Master Sourcing Screw Conveyor Parts: Your Comprehensive
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for screw conveyor parts
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, screw conveyor parts stand as pivotal components in the efficient handling of bulk materials across various industries. For B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of these parts is essential for optimizing operations and ensuring seamless supply chain management. This guide delves into the critical role that screw conveyor parts play, from enhancing productivity to minimizing downtime through timely replacements and maintenance.
This comprehensive resource will cover an array of topics, including the different types of screw conveyor parts, the materials used in their manufacture, and the stringent quality control measures that ensure reliability and performance. It also provides insights into the leading suppliers in the market, a breakdown of cost factors, and an analysis of current market trends that can influence purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will address frequently asked questions to clarify common uncertainties faced by international buyers.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge and tools needed for informed sourcing, this guide empowers businesses to make strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency and drive profitability. Whether you are looking to procure parts for new installations or replace existing components, this guide serves as your go-to resource for navigating the global market for screw conveyor parts.
Understanding screw conveyor parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shafted Screw Conveyors | Enclosed design with a central shaft; ideal for bulk materials | Agriculture, Food Processing, Mining | Pros: High efficiency, versatile for various materials. Cons: Potential for wear on the shaft; requires regular maintenance. |
| Shaftless Screw Conveyors | No central shaft; uses a spiral that moves materials along a trough | Waste Management, Recycling, Chemical Processing | Pros: Reduced wear, less maintenance; suitable for sticky materials. Cons: Limited to certain types of materials; can be less efficient for some applications. |
| Vertical Screw Conveyors | Designed for vertical lifting; compact footprint | Food Industry, Powder Handling | Pros: Space-saving, effective at elevating materials. Cons: Higher energy consumption; may require more frequent maintenance. |
| Screw Feeders | Controls material feed rates; often integrated with hoppers | Plastics, Food, Chemical Industries | Pros: Precise control over material flow; customizable designs. Cons: Can be more expensive due to additional features. |
| Screw Conveyor Kits | Pre-packaged components for easy assembly; customizable | Startups, Small Scale Operations | Pros: Cost-effective, quick setup; flexibility in design. Cons: May require additional parts for specific needs; assembly time can vary. |
Shafted Screw Conveyors
Shafted screw conveyors are the most common type, featuring a central shaft that supports a helical screw. This design is particularly effective for moving bulk materials in various industries such as agriculture and mining. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the material compatibility, as certain abrasive substances can cause wear on the shaft. Additionally, regular maintenance is necessary to prolong the lifespan of the components.
Shaftless Screw Conveyors
Shaftless screw conveyors utilize a spiral design without a central shaft, allowing for smoother material handling, especially for sticky or viscous substances. They are commonly used in waste management and chemical processing applications. Buyers should consider the specific material characteristics, as these conveyors may not be suitable for all types of bulk materials. While they require less maintenance, their efficiency can be affected by the type of material being conveyed.
Vertical Screw Conveyors
Vertical screw conveyors are engineered for lifting materials vertically, making them ideal for applications where space is limited, such as in food processing. Their compact design allows for efficient use of floor space. Buyers should be aware that while these conveyors save space, they may consume more energy and require more frequent maintenance compared to horizontal models. Evaluating the lifting height and material type is crucial before purchasing.
Screw Feeders
Screw feeders are specialized conveyors designed to control the flow rate of materials from hoppers into processing equipment. They are widely used in the plastics and food industries. Buyers should assess their specific flow control needs, as these feeders can be customized for various applications. The initial cost may be higher due to their advanced features, but the precise control can lead to significant efficiency gains.
Screw Conveyor Kits
Screw conveyor kits provide a convenient solution for businesses looking to assemble their own conveyors. These kits come with pre-packaged components that can be customized to suit specific needs. They are particularly beneficial for startups and small-scale operations that require flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should consider the total cost of additional parts and assembly time, as these factors can influence the overall project timeline and budget.
Related Video: Screw Conveyor vs. Screw Feeder
Key Industrial Applications of screw conveyor parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of screw conveyor parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Transporting grains and feed | Efficient bulk handling reduces labor costs and waste | Ensure corrosion-resistant materials for durability |
| Food Processing | Moving raw ingredients and finished products | Maintains hygiene standards and minimizes contamination | Compliance with food safety regulations and certifications |
| Mining | Conveying minerals and aggregates | Streamlined operations enhance productivity and reduce delays | Need for heavy-duty components to withstand harsh conditions |
| Waste Management | Handling recyclables and waste materials | Improves sorting efficiency and reduces landfill costs | Consider modular designs for easy maintenance and adaptability |
| Chemical Processing | Transferring powdered and granulated chemicals | Prevents product degradation and ensures consistent flow | Material compatibility with chemicals to avoid reactions |
Agriculture
In the agriculture sector, screw conveyor parts are essential for transporting grains and animal feed. These systems facilitate efficient bulk handling, which significantly reduces labor costs and minimizes waste during transit. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable and corrosion-resistant materials is crucial to withstand the environmental conditions and ensure longevity. Additionally, understanding local agricultural practices can help in customizing solutions that align with specific regional needs.
Food Processing
In food processing, screw conveyors play a vital role in moving raw ingredients and finished products through various stages of production. This application ensures that hygiene standards are maintained, minimizing the risk of contamination. International buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers that comply with stringent food safety regulations and certifications. The right sourcing strategy can help in selecting parts that not only meet hygiene requirements but also enhance operational efficiency.
Mining
The mining industry relies heavily on screw conveyors for the transportation of minerals and aggregates. These systems streamline operations, enhancing productivity while reducing delays in the supply chain. Buyers must consider the need for heavy-duty components that can withstand harsh conditions, including abrasive materials and extreme weather. Sourcing from manufacturers with experience in mining applications can provide insights into durable designs that ensure reliability in demanding environments.
Waste Management
Screw conveyor parts are critical in waste management for handling recyclables and waste materials efficiently. These systems improve sorting efficiency and can significantly reduce landfill costs by optimizing the recycling process. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, considering modular designs that allow for easy maintenance and adaptability can be beneficial. This flexibility can lead to better resource management and operational scalability as waste management needs evolve.
Chemical Processing
In the chemical processing sector, screw conveyors are used to transfer powdered and granulated chemicals safely. This application is crucial for preventing product degradation and ensuring a consistent flow of materials. Buyers should pay close attention to material compatibility to avoid any adverse reactions that could compromise product integrity. Sourcing components that meet industry standards will help in ensuring the safety and efficiency of chemical handling processes, especially for international buyers in regions with varying regulatory environments.
Related Video: screw conveyor part and motion in solidworks
Strategic Material Selection Guide for screw conveyor parts
When selecting materials for screw conveyor parts, international B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the operating environment, compatibility with transported materials, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in screw conveyor construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, with a high tensile strength that can withstand heavy loads. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle moderate pressure. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly coated or treated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can be a significant drawback, particularly in humid or corrosive environments. Regular maintenance and protective coatings are necessary to prolong its lifespan.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for transporting dry, non-corrosive materials. It is less suitable for applications involving wet or corrosive substances, where alternative materials may be required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN when sourcing carbon steel parts. In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, consider additional protective treatments.
Stainless Steel (304 and 316)
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications involving moisture or corrosive materials. It can handle temperatures up to 1500°F (815°C) and is suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which reduces maintenance costs over time. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel, which can be a limiting factor for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical handling due to its hygienic properties and resistance to contamination.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must verify the grade of stainless steel to ensure it meets specific industry standards. Compliance with food safety regulations is critical in the food and pharmaceutical industries, especially in regions with stringent health standards.
Plastic (Polyethylene and PVC)
Key Properties: Plastic materials such as polyethylene and PVC are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They can typically withstand temperatures up to 180°F (82°C) and are not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its low weight and resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for various applications. However, plastics may not be as durable as metals and can be prone to wear over time, particularly under mechanical stress.
Impact on Application: Plastic screw conveyor parts are ideal for transporting corrosive or abrasive materials, particularly in chemical processing and waste management applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials comply with local environmental regulations and standards. In regions with high temperatures, it’s essential to verify the thermal stability of the plastic being used.
Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steel combines carbon steel with other elements to enhance specific properties, such as strength and wear resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of alloy steel is its enhanced durability and performance under extreme conditions. However, it is typically more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is suitable for heavy-duty applications, including mining and bulk material handling, where high strength and resistance to wear are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy compositions and their compliance with international standards. The cost implications of sourcing alloy steel should also be factored into budgeting.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for screw conveyor parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General bulk material handling | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel 304/316 | Food processing, chemical handling | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to carbon steel | High |
| Plastic (PE/PVC) | Chemical processing, waste management | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under mechanical stress | Med |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy-duty applications (mining, etc.) | Enhanced strength and wear resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for screw conveyor parts
Manufacturing Processes for Screw Conveyor Parts
The manufacturing of screw conveyor parts is a multi-stage process that ensures durability, efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must understand these processes to make informed purchasing decisions.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Raw Materials: The primary materials used are carbon steel, stainless steel (304 and 316), and sometimes specialized alloys depending on the application. The choice of material impacts corrosion resistance, strength, and overall performance.
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into required dimensions using techniques like laser cutting or CNC machining. This precision ensures that the parts fit together seamlessly during assembly. -
Forming
– Shaping Processes: Forming techniques such as bending, rolling, and welding are employed to create the various components of screw conveyors. For instance, troughs are typically formed into a U-shape to facilitate material flow.
– Welding and Joining: Automated welding processes, including MIG and TIG welding, are commonly used to ensure robust joints that can withstand operational stresses. -
Assembly
– Component Assembly: Parts such as screws, troughs, and flanges are assembled using standardized bolts and fittings. This modular approach allows for easy replacement and maintenance.
– Alignment and Adjustment: Proper alignment of components is critical to minimize wear and ensure smooth operation. This step often involves precise measurements and adjustments. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Finishing processes such as sandblasting, painting, or powder coating enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetics. Depending on the application, additional treatments like galvanization may be applied.
– Quality Checks: Final inspections are conducted to ensure that each part meets specified tolerances and quality standards before shipment.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of screw conveyor parts to ensure reliability and safety. B2B buyers should be aware of the following QA processes and standards.
International Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: This is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems. Compliance indicates that the manufacturer has a systematic approach to managing their processes and ensuring quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers supplying to the oil and gas industry, adherence to API standards ensures that products meet specific operational criteria.
QC Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, quality checks are conducted at various stages. This includes monitoring weld integrity, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a thorough inspection is performed to verify that all components meet design specifications and quality standards.
Common Testing Methods
- Dimensional Testing: Measuring components against specified tolerances using calipers and gauges.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection ensure structural integrity without damaging the parts.
- Performance Testing: Some parts may undergo operational testing to simulate actual conditions, ensuring they function correctly within a screw conveyor system.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those in diverse markets like Africa and South America, verifying supplier quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable insights:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This includes reviewing their QA documentation, process flows, and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for quality assurance reports, including test results and certifications. These documents provide transparency and assurance of quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an additional layer of verification. These agencies can conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing process and product quality.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may face unique challenges related to quality control:
- Regulatory Differences: Each region may have different regulations regarding manufacturing and safety standards. Understanding these nuances is essential for compliance and ensuring product reliability.
- Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication with suppliers about quality expectations is vital. Buyers should be clear about their requirements and ensure that suppliers understand international quality standards.
- Logistical Considerations: Transporting parts internationally can introduce risks such as damage or delays. Ensuring that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping processes can mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for screw conveyor parts equips international B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with a robust quality assurance framework, buyers can ensure they procure reliable and high-quality components for their operations.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for screw conveyor parts Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of screw conveyor parts is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A comprehensive analysis reveals several cost components and influencers that can help buyers make informed decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly affects the pricing of screw conveyor parts. Common materials include carbon steel and stainless steel. Prices can fluctuate based on global commodity markets, impacting overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturing process. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America or Africa, manufacturers may offer competitive pricing. However, specialized labor for high-quality production can increase costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient operations can lower overhead, contributing to competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost but is necessary for specific parts. Buyers should consider this when evaluating quotes, especially for customized or complex components.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to the overall cost. Certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may also increase expenses but can enhance product value and buyer confidence.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs play a crucial role in total expenses. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties must be factored into the cost structure, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers include a profit margin that reflects their operational risks and market positioning. Understanding the industry standard margins can aid buyers in negotiation.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often result in lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-designed parts typically cost more due to the additional engineering and production processes involved. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials and certifications can lead to increased prices but may also result in lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan, impacting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but offer assurance in quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They determine who bears the costs and risks during shipping, which can significantly affect overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing. Being informed about the cost structure allows buyers to negotiate more effectively. Discussing bulk purchase discounts or long-term contracts can yield better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, operational efficiency, and longevity of the parts.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and regional pricing strategies that may affect overall costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these challenges.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Prices can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. It is essential for buyers to request detailed quotes that reflect their specific requirements and to stay updated on market trends to ensure they receive fair pricing.
By understanding the intricacies of cost components and pricing influencers, B2B buyers can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Spotlight on Potential screw conveyor parts Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘screw conveyor parts’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for screw conveyor parts
When navigating the procurement of screw conveyor parts, understanding the essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for informed decision-making. Below are the key specifications and terms that international B2B buyers should be familiar with to ensure optimal purchasing choices.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of materials based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. Common materials for screw conveyor parts include carbon steel, stainless steel (like 304 and 316), and specialty alloys.
– B2B Importance: The material grade influences durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Buyers should select materials that align with the operational environment (e.g., food processing requires stainless steel for hygiene). -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, such as length, diameter, or thickness. Tolerances are often specified in millimeters or inches.
– B2B Importance: Precise tolerances ensure parts fit together correctly, reducing wear and maintenance costs. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to equipment failure, impacting productivity. -
Screw Diameter
– Definition: The diameter of the screw flight, which directly affects the volume of material that can be transported.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the required screw diameter is essential for matching the conveyor’s capacity to the application needs. Larger diameters can move more material but may require more power. -
Flight Thickness
– Definition: The thickness of the screw flight, which can vary depending on the application.
– B2B Importance: Thicker flights are more durable and suited for heavy-duty applications, while thinner flights may be adequate for lighter materials. This affects the overall lifespan and maintenance frequency of the conveyor.
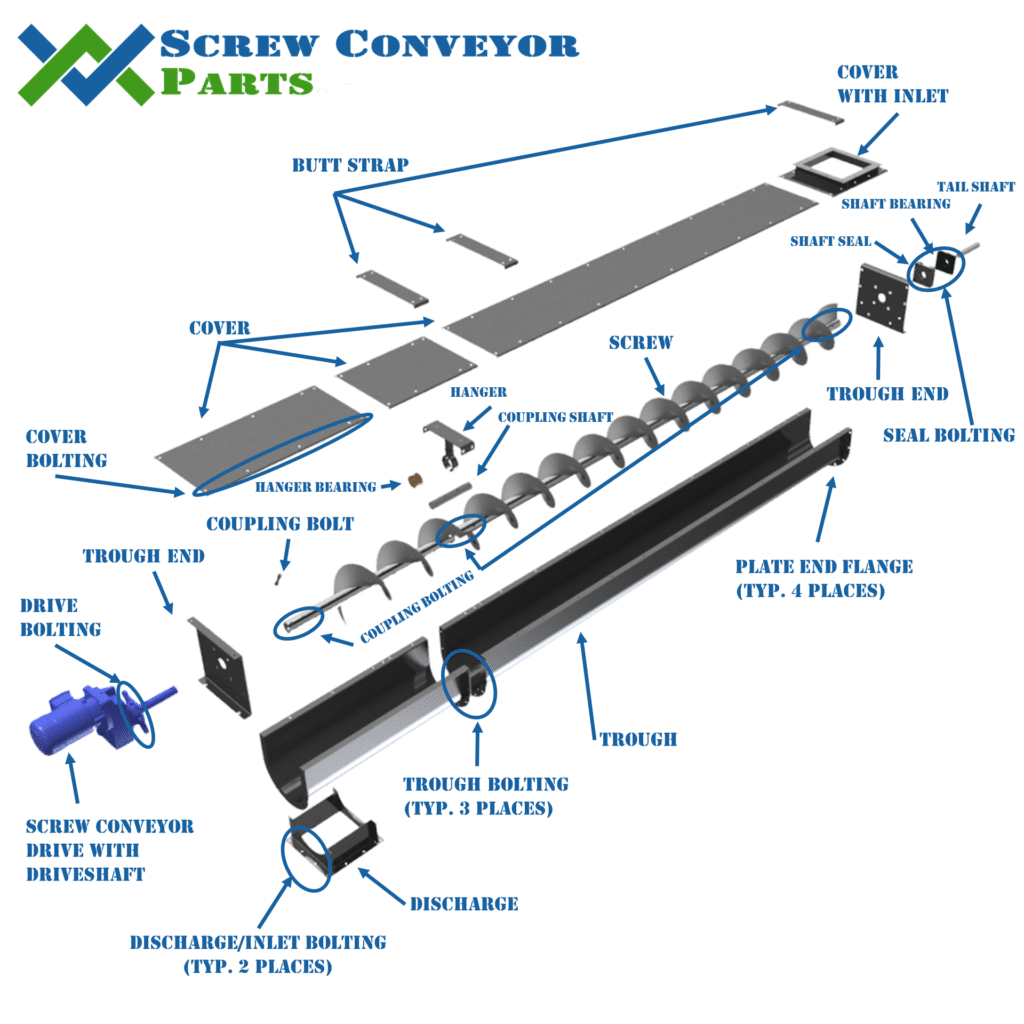
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Length of the Conveyor
– Definition: The total length of the screw conveyor from the inlet to the discharge point.
– B2B Importance: The length determines the overall footprint of the equipment and its capacity. Buyers must consider site space and the intended operational flow when selecting lengths. -
Drive Type
– Definition: The mechanism used to power the screw conveyor, which can include electric motors or hydraulic systems.
– B2B Importance: The choice of drive type affects energy consumption and efficiency. Understanding the operational requirements will help buyers select the most suitable drive system.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Importance: Understanding OEM specifications ensures compatibility and quality, as these parts are designed to fit specific equipment models. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Importance: Buyers should be aware of MOQ to avoid excess inventory or increased costs. Negotiating MOQs can lead to better pricing and supply chain efficiency. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specified products.
– B2B Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare multiple suppliers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they get the best value for their investments. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of standardized trade terms used in international contracts to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– B2B Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is critical for budgeting and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the lead time is essential for project planning and inventory management. Longer lead times can affect production schedules and require proactive supply chain management. -
Warranty
– Definition: A guarantee provided by the supplier regarding the quality and durability of the product.
– B2B Importance: A solid warranty can protect buyers against defects and unexpected failures, providing peace of mind and potential cost savings in repairs or replacements.
In summary, grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies can significantly enhance the decision-making process for international B2B buyers in the screw conveyor parts market. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right components but also in negotiating favorable terms and ensuring operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the screw conveyor parts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The screw conveyor parts sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient bulk material handling across various industries, including agriculture, mining, and food processing. Global market dynamics are influenced by several key factors, such as the rise of automation, the need for cost-effective solutions, and advancements in material technologies. International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note that the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and AI, is enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities in conveyor systems.
Emerging trends include a shift toward standardization of components, which simplifies sourcing and reduces lead times. Buyers can benefit from leveraging CEMA (Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association) standardized parts, ensuring compatibility and ease of replacement. Additionally, the growing emphasis on customization allows suppliers to offer tailored solutions that meet specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and minimizing downtime.
Another significant trend is the focus on localization in sourcing strategies. As supply chains have been disrupted by global events, many companies are seeking to source parts closer to their operations. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local manufacturers can provide quicker turnaround times and potentially lower shipping costs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the decision-making process for B2B buyers in the screw conveyor parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as companies recognize the importance of transparent supply chains. Buyers should look for suppliers that provide documentation of their sourcing practices and certifications that affirm their commitment to ethical labor standards and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability and quality.
Furthermore, the adoption of “green” materials, such as biodegradable plastics and sustainably sourced metals, is becoming a pivotal consideration. Buyers should engage with suppliers that offer products made from these materials, as this not only contributes to environmental conservation but can also enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of screw conveyor technology dates back to ancient times, with the earliest designs attributed to Archimedes in the 3rd century BC. However, modern screw conveyors began to take shape in the early 20th century, primarily as a response to the burgeoning industrial sector. The introduction of standardized parts in the mid-20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for greater compatibility and ease of maintenance.
As industries evolved, so too did the designs and materials used in screw conveyor parts. The transition from basic carbon steel to advanced alloys and stainless steel has significantly improved durability and resistance to corrosion. Today, screw conveyors are integral to automated systems, reflecting the ongoing technological advancements and the increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions in a globalized economy. International B2B buyers can benefit from understanding this evolution to make informed purchasing decisions that align with current and future market needs.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of screw conveyor parts
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for screw conveyor parts?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, their reputation, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region, to gauge reliability. Verify their manufacturing capabilities and ensure they adhere to international quality standards such as ISO certifications. Additionally, assess their responsiveness to inquiries and their willingness to provide technical support. A supplier’s ability to meet your specific needs, including customization options, can also indicate their suitability. -
Can screw conveyor parts be customized to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for screw conveyor parts to cater to specific operational requirements. This may include variations in size, materials, and design features. When requesting custom parts, provide detailed specifications and any relevant operational data to ensure compatibility. Be prepared for potential longer lead times associated with custom manufacturing. Discussing your needs upfront with suppliers can facilitate a smoother process and better end results. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for screw conveyor parts, and how does it affect pricing?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for screw conveyor parts can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from a few units to several hundred. Smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs due to setup fees and shipping expenses. For international buyers, consider consolidating orders to meet MOQs, which can lead to cost savings on shipping and bulk pricing. Always clarify MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs and ensure that your purchasing plans align with the supplier’s policies. -
What are standard lead times for sourcing screw conveyor parts internationally?
Lead times for screw conveyor parts can vary based on several factors, including the supplier’s location, the complexity of the order, and the shipping method chosen. Generally, expect lead times of 2-6 weeks for standard parts, while custom orders may take longer. International shipping can add additional time, particularly if customs clearance is required. Communicate with your supplier to obtain accurate timelines and plan your procurement accordingly to minimize operational disruptions. -
How can I ensure the quality of screw conveyor parts I purchase?
To ensure quality, request documentation such as quality assurance (QA) certifications, material test reports, and compliance with industry standards like CEMA (Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association). Many reputable suppliers will provide these documents upon request. Additionally, consider conducting an on-site visit to the supplier’s manufacturing facility if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify quality before shipment. Establishing a quality control agreement can also help manage expectations and standards. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international transactions?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region. Common arrangements include advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. For larger orders, negotiating favorable terms such as a partial upfront payment followed by payment upon shipment can help manage cash flow. Be mindful of currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees when dealing with international suppliers. Always document payment terms clearly in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing screw conveyor parts?
Logistics is a critical aspect of sourcing screw conveyor parts internationally. Assess shipping options, including air freight for speed and sea freight for cost efficiency. Understand the implications of customs duties and taxes on your final costs. Collaborate with your supplier to determine the best shipping method and ensure proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, verify that the supplier has experience handling international shipments to facilitate smoother logistics management. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers over screw conveyor parts?
To resolve disputes effectively, maintain clear communication with your supplier from the outset. Document all agreements and interactions to create a clear record. If issues arise, begin by discussing them directly with your supplier, focusing on finding a mutual solution. If necessary, escalate the matter to higher management. For international transactions, consider including mediation or arbitration clauses in your contracts to outline dispute resolution processes. Engaging a legal professional familiar with international trade may also be beneficial if disputes cannot be resolved amicably.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for screw conveyor parts
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing of screw conveyor parts is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By prioritizing CEMA standardized components, businesses can ensure compatibility and ease of maintenance, which is essential for minimizing downtime. Furthermore, establishing relationships with reliable suppliers not only streamlines procurement but also opens doors to custom solutions tailored to specific industry needs, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Buyers should leverage digital resources, such as technical articles and catalogs, to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the key components—from troughs to bolting kits—allows for comprehensive planning and effective inventory management.
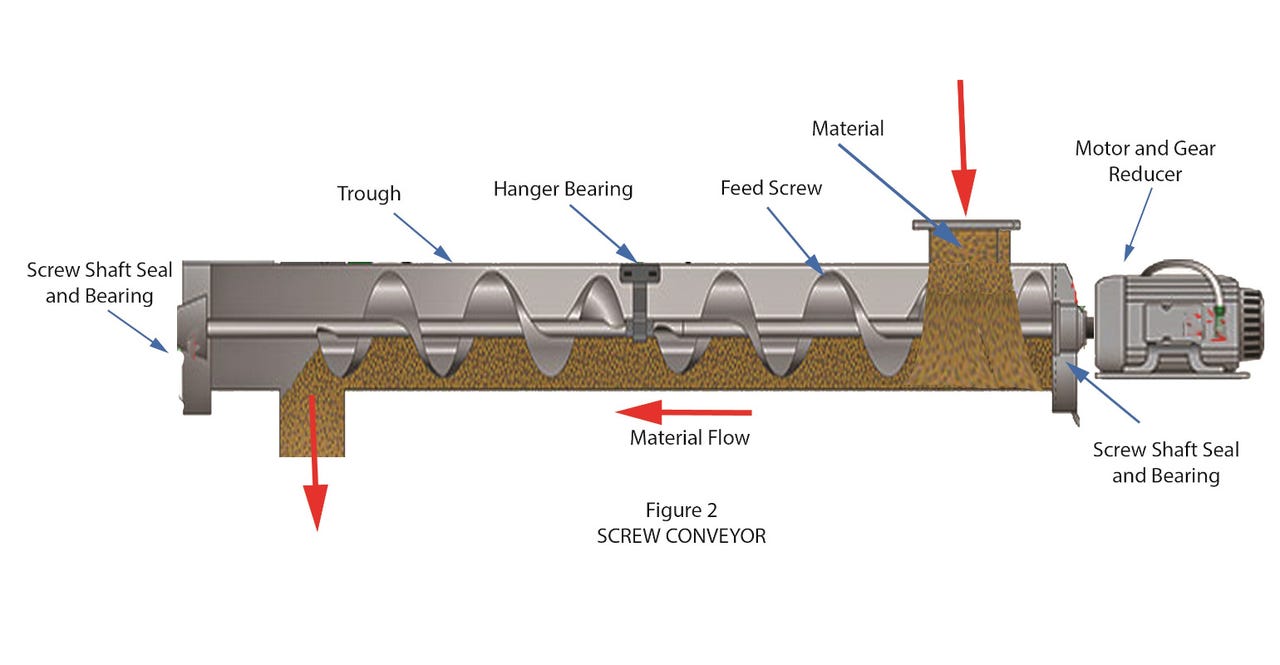
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, as industries continue to evolve and adopt advanced technologies, the demand for high-quality, durable screw conveyor parts will only increase. International buyers are encouraged to stay proactive in their sourcing strategies, ensuring they are well-prepared to meet future challenges and opportunities in the global marketplace. Engage with suppliers today to secure a competitive edge and drive your business forward.