Master Sourcing Strategies for Air to Air Heat Exchanger
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for air to air heat exchanger
In an era where energy efficiency and sustainability are paramount, air to air heat exchangers have emerged as critical components across various industries. These devices play a pivotal role in optimizing energy usage, reducing operational costs, and minimizing environmental impact. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of air to air heat exchangers is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both economic and ecological goals.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of air to air heat exchangers, examining their specific applications and benefits. It explores the materials used in their construction, providing insights into durability and performance factors. Furthermore, we will cover manufacturing and quality control processes, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable suppliers who meet international standards.
Additionally, the guide will address the cost considerations associated with procurement, including potential savings in energy expenditures. The market landscape will be analyzed, highlighting key trends and emerging technologies that can influence purchasing strategies. Lastly, a curated FAQ section will clarify common queries, empowering buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex market effectively.
By equipping you with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide aims to enhance your sourcing strategies, ensuring that you make well-informed decisions that drive efficiency and sustainability in your operations.
Understanding air to air heat exchanger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crossflow Heat Exchanger | Air flows perpendicular to one another | HVAC systems, industrial processes | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Lower efficiency than other types. |
| Counterflow Heat Exchanger | Air flows in opposite directions | Data centers, energy recovery systems | Pros: Higher efficiency, better heat transfer. Cons: More complex design, potentially higher cost. |
| Rotary Heat Exchanger | Uses a rotating wheel to transfer heat | Commercial buildings, residential HVAC | Pros: Excellent for humidity control, high efficiency. Cons: Maintenance can be challenging. |
| Plate Heat Exchanger | Thin plates for heat transfer, compact design | Food processing, chemical industries | Pros: High thermal efficiency, space-saving. Cons: Higher initial investment, potential for fouling. |
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger | Tubes within a shell for heat exchange | Oil and gas, power generation | Pros: Robust design, versatile applications. Cons: Bulky, may require more maintenance. |
Crossflow Heat Exchanger
Crossflow heat exchangers feature a design where the two air streams flow perpendicular to each other. This configuration is commonly utilized in HVAC systems and various industrial processes. Buyers should consider their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, which make them an attractive option for applications with moderate efficiency requirements. However, it’s essential to note that they may not achieve the high efficiency levels seen in counterflow designs, making them less suitable for energy-intensive environments.
Counterflow Heat Exchanger
In counterflow heat exchangers, the air streams flow in opposite directions, allowing for a more effective heat transfer process. This type is particularly advantageous for data centers and energy recovery systems, where efficiency is critical. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher efficiency and better heat transfer against the potentially higher complexity and cost of installation. This type is well-suited for applications where space and energy savings are paramount.
Rotary Heat Exchanger
Rotary heat exchangers utilize a rotating wheel to facilitate heat exchange between air streams. They are particularly effective in commercial buildings and residential HVAC systems, offering excellent humidity control alongside high efficiency. However, buyers should be aware that while they deliver superior performance, they may require more frequent maintenance due to their moving parts. This consideration is crucial for businesses looking to minimize operational downtime.
Plate Heat Exchanger
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin plates that facilitate heat transfer in a compact design. They are widely used in food processing and chemical industries, where high thermal efficiency is required. Buyers should consider their space-saving advantages and efficiency; however, the initial investment can be higher compared to other types. Additionally, the potential for fouling should be monitored to maintain performance, particularly in industries with high particulate matter.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Shell and tube heat exchangers are characterized by their robust design, featuring tubes enclosed within a shell. This type is commonly found in the oil and gas sector and power generation applications. Buyers appreciate their versatility and durability but should be mindful of their bulkiness and potential maintenance needs. This type is ideal for high-capacity applications where reliability is essential, but space constraints may limit its suitability in certain installations.
Related Video: Heat Exchangers Types | How Many Types of Heat Exchanger |
Key Industrial Applications of air to air heat exchanger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of air to air heat exchanger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Cooling processes in production lines | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs | Material compatibility, capacity requirements, and maintenance support |
| Food Processing | Temperature control in refrigeration systems | Maintains product quality and extends shelf life | Hygiene standards, energy consumption, and system integration |
| Data Centers | Thermal management for server cooling | Improves equipment reliability and reduces cooling costs | Airflow design, redundancy options, and ease of installation |
| HVAC Systems | Ventilation systems for commercial buildings | Improves indoor air quality and energy savings | Compliance with local regulations, energy efficiency ratings, and scalability |
| Pharmaceuticals | Climate control in production and storage facilities | Ensures compliance with safety standards and product integrity | Regulatory compliance, precision in temperature control, and supplier reliability |
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, air to air heat exchangers are vital for cooling processes in production lines. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures, which is essential for machinery efficiency and product quality. By integrating these systems, manufacturers can significantly enhance energy efficiency, leading to reduced operational costs. International buyers should consider material compatibility and capacity requirements to ensure the system meets specific production needs. Additionally, reliable maintenance support is crucial for minimizing downtime.
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, air to air heat exchangers play a critical role in temperature control for refrigeration systems. These systems help maintain product quality and extend shelf life by ensuring that food is kept at the appropriate temperature throughout processing and storage. Buyers should prioritize hygiene standards and energy consumption metrics when sourcing these units, as both are essential for compliance with food safety regulations. Integration with existing systems is also a key consideration to ensure seamless operations.
Data Centers
Data centers utilize air to air heat exchangers for effective thermal management of server cooling. These systems are designed to improve equipment reliability by maintaining optimal temperatures, which is crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring continuous operation. Additionally, they can significantly reduce cooling costs, making them a wise investment for data center operators. When sourcing, international buyers should focus on airflow design and redundancy options to enhance system reliability and ease of installation.
HVAC Systems
In HVAC applications, air to air heat exchangers are employed in ventilation systems for commercial buildings. These systems not only improve indoor air quality but also contribute to significant energy savings by recovering heat from exhaust air. Buyers should ensure that the units comply with local regulations regarding emissions and energy efficiency ratings. Scalability is another important consideration, as businesses may need to adjust their systems to accommodate changing occupancy levels or building expansions.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical sector, air to air heat exchangers are essential for climate control in production and storage facilities. These systems help ensure compliance with stringent safety standards and maintain the integrity of sensitive products. Buyers must consider regulatory compliance and the precision required in temperature control when sourcing these systems. Reliability of the supplier is also crucial, as downtime or temperature fluctuations can lead to significant financial losses and compliance issues.
Related Video: Air Cooled Heat Exchanger – Allied Heat Transfer
Strategic Material Selection Guide for air to air heat exchanger
When selecting materials for air to air heat exchangers, it is essential to consider various factors that can influence performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these heat exchangers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion, particularly when treated. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150°C and pressures of around 300 psi.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require special coatings to enhance its corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of air media and is often used in automotive and HVAC applications. Its lightweight nature can improve energy efficiency in transportation applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Europe, adherence to REACH regulations is crucial for material sourcing.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent strength, high-temperature resistance (up to 800°C), and superior corrosion resistance. It is available in various grades, with 304 and 316 being the most common for heat exchangers.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for harsh environments, but it comes at a higher cost compared to aluminum. Manufacturing processes can also be more complex due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly effective in applications involving aggressive media, such as those found in chemical processing or marine environments. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes it versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel sheets. In the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, selecting the right grade is vital for longevity.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating of up to 200°C. It is also antimicrobial, making it suitable for applications requiring hygiene.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of copper is its superior heat transfer efficiency, which can lead to reduced energy costs. However, copper is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, and its susceptibility to corrosion in certain environments can be a drawback.
Impact on Application: Copper is particularly effective in HVAC systems and refrigeration applications where efficient heat exchange is critical. Its antimicrobial properties can be beneficial in food processing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B280 for copper tubing. In regions like South America, where copper mining is prevalent, sourcing may be more cost-effective.
Plastic Composites
Key Properties: Plastic composites, such as polypropylene or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offer good chemical resistance and lower weight. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 80°C and pressures around 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and lower manufacturing costs. However, they are not suitable for high-temperature applications and may have lower structural integrity compared to metals.
Impact on Application: These materials are often used in applications involving less aggressive media, such as air conditioning systems in residential buildings. Their lightweight nature can also reduce installation costs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D1784 for PVC is essential. Buyers in Europe should also consider environmental regulations regarding plastic use and disposal.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for air to air heat exchanger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and HVAC applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and potential corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing and marine environments | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | HVAC and refrigeration systems | Superior heat transfer efficiency | Heavier and expensive | High |
| Plastic Composites | Residential air conditioning systems | Corrosion resistance and low cost | Limited temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for air to air heat exchangers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for air to air heat exchanger
Understanding Manufacturing Processes for Air to Air Heat Exchangers
The manufacturing of air to air heat exchangers involves several critical stages, each contributing to the efficiency and reliability of the final product. For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Key Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Materials: Common materials include aluminum, copper, and stainless steel, selected for their thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Buyers should inquire about the grade and source of materials used.
– Cutting and Shaping: Materials are cut to specified dimensions using techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting. This precision is crucial for performance, as even minor deviations can affect efficiency. -
Forming
– Bending and Molding: Techniques like stamping or extrusion are employed to form the fins and tubes. This stage is vital as it impacts the surface area and airflow characteristics of the heat exchanger.
– Welding: High-quality welding techniques, such as TIG or MIG welding, ensure strong joints that can withstand thermal and pressure stresses. Buyers should verify that suppliers use certified welders. -
Assembly
– Component Assembly: The various parts, including the core, casing, and seals, are assembled. This step often involves both manual and automated processes to ensure precision.
– Integration of Accessories: Depending on the application, additional components like sensors or control systems may be integrated during this phase. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing or powder coating enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Buyers should ensure that the finishing processes meet their environmental standards.
– Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure compliance with specifications before the product is packaged for shipping.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that air to air heat exchangers meet industry standards and customer expectations. For international B2B buyers, understanding the QA process can mitigate risks associated with product performance and reliability.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard emphasizes a quality management system (QMS) that ensures consistent product quality. Buyers should confirm that their suppliers are ISO 9001 certified, as it reflects a commitment to quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. Buyers in Europe must ensure that their suppliers adhere to these regulations.
- API Standards: In specific industries, such as oil and gas, adherence to API standards is crucial. Buyers should assess whether their suppliers meet these industry-specific standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Verification of raw materials against specifications before production begins. This includes checking for certifications and material properties. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Continuous monitoring during manufacturing. This may include random sampling and measurements to ensure processes are within acceptable limits. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Comprehensive testing of finished products. This involves checking for leaks, thermal performance, and dimensional accuracy. Buyers should request FQC reports as part of their procurement process.
Common Testing Methods
- Pressure Testing: Ensures that the heat exchanger can withstand operating pressures without leaking.
- Thermal Performance Testing: Assesses the efficiency of heat transfer under specified conditions.
- Corrosion Testing: Evaluates the resistance of materials to corrosive environments.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions, verifying the quality assurance measures of suppliers is critical. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier compliance:
-
Supplier Audits
– Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and adherence to standards. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audit services. -
Request Quality Reports
– Insist on receiving detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, testing methods used, and compliance with international standards. This documentation can serve as a basis for evaluating supplier reliability. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engage independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the quality of products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance, particularly for high-value orders.
Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers
Navigating quality control can vary by region. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the following:
- Cultural Differences: Understand that quality expectations may differ based on regional norms. Communication with suppliers about specific quality requirements is crucial.
- Regulatory Compliance: Be aware of local regulations that may affect product standards and certification requirements. This is especially important for buyers in regions with stringent import regulations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Ensure that suppliers have robust logistics plans to handle international shipping, which can impact product integrity. Discuss packaging and handling procedures to prevent damage during transit.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for air to air heat exchangers equips B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on quality standards, verifying supplier practices, and considering regional nuances, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure reliable performance from their heat exchangers.
Related Video: How It’s Made Air Conditioner In Factories | Air Conditioner Manufacturing Process @Techmachine_
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for air to air heat exchanger Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Air to Air Heat Exchangers
When sourcing air to air heat exchangers, B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure that encompasses multiple components. Key elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials such as aluminum and stainless steel vary in price and availability, influenced by global market trends and regional sourcing capabilities.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ widely based on geographic location. Countries with lower labor costs may provide an initial price advantage, but this must be balanced against potential quality concerns and long-term reliability.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment depreciation, and factory maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads, making it essential to assess a supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling requirements for specific designs can add to initial costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the supplier can amortize these costs over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance practices are essential for ensuring product reliability. Suppliers that maintain high QC standards may charge more, but this investment can reduce long-term operational costs and risks.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms chosen. Buyers should consider logistics as a critical element of total cost, particularly for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their cost base. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge whether they are receiving competitive pricing.
Price Influencers in the Sourcing Process
Several factors can influence the pricing of air to air heat exchangers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Buying in larger quantities often leads to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs and capabilities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized solutions can lead to higher costs due to additional engineering and production time. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to minimize unnecessary modifications.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also cost. Buyers should assess the balance between material quality and price to ensure optimal performance without overspending.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may command higher prices. However, these certifications often correlate with better reliability and longer product lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better reliability but could also charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping costs and risks. Buyers should clarify responsibility for logistics, insurance, and customs duties upfront.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing
To maximize value when sourcing air to air heat exchangers, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Always seek to negotiate terms and pricing. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your bargaining position.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the product’s lifecycle. This approach can help identify the most cost-effective solutions.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market dynamics that could impact pricing, such as material shortages or fluctuations in labor costs. This knowledge can aid in timing purchases strategically.
-
Understand Regional Differences: Pricing can vary significantly by region. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade agreements when sourcing.
-
Leverage Technology: Use digital platforms for sourcing and procurement to enhance transparency and streamline the buying process. This can lead to better pricing and improved supplier relationships.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to obtain the most accurate and current pricing information.
Spotlight on Potential air to air heat exchanger Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘air to air heat exchanger’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for air to air heat exchanger
Key Technical Properties of Air to Air Heat Exchangers
When considering air to air heat exchangers, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and durability. Understanding these specifications can greatly influence purchasing decisions for B2B buyers.
-
Material Grade: The material used in manufacturing heat exchangers significantly impacts their efficiency and lifespan. Common materials include aluminum and stainless steel, each providing different thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Buyers should evaluate material grades to align with environmental conditions, especially in regions with high humidity or corrosive elements.
-
Heat Transfer Efficiency: This property measures how effectively a heat exchanger can transfer heat from one air stream to another. Efficiency is usually expressed in terms of the overall heat transfer coefficient (U-value). A higher U-value indicates better performance, which can translate to energy savings and improved system reliability. B2B buyers should prioritize products with proven efficiency ratings to maximize their investment.
-
Pressure Drop: This specification indicates the resistance to airflow through the heat exchanger. A lower pressure drop means less energy is required to push air through the system, leading to lower operating costs. Understanding the pressure drop is vital for system design, particularly in applications where energy efficiency is paramount.
-
Tolerance Levels: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In heat exchangers, tight tolerances ensure proper fit and function within a system. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet the specified tolerances to avoid installation issues or operational inefficiencies.
-
Size and Dimensions: The physical size of the heat exchanger is crucial, as it must fit within the designated space in a facility. Buyers need to consider both the overall dimensions and the specific configurations (e.g., cross-flow, counter-flow) to ensure compatibility with existing systems. A precise fit is necessary to maintain optimal airflow and efficiency.
Common Trade Terminology in the Heat Exchanger Industry
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms associated with air to air heat exchangers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of heat exchangers, OEMs often supply components that meet specific performance and quality standards. Buyers should ensure that they source from reputable OEMs to guarantee product integrity.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their project needs while maintaining cost efficiency.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a detailed price quote for specific products or services. This process is crucial for comparing prices and terms across different vendors. B2B buyers should provide clear specifications in RFQs to receive accurate quotes.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with delivery. This knowledge is especially important for international transactions, as it can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
-
Thermal Performance Ratings: This term encompasses various metrics that indicate how well a heat exchanger performs under specific conditions. Ratings often include metrics like capacity, efficiency, and operational limits. Buyers should seek products with robust thermal performance ratings to ensure reliability and effectiveness in their applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right air to air heat exchanger for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the air to air heat exchanger Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global air to air heat exchanger market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing energy efficiency demands and the rising cost of energy. International B2B buyers are particularly focused on solutions that provide both cost savings and sustainability. Regions like Africa and South America are witnessing a surge in demand due to urbanization and industrial expansion, while Europe and the Middle East emphasize compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled heat exchangers are transforming the sector, allowing for real-time monitoring and optimization of energy use. This digital transformation is a crucial trend for international buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency. Moreover, modular designs and innovative materials are gaining traction, enabling easier installation and maintenance, which is particularly beneficial for buyers in developing markets.
Supply chain dynamics are also shifting, with an increasing preference for local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global logistics disruptions. Buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base to include both local and international players, ensuring a balance between cost-effectiveness and quality. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics will be essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of decision-making in the air to air heat exchanger sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques, which not only reduce carbon footprints but can also lead to cost savings in the long run.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with international labor standards and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Incorporating “green” materials, such as aluminum or high-performance plastics, can further enhance the sustainability profile of air to air heat exchangers. Buyers in regions like Europe, which has stringent sustainability mandates, will find that partnering with certified suppliers can also improve their market position and brand reputation.
Brief Evolution/History
The air to air heat exchanger technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially used primarily in HVAC systems, advancements in materials and design have expanded their application across various industries, including automotive and industrial manufacturing.
The introduction of more efficient heat transfer technologies, such as cross-flow and counter-flow designs, has increased the effectiveness of these systems. As global energy concerns became more pronounced, the focus shifted toward optimizing heat exchangers for better performance and lower environmental impact. This historical evolution underscores the importance of ongoing innovation and adaptation in meeting the needs of international B2B buyers today.
Understanding these trends and historical contexts equips buyers with the insights necessary to navigate the complexities of the air to air heat exchanger market, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of air to air heat exchanger
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of air to air heat exchangers?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, reputation, and compliance with international standards. Request references and case studies to assess their capabilities. Ensure they provide certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and any specific certifications relevant to your region, like CE marking in Europe or local compliance in Africa and South America. Conducting site visits or virtual audits can also help evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. -
Can I customize air to air heat exchangers to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for air to air heat exchangers. This may include alterations in size, material, and efficiency ratings based on your operational needs. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements and ask for prototypes or design simulations. Keep in mind that customized solutions may come with longer lead times, so factor this into your project timeline. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for air to air heat exchangers?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and are influenced by the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units. Lead times also depend on the customization level and supplier location; expect 4-12 weeks for standard models and longer for custom designs. Discuss these factors upfront to align your purchasing strategy with your inventory needs and project deadlines. -
What payment options are commonly accepted by suppliers in different regions?
Most international suppliers accept various payment methods, including bank transfers, letters of credit, and online payment platforms. Familiarize yourself with the preferred methods in your region, as practices can vary. For larger orders, consider negotiating payment terms such as partial upfront payments and balance upon delivery. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly documented in your purchase agreement to avoid disputes.
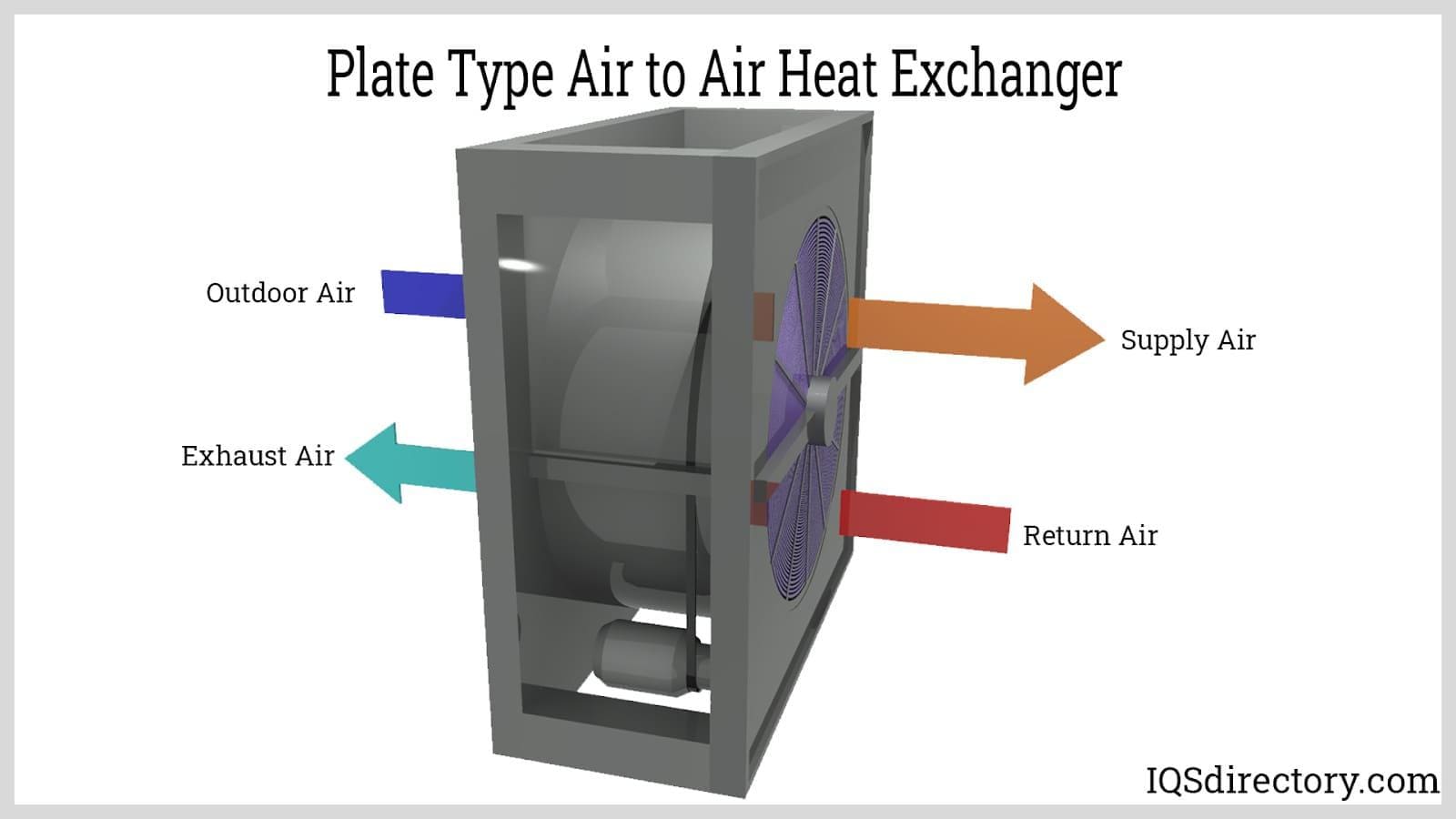
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for my air to air heat exchanger purchase?
Request detailed documentation regarding quality assurance processes from your supplier. This should include certifications like ISO 9001 and any specific industry standards relevant to your application. Ask for test reports, such as performance and durability tests, before finalizing your order. Additionally, consider third-party inspections if purchasing in large quantities or for critical applications, providing an extra layer of assurance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing air to air heat exchangers?
Logistics play a crucial role in international procurement. Evaluate shipping methods, costs, and transit times, as these can significantly impact your project schedule. Ensure your supplier provides packaging that minimizes damage during transit. Understand the import regulations and customs duties in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Collaborating with a freight forwarder can streamline the logistics process and help manage documentation. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers regarding air to air heat exchanger orders?
To mitigate disputes, establish clear communication and documentation practices from the outset. Define terms of service, delivery schedules, and quality expectations in your contracts. In case of a dispute, initiate a dialogue with the supplier to seek an amicable resolution. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your agreement regarding dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration, to facilitate a fair outcome. -
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor after purchasing air to air heat exchangers?
After installation, track KPIs such as energy efficiency, operational costs, and maintenance frequency. Monitor the heat exchanger’s performance against the specifications provided by the supplier to ensure it meets your operational needs. Regular assessments can help identify any deviations from expected performance, enabling you to address issues promptly and ensure a satisfactory return on investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for air to air heat exchanger
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of air-to-air heat exchangers is vital for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. By focusing on long-term supplier relationships, companies can leverage better pricing, quality assurance, and technological innovations. Key takeaways include the importance of assessing supplier capabilities, understanding regional market dynamics, and prioritizing sustainability in procurement decisions.
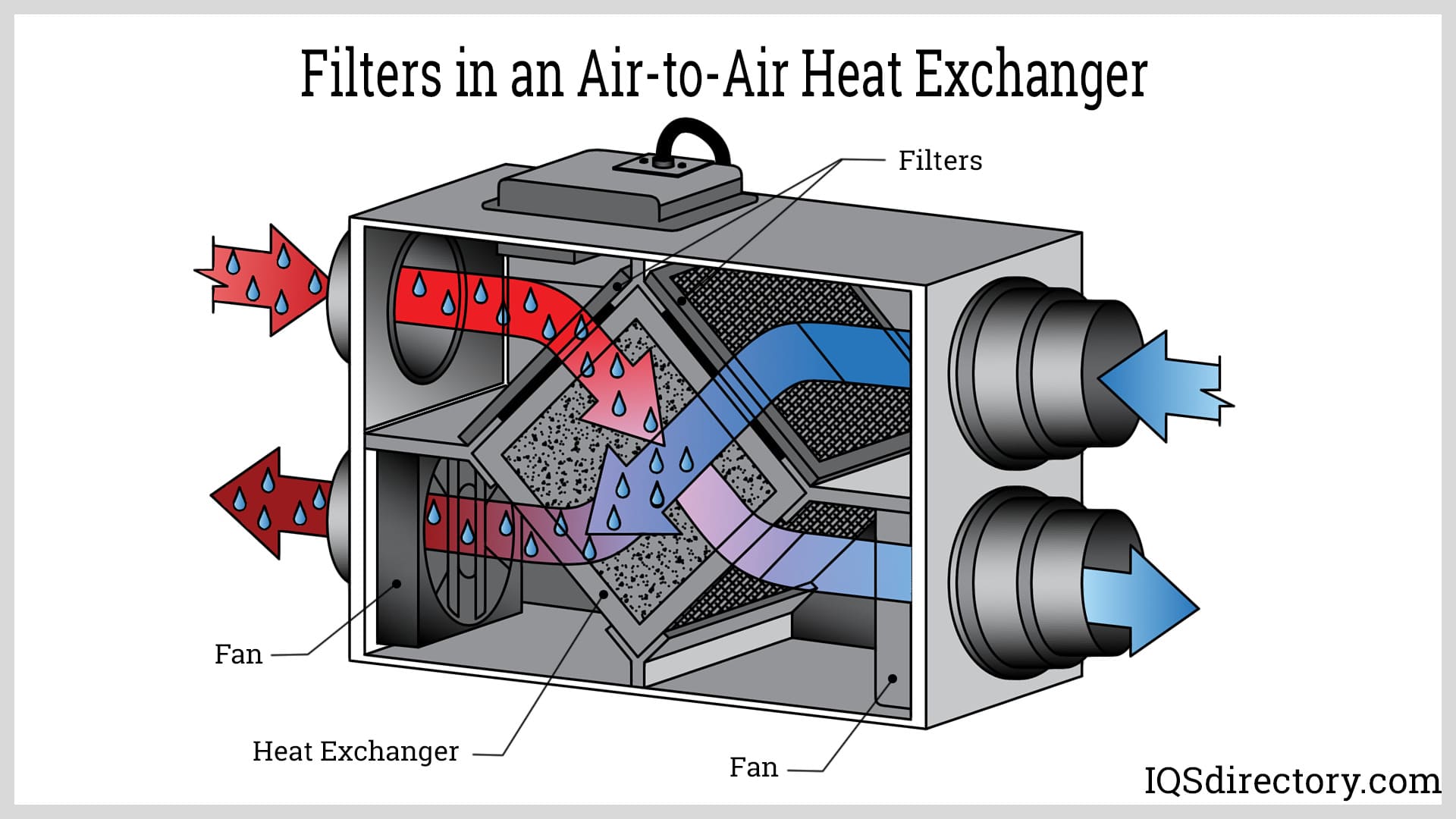
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Actionable Insights:
– Evaluate Suppliers: Conduct thorough assessments of potential suppliers’ technical expertise and reliability.
– Leverage Local Markets: Tap into regional suppliers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to minimize logistics costs and enhance supply chain resilience.
– Sustainability Matters: Prioritize vendors who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices, as this aligns with global trends and regulatory requirements.
Looking ahead, the demand for air-to-air heat exchangers is expected to grow, driven by an increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and climate control across industries. Now is the time for international buyers to embrace strategic sourcing as a pathway to innovation and competitive advantage. Engage with suppliers who not only meet current needs but also align with future trends to ensure your business remains at the forefront of the market.