Master Sourcing High-Quality Electromagnetic Coils for Your
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electromagnetic coil
Electromagnetic coils are the backbone of countless modern technologies, playing a pivotal role in electrical devices ranging from motors and transformers to medical equipment and consumer electronics. Their ability to generate controllable magnetic fields makes them indispensable in both industrial applications and everyday devices. As global industries evolve, the demand for high-quality electromagnetic coils continues to rise, presenting a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for navigating the complex landscape of electromagnetic coils. It covers a variety of crucial topics, including the different types of coils, the materials used in their production, manufacturing processes, quality control standards, and leading suppliers across the globe. Furthermore, it addresses cost considerations and market trends, empowering buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets such as Turkey and France—this guide provides actionable insights that facilitate effective sourcing. Understanding the nuances of electromagnetic coils not only enhances procurement strategies but also ensures compatibility and efficiency in applications. By leveraging the information provided, buyers can confidently navigate the global market, ensuring they select the best solutions for their specific needs.
Understanding electromagnetic coil Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solenoid Coil | A coil designed to produce linear motion when energized. | Automotive actuators, industrial automation, valves. | Pros: Simple design, reliable operation. Cons: Limited to linear applications. |
| Induction Coil | Utilizes alternating current to create a magnetic field. | Transformers, induction heating, wireless charging. | Pros: Efficient energy transfer. Cons: Can generate heat, requiring cooling solutions. |
| Ignition Coil | Converts low voltage to high voltage for ignition systems. | Automotive ignition systems, small engines. | Pros: Essential for engine performance. Cons: Limited lifespan under high stress. |
| Toroidal Coil | Coil wound in a circular shape, minimizing electromagnetic interference. | Power supplies, inductors, RF applications. | Pros: Compact design, efficient magnetic field. Cons: Higher manufacturing costs. |
| Field Coil | Generates a magnetic field in electric motors and generators. | Electric motors, generators, magnetic levitation systems. | Pros: Strong magnetic fields, customizable. Cons: Requires careful design to optimize performance. |
Solenoid Coil
Solenoid coils are primarily used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through linear motion. Their straightforward design makes them reliable for applications such as automotive actuators and industrial automation. When purchasing solenoid coils, buyers should consider the voltage and current specifications, as well as the coil’s stroke length and force output, to ensure compatibility with their systems.
Induction Coil
Induction coils are known for their ability to generate a magnetic field using alternating current. They are widely utilized in transformers and induction heating applications, as well as in wireless charging technologies. B2B buyers should evaluate the coil’s power rating, frequency response, and thermal management requirements. Understanding these factors can significantly impact the efficiency and performance of the final application.
Ignition Coil
Ignition coils are specialized electromagnetic coils that step up voltage from the battery to ignite the fuel-air mixture in internal combustion engines. Their role is critical in automotive applications, particularly in ignition systems for cars and small engines. Buyers should assess the coil’s voltage rating, resistance, and overall durability, as these elements affect engine performance and reliability, especially under high-stress conditions.
Toroidal Coil
Toroidal coils are characterized by their circular, doughnut-shaped design, which helps to minimize electromagnetic interference and improve efficiency. They are commonly used in power supplies and RF applications, providing compact solutions for various electronic devices. Buyers should focus on the coil’s inductance, core material, and winding specifications to ensure optimal performance while also being mindful of potentially higher manufacturing costs associated with their production.
Field Coil
Field coils are essential components in electric motors and generators, generating the magnetic field necessary for their operation. They can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements, making them versatile for applications like magnetic levitation systems. When purchasing field coils, B2B buyers should consider the required magnetic field strength, coil dimensions, and the overall design of the motor or generator to ensure compatibility and efficiency in their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of electromagnetic coil
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electromagnetic Coil | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Ignition Systems | Enhanced engine performance and fuel efficiency | Ensure compliance with automotive standards and certifications. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbines | Improved energy conversion efficiency | Look for suppliers with experience in custom coil designs for specific turbine models. |
| Medical Devices | MRI Machines | Precise imaging and diagnostics capabilities | Source from manufacturers with ISO certifications and proven track records in medical applications. |
| Industrial Automation | Solenoid Valves | Increased operational efficiency and automation | Consider suppliers that offer tailored solutions and rapid prototyping capabilities. |
| Consumer Electronics | Speakers and Microphones | Enhanced audio quality and user experience | Focus on suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and custom configurations for specific audio applications. |
Automotive Applications
In the automotive sector, electromagnetic coils are integral to ignition systems. They generate the high voltage needed to ignite fuel in combustion engines, significantly enhancing performance and fuel efficiency. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing coils that meet stringent automotive standards is crucial. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers with relevant certifications and a track record of reliability to ensure long-term performance in diverse environmental conditions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Renewable Energy Utilization
Electromagnetic coils are vital in wind turbines, where they function as part of the generator system. These coils convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, improving overall energy conversion efficiency. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, selecting suppliers experienced in custom coil designs tailored to specific turbine models is essential. This ensures compatibility and maximizes energy output, aligning with regional renewable energy initiatives.
Medical Device Integration
In medical devices, especially MRI machines, electromagnetic coils are used to create the strong magnetic fields necessary for imaging. The precision and reliability of these coils directly impact diagnostic capabilities. Buyers from Africa and Europe should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with ISO certifications and proven expertise in medical applications. This ensures compliance with health regulations and enhances the safety and effectiveness of medical imaging technologies.
Industrial Automation Solutions
Electromagnetic coils are commonly used in solenoid valves within industrial automation systems. These coils control the flow of fluids and gases, thereby increasing operational efficiency and enabling automation. Buyers should consider suppliers that offer tailored solutions and rapid prototyping capabilities, allowing for quick adaptation to specific operational needs. This is particularly important in fast-paced industrial environments in South America and the Middle East.
Consumer Electronics Enhancement
In consumer electronics, electromagnetic coils are essential components of speakers and microphones, where they enhance audio quality and user experience. For international B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and custom configurations for specific audio applications is crucial. This ensures that the final products meet consumer expectations for sound clarity and performance, especially in competitive markets in Europe and Africa.
Related Video: Eddy currents & their applications (& how to reduce them) | Electromagnetic induction | Khan Academy
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electromagnetic coil
When selecting materials for electromagnetic coils, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option, especially for international B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The choice of material can significantly affect performance, manufacturing complexity, and compliance with regional standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in electromagnetic coils.
Copper Wire
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and ductility. It can handle high temperatures (up to 200°C) and has a relatively low resistance to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper wire is its superior conductivity, which improves the efficiency of electromagnetic coils. However, it is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum and can be prone to oxidation if not properly coated. Manufacturing processes for copper coils can be complex due to the need for precise winding techniques.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and reliability, such as in transformers and electric motors. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile across industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B3 (for copper wire) and consider the availability of copper in their region. Countries with strict environmental regulations may have additional compliance requirements.
Aluminum Wire
Key Properties: Aluminum has good electrical conductivity (about 60% that of copper), is lightweight, and resistant to corrosion due to its natural oxide layer. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easier to handle and reduces overall product weight, which is advantageous in applications like automotive and aerospace. However, its lower conductivity compared to copper means that larger wire sizes may be needed, potentially increasing manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum coils are suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in portable devices. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for outdoor or marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the relevant standards, such as ASTM B231 for aluminum conductors. Additionally, the cost-effectiveness of aluminum can vary by region, influenced by local market conditions.
Steel Core
Key Properties: Steel cores enhance the magnetic field strength of electromagnetic coils. They are durable and can withstand high mechanical stress, with temperature ratings typically around 300°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using a steel core is the significant increase in magnetic field strength, which can improve coil performance. However, steel can be heavier and may require additional treatment to prevent rust, adding to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel cores are commonly used in industrial applications where strong magnetic fields are necessary, such as in heavy machinery and industrial transformers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of treated steel to prevent corrosion in humid environments, particularly relevant in regions like Africa and parts of South America.
Ferrite Material
Key Properties: Ferrite materials are ceramic compounds made from iron oxide mixed with other metals. They exhibit high magnetic permeability and low electrical conductivity, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Pros & Cons: Ferrite cores are lightweight and provide excellent magnetic properties, which enhance coil efficiency. However, they can be brittle and may not withstand high mechanical stress, limiting their application in heavy-duty environments.
Impact on Application: Ferrite materials are widely used in applications such as RF transformers and inductors, especially in telecommunications and consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ferrite materials meet specific standards, such as JIS C 2502 in Japan or DIN 50144 in Europe. The sourcing of ferrite materials can vary significantly, impacting lead times and costs.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electromagnetic coil | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Wire | Transformers, electric motors | Superior conductivity and efficiency | Higher cost and oxidation risk | High |
| Aluminum Wire | Portable devices, automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity requiring larger sizes | Medium |
| Steel Core | Industrial machinery, transformers | Increased magnetic field strength | Heavier and requires rust prevention treatment | Medium |
| Ferrite Material | RF transformers, inductors | Excellent magnetic properties for high-frequency | Brittle and limited mechanical stress tolerance | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for electromagnetic coils, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electromagnetic coil
Electromagnetic coils are integral components in numerous electronic applications, necessitating precise manufacturing processes and stringent quality assurance measures. For international B2B buyers, understanding these aspects is crucial for selecting reliable suppliers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of electromagnetic coils involves several key stages, each requiring specialized techniques to ensure high-quality output.
1. Material Preparation
The first step is selecting the appropriate materials, which typically include copper or aluminum wire for winding, and various core materials such as ferrite or iron. The wire is often coated with an insulating layer to prevent short circuits. Material quality is critical; therefore, suppliers should provide material certificates to verify compliance with specifications.
2. Forming
This stage involves winding the prepared wire around a core. The winding process can be done manually or through automated machines, depending on the complexity and volume of production. Techniques such as multi-layer winding and automatic winding machines are commonly used to enhance efficiency and precision. B2B buyers should inquire about the winding techniques used by their suppliers, as this impacts the coil’s performance.
3. Assembly
After winding, the coils undergo assembly, where components such as connectors and terminals are added. This step may also involve integrating the coil with other electronic components. For custom applications, precise assembly is crucial, and suppliers should be able to demonstrate their capabilities in handling complex assemblies.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes include encapsulation, insulation, and protective coatings to enhance durability and performance. Encapsulation can protect coils from environmental factors, which is particularly important for applications in harsh conditions. Buyers should ensure that the finishing processes comply with industry standards to guarantee product longevity.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in electromagnetic coil manufacturing is paramount, ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications and performance standards.
International Standards
Adhering to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, is essential for manufacturers. This standard outlines a framework for consistent quality management systems, which helps in maintaining high production standards. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (European Conformity) for the European market or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications can further validate a supplier’s commitment to quality.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically conducted at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products before they are shipped.
B2B buyers should request details about the QC processes employed by suppliers, including specific checkpoints and the frequency of inspections.
Testing Methods
Common testing methods for electromagnetic coils include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying resistance, inductance, and current capacity.
- Thermal Testing: Assessing performance under varying temperature conditions.
- Mechanical Testing: Ensuring structural integrity and resistance to physical stress.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide testing reports and certificates that demonstrate compliance with these methods.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into their processes and adherence to quality standards. This is especially important when dealing with overseas suppliers.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers assess the supplier’s consistency in meeting specifications. These reports should include data from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide unbiased evaluations of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. This is particularly beneficial for buyers in regions with limited access to local suppliers.
Regional Considerations
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is important to consider regional standards and requirements. Different regions may have specific certifications or compliance requirements that suppliers must meet. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while Middle Eastern buyers might focus on local standards relevant to their markets.
Furthermore, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality standards. Establishing clear channels of communication with suppliers can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that quality expectations are aligned.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for electromagnetic coils is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and the relevant quality control standards, buyers can select suppliers that meet their specific needs and ensure the reliability of their electromagnetic coil applications. By actively engaging in supplier audits, requesting quality reports, and considering regional standards, buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and reduce risks associated with international sourcing.
Related Video: 18650 Cell Manufacturing Process, Automatic Production Line
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electromagnetic coil Sourcing
Electromagnetic coils are essential components in various industries, and their sourcing involves a careful analysis of costs and pricing structures. Understanding these elements can significantly benefit international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver for electromagnetic coils is the materials used, including copper or aluminum wire and the core materials (often iron or ferrite). Fluctuations in global metal prices can directly impact the overall cost. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally to mitigate costs associated with imports.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the geographical location of the manufacturer. In regions with high labor costs, such as Western Europe, it is essential to evaluate the balance between quality and expense. Countries in Africa or South America may offer competitive labor rates, which can be advantageous for buyers looking to minimize costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to the production environment, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory rent. Manufacturers with efficient processes and modern facilities may pass on lower overhead costs to buyers, making it vital to assess their operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom coils often require specialized tooling, which can add to the initial costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs upfront and consider suppliers who offer cost-effective tooling solutions or amortize these costs over larger order volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Quality assurance processes ensure that the coils meet the specified standards. Implementing stringent QC measures can increase costs, but this investment is crucial for preventing defects and ensuring product reliability. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications (ISO, UL, etc.) that can guarantee quality.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the shipping method, distance, and logistics provider. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is critical as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can significantly influence total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to their costs to ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning, brand reputation, and customer relationship dynamics.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of electromagnetic coils:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs while maximizing cost efficiency.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs may incur higher costs due to the complexity involved. It’s advisable to collaborate closely with suppliers to understand how customization impacts pricing.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. Buyers should evaluate whether higher-quality materials justify the additional costs based on their application requirements.
-
Quality and Certifications: Coils with higher quality standards or certifications may come at a premium. However, investing in quality can lead to lower failure rates and reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer companies might offer competitive rates to gain market entry.
-
Incoterms: Different shipping terms can significantly alter the final price. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals and avoid unexpected costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for repeat business.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also shipping, handling, and potential warranty or service costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing disparities. For example, sourcing from manufacturers in lower-cost regions may reduce overall expenses, but consider additional factors such as lead times and shipping logistics.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including their capabilities, market reputation, and customer reviews. This can help mitigate risks associated with quality and service delivery.
In summary, the sourcing of electromagnetic coils involves a multifaceted approach to understanding costs, pricing structures, and negotiation strategies. By considering the outlined factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Spotlight on Potential electromagnetic coil Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electromagnetic coil’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electromagnetic coil
Electromagnetic coils are pivotal components in a wide range of electrical applications, from industrial machinery to consumer electronics. Understanding their technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when navigating international markets. Here’s a breakdown of essential specifications and jargon related to electromagnetic coils.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing the coil, typically copper or aluminum wire, and the core material (such as iron or ferrite).
– Importance: Higher-grade materials enhance conductivity and durability, impacting the coil’s efficiency and lifespan. Buyers should consider material grade to ensure optimal performance in their specific applications. -
Wire Gauge
– Definition: The thickness of the wire used in the coil, measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG).
– Importance: The wire gauge affects the resistance and current-carrying capacity of the coil. Selecting the appropriate gauge is essential for achieving the desired electromagnetic properties while ensuring safety and efficiency. -
Inductance Value
– Definition: A measure of the coil’s ability to store energy in a magnetic field, typically expressed in henries (H).
– Importance: Understanding the inductance is vital for applications requiring precise electromagnetic characteristics. Buyers need to match the inductance with their device specifications to ensure functionality. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value, often expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: Tighter tolerances ensure that the coils meet specific performance standards. In high-precision industries, such as aerospace or medical devices, maintaining strict tolerances is critical to product reliability. -
Temperature Rating
– Definition: The maximum temperature at which the coil can operate without degrading.
– Importance: Temperature ratings are crucial for applications in extreme environments. Buyers should ensure that the coils can withstand operational conditions to prevent failures or reduced efficiency. -
Electrical Resistance
– Definition: The opposition to the flow of electric current, measured in ohms (Ω).
– Importance: Low resistance is desirable for efficiency, as it minimizes energy loss. Understanding resistance helps buyers choose coils that align with their energy efficiency goals.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often seek OEM parts to ensure compatibility and reliability in their systems. Understanding OEM relationships can lead to better sourcing decisions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules to avoid overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers compare prices and terms from different suppliers. It is a critical step in ensuring competitive pricing and favorable conditions. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms ensures clarity on shipping, liability, and costs. Buyers should specify Incoterms in contracts to avoid misunderstandings during international shipping. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time between the initiation of an order and the completion of the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory control. Buyers should factor in lead times when coordinating production schedules to ensure timely delivery. -
Custom Coils
– Definition: Electromagnetic coils designed and manufactured to meet specific customer requirements.
– Importance: Custom coils can optimize performance for unique applications. Buyers should discuss their specifications with manufacturers to leverage custom solutions effectively.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategies and product performance in the competitive landscape of electromagnetic coils.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electromagnetic coil Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electromagnetic coil sector is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and advanced industrial automation. Key trends shaping this market include the integration of smart technologies and IoT solutions, which enhance the functionality of electromagnetic coils in various applications—from automotive to medical devices. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective sourcing strategies.
One emerging trend is the shift towards custom coil manufacturing. Companies are increasingly seeking tailored solutions that meet specific performance requirements, thus fostering partnerships with manufacturers who can provide flexibility and innovation. Additionally, the rise of sustainable practices is influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are looking for manufacturers who not only comply with international quality standards but also demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly processes.
Another vital factor is the geopolitical landscape affecting supply chains. For buyers in regions like Turkey and France, it’s essential to consider the stability of suppliers and the impact of trade policies. Moreover, the ongoing transition towards digitization in manufacturing processes is enabling better visibility and efficiency in sourcing electromagnetic coils, allowing buyers to make more informed decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies across industries, including the electromagnetic coil sector. The environmental impact of coil production—especially regarding energy consumption and waste generation—necessitates a shift towards greener practices. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers that implement sustainable manufacturing processes, such as using energy-efficient machinery and minimizing waste through recycling initiatives.
Ethical sourcing is equally crucial. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and have transparent supply chains. This not only mitigates risks associated with unethical practices but also enhances brand reputation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials in the production of electromagnetic coils is gaining traction. Materials that are recyclable or have a lower environmental footprint are becoming preferred choices for manufacturers. B2B buyers should actively seek out suppliers who can demonstrate their use of sustainable materials and practices, ensuring that their procurement decisions align with global sustainability goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The development of electromagnetic coils dates back to the early days of electrical engineering in the 19th century. Initially used in simple devices such as telegraphs, the technology has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques. The introduction of digital technologies has further transformed coil design and production, allowing for greater precision and customization.
In recent decades, the rise of renewable energy and electric mobility has positioned electromagnetic coils as critical components in modern applications. Today, they play a vital role in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Understanding this historical context can provide B2B buyers with insights into the technological advancements and market shifts that define the current landscape of the electromagnetic coil industry.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electromagnetic coil
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of electromagnetic coils?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, certifications (like ISO 9001), and customer reviews. Assess their production capabilities to ensure they can meet your specific requirements, including customization options. Request samples to evaluate the quality of their coils. Additionally, consider their financial stability and ability to fulfill orders in a timely manner. Engaging with suppliers from regions with strong manufacturing reputations, such as Europe and the U.S., can also provide an added layer of assurance. -
Can I customize electromagnetic coils to suit my specific application?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electromagnetic coils. You can specify wire gauge, core materials, dimensions, and winding techniques. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly during the design phase. Manufacturers like HBR Industries and Globatronix specialize in turning customer designs into tangible products, which ensures that the coils meet your precise needs. Be prepared to share application details and performance expectations to facilitate the customization process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electromagnetic coils?
MOQs vary by supplier and can range from as low as 50 units to several hundred, depending on the complexity of the coil design. Lead times typically range from 2 to 8 weeks, influenced by the order size and customization level. For urgent needs, inquire about expedited services, but be aware that this may incur additional costs. Establishing a relationship with your supplier can help negotiate favorable terms regarding MOQs and lead times. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electromagnetic coils internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly based on the supplier’s location and policies. Common terms include advance payment, net 30/60 days, or letters of credit for larger orders. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like PayPal, bank transfers, or escrow services to protect your interests. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for electromagnetic coils?
Request documentation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Many manufacturers conduct rigorous testing on their coils, including electrical and thermal performance tests. Ask for test reports or certifications that verify compliance with international standards. Regular audits and inspections can also be scheduled to maintain quality assurance throughout the production process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electromagnetic coils?
When importing, consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Partnering with a logistics provider who specializes in international trade can streamline the process. Ensure that the supplier provides proper documentation, including invoices and packing lists, to facilitate customs clearance. Additionally, consider the delivery terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to understand who is responsible for shipping costs and risks during transit. -
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively managed?
To manage disputes, establish clear terms in your contract regarding quality expectations, delivery timelines, and payment conditions. Maintain open communication with your supplier to address issues promptly. If disputes arise, try to resolve them amicably through negotiation. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods. Including a dispute resolution clause in your contracts can provide a structured approach to handling conflicts. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with suppliers of electromagnetic coils?
Building a strong relationship with suppliers involves regular communication and feedback on their products and services. Establishing trust through transparency can lead to better pricing and priority service. Engage in collaborative planning to forecast your needs and ensure they can meet your future demands. Regularly review performance metrics and address any concerns promptly. Participating in joint development projects can also strengthen partnerships and foster innovation.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electromagnetic coil
As the global demand for electromagnetic coils continues to rise, particularly in industries such as renewable energy, automotive, and medical devices, the importance of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with reliable manufacturers that offer customizable solutions tailored to specific needs. By leveraging local suppliers and exploring global networks, companies can enhance their supply chain resilience, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
Key takeaways for buyers include the necessity of thorough supplier evaluations, understanding technical specifications, and ensuring compliance with international standards. Engaging with manufacturers that offer quick turnaround times and prototyping capabilities can significantly streamline product development processes.
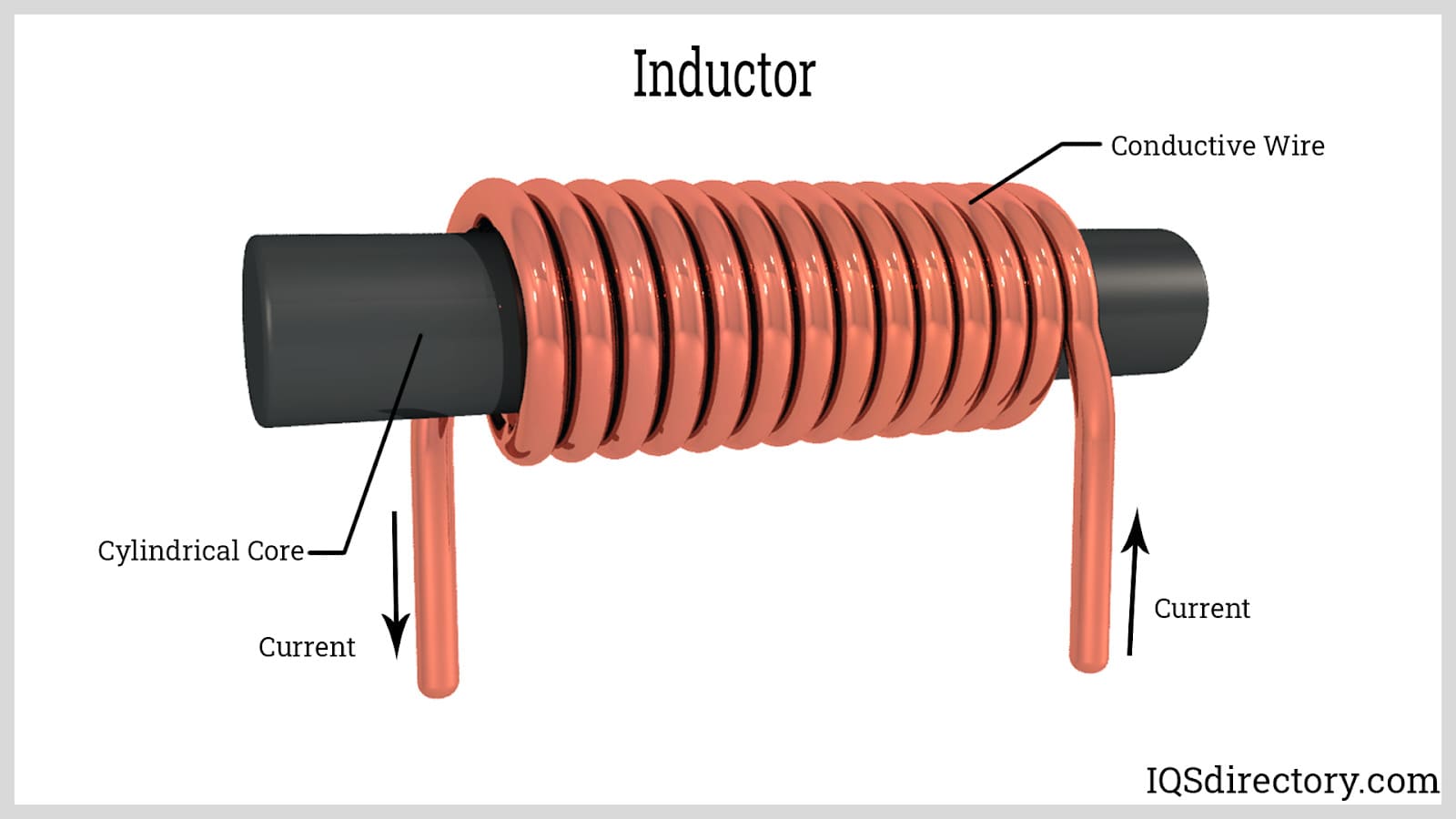
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, the innovations in coil technology and the increasing integration of smart technologies in electromagnetic applications present exciting opportunities. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market trends and emerging technologies to capitalize on these advancements. Take action today by assessing your sourcing strategies and exploring partnerships that align with your business goals to ensure a competitive edge in the evolving marketplace.