers must evaluate the critical nature of their applications and the associated costs of RTJ gaskets, ensuring they align with operational budgets and safety standards.
Related Video: 6 Tips for Choosing the Best Gasket – Materials, Types, Uses
Key Industrial Applications of gasket materials
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gasket materials | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Sealing in pipelines and refineries | Prevents leaks, ensuring safety and compliance | Chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance, certification standards |
| Water Treatment | Gaskets in filtration and distribution systems | Reduces maintenance costs, ensures system integrity | UV resistance, compatibility with chemicals, long-term durability |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission gaskets | Enhances performance, reduces downtime | Temperature resistance, vibration dampening, OEM specifications |
| Food & Beverage | Seals in processing and packaging equipment | Ensures product safety and compliance with regulations | Food-grade materials, temperature tolerance, ease of cleaning |
| HVAC | Gaskets in heating and cooling systems | Improves energy efficiency, minimizes downtime | Weather resistance, compatibility with refrigerants, dimensional accuracy |
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas industry, gasket materials are crucial for sealing applications in pipelines and refineries. They prevent leaks that could lead to hazardous spills, ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations. Buyers must prioritize materials with high chemical resistance and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. Additionally, certifications from recognized regulatory bodies are essential to verify that the materials meet industry standards, particularly in regions like the Middle East, where operational conditions can be severe.
Water Treatment
Gasket materials play a vital role in water treatment facilities, particularly in filtration and distribution systems. They help maintain the integrity of water systems by preventing leaks, which can lead to contamination and costly repairs. For international buyers in Africa and South America, it’s important to source gaskets that offer UV resistance and compatibility with various chemicals used in water treatment processes. Long-term durability is also a key consideration, as frequent replacements can significantly increase operational costs.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, gaskets are essential for ensuring proper sealing in engines and transmissions. This application enhances vehicle performance while reducing the likelihood of downtime due to leaks. Buyers should focus on materials that offer excellent temperature resistance and vibration dampening properties. For those in Europe, especially Italy, adhering to OEM specifications is critical to ensure that replacement parts meet the necessary performance standards and regulatory compliance.
Food & Beverage
Gaskets are used extensively in the food and beverage industry to ensure safe processing and packaging. These materials must comply with strict health regulations to prevent contamination. Buyers need to ensure that the gasket materials are food-grade, temperature-resistant, and easy to clean. In regions with diverse food production practices, such as South America, sourcing gaskets that meet local and international safety standards is crucial for maintaining product integrity and consumer trust.
HVAC
In HVAC systems, gaskets are key components that help seal heating and cooling units. They improve energy efficiency by preventing air leaks and minimizing operational downtime. Buyers should consider materials that are weather-resistant and compatible with various refrigerants. For international procurement, especially in regions with extreme climates like the Middle East, ensuring dimensional accuracy and durability in gasket materials is essential for long-term performance and reliability.
Related Video: Neoprene Gasket Material – Properties, Types & Applications
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gasket materials
When selecting gasket materials for international B2B applications, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material type. This section analyzes four common gasket materials: Natural Rubber, EPDM, Neoprene, and Silicone Rubber. Each material’s performance characteristics, suitability for specific applications, and considerations for international buyers are discussed.
Natural Rubber (NR)
Key Properties: Natural rubber exhibits high elasticity and good abrasion resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility. However, it has limited chemical and temperature resistance, with a typical temperature range of -20°C to 70°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of NR is its cost-effectiveness and resilience in mild conditions. It is affordable and widely available, which is beneficial for budget-conscious projects. However, its limitations include poor performance in environments with oils, fuels, or extreme temperatures, which can lead to premature failure.
Impact on Application: NR is commonly used in water supply systems and automotive applications. Its compatibility with water makes it a popular choice, but industries dealing with aggressive chemicals should avoid this material.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards and regulations. Natural rubber may not meet stringent requirements in sectors such as oil and gas, where more robust materials are necessary.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Key Properties: EPDM offers excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, steam, and a wide range of chemicals. It can operate effectively within a temperature range of -50°C to 150°C, making it versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of EPDM is its durability and resistance to environmental factors, which minimizes maintenance costs. However, it is not compatible with oils and fuels, which can limit its application in certain industries.
Impact on Application: EPDM is ideal for outdoor piping, water treatment plants, and HVAC systems, particularly in regions with high UV exposure. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for aqueous solutions, but users must avoid applications involving hydrocarbons.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should be aware of compliance standards like ASTM and DIN when sourcing EPDM. Its widespread acceptance in various markets makes it a reliable choice, but buyers should confirm compatibility with specific media.
Neoprene (CR)
Key Properties: Neoprene exhibits good resistance to oils, chemicals, and flame, with a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C. This makes it a balanced choice for many industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: The versatility of Neoprene allows it to serve in multiple sectors, including oil and gas and HVAC. Its reliability in moderate chemical and temperature environments is a significant advantage. However, it may not perform well in extreme conditions, which could limit its use in specialized applications.
Impact on Application: Neoprene is particularly effective in environments exposed to lubricants and coolants, making it suitable for refrigeration and marine applications. Its flame retardancy adds a layer of safety in critical operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia should consider local regulations regarding material safety and performance. Neoprene’s widespread use and compliance with international standards make it a favorable option for diverse applications.
Silicone Rubber
Key Properties: Silicone rubber is known for its wide temperature tolerance, ranging from -60°C to 230°C. It is chemically inert and complies with food and medical-grade standards, making it suitable for sensitive applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of silicone is its high purity and performance under extreme temperatures, which is crucial for food and pharmaceutical industries. However, it tends to be more expensive and less tear-resistant than other materials, which may impact cost-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Silicone is ideal for applications in the food and beverage sector, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. Its compatibility with a wide range of media makes it a versatile choice, but buyers must consider its higher cost.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe should ensure that silicone materials meet stringent regulatory standards, particularly for food and medical applications. The higher initial investment can be justified by the long-term reliability and safety it provides.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for gasket materials | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Water supply systems | Cost-effective and flexible | Limited chemical resistance | Low |
| EPDM | Outdoor piping, water treatment | Excellent weather and ozone resistance | Not compatible with oils and fuels | Medium |
| Neoprene | Oil & gas, HVAC | Versatile with good chemical resistance | Not optimal for extreme conditions | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber | Food & beverage, pharmaceuticals | High purity and extreme temperature performance | Higher cost and less tear-resistant | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gasket materials
The manufacturing processes for gasket materials and the associated quality assurance measures are critical to ensuring that these components meet the stringent demands of various industries. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can enhance procurement strategies and supplier selection.
Manufacturing Processes for Gasket Materials
The production of gasket materials typically involves several key stages, each of which is crucial to the final product’s performance and reliability.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. Depending on the type of gasket material—be it rubber, PTFE, or metal—suppliers must ensure that materials are of high quality and compliant with relevant standards.
- Sourcing: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate a reliable supply chain for raw materials, ensuring consistency in quality.
- Material Testing: Incoming materials undergo rigorous testing to verify their properties, such as tensile strength, elasticity, and chemical resistance.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they are formed into the desired shapes. This can involve various techniques, including:
- Die Cutting: Commonly used for rubber and composite gaskets, where sheets are cut into specific shapes using steel dies.
- CNC Machining: Employed for more intricate designs or when using materials like PTFE or metal, offering precision and repeatability.
- Compression Molding: Often used for rubber gaskets, where material is placed in a mold and heat is applied to cure the rubber.
The choice of forming technique can significantly affect the gasket’s final properties, including its sealing capability and durability.
3. Assembly
In cases where gaskets comprise multiple components or layers, assembly becomes essential. This stage might involve:
- Layer Bonding: Techniques such as adhesive bonding or heat sealing are used to ensure that layers adhere properly and provide a robust seal.
- Pre-assembly Testing: Components may be tested for compatibility and fit before final assembly to prevent issues later in production.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes that enhance the gasket’s performance and appearance.
- Trimming and Sizing: Excess material is trimmed, and gaskets are sized according to specifications.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as coating or polishing can be applied to improve resistance to chemicals or enhance surface finish.
- Final Quality Checks: Each gasket undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets design specifications before packaging.
Quality Assurance for Gasket Materials
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that gaskets perform reliably in their intended applications.
International Standards
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to recognized international standards, which may include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that suppliers maintain consistent quality throughout their manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for suppliers in Europe, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For suppliers dealing with oil and gas applications, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards ensure that products meet industry-specific requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help catch any defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final products are subjected to rigorous testing to verify performance, including leak testing, pressure testing, and dimensional checks.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be familiar with various testing methods that suppliers might employ, such as:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the material’s strength and elasticity.
- Compression Testing: Evaluates how well a gasket can withstand compressive forces.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Assesses how materials react to different chemicals they may encounter in their applications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality management practices.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share detailed quality reports and certifications to demonstrate compliance with standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection bodies can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing gasket materials internationally, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers must navigate various regulatory landscapes.
- Regional Standards: Be aware that different regions may have specific standards and certifications that apply to gasket materials. Buyers should verify that suppliers can meet both local and international compliance requirements.
- Documentation: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation, including certificates of compliance, test results, and material safety data sheets (MSDS).
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can enhance communication and negotiation with suppliers, leading to better outcomes.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for gasket materials, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions. This knowledge not only enhances procurement strategies but also fosters long-term supplier relationships that contribute to operational success.
Related Video: How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gasket materials Sourcing
When sourcing gasket materials, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is critical for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here’s a breakdown of the essential cost components and price influencers, alongside actionable insights for effective procurement.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts the overall cost. For instance, natural rubber is generally less expensive compared to high-performance silicone or metal gaskets. The specific application requirements—such as temperature tolerance and chemical resistance—will dictate the material choice.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the region and manufacturing processes. For example, countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this could affect quality. It’s crucial to balance cost and expertise to ensure reliable production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with production facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. A well-optimized facility can reduce overhead costs, which can be reflected in the pricing offered to buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial costs for tooling can be significant, particularly for custom gaskets. Buyers should consider whether the investment in specialized tooling will lead to cost savings over time, especially in high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures the reliability and longevity of gasket materials. While this may add to initial costs, it can prevent costly failures and downtime in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Buyers should factor in these costs when comparing suppliers, particularly for international procurement.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margins in the final pricing. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid overcommitting on inventory.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized gaskets can drive up costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications upfront to avoid unexpected price increases later in the process.
-
Quality/Certifications: High-quality materials with certifications may come at a premium. Buyers in regulated industries (like pharmaceuticals or food processing) must prioritize certified materials for compliance, even if they are more expensive.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but can provide better assurance of performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for calculating total landed costs. These terms can affect who bears the shipping costs and risks, impacting the overall pricing for buyers.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your requirements and the market rates. Leverage multiple quotes to strengthen your bargaining position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond initial pricing. Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, replacement, and operational costs associated with gasket materials.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of potential price fluctuations due to currency exchange rates, tariffs, and regional market conditions. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing stability.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary widely based on specific requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always consult with suppliers for accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to your sourcing needs.
By leveraging these insights, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and ensure the reliability of their operations across various industries.
Spotlight on Potential gasket materials Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘gasket materials’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gasket materials
Key Technical Properties of Gasket Materials
Understanding the essential technical specifications of gasket materials is crucial for international B2B buyers. These properties can significantly influence the performance and longevity of sealing solutions in various industrial applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade indicates the quality and composition of the gasket material. Different grades offer varying levels of resistance to temperature, pressure, and chemicals. For example, a higher-grade silicone gasket may withstand extreme temperatures better than a standard rubber gasket. Buyers should select the appropriate material grade based on the specific demands of their applications to avoid premature failures. -
Thickness Tolerance
Thickness tolerance refers to the allowable variance in the thickness of the gasket material. A tighter tolerance can result in a more reliable seal, especially in high-pressure environments. Inconsistent thickness can lead to leaks or failures. Understanding the required tolerance levels is essential for buyers to ensure compatibility with their equipment and to maintain operational safety. -
Temperature Resistance
This property defines the maximum and minimum temperatures a gasket can endure without losing its sealing capabilities. Different materials, such as EPDM or silicone, have distinct temperature resistance ranges. Buyers must assess their operational temperature requirements to select a gasket that will perform reliably throughout its service life. -
Chemical Compatibility
Gasket materials must be compatible with the substances they will encounter in their application. For instance, neoprene gaskets are suitable for oil and gas applications due to their chemical resistance, while EPDM is not. Buyers should verify the chemical exposure their gaskets will face to prevent degradation and ensure long-term functionality. -
Compression Set
Compression set measures how well a gasket material retains its shape after being compressed. A low compression set indicates that the material can maintain its sealing properties over time, even under pressure. For B2B buyers, selecting materials with low compression set values is crucial for applications that require long-term sealing without frequent replacement.
Common Trade Terms in Gasket Sourcing
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline the procurement process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or components that are used in another company’s end product. In the gasket industry, sourcing from OEMs can assure buyers of high-quality materials that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for buyers to ensure they can meet their needs without overcommitting resources. It can also affect pricing, as larger orders may lead to discounts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from different suppliers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is essential for B2B buyers involved in international transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is critical for buyers to manage their inventory effectively and ensure that production schedules are met without delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing gasket materials, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and compliance with industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the gasket materials Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The gasket materials sector is currently experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. Increasing industrial activities, particularly in the oil and gas, automotive, and manufacturing sectors across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are propelling demand for high-quality sealing solutions. Buyers must navigate a fragmented market characterized by diverse material options ranging from traditional rubber to advanced composites and metallic solutions.
Emerging trends include the integration of digital technologies in sourcing processes. B2B buyers are leveraging platforms that provide real-time pricing, inventory tracking, and supplier ratings, enhancing transparency and decision-making. Additionally, the shift towards customization is notable, as companies seek gaskets tailored to specific operational requirements, improving performance and reducing downtime.
Another critical dynamic is the increasing emphasis on supply chain resilience. Disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic have prompted buyers to rethink their sourcing strategies, favoring suppliers with robust logistics and local manufacturing capabilities. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory compliance and timely delivery are paramount.
In summary, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these market dynamics and trends to enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers that align with their operational goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has emerged as a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the gasket materials sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of gasket materials necessitate a focus on sustainability for B2B buyers. Companies are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprints, prompting a shift towards eco-friendly materials and practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally vital. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and possess certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety). These certifications not only reflect a commitment to sustainability but also enhance the credibility and reliability of the supply chain.
The adoption of green materials, such as biodegradable elastomers and recycled composites, is gaining traction. For example, sourcing gaskets made from sustainable materials can significantly reduce environmental impact while meeting regulatory standards in various industries. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate the sustainability profiles of potential suppliers and to consider the long-term benefits of investing in environmentally responsible products.
By integrating sustainability and ethical sourcing into their procurement processes, international B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives while ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent regulations.
Brief Evolution/History
The gasket materials sector has evolved significantly over the last century, transitioning from simple natural rubber and cork materials to a diverse range of advanced synthetic and composite options. Initially, gaskets were primarily used in steam engines and early automotive applications. With the industrial revolution and the rise of complex machinery, the demand for more resilient and reliable sealing solutions grew.
In recent decades, technological advancements have revolutionized gasket manufacturing processes, enabling the production of high-performance materials such as PTFE, silicone, and metallic gaskets. This evolution has been driven by the need for gaskets that can withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposures in various industries. Today, the focus is not only on performance but also on sustainability and ethical sourcing, reflecting broader societal trends toward environmental responsibility and transparency in supply chains.
Related Video: Made in the world: Better understanding global trade flows
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gasket materials
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of gasket materials?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Look for customer reviews and case studies to gauge their reliability and service levels. Additionally, request samples of their products to assess quality firsthand. Engage in direct conversations to understand their production capabilities and responsiveness. Establishing a long-term relationship with a supplier can also be beneficial, so consider their financial stability and history in the industry. -
What customization options are typically available for gasket materials?
Many suppliers offer customization services, allowing you to tailor gasket materials to specific dimensions, shapes, and performance characteristics. Common customizations include altering material thickness, incorporating specific additives for enhanced performance, or producing gaskets with unique cutouts or profiles. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and application requirements. It’s advisable to request prototypes to ensure the final product meets your needs before placing a larger order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for gasket materials?
Minimum order quantities vary widely depending on the supplier and the type of gasket material. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 50 pieces to several hundred. Lead times are also contingent on the complexity of the order; standard gaskets may take 2-4 weeks, while custom designs could extend this to 6-8 weeks or more. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid unexpected delays, and consider establishing a buffer stock to manage supply chain uncertainties. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing gasket materials internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers and regions. Common practices include upfront payments, payment upon delivery, or a mix of both. For larger orders, consider negotiating terms like a letter of credit, which can provide security for both parties. Ensure you understand the currency used for transactions and any potential fees associated with international payments. Establishing a clear payment schedule and adhering to it can help maintain a good relationship with your supplier. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with certifications?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications from suppliers, such as ISO and ASTM standards relevant to gasket materials. Conduct periodic audits of the supplier’s production processes and ask for test reports on batch samples to verify compliance. Additionally, consider third-party inspections for critical orders, especially for industries with stringent regulatory requirements. Maintaining open communication about quality expectations with your supplier is essential for long-term compliance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing gasket materials?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Assess the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including available shipping methods and transit times to your location. Be aware of customs regulations and potential tariffs that could affect costs and delivery times. Work with logistics providers experienced in international shipping to streamline the process. It’s also wise to plan for contingencies in case of delays, especially if your operations depend on timely deliveries. -
How should I handle disputes with gasket material suppliers?
Disputes can arise over product quality, delivery times, or contractual obligations. It’s essential to have a clear contract that outlines the terms and conditions, including dispute resolution processes. Start by addressing issues directly with the supplier to seek an amicable resolution. If necessary, escalate the matter through mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract. Document all communications and agreements to support your position if the dispute escalates.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What are the key industry trends affecting gasket material sourcing?
Current trends include an increasing demand for sustainable materials and innovations in material science, such as advanced composites and eco-friendly options. The rise of digital sourcing platforms is also changing how buyers connect with suppliers, making it easier to compare products and prices. Additionally, geopolitical factors can influence supply chain dynamics, necessitating flexibility in sourcing strategies. Staying informed about these trends can help you make proactive sourcing decisions and adapt to market changes effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gasket materials
In summary, strategic sourcing of gasket materials is essential for international B2B buyers navigating diverse industrial landscapes across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the unique properties and applications of various gasket types—from natural rubber to advanced silicone—enables buyers to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and compliance with regional regulations.
Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating supplier credibility, balancing cost with quality, and leveraging digital tools for effective sourcing. By prioritizing reliable materials and suppliers, organizations can minimize downtime and reduce long-term operational costs.
As global markets continue to evolve, the demand for high-performance gasket solutions will only increase. B2B buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with suppliers who offer innovation and robust after-sales support. By doing so, you not only secure superior sealing solutions but also position your business for sustainable growth in a competitive landscape. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategy today, ensuring your operations are equipped with the best gasket materials for tomorrow’s challenges.