Master Sourcing Helical Compression Springs: A B2B Buyer’s
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for helical compression spring
As the global marketplace evolves, the demand for high-quality industrial components has never been more critical. Among these, helical compression springs stand out as essential elements in a wide range of applications, from automotive and aerospace to manufacturing and medical devices. Their ability to absorb and release energy efficiently makes them vital for ensuring the reliability and performance of machinery. However, sourcing these components can be a complex process, particularly for international B2B buyers navigating diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for procurement professionals looking to streamline their sourcing decisions. It delves into various types of helical springs, including compression, extension, and torsion springs, each tailored to specific applications and operational requirements. Additionally, it covers critical materials and engineering considerations, enabling buyers to weigh the trade-offs between cost and performance effectively.
Equipped with insights into manufacturing processes, quality control standards, and the nuances of supplier selection, this guide helps buyers identify reputable manufacturers, assess customization capabilities, and establish long-term partnerships. Furthermore, it addresses pricing dynamics and market trends, offering tools for negotiation and budget management.
By providing actionable insights tailored to the unique challenges faced by international buyers, this guide empowers B2B procurement teams to make informed decisions that align with their operational and regulatory realities.
Understanding helical compression spring Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Spring | Open-coil, resists compressive force, variable shapes (cylindrical, conical) | Automotive suspensions, industrial machinery, valves | Versatile, cost-effective, withstands high loads; potential for buckling in long lengths |
| Extension Spring | Closed-coil, tension force, loops/hooks at both ends | Garage doors, agricultural equipment, conveyors | Easy installation, strong pull action; risk of deformation if overloaded |
| Torsion Spring | Helical coil with leg arms, resists rotational (twisting) force | Hinges, clutches, automotive trunk lids | Handles angular movement, custom leg shapes; precise force calibration needed |
| Conical Spring | Tapered coil (cone-shaped), variable diameter, solid height minimized | Battery contacts, electrical switches, shock absorbers | Compact stacking, constant spring rate; limited length, more complex manufacture |
| Die Spring | Heavy-duty, rectangular wire, colored for load rating | Press tools, molds, high-load industrial setups | High fatigue life, standardized ratings; stiffer, limited deflection range |
Compression Spring
Compression springs are designed to resist compressive forces and are typically open-coil. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive suspensions to industrial machinery. When purchasing, buyers should consider load capacity, material compatibility (such as stainless steel for corrosion resistance), and dimensional tolerances. Customization options are widely available, particularly from manufacturers in Asia and Europe, which can help meet specific operational requirements.
Extension Spring
Extension springs operate under tension and are characterized by closed coils with loops or hooks at both ends. They are commonly used in applications like agricultural machinery and conveyors. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to focus on the quality of materials used and the design of attachment points, as failures often occur there. Confirming the maximum extension limits and expected cycle life with suppliers can prevent premature spring failure, ensuring operational reliability.
Torsion Spring
Torsion springs are engineered to store and release rotational energy, featuring helical coils with extended arms. They are essential in applications such as hinges and automotive trunk lids. Buyers should pay close attention to the spring’s angular deflection capacity and leg configuration, as improper specifications can lead to misalignment and wear. Engaging with manufacturers that provide prototyping services and test data is recommended to ensure the spring meets precise operational needs.
Conical Spring
Conical springs have a tapered design, which allows for minimal solid height and stability under compression. They are typically used in applications like battery contacts and shock absorbers. Buyers should note that while they offer advantages in compact stacking and a constant spring rate, their manufacturing complexity can lead to higher costs. It is essential to evaluate the specific requirements for length and load capacity when considering conical springs.
Die Spring
Die springs are heavy-duty springs made from rectangular wire, often color-coded to indicate load ratings. They are primarily used in high-load industrial applications, such as press tools and molds. Buyers benefit from their high fatigue life and standardized ratings, but should be aware of their limitations in deflection range. When sourcing die springs, it is important to confirm load specifications and compatibility with existing systems to ensure optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of helical compression spring
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Helical Compression Spring | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Suspension systems | Enhances vehicle stability and comfort | Load capacity, corrosion resistance, and customization |
| Aerospace | Actuation mechanisms | Ensures precise control and reliability in flight systems | Material quality, weight considerations, and certifications |
| Manufacturing | Industrial machinery | Facilitates efficient operation and energy absorption | Tolerance specifications, fatigue life, and delivery time |
| Medical Devices | Precision instruments | Provides accurate and reliable measurements | Biocompatibility, dimensional accuracy, and testing data |
| Consumer Electronics | Portable devices | Supports compact design while maintaining functionality | Size constraints, material selection, and cost-efficiency |
Automotive
In the automotive sector, helical compression springs are essential components in suspension systems. They absorb shocks and vibrations, enhancing vehicle stability and passenger comfort. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to consider factors such as load capacity and corrosion resistance, given the diverse environmental conditions. Customization options should also be evaluated to ensure compatibility with specific vehicle designs.
Aerospace
Helical compression springs are integral to actuation mechanisms in aerospace applications. They provide precise control over various systems, ensuring reliability during flight operations. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should focus on material quality and weight considerations, as these factors directly impact performance and safety. Additionally, suppliers must hold relevant certifications to comply with stringent aerospace standards.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, helical compression springs play a vital role in various industrial machinery, facilitating efficient operation and energy absorption. They are used in applications ranging from conveyor systems to heavy machinery. B2B buyers should prioritize tolerance specifications and fatigue life when sourcing these components, as they directly influence operational efficiency. Timely delivery is another critical factor, especially in industries where downtime can lead to significant financial losses.
Medical Devices
Helical compression springs are crucial in the design of precision instruments used in medical devices. They ensure accurate and reliable measurements, which are essential for patient safety and effective treatment. Buyers, particularly from Europe, need to ensure that the springs meet biocompatibility standards and possess dimensional accuracy. Requesting test data from suppliers can help mitigate risks associated with product performance in critical medical applications.
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics sector, helical compression springs are often employed in portable devices to support compact designs while maintaining functionality. They are found in various applications, from mobile phones to laptops. Buyers should consider size constraints and material selection to ensure that the springs can withstand repeated use without failure. Cost-efficiency is also a significant factor, especially in highly competitive markets in South America and Africa.
Related Video: Helical Compression spring | Lecture – 1| Design of helical compression spring
Strategic Material Selection Guide for helical compression spring
When selecting materials for helical compression springs, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of helical compression springs: high-carbon steel, stainless steel, music wire, and alloy steel. Each material presents unique properties and considerations that can influence the decision-making process.
High-Carbon Steel
High-carbon steel is a popular choice for helical compression springs due to its excellent strength and elasticity. Typically containing 0.6% to 1.0% carbon, this material offers a high tensile strength and good fatigue resistance.
Pros: High-carbon steel springs are generally more cost-effective than other materials, making them suitable for mass production. They also exhibit excellent performance under high load conditions.
Cons: However, high-carbon steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. Buyers must consider protective coatings or finishes to enhance durability.
Impact on Application: This material is ideal for applications in automotive and industrial machinery where strength is paramount. However, it may not be suitable for applications involving exposure to corrosive media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A228 or DIN 17223 is crucial. Buyers should also evaluate the availability of coatings and finishes to meet local environmental regulations.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel springs, particularly those made from grades like 302 and 316, are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and durability. These materials contain chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its ability to withstand harsh environments, making it ideal for applications in the food processing, medical, and marine industries.
Cons: The higher cost of stainless steel compared to carbon steel can be a deterrent for some buyers. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex, which may lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suited for applications requiring hygiene and resistance to corrosion, such as in medical devices or food processing equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A313 or JIS G4305 is essential. Buyers should also consider the specific grade of stainless steel based on the application to ensure optimal performance.
Music Wire
Music wire is a type of high-carbon steel that is specifically designed for spring applications. It offers superior tensile strength and is often used in precision applications.
Pros: Music wire springs can handle high loads and provide excellent fatigue resistance. They are also relatively inexpensive, making them a popular choice for many applications.
Cons: Like high-carbon steel, music wire is prone to corrosion, necessitating protective treatments for long-term use in adverse environments.
Impact on Application: Music wire is commonly used in applications such as electronics and automotive components, where precision and strength are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM A228 standards and consider the need for protective coatings based on the application environment.
Alloy Steel
Alloy steel springs, which may include materials like 6150 or 5160, offer enhanced properties through the addition of elements such as chromium and vanadium.
Pros: These materials provide excellent strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing and higher costs associated with alloy steels can be a disadvantage for some buyers. Additionally, they may require specific heat treatment processes to achieve desired properties.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is particularly suitable for applications in automotive and aerospace industries, where performance and reliability are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A313 or DIN 17200 and consider the specific requirements for heat treatment and finishing.
| Material | Typical Use Case for helical compression spring | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Carbon Steel | Automotive suspensions, industrial machinery | Cost-effective, high strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Music Wire | Electronics, automotive components | Superior tensile strength | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy-duty automotive, aerospace applications | Enhanced strength and fatigue resistance | Higher cost, requires heat treatment | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions when sourcing helical compression springs, ensuring that they choose the right material for their specific applications and operational environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for helical compression spring
Manufacturing Processes for Helical Compression Springs
The production of helical compression springs involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from diverse global markets.
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials for helical compression springs include high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys.
- Material Selection: Buyers should consider the application’s specific requirements such as load capacity, environmental conditions (corrosion resistance), and fatigue strength.
- Wire Sizing: The wire used to create the springs is typically available in various diameters. Precision in wire sizing is crucial to achieving the desired spring rate and load characteristics.
2. Forming
Once the material is prepared, the forming process begins. This stage involves shaping the wire into the helical form.
- Coiling Techniques: The wire is coiled using either a CNC spring machine or a conventional coiling machine. CNC machines offer enhanced precision, allowing for tighter tolerances and complex shapes, which are increasingly demanded in modern applications.
- Spring Geometry: The design specifications, including the number of coils, diameter, and pitch, are defined at this stage. Buyers should provide detailed drawings to ensure manufacturers understand their requirements fully.
3. Assembly
In some cases, especially for complex assemblies involving multiple springs or components, the assembly process may be necessary.
- Joining Methods: Techniques such as welding, threading, or using end fittings are employed to assemble the springs into final products or sub-assemblies. Buyers should inquire about the methods used to ensure they align with their quality and durability requirements.
4. Finishing
The finishing process enhances the spring’s performance and longevity.
- Surface Treatments: Options such as shot peening, coating, or plating can be applied to improve fatigue resistance and protect against corrosion. Buyers should specify their environmental conditions to select the appropriate treatment.
- Heat Treatment: This process is essential for achieving the desired mechanical properties. Heat treatment can enhance hardness and elasticity, critical for compression springs operating under high loads.
Quality Assurance for Helical Compression Springs
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the springs meet international standards and customer expectations.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be familiar with the following quality standards:
- ISO 9001: This is the international standard for quality management systems (QMS). Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to consistent quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For applications in the oil and gas industry, API certification ensures that the springs meet specific performance criteria.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated into the manufacturing process at various checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the raw materials for compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early, minimizing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection ensures that finished springs meet all design specifications and performance criteria.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of helical compression springs:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the material.
- Fatigue Testing: Assesses the spring’s performance under repeated loading and unloading cycles.
- Dimensional Inspection: Uses gauges and calipers to verify that the springs meet specified dimensions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality management systems.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports, including results from various testing stages.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing process and final products can offer an unbiased view of quality.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific challenges:
- Regulatory Differences: Different countries may have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding local compliance is crucial for smooth transactions.
- Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices can vary by region, affecting negotiations and quality expectations. Establishing clear communication channels is vital.
- Logistical Challenges: Transportation and shipping logistics can impact delivery times and product integrity. Buyers should consider these factors when planning orders.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for helical compression springs is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, production techniques, and rigorous quality control, buyers can ensure they source high-quality springs that meet their operational needs and regulatory standards.
Related Video: The Process of Manufacturing Giant Springs A Spring Factory in China
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for helical compression spring Sourcing
Navigating the costs associated with sourcing helical compression springs requires a detailed understanding of several critical components and influencing factors. This analysis will provide B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with actionable insights to make informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts the cost of helical springs. Common materials include high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. Each material offers different performance characteristics, and prices can vary based on market demand and regional availability. For instance, stainless steel tends to be more expensive due to its corrosion resistance properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing region. Countries with lower labor costs might offer competitive pricing; however, this may come with trade-offs in quality and reliability. Understanding the local labor market dynamics can help buyers evaluate potential risks.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with production facilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with advanced production technologies or high-quality standards may charge higher overhead, which can influence overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation of molds and dies necessary for producing custom springs. If specific designs or large quantities are required, these costs can become significant. Buyers should inquire about tooling fees upfront, especially for custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes ensure that springs meet required specifications and safety standards. Manufacturers with ISO certifications or other quality marks may include these costs in their pricing, but this can provide peace of mind regarding product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are a critical factor, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, freight methods, and customs duties can significantly affect the total cost. Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who bears the cost and risk during shipping.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary based on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the level of customization or service provided.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can heavily influence pricing. Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs, allowing buyers to negotiate better deals. However, buyers must ensure they can utilize the volume effectively to avoid excess inventory costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific tolerances can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements and be prepared to discuss how these will affect pricing.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality standards or certifications usually come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in certified products against potential long-term savings from reduced failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a crucial role in pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more but offer better guarantees and support, which can mitigate risks.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers early in the negotiation process. Discussing pricing openly can lead to better deals, especially when presenting competitive offers from other manufacturers.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which encompasses not only the purchase price but also maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs. Investing in higher-quality springs may reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, be aware of currency fluctuations and their potential impact on pricing. Additionally, consider regional economic conditions that may affect supplier pricing strategies.
Disclaimer
Prices can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including market conditions and supplier negotiations. This analysis provides indicative insights, and buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier vetting to obtain accurate pricing.
Spotlight on Potential helical compression spring Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘helical compression spring’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for helical compression spring
When sourcing helical compression springs, understanding their technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines essential specifications and common trade terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– The material from which the spring is made significantly affects its performance, durability, and cost. Common materials include high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. Buyers must consider the operating environment; for instance, stainless steel is preferred for corrosive settings, while high-carbon steel is often chosen for its strength and cost-effectiveness. -
Spring Rate
– Defined as the amount of force required to compress the spring by a unit of length (usually expressed in pounds per inch or Newtons per millimeter), the spring rate is a critical parameter that determines how much load the spring can support. A precise understanding of the required spring rate ensures that the spring will perform effectively in its intended application. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the spring’s dimensions and performance characteristics. Tight tolerances are essential for applications requiring high precision, such as aerospace or medical devices. When engaging with suppliers, it’s vital to specify the required tolerances to avoid issues with fit and function. -
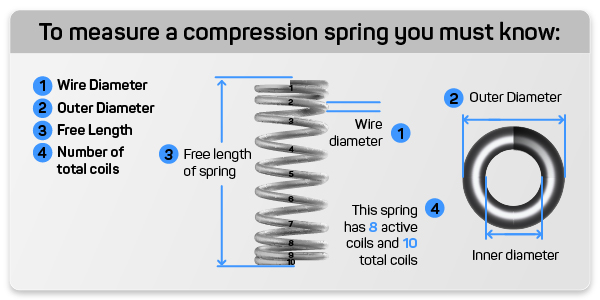
Free Length
– This measurement indicates the length of the spring when it is not under any load. Understanding the free length is crucial for ensuring that the spring fits appropriately within the assembly and functions as intended when compressed. -
Load Capacity
– Load capacity refers to the maximum weight a spring can bear without permanent deformation or failure. Buyers should assess the load requirements of their applications to ensure that the springs sourced can handle the necessary forces without compromising performance. -
End Type
– The design of the spring’s ends can significantly affect its installation and performance. Common end types include closed, open, and ground ends. Specifying the correct end type is essential to ensure compatibility with the assembly and to avoid issues such as misalignment or premature wear.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of helical compression springs, understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring that the sourced springs meet specific design and quality standards required for original equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to align with their production needs without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ helps suppliers offer accurate quotes, facilitating better price negotiations and procurement planning. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining shipping responsibilities, costs, and risk management, particularly when sourcing from global suppliers. -
Lead Time
– This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Buyers should be aware of lead times to effectively manage their inventory and production schedules. Clear communication with suppliers about lead times is essential to avoid production delays. -
Quality Assurance (QA)
– QA refers to the systematic process of ensuring that products meet specified quality standards before they reach the market. Buyers should inquire about the QA protocols of potential suppliers to ensure that the helical compression springs sourced will perform reliably and meet industry standards.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies for helical compression springs, leading to improved operational efficiency and product performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the helical compression spring Sector
Global Drivers and Key Trends
The helical compression spring market is witnessing significant evolution due to several global drivers. Increased demand for automation and precision engineering across industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, is propelling the growth of the sector. Emerging technologies like 3D printing and advanced materials are enhancing the design and functionality of helical springs, allowing for greater customization and efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these trends is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
Furthermore, there is a marked shift towards digitalization in the sourcing process. Platforms offering real-time data analytics, supplier performance tracking, and blockchain technology for transparency are becoming increasingly popular. These technologies help buyers mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and ensure timely deliveries. Additionally, understanding regional market dynamics, such as fluctuating material costs and the impact of trade policies, is crucial for effective procurement strategies. Buyers must remain agile, adapting to changes in lead times and sourcing strategies to maintain competitiveness in their respective markets.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Sustainability is no longer a mere trend but a critical factor for B2B buyers in the helical compression spring sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitative labor practices and environmental harm. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in the global market. Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials—such as bio-based or recyclable alloys—can significantly enhance a supplier’s appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also align with the values of their end customers, thereby enhancing brand loyalty and market positioning.
Brief Evolution/History
The helical compression spring has a rich history that dates back to the industrial revolution, where it played a pivotal role in machinery design. Originally crafted from wrought iron, the transition to high-carbon steel and various alloys in the 20th century allowed for enhanced durability and performance. The advent of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as CNC machining and automated production lines, has further refined the design and production of helical springs. Today, these springs are integral components in a wide range of applications, from automotive suspensions to medical devices, underscoring their versatility and importance in modern engineering. Understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and materials that can influence their sourcing decisions.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of helical compression spring
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for helical compression springs?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, manufacturing capabilities, and certifications (such as ISO 9001). Request samples to assess quality and ask for references from previous clients. It’s essential to evaluate their ability to meet specific customization needs and their responsiveness during communication. Additionally, consider their production capacity and whether they can handle your required volume, especially if you’re in a region with fluctuating demand. -
Can I customize helical compression springs for my specific application?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for helical compression springs. You can specify dimensions, wire diameter, coil shape, and material types based on your application’s requirements. When discussing customization, provide detailed technical drawings and specifications to ensure the supplier fully understands your needs. Be prepared to collaborate during the design process, as this can enhance the final product’s suitability for your application. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for helical compression springs?
MOQs can vary significantly by supplier and can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times generally depend on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss your needs upfront to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a first-time buyer or require urgent delivery. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for new partnerships. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification from my suppliers?
To ensure quality, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes and relevant certifications. ISO certifications are a good indicator of adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, inquire about their testing protocols for spring performance, fatigue life, and material integrity. Establishing a clear quality agreement before placing an order can also help mitigate risks associated with product defects. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted in international B2B transactions for helical springs?
Common payment methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, and online payment platforms. Each method has its pros and cons in terms of security and speed. For large transactions, letters of credit can provide added protection, ensuring that payment is made only upon meeting specified conditions. Discuss payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings, and consider negotiating terms that offer security for both parties. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping for my helical spring orders?
When managing logistics, consider the supplier’s location, shipping options, and import/export regulations specific to your country. Work with freight forwarders who have experience in handling industrial components to ensure efficient customs clearance and delivery. Discuss shipping terms (Incoterms) with your supplier to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risk during transit. Additionally, keep track of shipping schedules to anticipate any delays. -
What steps can I take if a dispute arises with my supplier?
In the event of a dispute, start by reviewing the contract and any agreements made regarding quality, delivery, and payment terms. Open a line of communication with the supplier to discuss the issue and seek a resolution amicably. If necessary, escalate the matter through formal channels, such as mediation or arbitration, as outlined in your contract. Maintaining thorough documentation of all communications and agreements can be invaluable in resolving disputes effectively. -
What are the common challenges faced by international buyers of helical compression springs?
Common challenges include navigating regulatory compliance, dealing with currency fluctuations, and managing varying lead times. Cultural differences in business practices can also impact negotiations and communication. To mitigate these challenges, conduct thorough market research, develop strong relationships with suppliers, and consider working with local agents who understand the regional landscape. Additionally, staying informed about global supply chain dynamics can help you anticipate potential disruptions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for helical compression spring
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of helical compression springs is pivotal for B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product reliability. By understanding the various types of springs, their applications, and the materials involved, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. Furthermore, navigating the complexities of the global supply chain, including vetting suppliers and understanding pricing dynamics, is crucial for mitigating risks associated with procurement.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis should be on establishing long-term partnerships with reputable manufacturers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and innovation. This not only ensures the integrity of the components but also fosters collaboration for future projects.
As the landscape of international trade continues to evolve, staying ahead of market trends and technological advancements in spring manufacturing will be essential. Buyers are encouraged to leverage the insights gained from this guide to enhance their sourcing strategies, ultimately driving growth and competitiveness in their respective industries. Engage with your suppliers proactively, and explore opportunities for customization and innovation that can set your products apart in a crowded marketplace.