Master Sourcing Plug In Transformers: Strategies for Global
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plug in transformer
In the contemporary energy landscape, plug-in transformers play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient power distribution and enhancing the reliability of electrical systems. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for modernization and sustainability, the demand for these essential components has surged. For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of sourcing plug-in transformers is not just advantageous—it is critical for maintaining operational continuity and driving growth.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview designed to equip decision-makers with the insights necessary for successful procurement. It delves into various transformer types, highlighting their specific applications and advantages, and explores material selection to help buyers make informed choices based on efficiency and lifecycle costs. A thorough examination of manufacturing and quality control processes will enable buyers to assess supplier capabilities effectively, while strategies for supplier assessment will aid in identifying reliable partners in diverse markets.
Additionally, this guide outlines the pricing dynamics and cost structures affecting the transformer market, providing transparency that empowers buyers to negotiate favorable terms. With practical answers to frequently asked questions on lead times, warranty provisions, and compliance, this resource is tailored to facilitate informed sourcing decisions. By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the global market for plug-in transformers, ensuring their operations are robust, resilient, and ready for future challenges.
Understanding plug in transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plug-In Power Transformer | Compact design, designed for easy installation; typically oil or resin insulated | Industrial machinery, renewable energy systems | Efficient power handling; however, may have limited capacity options. |
| Plug-In Distribution Transformer | Lower voltage, step-down functionality; often mounted on poles or pads | Utility distribution, commercial buildings | Cost-effective for localized power; may have higher losses at low loads. |
| Plug-In Dry-Type Transformer | Air-cooled, no oil; uses solid insulation materials | Indoor applications, data centers | Safer and easier to maintain; limited power capacity compared to oil-filled types. |
| Plug-In Instrument Transformer | High precision for measurement; small footprint | Metering, control systems | Highly accurate; however, not suitable for power conversion. |
| Plug-In Autotransformer | Single winding design; compact with tap settings | Voltage regulation, industrial applications | Economical and space-saving; lacks electrical isolation. |
Plug-In Power Transformer
Plug-in power transformers are designed for high-capacity applications, providing efficient power handling in compact formats. Their construction often includes oil or resin insulation, ensuring effective cooling and safety. These transformers are ideal for industrial machinery and renewable energy systems, making them a strategic choice for B2B buyers focused on optimizing power distribution. However, buyers should consider potential limitations in capacity and the need for specialized installation and maintenance services.
Plug-In Distribution Transformer
These transformers are essential for stepping down voltage for local distribution, making them prevalent in utility networks and commercial buildings. Their simpler installation and lower costs make them attractive for B2B buyers, particularly in rapidly growing markets across Africa and South America. However, buyers should be aware of their potential higher losses when operating below optimal load levels, which could impact long-term efficiency and operational costs.
Plug-In Dry-Type Transformer
Plug-in dry-type transformers utilize air cooling and solid insulation, making them safer for indoor applications, such as data centers and healthcare facilities. Their design eliminates the risks associated with oil leaks, a crucial consideration in densely populated areas. While they require less maintenance and offer a more environmentally friendly option, buyers need to weigh their limited power capacity against the safety benefits and higher initial investment.
Plug-In Instrument Transformer
Instrument transformers are specialized devices designed for precise measurement and monitoring of electrical parameters. They are typically smaller and feature high accuracy, making them suitable for metering and control systems in various industrial applications. However, B2B buyers should note that these transformers do not facilitate power conversion, limiting their functionality to measurement and protection. The focus should be on ensuring reliability and accuracy when selecting suppliers.
Plug-In Autotransformer
Autotransformers are characterized by their compact design and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for voltage regulation in industrial settings. Their single winding with tap settings allows for efficient voltage adjustments. However, buyers should consider the lack of electrical isolation, which may pose risks in safety-critical applications. It is essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application to determine if the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
Related Video: Attention is all you need (Transformer) – Model explanation (including math), Inference and Training
Key Industrial Applications of plug in transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plug in transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Integration with solar and wind farms | Efficient voltage regulation and grid stability | Local compliance, efficiency ratings, and supplier reliability |
| Data Centers | Power supply management | Enhanced energy efficiency and uptime | Quality certifications, lead times, and after-sales support |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Machine tool power supply | Improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Customization options and sourcing from reputable manufacturers |
| Transportation & Rail | Electrification of rail systems | Increased reliability and reduced operational costs | Compliance with safety standards and local regulations |
| Mining & Resources | Power distribution in remote sites | Reliable energy supply and operational continuity | Logistics support and supplier experience in harsh environments |
Renewable Energy
Plug-in transformers play a crucial role in renewable energy sectors, particularly in solar and wind farms. These transformers facilitate the integration of variable power generation into the grid by ensuring consistent voltage levels and enhancing grid stability. For international buyers, especially in regions with growing renewable initiatives like Africa and South America, sourcing transformers that comply with local standards and possess high efficiency ratings is essential. Additionally, selecting suppliers with proven reliability can mitigate risks associated with project delays and ensure long-term operational success.
Data Centers
In the data center industry, plug-in transformers are vital for managing power supply and ensuring uninterrupted operations. They help in optimizing energy consumption while maintaining the necessary power quality for sensitive equipment. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing transformers that meet stringent quality certifications and have a track record of reliability. Given the high stakes of data center uptime, understanding lead times and ensuring robust after-sales support are critical factors that can influence procurement decisions.
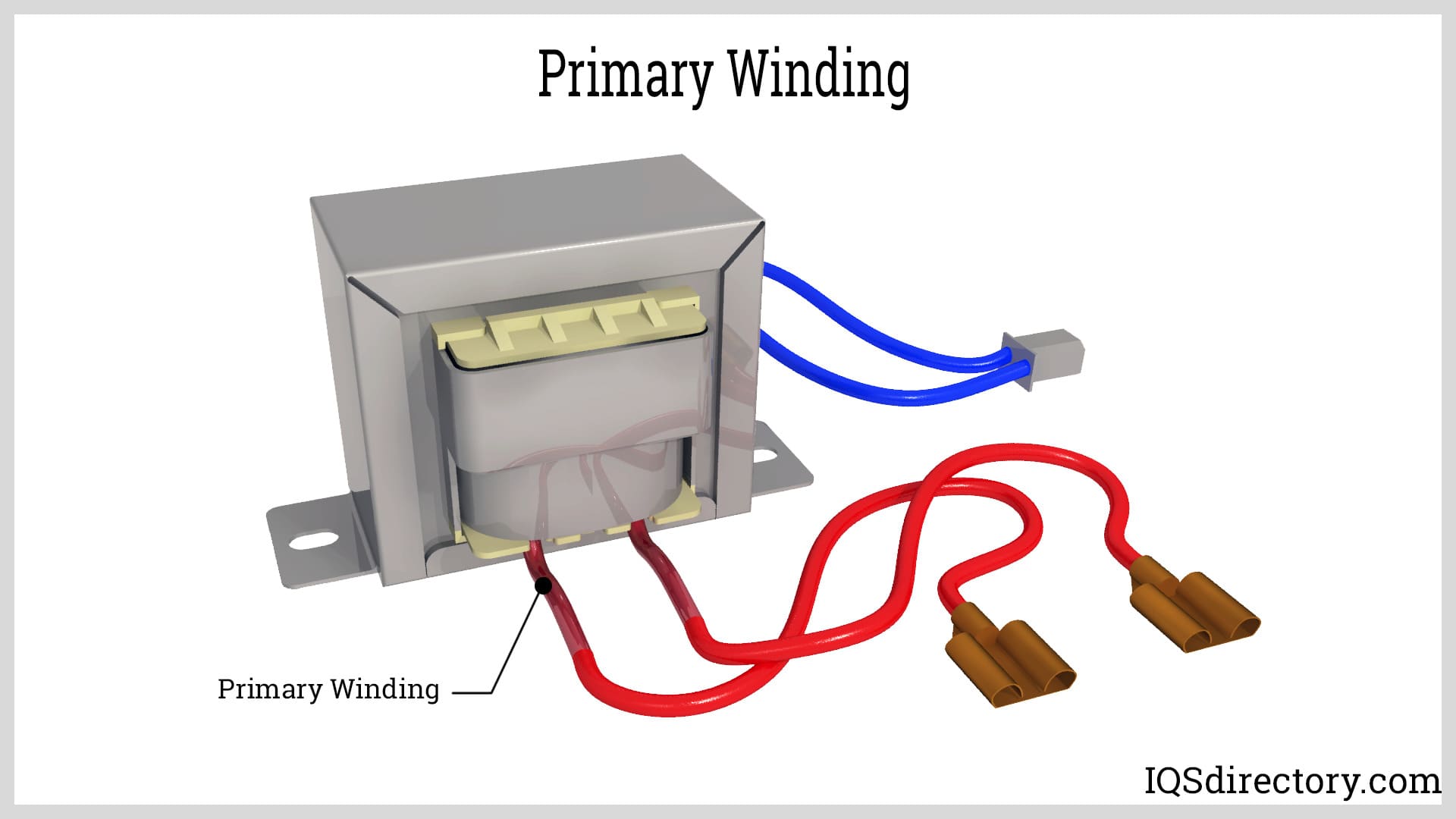
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Industrial Manufacturing
Plug-in transformers are integral to powering machine tools in industrial manufacturing settings. They provide stable power supply and voltage regulation, which are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Buyers in this sector should look for customization options to meet specific machinery requirements and assess the manufacturer’s reputation for quality and reliability. Given the competitive landscape in manufacturing, securing transformers that enhance productivity can yield significant cost savings and operational advantages.
Transportation & Rail
In the transportation sector, particularly rail systems, plug-in transformers are essential for electrifying trains and ensuring reliable power distribution. They contribute to increased operational reliability and lower costs associated with fuel consumption. For international buyers, it is important to ensure compliance with safety standards and local regulations, which can vary significantly by region. Partnering with suppliers experienced in transportation projects can also provide valuable insights into best practices and potential challenges.
Mining & Resources
In remote mining operations, plug-in transformers provide a reliable energy supply necessary for continuous operations in challenging environments. They help in distributing power efficiently across various mining equipment, ensuring operational continuity. B2B buyers in this sector should consider logistics support when sourcing transformers, as transportation and installation in remote areas can be complex. Additionally, selecting suppliers with experience in harsh conditions can enhance the likelihood of successful project execution and minimize operational disruptions.
Related Video: How does a Transformer work ?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plug in transformer
When selecting materials for plug-in transformers, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here’s an analysis of four common materials used in plug-in transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures and has a melting point of approximately 1,984°F (1,085°C), making it suitable for high-load applications.
Pros & Cons:
Copper offers high durability and efficiency, which translates to lower energy losses. However, it is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum, which can impact the overall cost of the transformer. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, as copper is relatively easy to work with, but the high cost may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application:
Copper is highly compatible with various media, ensuring efficient energy transfer in transformers. It is particularly effective in applications requiring high reliability and minimal energy loss.
Specific Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper rod and wire. In regions like Africa and South America, where budget constraints may be significant, the higher initial investment in copper must be justified by long-term operational savings.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum has a lower density than copper, making it lighter and easier to handle. It has good electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper, and is resistant to corrosion, which is beneficial in humid environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness, as it is significantly cheaper than copper. However, it has lower conductivity, which can lead to higher energy losses over time. Manufacturing processes for aluminum can be more complex due to its malleability and thermal expansion properties.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in mobile transformer units. However, it may not be ideal for high-load applications where efficiency is paramount.
Specific Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B231 for aluminum conductors. In regions such as the Middle East, where environmental conditions can be harsh, ensuring proper insulation and protection against corrosion is essential.
Steel
Key Properties:
Steel, particularly grain-oriented electrical steel (GOES), is commonly used in transformer cores due to its high magnetic permeability and strength. It can withstand high pressures and has good thermal stability.
Pros & Cons:
Steel is durable and can be manufactured in various forms to suit different transformer designs. However, it is heavier than copper and aluminum, which can complicate installation. The cost of steel can fluctuate based on global market conditions.
Impact on Application:
Steel is critical for the core of transformers, impacting efficiency and performance. Its magnetic properties enhance the transformer’s ability to transfer energy effectively.
Specific Considerations for Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM A677 for electrical steel is crucial. Buyers in Europe should also consider EU regulations on material sourcing and sustainability, which may affect the choice of steel suppliers.
Insulation Materials (e.g., Resin or Oil)
Key Properties:
Insulation materials, whether resin-based or oil-based, are essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of transformers. They must withstand high temperatures and provide excellent dielectric strength.
Pros & Cons:
Resin insulation is safer and requires less maintenance compared to oil, which can pose fire hazards. However, resin can be more expensive and may not perform as well in extreme conditions. Oil insulation, while effective, requires careful handling and disposal.
Impact on Application:
The choice of insulation affects the transformer’s operational safety and efficiency. Resin is preferred for indoor applications, while oil is often used in larger, outdoor transformers.
Specific Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international insulation standards such as IEC 60216 for thermal endurance. In regions with strict environmental regulations, such as Europe, opting for resin insulation may be more favorable.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for plug in transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-load applications | Excellent conductivity and durability | High cost | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, mobile transformers | Cost-effective | Lower conductivity | Medium |
| Steel | Transformer cores | Strong and durable | Heavier, fluctuating prices | Medium |
| Insulation | Safety and efficiency | Safer and lower maintenance (resin) | Higher cost (resin), handling issues (oil) | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials used in plug-in transformers, enabling informed decisions that align with operational requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plug in transformer
In the global market for plug-in transformers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is crucial for B2B buyers looking to ensure reliability and performance. This section outlines the key stages of manufacturing, important quality control measures, and how buyers can effectively verify supplier quality, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes for Plug-in Transformers
The manufacturing of plug-in transformers involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Key materials include:
- Copper or Aluminum Windings: These conductors are essential for energy transfer. Copper is favored for its conductivity, while aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective.
- Insulation Materials: Insulation is crucial for safety and performance. Common materials include resin, paper, and synthetic compounds that withstand high voltages.
- Core Materials: Grain-oriented electrical steel is often used for the magnetic core to enhance efficiency.
Key Techniques:
– Quality Sourcing: Engage suppliers who provide certified materials, ensuring compliance with international standards.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes to create the necessary components of the transformer. This includes:
- Winding: Conductors are wound around the core to create the primary and secondary coils. Precision is critical here to ensure optimal electrical performance.
- Core Assembly: The magnetic core is assembled, often involving stacking laminated steel sheets to reduce energy losses.
Key Techniques:
– Automated Winding Machines: These enhance precision and reduce human error during the winding process.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage combines all components into a functional transformer. This involves:
- Mounting Components: The windings and core are securely mounted in a casing, which can be either oil-filled or dry-type, depending on the design.
- Electrical Connections: Connections between the coils and external terminals are made, ensuring robust contact and minimal resistance.
Key Techniques:
– Modular Assembly Systems: These systems facilitate efficient production and allow for easier upgrades or repairs.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves several finishing processes:
- Sealing and Insulation: The transformer is sealed to protect against environmental factors. Additional insulation may be applied to ensure safety.
- Testing and Calibration: Before leaving the factory, transformers undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specifications.
Key Techniques:
– Vacuum Pressure Impregnation (VPI): Used for oil-filled transformers to enhance insulation and prevent moisture ingress.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance is paramount in the production of plug-in transformers. Adhering to international and industry-specific standards ensures reliability and safety.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is vital for manufacturers to demonstrate consistent quality.
- CE Marking: For transformers sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety and environmental regulations.
- API Standards: For transformers used in oil and gas sectors, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet quality specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps identify defects early in the manufacturing process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection and testing phase before the product is shipped to customers.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods for plug-in transformers include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that the transformer operates within specified voltage and current limits.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses the thermal performance and cooling efficiency of the transformer.
- Dielectric Testing: Checks insulation integrity to prevent electrical failures.
Verifying Supplier Quality
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality practices of suppliers, especially when sourcing from regions with varying regulatory standards.
Audits and Reports
- Factory Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with standards.
- Supplier Quality Reports: Request regular reports detailing the outcomes of quality checks and testing performed during production.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These services can:
- Verify compliance with international standards.
- Conduct independent testing of transformers before shipment.
- Provide certification that can be crucial for regulatory compliance in the buyer’s region.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols of plug-in transformers is essential. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with a robust quality control framework, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. Engaging in thorough supplier assessments, audits, and third-party inspections will further ensure that the transformers sourced meet the highest standards of quality and reliability. This due diligence is not only beneficial for immediate project success but also crucial for long-term operational resilience.
Related Video: Extreme Power Transformer Manufacturing Process – How It’s Made
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plug in transformer Sourcing
In the sourcing of plug-in transformers, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will explore the key components that contribute to the pricing of plug-in transformers and provide actionable insights for effective procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of materials is a significant factor, including copper or aluminum windings, insulation systems, and the core materials. Prices for these commodities fluctuate based on global market conditions. For instance, copper prices have seen substantial increases, which can directly impact transformer costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but buyers must also consider the trade-off in quality and expertise. Skilled labor is crucial for ensuring high-quality production standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate overhead costs, but buyers should assess whether suppliers have invested in modern, efficient production technologies.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which can increase initial costs. However, once established, these costs may be amortized over a larger production run, potentially lowering the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes are essential to ensure that transformers meet required standards and certifications. While increased QC measures can raise production costs, they ultimately enhance product reliability and reduce long-term operational risks.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Buyers should account for the logistics of getting the product from the manufacturer to their location, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market competition and the complexity of the product. A higher margin may reflect specialized technology or superior service levels, while a lower margin might indicate a more competitive pricing strategy.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of plug-in transformers, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing larger quantities can lead to discounts. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better terms for bulk orders, which can significantly lower the unit price.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized solutions often carry a premium. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary costs while ensuring that essential specifications are met.
-
Quality/Certifications: Transformers that comply with international standards or possess specific certifications may command higher prices due to their reliability and safety assurances.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and on-time delivery may charge more than newer entrants.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect total costs. For example, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may offer convenience but could result in higher overall expenses due to customs duties and taxes.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open dialogue with suppliers to negotiate terms. Highlighting your purchasing volume and long-term potential can leverage better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors like maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs when evaluating suppliers.
-
International Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional economic factors that may influence pricing. For example, tariffs, local regulations, and currency fluctuations can affect costs for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Pricing for plug-in transformers can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. It is advisable to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
By understanding these cost structures and price influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Spotlight on Potential plug in transformer Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘plug in transformer’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plug in transformer
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with plug-in transformers is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only informs procurement decisions but also enhances negotiation capabilities and supplier collaboration.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in the transformer, primarily copper or aluminum for windings, and specific grades of steel for the core.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade materials generally improve conductivity and efficiency, leading to lower operational costs. Buyers should assess whether the material grade meets local standards and the specific requirements of their applications, particularly in regions with varying environmental conditions. -
Voltage Rating
– Definition: The maximum voltage that the transformer can handle safely and effectively.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the correct voltage rating is critical to prevent failures or safety hazards. Buyers must ensure that the voltage rating aligns with the operational voltage of their systems, especially when integrating into existing grids. -
Power Rating (kVA)
– Definition: The capacity of the transformer, measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA), indicating how much power it can handle.
– B2B Importance: Understanding power ratings helps buyers determine the appropriate transformer for their needs. Oversizing can lead to higher costs, while undersizing may cause inefficiencies and operational issues. Accurate power rating assessment is essential for effective project planning. -
Efficiency Class
– Definition: A measure of how efficiently the transformer converts electrical energy, often classified into efficiency classes (such as Class A, B, or C).
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency translates to lower energy losses and reduced operational costs over time. Buyers should prioritize efficiency classes that meet local regulations and sustainability goals, particularly in regions focused on energy conservation. -
Insulation Type
– Definition: The materials and technology used to insulate the windings and core, which can be oil-based or dry-type (resin).
– B2B Importance: The insulation type affects safety, maintenance, and environmental impact. For instance, dry-type transformers are preferable in urban areas due to their lower fire risk. Buyers should evaluate insulation options based on application-specific requirements and local safety regulations.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces components or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers who adhere to quality standards and can provide support during the procurement process. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their project needs, especially in regions where cash flow can be a constraint. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information and terms for specific products.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers compare offers systematically and ensures transparency in the procurement process. Crafting a detailed RFQ can lead to better pricing and service terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define who is responsible for costs and risks at each stage of shipping. Proper understanding can prevent disputes and ensure smoother logistics. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Knowing lead times helps buyers plan their projects and manage expectations. In light of the recent supply chain challenges, understanding lead times is more critical than ever for timely project execution.
By comprehensively understanding these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and operational efficiency in the transformer market.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the plug in transformer Sector
The global market for plug-in transformers is experiencing significant transformations driven by various factors. As nations push towards renewable energy sources, the demand for efficient power distribution systems has surged, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America. This shift is motivated by the increasing electrification needs, urbanization, and the integration of renewable energy projects that require reliable transformer solutions. In Europe and the Middle East, regulatory frameworks are becoming stricter, emphasizing the need for high-efficiency transformers that can minimize losses and enhance grid stability.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends highlight a growing preference for modular and scalable transformer designs, which allow for easier integration into existing infrastructure. Digitalization is also reshaping procurement practices, with technologies such as IoT and AI being utilized for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of transformers. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who offer not only high-quality products but also advanced technological capabilities that can support smart grid initiatives.
For international B2B buyers, understanding the complexities of the global supply chain is paramount. Recent disruptions, including the COVID-19 pandemic, have led to extended lead times—now averaging between 120 to 210 weeks for large transformers. Buyers must conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, focusing on their capacity to deliver on time, quality assurance processes, and financial stability. Furthermore, fluctuating raw material prices, particularly for copper and steel, necessitate strategic negotiations to secure favorable pricing and terms.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the plug-in transformer sector. Environmental impact considerations are driving buyers to prioritize transformers that utilize eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. The industry’s shift toward sustainability is not merely regulatory; it is a market expectation. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards and certifications.
Ethical sourcing practices are essential in ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. This includes verifying that materials are sourced responsibly and that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) provide reassurance to buyers looking to enhance their sustainability credentials. Additionally, utilizing “green” materials, such as recycled metals or biodegradable insulation, can contribute to a lower carbon footprint, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and investors alike.
Brief Evolution/History
The concept of plug-in transformers has evolved significantly since their inception, responding to the growing complexities of energy distribution. Initially designed for basic voltage transformation, modern plug-in transformers now integrate advanced technologies, including smart monitoring systems that enhance operational efficiency. As energy demands have grown, particularly with the rise of renewable energy, the designs have adapted to accommodate higher capacities and improved safety features. This evolution reflects not only technological advancements but also the urgent need for sustainable solutions in the face of climate change and energy transition challenges.
Overall, the plug-in transformer market is at a pivotal point, with B2B buyers needing to navigate a complex landscape that balances technological innovation, sustainability, and supply chain resilience. By staying informed on market dynamics and trends, buyers can position themselves to make strategic procurement decisions that support long-term business success.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plug in transformer
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for plug-in transformers?
When vetting suppliers for plug-in transformers, focus on their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Request third-party certifications such as ISO 9001 or IEC standards to ensure quality and reliability. Evaluate their experience in your specific market and their track record for on-time delivery. Additionally, consider their financial stability and customer reviews to gauge their reputation in the industry. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who have robust after-sales support can also be beneficial for long-term partnerships. -
Can I customize plug-in transformers to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for plug-in transformers to meet specific operational needs. This can include adjustments in voltage ratings, insulation types, and physical dimensions. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and ensure that the supplier can accommodate your requirements. Be aware that customized transformers may have longer lead times, so it’s crucial to factor this into your procurement schedule. Request prototypes or mock-ups if possible to evaluate performance before full-scale production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for plug-in transformers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for plug-in transformers can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the transformers. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units to several dozen. Lead times are currently extended due to global supply chain disruptions, often ranging from 12 to 30 weeks. For customized transformers, lead times can increase further. It’s advisable to communicate your requirements clearly and ask for confirmed timelines to avoid delays in your projects. -
What payment terms are common for international orders of plug-in transformers?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. For large orders, consider negotiating flexible payment options based on milestones. Letter of Credit (LC) is a preferred method for many international transactions, as it provides security for both parties. Ensure that you clarify all payment terms in the contract to prevent misunderstandings and protect your investment. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for plug-in transformers?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications and testing reports from your supplier. Key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 for quality management and relevant IEC standards for electrical equipment. It is also beneficial to conduct factory audits or inspections, either personally or through a third-party service. Additionally, inquire about their testing procedures, such as routine quality checks and acceptance testing, to confirm that the transformers meet your specifications before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing plug-in transformers?
Logistics play a crucial role in the procurement of plug-in transformers. Consider the shipping methods, freight costs, and potential tariffs or duties that may apply to international shipments. Ensure that the supplier can provide proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. It’s also wise to plan for potential delays in customs clearance, especially in countries with stringent import regulations. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling heavy machinery to streamline the process. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers over plug-in transformers?
To handle disputes effectively, first, attempt to resolve issues through direct communication with the supplier. Document all correspondence to maintain a clear record of the discussions. If a resolution cannot be reached, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution mechanisms, which may include mediation or arbitration. It’s advisable to include a jurisdiction clause in your contract to determine where legal disputes will be resolved. Always prioritize maintaining a professional relationship, as the B2B landscape relies on trust and collaboration. -
What are the implications of sourcing plug-in transformers from different regions?
Sourcing plug-in transformers from various regions can have implications for cost, lead time, and compliance with local regulations. For instance, suppliers in Europe may adhere to stricter environmental and safety standards than those in other regions. Additionally, geopolitical factors can influence pricing and availability, particularly in Africa and South America, where infrastructure may vary. Conduct thorough market research to understand regional dynamics and choose suppliers that align with your operational requirements and corporate social responsibility goals.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plug in transformer
In the dynamic landscape of the global transformer market, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse types of transformers, such as power and distribution variants, allows companies to select the most appropriate solutions for their specific infrastructure needs. Given the challenges of rising lead times and escalating costs—exacerbated by supply chain disruptions—buyers must prioritize supplier reliability and quality assurance.
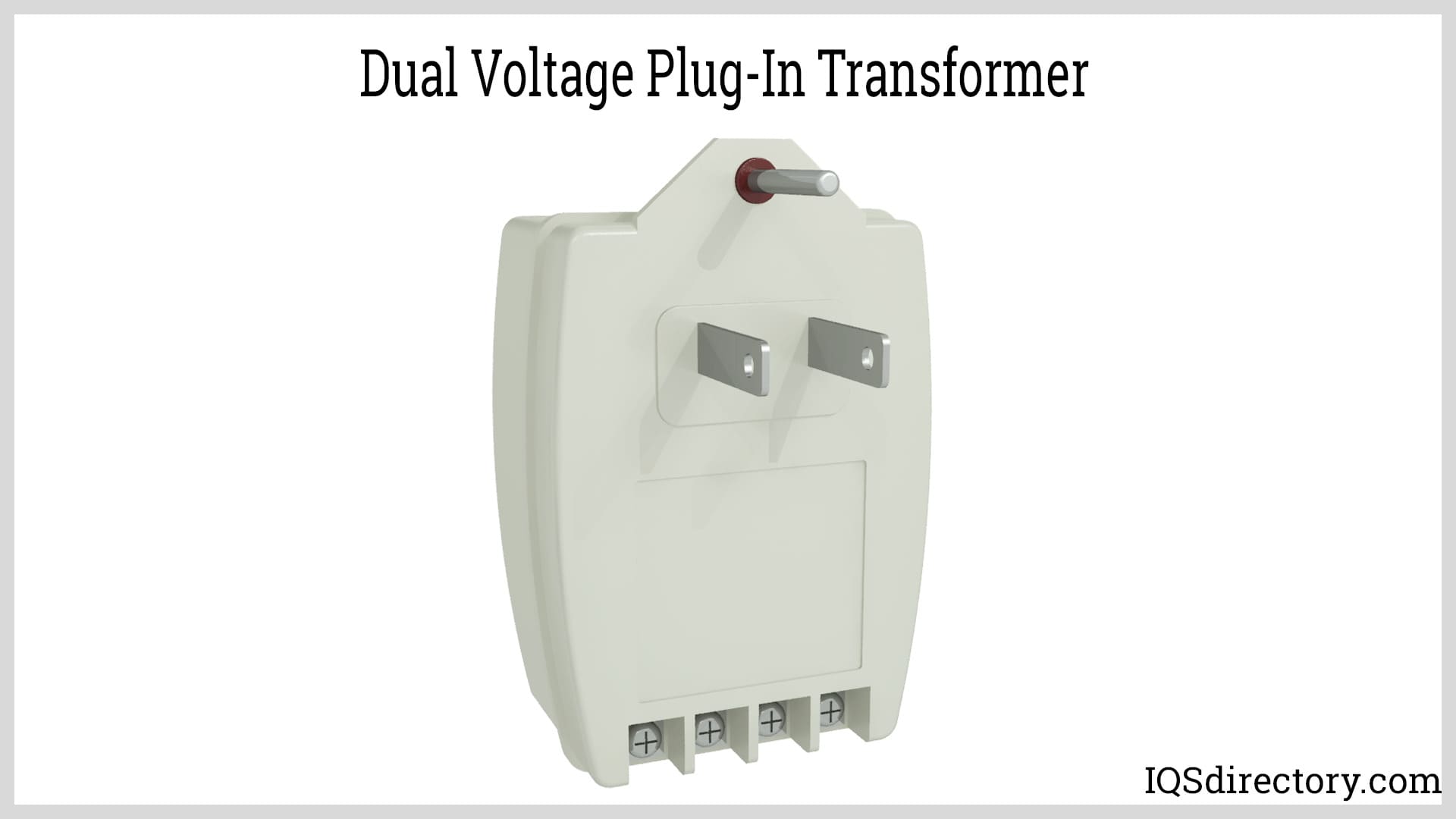
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Moreover, navigating local regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance with sustainability standards are crucial for long-term success. As the energy sector continues to evolve, embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices will not only enhance operational efficiency but also position companies favorably in the marketplace.
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the call to action is clear: invest in thorough supplier assessments, leverage global networks, and remain adaptable to the shifting demands of the industry. By doing so, organizations can secure not just immediate project success but also build resilient supply chains that will thrive in the face of future challenges. The future of energy infrastructure is bright—make the strategic choices today that will empower your business tomorrow.