Master Sourcing Pneumatic Cylinder Components for Enhanced
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pneumatic cylinder components
In today’s competitive landscape, pneumatic cylinder components are indispensable for businesses across diverse industries, from manufacturing to automation. These components are crucial for achieving efficient motion control, ensuring that operations run smoothly with minimal downtime. As B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their production capabilities, understanding the intricacies of pneumatic cylinders becomes essential.
This comprehensive guide serves as an invaluable resource, detailing the various types of pneumatic cylinders, the materials they are made from, and the manufacturing and quality control processes involved. Buyers will gain insights into the different applications of pneumatic cylinders, empowering them to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Furthermore, the guide explores supplier options, cost considerations, and market trends, equipping international buyers with the knowledge required to navigate the global sourcing landscape effectively.
By addressing frequently asked questions and providing actionable strategies, this guide aims to enhance the decision-making process for B2B buyers. Whether you’re in the UK or Kenya, understanding the nuances of pneumatic cylinder components will not only streamline your procurement process but also contribute to long-term cost savings and operational efficiency. Dive in to unlock the potential of pneumatic technology and elevate your business to new heights.
Understanding pneumatic cylinder components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Acting Pneumatic Cylinder | Operates in one direction; uses a spring for return | Packaging, Material Handling | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited motion; less versatile. |
| Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinder | Moves in both directions; uses compressed air for both | Robotics, Automation, Assembly Lines | Pros: Greater versatility, higher efficiency. Cons: More complex, higher maintenance. |
| Compact Pneumatic Cylinder | Space-saving design; high force-to-size ratio | Medical Devices, Small Automation Systems | Pros: Ideal for tight spaces. Cons: Limited stroke length. |
| Rotary Pneumatic Cylinder | Provides rotational motion; suitable for precise positioning | Automotive Manufacturing, Packaging | Pros: Accurate rotation, versatile applications. Cons: Typically more expensive. |
| Magnetic Pneumatic Cylinder | Integrated magnets for position sensing | Automation, Control Systems | Pros: Enhanced precision, easy stroke monitoring. Cons: May require specialized installation. |
Single-Acting Pneumatic Cylinder
Single-acting pneumatic cylinders are designed to operate in one direction, utilizing a mechanical spring to return the piston to its original position. They are ideal for applications such as packaging and material handling where only one-way motion is necessary. When purchasing, consider the operational environment, as these cylinders are often simpler and more cost-effective but lack the versatility of double-acting models.
Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinder
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders can move the piston in both directions, relying on compressed air for both extension and retraction. This type is widely used in robotics, automation, and assembly lines where precise control and efficiency are critical. Buyers should assess their specific application needs, as these cylinders offer greater flexibility but come with increased complexity and maintenance requirements.
Compact Pneumatic Cylinder
Compact pneumatic cylinders are engineered for environments where space is at a premium, delivering a high force-to-size ratio. They are commonly used in medical devices and small automation systems. When considering a compact cylinder, it is crucial to evaluate the required stroke length and operational performance, as their design may limit the range of motion compared to standard cylinders.
Rotary Pneumatic Cylinder
Rotary pneumatic cylinders provide rotational motion instead of linear movement, making them essential for tasks requiring precise positioning, such as in automotive manufacturing and packaging processes. These cylinders offer high accuracy and versatility, but buyers should be prepared for a higher initial investment and potential complexity in integration with existing systems.
Magnetic Pneumatic Cylinder
Magnetic pneumatic cylinders incorporate integrated magnets that help in determining the position of the piston, which is particularly beneficial in automation and control systems. These cylinders excel in applications requiring precise stroke monitoring and positioning accuracy. However, they may necessitate specialized installation and setup, so buyers should factor in these considerations when planning their procurement strategy.
Related Video: Pneumatic Cylinder Working explained (Animation)
Key Industrial Applications of pneumatic cylinder components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pneumatic cylinder components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Increases production efficiency and reduces labor costs | Quality standards, compatibility with existing machinery, and lead times |
| Packaging | Filling, sealing, and labeling machines | Enhances speed and accuracy of packaging processes | Reliability, maintenance support, and adaptability to various packaging types |
| Automotive | Robotic arms for precision part assembly | Improves precision and reduces human error | Precision engineering, customization options, and supplier reliability |
| Aerospace | Material handling and testing systems | Ensures safety and compliance with industry standards | Certifications, technical support, and performance tracking |
| Medical Devices | Actuation in surgical and diagnostic equipment | Guarantees precision and reliability in critical applications | Regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and availability of spare parts |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, pneumatic cylinder components are vital for automating assembly lines. They facilitate the movement of components and products along the production flow, significantly enhancing production efficiency while reducing labor costs. Pneumatic cylinders enable fast and precise movements, which are essential for maintaining high throughput. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers that meet quality standards and offer components compatible with their existing machinery to avoid costly downtimes.
Packaging
Pneumatic cylinders play a crucial role in packaging applications, particularly in filling, sealing, and labeling machines. Their ability to execute rapid and accurate motions ensures that packaging lines operate smoothly, enhancing overall productivity. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing reliable pneumatic components is essential, as it directly impacts the speed and accuracy of packaging processes. Key considerations include the reliability of the components, the availability of maintenance support, and their adaptability to various packaging types.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, pneumatic cylinders are integral to robotic arms used for precision part assembly. These components provide the necessary force and control for tasks requiring high accuracy, thus reducing human error and improving overall quality. International B2B buyers must focus on suppliers that offer precision-engineered products tailored to their specific needs. Customization options and the reliability of the supplier are critical factors to consider to ensure seamless integration into existing production lines.
Aerospace
Pneumatic cylinders are utilized in aerospace for material handling and testing systems, where safety and compliance with strict industry standards are paramount. These components help automate the movement of materials and parts during the manufacturing and testing phases, ensuring that operations are efficient and safe. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that hold relevant certifications and can provide technical support, as well as performance tracking capabilities to monitor the effectiveness of pneumatic systems.
Medical Devices
In the medical devices sector, pneumatic cylinders are essential for actuation in surgical and diagnostic equipment. They ensure precision and reliability in critical applications, which is vital for patient safety and effective medical outcomes. International B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with regulatory standards and provide high-quality components. Additionally, the availability of spare parts and quality assurance processes are crucial factors to consider when sourcing pneumatic cylinder components for medical applications.
Related Video: Pneumatic Cylinder: How Does It Work?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pneumatic cylinder components
When selecting materials for pneumatic cylinder components, it’s critical to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material type. This understanding can significantly influence operational performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in pneumatic cylinder components, tailored for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for various environments. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and pressures around 10 bar, depending on the specific alloy used.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of aluminum include its low weight, which can enhance the efficiency of pneumatic systems, and its resistance to rust and corrosion. However, it can be more expensive than some alternatives and may not be as durable under high-stress conditions, leading to potential deformation over time.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of pneumatic media, including air and non-corrosive gases. Its lightweight nature makes it suitable for applications requiring quick movements, such as in robotics and automation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing aluminum components may involve higher costs due to import tariffs and logistics.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 400°C and pressures exceeding 20 bar, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to wear and tear. However, it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which may not be suitable for all applications, especially where weight is a concern.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is ideal for applications involving corrosive media, such as in the food and beverage industry or chemical processing. Its robustness ensures long-term reliability in challenging environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe, particularly the UK, should consider compliance with EU regulations regarding material safety. In the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, stainless steel’s thermal properties are advantageous.
Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often a mix of polymers and fibers, offer unique properties such as lightweight and high strength. They can typically handle moderate temperatures (up to 80°C) and pressures, depending on the specific formulation.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of composites is their low weight and resistance to corrosion. However, they can be more complex to manufacture and may not withstand high-pressure applications as effectively as metals.
Impact on Application:
Composites are suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace or automotive sectors. Their resistance to various chemicals also makes them versatile for different media.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for composite materials across regions. In Africa and South America, local suppliers may have limited offerings, necessitating imports that could increase costs.
Brass
Key Properties:
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its good machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 200°C and pressures around 15 bar.
Pros & Cons:
Brass offers excellent durability and is relatively easy to work with, making it a popular choice for fittings and connectors. However, it can be susceptible to dezincification in certain environments, which may lead to premature failure.
Impact on Application:
Brass is often used in pneumatic fittings and components that require precise machining. Its compatibility with various gases and fluids makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of brass components in their region and any associated import duties. Compliance with standards such as JIS in Japan or ASTM in the US is also essential for ensuring quality.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for pneumatic cylinder components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight cylinders in robotics and automation | Excellent corrosion resistance | Can deform under high stress | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty applications in harsh environments | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Composite | Aerospace and automotive lightweight components | Low weight and corrosion resistance | Complex to manufacture | Medium |
| Brass | Fittings and connectors in pneumatic systems | Good machinability | Susceptible to dezincification | Medium |
This guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for pneumatic cylinder components, ensuring informed decisions that align with operational requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pneumatic cylinder components
Pneumatic cylinders are essential components in various industrial applications, and understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source these components effectively. This section outlines the typical manufacturing processes and quality control measures that ensure pneumatic cylinder components meet high standards of performance and reliability.
Manufacturing Processes for Pneumatic Cylinder Components
The production of pneumatic cylinder components involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets required specifications and performance standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves selecting and preparing raw materials, typically aluminum, steel, or composite materials, depending on the application requirements. The material choice impacts the durability, weight, and corrosion resistance of the finished product.
- Material Inspection: Suppliers should conduct initial inspections to verify that the raw materials meet specified standards. This includes checking for impurities, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties.
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are then cut and shaped into the required dimensions using techniques such as laser cutting, water jet cutting, or CNC machining.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials undergo various forming processes to create the components of the pneumatic cylinder.
- Machining: Precision machining is employed to create features such as mounting holes, grooves, and threads. This process often uses CNC lathes and mills to achieve the required tolerances.
- Extrusion: For certain components, such as barrels, extrusion processes may be used to create long, continuous shapes. This is particularly common with aluminum components.
- Welding and Joining: Components may be welded or assembled using fasteners. Techniques such as TIG welding or MIG welding are common for joining metal parts, ensuring strong structural integrity.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final pneumatic cylinder unit.
- Component Integration: This involves fitting together the barrel, piston, rod, and end caps. Careful alignment is crucial to ensure the cylinder operates smoothly.
- Sealing and Lubrication: Seals and O-rings are installed to prevent air leaks. Proper lubrication is applied to moving parts to reduce friction and wear during operation.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the appearance and performance of the pneumatic cylinder components.
- Surface Treatment: Common surface treatments include anodizing, powder coating, or painting. These treatments improve corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Final Inspection: Before shipping, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure all components meet design specifications and quality standards.
Quality Assurance Practices
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of pneumatic cylinder components. Implementing robust QC measures ensures that products are reliable and meet international standards.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with key international standards that govern the quality of pneumatic cylinder components:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) standards are crucial for pneumatic cylinders used in oil and gas applications.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is typically conducted at several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing processes help identify and rectify issues early. This includes monitoring machining tolerances and assembly alignment.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to verify functionality, performance, and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are essential for validating the quality and performance of pneumatic cylinder components:
- Pressure Testing: This verifies that the cylinder can withstand operational pressures without leaking.
- Functional Testing: Cylinders are tested for operational performance, including stroke length, speed, and responsiveness.
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers, manufacturers ensure that all components meet specified dimensions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures implemented by their suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including inspection and testing results, helps buyers assess the reliability of the supplier’s products.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of verification, ensuring that products meet specified standards before they are shipped.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital:
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural differences in business practices that may affect quality control processes. Establishing clear communication channels can mitigate misunderstandings.
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations that may affect the import of pneumatic cylinder components, ensuring compliance with both international and local standards.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Assess the entire supply chain for potential risks that could impact product quality. This includes evaluating transportation and storage conditions that may affect component integrity.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for pneumatic cylinder components, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Amazing Production Process with Modern Machines and Skilful Workers
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pneumatic cylinder components Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of pneumatic cylinder components is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize procurement strategies. This analysis focuses on key cost components, pricing influencers, and actionable tips for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Pneumatic Cylinder Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in pneumatic cylinder manufacturing include aluminum, stainless steel, and various polymers. The choice of material significantly impacts the overall cost, with high-grade materials typically commanding a premium due to their enhanced durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturing process. Automated manufacturing can reduce labor costs, but skilled labor is essential for quality assembly and maintenance. Buyers should consider the labor landscape in the supplier’s location when assessing total costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility costs, and equipment maintenance. Overhead costs are often factored into the pricing of components, making it essential for buyers to understand the operational efficiency of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom components. These costs are usually amortized over the production run, affecting pricing based on order volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes ensure product reliability and performance. Suppliers with robust QC measures may charge higher prices, but this investment often translates to lower failure rates and reduced operational disruptions for buyers.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance from the supplier, chosen shipping methods, and Incoterms. Buyers should evaluate these factors as they significantly influence the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin based on their operational costs and market conditions. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
Pricing Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing. Larger orders typically yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized components often incur higher costs due to additional design and manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define requirements to avoid unforeseen expenses.
-
Materials: The specific materials requested can influence pricing significantly. Specialty materials or certifications (like ISO or ATEX) can lead to increased costs, but they may be necessary for certain applications.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality standards or certifications can lead to elevated prices. However, investing in quality may reduce long-term costs associated with maintenance and replacements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but offer better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for calculating total landed costs. Buyers should clarify responsibilities for shipping and insurance to avoid unexpected charges.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
-
Negotiate: Leverage volume purchasing and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and downtime costs.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to benchmark prices and identify competitive suppliers. Understanding market rates can strengthen negotiation positions.
-
Assess Logistics: Consider suppliers’ locations and logistics capabilities. Proximity can reduce shipping times and costs, while efficient logistics can streamline operations.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences, especially when dealing with suppliers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Currency fluctuations and local economic conditions can influence pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential pneumatic cylinder components Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘pneumatic cylinder components’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pneumatic cylinder components
In the realm of pneumatic cylinders, understanding essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right components but also facilitates smoother negotiations and transactions across diverse markets.
Critical Technical Specifications
-
Material Grade
The material used in pneumatic cylinder components, such as aluminum, stainless steel, or composite materials, affects durability, weight, and corrosion resistance. For example, stainless steel is preferred in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs. Understanding material grades helps buyers choose components that meet their specific operational environments. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions of the pneumatic cylinder components. This specification is vital because tight tolerances can enhance the performance and reliability of pneumatic systems. In industries requiring high precision, such as automotive or aerospace, ensuring that components meet specified tolerances can prevent system failures and increase overall efficiency. -
Stroke Length
The stroke length determines how far the piston can move within the cylinder. This is a critical factor for B2B buyers as it directly impacts the application of the cylinder in various processes. For instance, longer strokes may be necessary for tasks that require significant movement, while shorter strokes may suffice for compact applications. Understanding stroke length aids in selecting the right cylinder for specific applications. -
Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure a pneumatic cylinder can handle. It is essential for ensuring that the cylinder operates safely and efficiently within its intended application. Buyers should match the pressure rating with their operational requirements to avoid equipment failures and safety hazards. -
Operating Temperature Range
The temperature range specifies the conditions under which the pneumatic cylinder can operate effectively. This property is particularly important for industries in extreme climates or those involving heat-generating processes. Selecting a cylinder that can withstand the expected temperature range helps maintain performance and reliability.
Common Trade Terminology
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For B2B buyers, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM is crucial, as it often indicates the quality and compatibility of the components with existing systems.
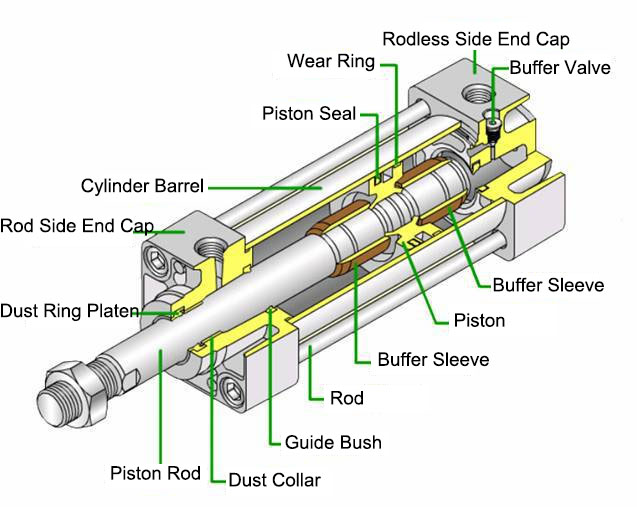
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost calculations. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively and avoid excess stock.
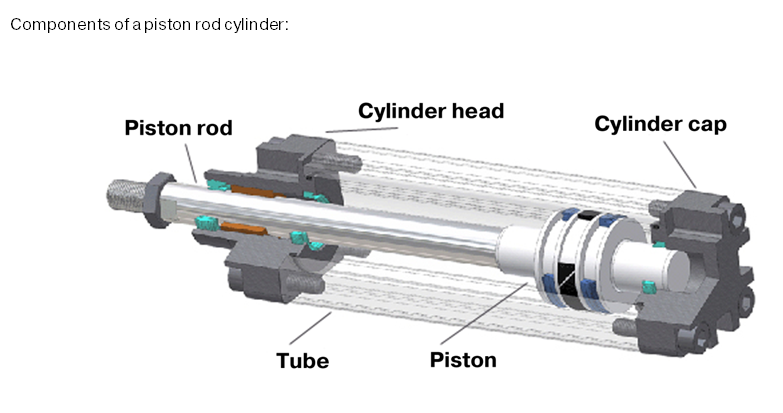
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is essential for comparing costs and negotiating terms, making it a critical step in procurement for B2B buyers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications, ensuring smoother cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. For international buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and managing inventory, particularly in industries where timely delivery is essential for maintaining operational efficiency. -
Cylinder Type
This term encompasses the different configurations of pneumatic cylinders, such as single-acting and double-acting cylinders. Recognizing the types of cylinders available helps buyers select the appropriate solution for their specific applications, enhancing system efficiency and performance.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential specifications and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their operations and ensure successful procurement of pneumatic cylinder components.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the pneumatic cylinder components Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global pneumatic cylinder components market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and packaging. As businesses seek to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs, pneumatic cylinders’ reliability and performance make them a preferred choice for motion control solutions. Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0 and IoT are reshaping sourcing trends, allowing for more efficient inventory management and predictive maintenance, which are particularly beneficial for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key trends influencing the market include the shift towards customization of pneumatic components to meet specific operational needs, as well as the growing importance of integrated systems that combine pneumatic cylinders with sensors and control units. Buyers from diverse regions should also consider the impact of geopolitical factors, such as trade policies and tariffs, which can affect sourcing strategies. Furthermore, suppliers are increasingly focusing on developing lightweight and compact designs that offer high performance in limited spaces, catering to industries with stringent space constraints.
As B2B buyers navigate these market dynamics, understanding regional demand variations and aligning sourcing strategies with technological advancements will be crucial. This approach not only fosters competitive advantages but also enhances overall operational performance.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal aspect of procurement strategies in the pneumatic cylinder components sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint through energy-efficient production methods and responsible sourcing of materials.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, particularly in regions where labor practices may be scrutinized. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers who adhere to international labor standards and promote fair working conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable components and biodegradable lubricants, into pneumatic cylinder designs can further enhance sustainability. B2B buyers should engage with suppliers who are innovating in this space, as this not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Brief Evolution/History
The pneumatic cylinder has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, these devices were primarily mechanical and limited in functionality. However, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of more sophisticated pneumatic systems, characterized by increased efficiency and versatility.
The introduction of automation in the late 20th century further propelled the adoption of pneumatic cylinders across various industries. Today, these components are integral to many automated processes, providing reliable and efficient motion control. As technology continues to advance, the future of pneumatic cylinders promises even greater innovation, focusing on enhanced performance, sustainability, and integration with digital technologies.
B2B buyers are advised to stay informed about these historical trends, as understanding the evolution of pneumatic technologies can provide valuable insights into future developments and potential sourcing opportunities.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pneumatic cylinder components
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of pneumatic cylinder components?
Vetting suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability. Start by researching the supplier’s reputation through industry reviews and customer testimonials. Verify certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, request samples to assess product quality and performance. Consider suppliers with a proven track record in international trade, especially those familiar with import regulations and logistics specific to your region, whether it be Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. -
Are customization options available for pneumatic cylinder components?
Many suppliers offer customization to meet specific operational requirements. This can include adjustments in size, stroke length, material, or even specialized features like cushioning or mounting styles. When considering customization, ensure you communicate your exact needs clearly and confirm the supplier’s capability to meet these specifications. This not only enhances performance but can also lead to more efficient operations in your applications. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for pneumatic cylinders?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 100 units for standard products, while custom components may require higher orders. Lead times also depend on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity; typical lead times range from 4 to 12 weeks. Always confirm these details upfront to align your purchasing strategy with your production schedule and avoid potential delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly based on the supplier and your negotiation. Common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal, with terms often requiring a deposit (20-30%) upfront and the balance upon shipment. It’s advisable to establish clear payment conditions in the contract, including currency exchange rates and payment timelines, to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for pneumatic components?
Ensuring product quality starts with selecting suppliers that provide comprehensive documentation and certifications. Request certificates of conformity, test reports, and quality assurance processes in place. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures, including testing protocols for performance and durability. Regular audits and site visits can further help in maintaining quality standards throughout the supply chain. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing pneumatic cylinders?
Logistics play a vital role in international sourcing. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance processes, and potential tariffs. Work with logistics providers experienced in your target markets to streamline the import process. Additionally, ensure your supplier can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including commercial invoices and packing lists, to avoid delays. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding pneumatic cylinder orders?
Disputes can arise from quality issues, delivery delays, or contract misunderstandings. It is essential to have a clear contract that outlines terms, responsibilities, and dispute resolution processes. If a dispute occurs, maintain open communication with the supplier to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration, especially if the supplier is located internationally. Document all correspondence and agreements to support your case. -
What are the key factors to consider when assessing the total cost of ownership for pneumatic cylinders?
The total cost of ownership (TCO) encompasses not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. Evaluate the expected lifespan of the cylinders, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements. Choosing high-quality components may result in higher upfront costs but can lead to significant savings over time due to reduced failure rates and maintenance needs. Always conduct a thorough cost analysis when sourcing to make informed purchasing decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pneumatic cylinder components
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of pneumatic cylinder components is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding the various types of pneumatic cylinders—such as single-acting and double-acting—along with their specific applications can significantly impact production capabilities. Prioritizing quality, supplier reliability, and compliance with international standards will ensure that businesses not only meet their operational needs but also position themselves for growth in competitive markets.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate their procurement strategies, leveraging local and global suppliers can provide a balanced approach to sourcing. Engaging with suppliers who offer tailored solutions and technical support can further optimize performance and drive innovation.
Looking ahead, the demand for pneumatic cylinders is set to grow, particularly in automation-heavy industries. B2B buyers should stay informed about advancements in technology and sustainability practices within the pneumatic sector. By embracing strategic sourcing practices today, businesses can secure a competitive advantage and prepare for the evolving landscape of industrial automation. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategy and explore new partnerships that align with your operational goals.