Master Sourcing Industrial Agitators: Your Comprehensive
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial agitator
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, industrial agitators play a pivotal role in enhancing process efficiency across various sectors, including chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and wastewater treatment. These essential devices facilitate the mixing and blending of liquids, ensuring uniformity and optimal reaction conditions. For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of agitators is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international buyers by providing in-depth insights into the world of industrial agitators. It covers a wide range of topics, including different types of agitators, the materials used in their construction, manufacturing and quality control processes, and a detailed analysis of suppliers. Additionally, it addresses cost considerations and market trends, ensuring that buyers have all the information necessary to navigate their sourcing journey effectively.
With a focus on actionable insights and practical guidance, this resource aims to demystify the complexities surrounding industrial agitators. By leveraging the knowledge contained within this guide, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately drive business growth. Whether you’re sourcing for a new facility or upgrading existing equipment, this guide is your essential roadmap to success in the global market for industrial agitators.
Understanding industrial agitator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paddle Agitators | Flat blades that create gentle mixing | Food processing, wastewater treatment | Pros: Efficient for low viscosity; Cons: Limited shear capabilities. |
| Anchor Agitators | Fixed blades that scrape tank walls | Paints, adhesives, and viscous materials | Pros: Excellent for high-viscosity fluids; Cons: Slower mixing speed. |
| High Shear Mixers | High-speed rotor/stator setup for emulsification | Cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food emulsions | Pros: Effective for emulsifying and dispersing; Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Top-Entry Agitators | Versatile design with adjustable speeds | Chemical processing, petrochemicals | Pros: Adaptable to various applications; Cons: May require significant maintenance. |
| Side-Entry Agitators | Installed on the side of tanks, ideal for large volumes | Oil and gas, large-scale chemical processing | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Limited mixing depth. |
Paddle Agitators
Paddle agitators feature flat blades that provide gentle mixing, making them ideal for applications involving low-viscosity fluids. They are commonly used in food processing and wastewater treatment. When considering paddle agitators, buyers should evaluate the required mixing speed and the potential for shear, as these agitators may not be suitable for applications requiring high shear rates.
Anchor Agitators
Anchor agitators are characterized by their fixed blades that scrape the walls of the tank, allowing them to handle high-viscosity fluids effectively. They are widely used in industries like paints and adhesives. Buyers should consider the viscosity of the materials being mixed and the desired mixing speed, as anchor agitators tend to operate more slowly compared to other types, which may affect processing times.
High Shear Mixers
High shear mixers utilize a high-speed rotor/stator configuration to emulsify and disperse materials efficiently. They are particularly effective in industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food emulsions. For B2B buyers, key considerations include energy consumption and the specific emulsification requirements of their products, as these mixers can consume more energy than traditional agitators.
Top-Entry Agitators
Top-entry agitators are versatile and feature adjustable speeds, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, particularly in chemical processing and petrochemicals. Their adaptability allows for customization based on the specific mixing needs of the operation. Buyers should assess the maintenance requirements and the potential need for speed adjustments to optimize performance.
Side-Entry Agitators
Designed for installation on the side of tanks, side-entry agitators are ideal for large volumes of liquids, making them popular in the oil and gas sector and large-scale chemical processing. They save space and can be more efficient in large tank setups. However, buyers must consider the limitations in mixing depth and the specific design requirements for their tank configurations when selecting this type of agitator.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of industrial agitator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Industrial Agitator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Manufacturing | Mixing of chemicals for reactions and formulations | Ensures uniformity and quality in product output | Material compatibility, energy efficiency, and maintenance needs |
| Food and Beverage | Homogenization of sauces, dressings, and emulsions | Improves product consistency and shelf life | Hygiene standards, ease of cleaning, and certification requirements |
| Pharmaceutical | Suspension of active ingredients in liquids | Enhances bioavailability and effectiveness of medications | Compliance with regulations, precision in mixing, and scale-up capabilities |
| Water Treatment | Mixing of chemicals for wastewater treatment | Optimizes chemical usage and enhances treatment efficiency | Environmental regulations, material durability, and energy consumption |
| Paint and Coatings | Dispersing pigments in liquid formulations | Achieves desired color consistency and product stability | Viscosity handling, mixing speed, and equipment adaptability |
Chemical Manufacturing
In the chemical industry, industrial agitators are crucial for mixing various chemicals to ensure thorough reactions and consistent formulations. They help in achieving uniformity in product quality, which is vital for compliance with safety and regulatory standards. Buyers should consider the agitator’s material compatibility with corrosive substances, energy efficiency to reduce operational costs, and ease of maintenance to minimize downtime.
Food and Beverage
In food and beverage applications, industrial agitators are employed to homogenize sauces, dressings, and emulsions. This ensures that products maintain consistency and quality over time, enhancing consumer satisfaction. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is essential to focus on hygiene standards, ease of cleaning, and necessary certifications that comply with local food safety regulations.
Pharmaceutical
In the pharmaceutical sector, agitators are used to suspend active ingredients in liquid formulations, which is critical for enhancing the bioavailability of medications. The precision in mixing provided by industrial agitators ensures that the final product is effective and compliant with stringent health regulations. Key considerations for buyers include adherence to regulatory standards, the ability to scale up production, and the precision of the mixing process.
Water Treatment
In water treatment facilities, industrial agitators mix chemicals used for treating wastewater, optimizing the chemical dosage for maximum efficiency. This not only enhances treatment outcomes but also reduces the overall environmental impact. Buyers should focus on sourcing agitators that comply with environmental regulations, possess durable materials to withstand harsh conditions, and ensure low energy consumption to promote sustainability.
Paint and Coatings
In the paint and coatings industry, industrial agitators are essential for dispersing pigments within liquid formulations. This process is vital for achieving color consistency and stability in the final product. Buyers should prioritize agitators that can handle varying viscosities, provide adjustable mixing speeds, and adapt to different formulations to ensure flexibility in production processes.
Related Video: Jacketed Mixing Tank with agitator, Industrial Stirrer
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial agitator
When selecting materials for industrial agitators, it is crucial to consider the specific properties and applications of various materials. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in industrial agitator construction, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is available in various grades, with 304 and 316 being the most common for industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is durable and has a long lifespan, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex, particularly for custom designs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for a wide range of media, including corrosive chemicals, making it ideal for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not contaminate the products being mixed.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, the preference for high-grade stainless steel (e.g., 316) is common due to stringent regulations regarding food safety and chemical handling.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is strong and can be manufactured at a lower cost than stainless steel. It has good mechanical properties but is less resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its affordability and ease of fabrication. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion limits its use in applications involving aggressive chemicals or moisture.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is often used in applications where the media is not corrosive, such as in water treatment or mixing non-corrosive liquids. Its lower cost makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in humid climates, such as parts of Africa and South America, should consider protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Compliance with local standards may also dictate the use of specific grades of carbon steel.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a lightweight thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption. It can operate effectively within a wide temperature range.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of polypropylene is its resistance to a wide array of chemicals, making it suitable for aggressive media. However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which can limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for mixing corrosive liquids, especially in the chemical and food industries. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not alter the properties of the media being mixed.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the selected polypropylene grade complies with food safety standards, particularly in Europe and North America. Additionally, understanding the temperature limits of polypropylene is essential for proper application.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons:
Titanium’s primary advantage is its durability and ability to withstand extreme conditions, making it suitable for high-performance applications. However, it is significantly more expensive than other materials, which can be a barrier for some projects.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is often used in industries such as aerospace and marine, where exposure to aggressive chemicals and high pressures is common. Its lightweight nature also makes it advantageous in applications where weight is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Due to its cost, titanium is often used in specialized applications. Buyers should evaluate whether the benefits justify the expense and ensure compliance with relevant international standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial agitator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chemical and pharmaceutical mixing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Water treatment and non-corrosive liquids | Affordable and easy to fabricate | Susceptible to rust and corrosion | Low |
| Polypropylene | Mixing aggressive chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace and marine applications | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Very high cost | High |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions on material selection for industrial agitators, considering both performance and compliance with industry standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial agitator
Manufacturing Processes for Industrial Agitators
Manufacturing industrial agitators involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the rigorous demands of various industries, including chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and more. Below is a detailed overview of the typical manufacturing process, emphasizing key techniques and considerations for B2B buyers.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of the manufacturing process is material preparation, where the selection of appropriate materials is crucial. Common materials used in the production of industrial agitators include stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys, chosen based on factors such as corrosion resistance, strength, and compatibility with the substances being mixed.
- Material Sourcing: Buyers should verify that suppliers use high-grade materials that comply with international standards. This can include checking for certifications like ASTM or EN standards for metals.
- Pre-treatment: Materials often undergo pre-treatment processes like cleaning, cutting, and surface preparation to enhance adhesion for coatings and to ensure uniformity in the final product.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This stage typically includes processes such as machining, welding, and casting.
- Machining: Components like shafts and impellers are precision-machined to ensure they meet exact specifications. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is commonly employed for its accuracy and efficiency.
- Welding and Assembly: For larger agitators, various parts are welded together. The welding process must be carefully controlled to prevent defects that could compromise performance.
- Casting: In some cases, components are cast from molten metal to achieve complex shapes that would be difficult to machine.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves bringing together all the components of the agitator into a single unit.
- Sub-Assembly: Smaller components are first assembled into sub-units. For example, impellers are often assembled separately before being attached to the main shaft.
- Final Assembly: The final assembly combines all sub-units, ensuring that all parts fit together correctly and that the agitator operates as intended.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the durability and appearance of the agitators.
- Surface Treatments: This can include polishing, coating (e.g., epoxy or powder coating), and passivation for stainless steel components to improve resistance to corrosion.
- Quality Checks: At this stage, initial quality checks are performed to ensure that the finishing meets specified standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for industrial agitators. Buyers should be aware of the standards and practices that ensure the reliability and safety of their products.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Suppliers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards specifically for equipment used in the petroleum and natural gas industries, ensuring that products are suitable for their intended applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are conducted to monitor processes and identify any defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the agitators are fully assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing to verify functionality and adherence to specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of industrial agitators:
- Hydraulic Testing: This method checks for leaks and structural integrity by subjecting the agitator to pressure.
- Performance Testing: Agitators are tested under operational conditions to assess mixing efficiency and flow patterns.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are used to identify material defects without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier compliance:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of your suppliers’ facilities to assess their manufacturing and quality control processes. This may include reviewing documentation and observing production practices.
- Quality Assurance Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports that outline the testing methods used, results, and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s quality control practices.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
Navigating quality control and certification nuances is essential for international B2B buyers. Here are some considerations:
- Local Regulations: Understand the regulatory landscape in your region, as requirements may vary significantly. For instance, the Middle East may have different certification needs compared to Europe.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that quality documentation is available in a language that your team understands to avoid misinterpretations.
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural differences in communication and business practices, which may affect supplier interactions and negotiations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for industrial agitators, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Related Video: Most Satisfying Factory Production Processes And Heavy-Duty Factory Machines!
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial agitator Sourcing
When sourcing industrial agitators, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The following analysis breaks down the key components of cost and the factors that influence pricing.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost of an agitator. Common materials include stainless steel, which offers durability and corrosion resistance, and various polymers for specific applications. Higher quality materials typically lead to increased costs but can enhance the lifespan and efficiency of the agitator.
-
Labor: Labor costs include the expenses associated with skilled workers involved in manufacturing the agitators. Regions with higher labor costs, like Western Europe, may see increased pricing compared to areas in Africa or South America where labor may be less expensive.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs of production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with advanced facilities and technologies may have higher overhead costs, which can influence the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for specific agitator designs can be significant. Custom agitators, designed to meet unique specifications, will incur higher tooling costs, which are often passed on to the buyer.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes ensure the reliability and performance of the agitators. Suppliers with extensive QC measures may charge more, but this investment can lead to reduced operational issues down the line.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are vital considerations, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can significantly affect the final cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers and suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to substantial discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom agitators tailored to specific processes may incur additional costs. Clearly defining requirements can help manage expectations and control costs.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials directly affects pricing. Buyers should balance the need for quality against budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Compliance with industry standards and certifications can impact costs. Ensure that suppliers provide relevant certifications that justify their pricing.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and service quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is essential for international buyers. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, which can affect overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage volume purchases and long-term partnerships to negotiate better deals.
-
Cost Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, buyers in Europe may face higher base prices but could benefit from advanced technology and support services.
-
Local Regulations: Understand local regulations that may affect costs, such as import tariffs or environmental compliance, especially when sourcing from different regions.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices across suppliers and regions. This helps in making informed decisions and finding the best value.
Disclaimer
Pricing for industrial agitators can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and changes in material costs. It is advisable for buyers to conduct their own assessments and obtain quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential industrial agitator Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘industrial agitator’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial agitator
Key Technical Properties of Industrial Agitators
Understanding the essential technical properties of industrial agitators is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in sectors like chemical processing, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. Here are the critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in agitator construction significantly affects durability and resistance to corrosion. Common materials include stainless steel, which is preferred for its resistance to oxidation and cleanliness, and carbon steel, which is often used for less corrosive applications. Selecting the right material ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs. -
Impeller Design
The shape and design of the impeller influence mixing efficiency and the type of application. Various designs, such as axial flow or radial flow impellers, cater to different mixing requirements. Understanding the impeller design helps in achieving desired mixing outcomes, such as shear rates and flow patterns, essential for process optimization.
-
Power Rating
This specification indicates the energy consumption of the agitator, usually measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). Selecting an agitator with appropriate power ensures effective mixing while managing energy costs. It’s vital for buyers to assess the power requirements based on the viscosity and volume of the materials being mixed. -
Speed Range
The operational speed of an agitator, typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is crucial for achieving the desired mixing intensity. Different applications may require varying speeds; for instance, high-speed agitation is necessary for emulsifying, while low-speed agitation is suitable for blending. Understanding the required speed range can help buyers select the right equipment for their processes. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerances refer to the allowable variations in dimensions and performance specifications. Tight tolerances are essential in applications requiring precise mixing, such as in pharmaceuticals. Knowledge of tolerances helps buyers ensure that the agitators meet industry standards and application-specific requirements. -
Tank Compatibility
The design and size of the agitator must match the tank specifications. Factors such as tank diameter, height, and shape influence the selection process. Ensuring compatibility is vital for efficient operation and process effectiveness.
Common Trade Terminology in the Agitator Industry
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communications and negotiations. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components or equipment that may be marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and assess product quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers need to be aware of MOQs to ensure that their purchasing plans align with supplier requirements, which can impact inventory management and cost-efficiency.
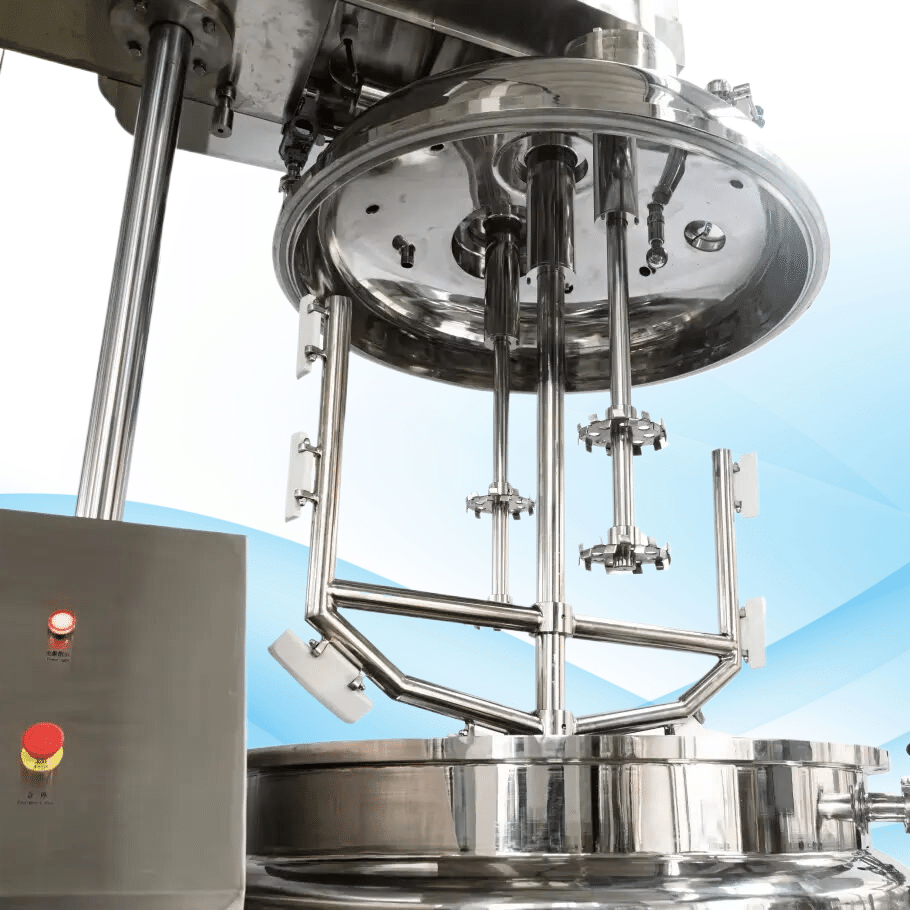
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request from a buyer to suppliers to submit price quotes for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and terms, ensuring they receive the best deal for their agitator needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery terms, which are crucial for international transactions. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing supply chain efficiency, especially in industries with tight timelines. -
Customization
Customization refers to modifying agitators to meet specific operational needs. Buyers should consider their unique requirements, as customized solutions can enhance performance and efficiency in their processes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring industrial agitators, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the industrial agitator Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The industrial agitator market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand across various sectors such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and water treatment. Key trends influencing this market include the rise of automation and digitalization in manufacturing processes. Advanced technologies such as IoT and AI are enhancing the efficiency and precision of agitators, allowing for better process control and reduced operational costs. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these technological advancements is critical for making informed sourcing decisions.
Another notable trend is the shift towards customized agitators tailored to specific processes and materials. This customization is becoming essential as industries seek to improve product quality and operational efficiency. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer flexible design options and can accommodate unique requirements. Additionally, the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency is shaping purchasing decisions, with buyers looking for agitators that consume less power without compromising performance.
International buyers must also be aware of regional market dynamics. In Africa and South America, there is a growing investment in infrastructure and industrialization, which is expected to drive demand for industrial agitators. Conversely, European buyers are more focused on compliance with stringent regulations and sustainability standards, influencing their sourcing strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for buyers in the industrial agitator sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of products are under scrutiny, leading to a demand for greener solutions. B2B buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies aim to establish supply chains that are not only economically viable but also socially responsible. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that provide transparency about their sourcing practices and certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other recognized green certifications. These certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the use of recyclable or biodegradable materials in the production of agitators is gaining traction. Buyers should engage with suppliers who can demonstrate their efforts in minimizing waste and promoting circular economy practices. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, companies can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
Brief Evolution/History
The industrial agitator has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century. Initially, these devices were rudimentary, primarily using mechanical stirring methods to mix liquids. Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have led to the development of more sophisticated designs, including magnetic and pneumatic agitators.
By the mid-20th century, the integration of automation and control systems marked a turning point, allowing for precise mixing and better process management. Today, the industry is witnessing a further transformation with the advent of smart technologies, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of mixing processes. This evolution underscores the importance of adaptability in sourcing strategies for international buyers looking to stay competitive in a rapidly changing marketplace.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial agitator
-
1. How can I effectively vet suppliers for industrial agitators?
When sourcing industrial agitators, it’s essential to conduct thorough supplier vetting. Begin by researching the supplier’s industry reputation through online reviews and trade forums. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region or industry. Assess their manufacturing capabilities by visiting their facility if possible or conducting virtual tours. Additionally, verify their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate quality management practices. Establishing a solid communication line can also reveal a supplier’s responsiveness and reliability. -
2. What customization options are available for industrial agitators?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific operational needs. When discussing customization, consider factors such as the agitator’s size, material (e.g., stainless steel for corrosive environments), and impeller design tailored to your application (e.g., high shear or low shear). Ensure you communicate your process requirements clearly to the supplier. Additionally, inquire about the implications of customization on lead times and costs, as bespoke solutions may require longer production periods. -
3. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead time for industrial agitators?
The MOQ for industrial agitators varies significantly among suppliers and can depend on the level of customization required. Generally, standard models may have an MOQ of 1-5 units, while custom designs might necessitate larger orders. Lead times can range from a few weeks for stock items to several months for customized units. It’s crucial to discuss these aspects upfront with potential suppliers to align your procurement timeline with production capabilities. -
4. How do I ensure quality assurance and certification for my agitators?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation from suppliers that outlines their quality control processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Additionally, inquire about testing protocols for the agitators, including performance tests and compliance with industry standards. Some suppliers may also offer third-party inspection services, which can provide an added layer of assurance regarding the product’s quality before shipment. -
5. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of industrial agitators?
Payment terms can vary widely based on supplier policies and the buyer’s relationship with them. Common options include advance payments (30-50% upfront), net terms (30, 60, or 90 days after delivery), and letters of credit for larger orders. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms that protect your interests while also being acceptable to the supplier. Always document these terms in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings later. -
6. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing agitators internationally?
Logistical considerations are critical when sourcing industrial agitators from abroad. Assess shipping methods, including air versus sea freight, based on cost and urgency. Understand the customs regulations in your country, as tariffs and duties can significantly affect the total landed cost. Additionally, factor in the supplier’s location and the potential impact on lead times. It’s also wise to discuss logistics with your supplier to ensure they can provide necessary shipping documentation and support. -
7. How can I resolve disputes with suppliers effectively?
To effectively resolve disputes, first, maintain clear and open communication with your supplier to address issues as they arise. Document all communications and agreements to have a record of expectations. If a dispute escalates, refer to your contract, which should outline the procedures for conflict resolution, including mediation or arbitration. Engaging a legal professional familiar with international trade can also help navigate complex issues. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can often prevent disputes from occurring in the first place. -
8. What are the best practices for after-sales support for industrial agitators?
After-sales support is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your industrial agitators. Verify that the supplier offers comprehensive support, including installation assistance, operational training, and maintenance services. Ask about the availability of spare parts and the lead times for obtaining them. Establish a clear point of contact for after-sales inquiries and ensure that the supplier provides a warranty for the agitators. Regular follow-ups can help maintain a strong partnership and ensure any issues are promptly addressed.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial agitator
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of industrial agitators is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring quality across diverse industries, from chemical processing to food production. Key takeaways include the importance of understanding specific mixing requirements, evaluating supplier capabilities, and considering the total cost of ownership, which encompasses not just the purchase price but also maintenance and operational costs.
Strategic sourcing empowers buyers to leverage competitive pricing and innovative technology, ultimately enhancing product quality and reducing lead times. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to source high-quality agitators from reliable manufacturers can significantly impact their operational success.
As the global market evolves, staying informed about advancements in agitator technology and supplier trends will be crucial. Embrace the opportunity to connect with leading manufacturers and explore tailored solutions that meet your unique needs. Now is the time to act—invest in strategic sourcing to drive your business forward and achieve sustainable growth.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)