Master Sourcing Strategies for Ball Bering: Your Essential
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ball bering
In the competitive landscape of global trade, ball bearings serve as critical components that enhance the efficiency and reliability of countless applications across various industries. From the automotive sector in Germany to agricultural machinery in Nigeria, these essential parts minimize friction and wear, ultimately driving down operational costs and extending equipment lifespan. However, the complexities of sourcing the right ball bearings can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This guide is designed to equip you with the insights necessary to navigate the intricacies of the ball bearing market. It offers a comprehensive overview of types of ball bearings and their specific applications, ensuring you select the best fit for your needs. You’ll gain valuable knowledge about material choices that can withstand local environmental conditions, as well as the manufacturing and quality control standards that guarantee product reliability.
Additionally, the guide delves into effective supplier selection and sourcing strategies, enabling you to evaluate potential partners based on performance and reputation. Understanding pricing dynamics and market trends will empower you to negotiate better deals, while our FAQ section addresses common procurement concerns.
By leveraging this guide, you will be better positioned to make informed sourcing decisions, reduce risks, and build resilient supply chains tailored to your operational demands.
Understanding ball bering Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swivel Ball Bearing Wheel | Rotates 360°, ball races in fork mount, high maneuverability | Carts, trolleys, medical equipment, furniture | Excellent mobility; may have reduced load capacity and possible wobble under heavy loads |
| Rigid (Fixed) Ball Bearing Wheel | Fixed alignment, ball bearing at wheel center, straight tracking | Conveyor lines, assembly systems, dollies | Stable, sturdy tracking; lacks directional flexibility for turning |
| Double Ball Bearing Wheel | Two concentric ball races for increased load & stability | Material handling, heavy industrial carts | Higher durability and smoother rolling; typically higher cost |
| Sealed Ball Bearing Wheel | Bearings enclosed by seals to block dust, moisture, contaminants | Food processing, outdoor equipment, harsh environments | Extended service life, low maintenance; limited application in high-temp areas |
| Flanged Ball Bearing Wheel | Integrated flange to prevent lateral movement off tracks | Sliding doors, rail-guided machinery, gates | Prevents derailment and enhances safety; requires matching tracks |
Swivel Ball Bearing Wheel
Swivel ball bearing wheels are designed for 360-degree rotation, making them ideal for applications requiring tight maneuverability. They are particularly suitable for carts, medical equipment, and office furniture that need to navigate confined spaces. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess load capacity and the wheel material to ensure compatibility with flooring types. Additionally, investing in higher-quality models can mitigate issues such as wobbling under heavy loads.
Rigid (Fixed) Ball Bearing Wheel
Rigid ball bearing wheels are characterized by their fixed alignment, which allows for straight tracking without the ability to swivel. These wheels are commonly used in conveyor lines and assembly systems, where stable and consistent movement is essential. B2B buyers should consider their operational layout, as these wheels require more space for maneuvering. Their durability makes them a cost-effective choice for applications that prioritize stability over flexibility.
Double Ball Bearing Wheel
Featuring two concentric ball races, double ball bearing wheels provide enhanced load distribution and stability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Industries that utilize material handling equipment or industrial carts benefit significantly from their durability and smooth operation. Buyers should evaluate the long-term ROI, as the initial investment may be higher, but the reduced maintenance and operational downtime can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Sealed Ball Bearing Wheel
Sealed ball bearing wheels protect the bearings from dust, moisture, and contaminants, making them suitable for harsh environments like food processing and pharmaceuticals. These wheels are designed for low maintenance, as the sealed bearings require less frequent lubrication. However, B2B buyers must consider the limitations in high-temperature applications, as seals may degrade under extreme conditions. Prioritizing quality in sealed designs can enhance service life and operational reliability.
Flanged Ball Bearing Wheel
Flanged ball bearing wheels incorporate an integrated flange that prevents lateral movement off tracks, enhancing safety in applications such as sliding doors and rail-guided machinery. This design is crucial for preventing derailment in high-traffic areas. When sourcing flanged wheels, buyers should ensure compatibility with existing track systems and assess the overall load capacity. Investing in high-quality flanged wheels can lead to improved safety and operational efficiency in various applications.
Related Video: What is Bearing? Types of Bearings and How they Work?
Key Industrial Applications of ball bering
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ball bering | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Wheel assemblies in vehicles | Enhanced performance, reduced wear, and improved safety | Compliance with automotive standards, material durability, and supplier reliability |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery and equipment | Increased efficiency in operations, lower maintenance costs | Adaptation to local climates, load capacity, and corrosion resistance |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Conveyor systems for material handling | Streamlined operations, reduced downtime, and increased throughput | Compatibility with existing systems, load ratings, and sourcing from certified manufacturers |
| Food Processing | Equipment in food handling and packaging | Improved hygiene, reduced contamination risks, and extended equipment lifespan | Sealed designs for cleanliness, compliance with food safety standards, and reliable performance in harsh conditions |
| Construction | Lifting and hoisting equipment | Enhanced safety, improved load handling, and operational efficiency | Heavy-duty ratings, resistance to environmental factors, and supplier certifications |
Automotive Applications
In the automotive sector, ball bearings are integral to wheel assemblies, facilitating smooth rotation and enhancing vehicle performance. They help reduce friction, which translates to better fuel efficiency and lower wear on tires. For international buyers, especially in Europe and Africa, it is crucial to source bearings that comply with stringent automotive standards. Considerations should include the bearing material’s durability and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring longevity and safety in diverse driving conditions.
Agricultural Machinery
Ball bearings are essential in various agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, where they support moving parts and enhance operational efficiency. Their role in minimizing friction leads to lower maintenance costs and increased reliability during peak operation seasons. Buyers in Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing bearings that are resistant to dust and moisture, as these factors can significantly affect performance in outdoor environments. Evaluating local supplier capabilities for timely delivery and support is also critical.
Logistics and Warehousing
In logistics and warehousing, ball bearings are utilized in conveyor systems, enabling smooth material handling and reducing downtime. This application is vital for maintaining high throughput in warehouses and distribution centers. International buyers should focus on sourcing bearings that match the load ratings and operational requirements of their systems. It is also essential to work with suppliers who can provide certifications to ensure product quality and reliability.
Food Processing
Ball bearings in food processing equipment must meet strict hygiene and safety standards. Sealed ball bearings are particularly valuable as they prevent contamination, thereby extending the lifespan of machinery used in food handling and packaging. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should ensure that the bearings sourced comply with food safety regulations. Additionally, understanding the specific environmental conditions—such as temperature and humidity—will help in selecting the right bearing materials.
Construction Equipment
In the construction industry, ball bearings are critical components in lifting and hoisting equipment. They enhance safety and operational efficiency by improving load handling capabilities. B2B buyers in this sector need to focus on sourcing heavy-duty ball bearings that can withstand harsh working conditions, including exposure to dust, moisture, and varying temperatures. Supplier certifications and proven reliability are key factors in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of these critical components.
Related Video: How Ball Mills Work (Engineering and Mining)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ball bering
When selecting materials for ball bearings, B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors that directly affect performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in ball bearings, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and implications for specific applications. This analysis is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where local conditions and regulatory standards can significantly influence material choice.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It typically withstands temperatures up to 300°C and pressures of around 200 MPa, making it suitable for a wide range of environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and oxidation, which is critical in humid or corrosive environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, potentially increasing lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel ball bearings are ideal for applications in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and marine industries, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to minimize costs and ensure timely delivery, especially in regions with challenging logistics.
Chrome Steel
Key Properties: Chrome steel is characterized by its high hardness and wear resistance, with a temperature rating of around 150°C and a pressure rating of approximately 300 MPa.
Pros & Cons: Chrome steel is often favored for its durability and performance in high-load applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly protected, which may limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: This material is commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery applications, where high precision and load-bearing capabilities are required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that suppliers adhere to relevant manufacturing standards and certifications, such as JIS and ISO, to guarantee product quality and reliability.
Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties: Plastic ball bearings, often made from materials like Nylon or PEEK, offer low friction and are resistant to chemicals and moisture. They typically operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic ball bearings is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for applications in harsh environments. However, they may not handle high loads as effectively as metal alternatives and can be more expensive to manufacture.
Impact on Application: These bearings are ideal for applications in the chemical industry, food processing, and environments where metal components would corrode.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the chemical compatibility of plastic bearings with specific media used in their applications and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials.
Ceramic
Key Properties: Ceramic ball bearings are renowned for their exceptional hardness, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to corrosion and wear. They can operate effectively at temperatures exceeding 1000°C and are suitable for high-speed applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of ceramic bearings is their longevity and reduced maintenance needs. However, they are typically more expensive and can be brittle, making them less suitable for applications involving shock loads.
Impact on Application: Ceramic bearings are often used in aerospace, high-performance automotive, and medical devices, where precision and durability are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the higher initial costs associated with ceramic bearings and evaluate the total cost of ownership, including potential savings from reduced maintenance and longer service life.
| Material | Typical Use Case for ball bearing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Chrome Steel | Automotive, industrial machinery | High durability and load capacity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic (Polymer) | Chemical industry, food processing | Lightweight, chemical resistant | Limited load capacity | Medium |
| Ceramic | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | Exceptional hardness, low maintenance | Higher cost, brittleness | High |
This table summarizes the key insights for international B2B buyers, providing a quick reference for material selection based on application requirements and cost considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ball bering
Ball bearings are critical components across numerous industries, and understanding their manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards is essential for B2B buyers aiming to procure reliable products. This section delves into the stages of manufacturing, quality control measures, relevant international standards, and actionable insights for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of ball bearings involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets the necessary performance and reliability standards.
1. Material Preparation
The choice of materials is foundational in ball bearing manufacturing. Common materials include:
- Steel: Most widely used due to its excellent strength and durability.
- Ceramics: Offer superior resistance to corrosion and wear, ideal for high-performance applications.
- Plastic: Used in lightweight applications where corrosion resistance is critical.
During this stage, raw materials are sourced and inspected for quality. The procurement process should emphasize the origin of materials, especially for buyers in regions with stringent regulations on material sourcing, such as the European Union.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the raw materials into the desired form. Key techniques include:
- Cold Heading: A process where metal is shaped at room temperature, preserving its strength.
- Forging: Involves shaping materials through compressive forces, enhancing mechanical properties.
- Casting: Used for complex shapes, though less common for high-performance bearings.
Buyers should inquire about the forming techniques used by suppliers, as they significantly impact the performance characteristics of the bearings.
3. Assembly
In this phase, various components (inner and outer rings, balls, and cages) are assembled. The precision of assembly is crucial; misalignment can lead to premature failure. Techniques include:
- Automatic Assembly Lines: Enhance efficiency and precision.
- Manual Assembly: Used for specialized or low-volume products, where craftsmanship is paramount.
It is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that suppliers have stringent assembly protocols in place to maintain quality.
4. Finishing
The finishing process includes surface treatment and inspection. Techniques may involve:
- Grinding: Ensures precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
- Heat Treatment: Improves hardness and durability, especially for steel bearings.
- Coating: Provides corrosion resistance and reduces friction.
Buyers should verify the finishing processes to ensure they meet the specific application requirements, particularly in harsh environments.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is vital for ensuring that ball bearings perform reliably in their intended applications. Buyers should be familiar with the following quality control measures and standards.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for manufacturers aiming for international credibility.
- ISO/TS 16949: Specifically for the automotive industry, ensuring that suppliers meet stringent automotive quality standards.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
For buyers, understanding these certifications can help assess supplier reliability and product quality.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically structured around several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products before shipment.
Implementing these checkpoints helps minimize defects and enhances overall product reliability.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the quality of ball bearings:
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensures that all components meet specified tolerances.
- Load Testing: Assesses the bearing’s ability to withstand operational loads.
- Vibration Analysis: Detects potential issues related to imbalance or misalignment.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports of these tests from suppliers to ensure compliance with quality standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To effectively verify a supplier’s quality control processes, buyers can implement the following strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site inspections to assess manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices.
- Request Documentation: Obtain quality control reports, certifications, and test results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspectors to evaluate product quality before shipment.
These actions are especially crucial for international buyers from diverse markets, where regulatory compliance may vary significantly.
Navigating Certification Nuances
International buyers must be aware of the nuances associated with certifications and quality standards across different regions. For instance:
- Europe: CE marking is essential for compliance with local regulations, while ISO certifications are highly regarded.
- Africa and South America: Buyers should prioritize suppliers with experience in local market conditions and regulations.
- Middle East: Understanding regional standards, such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) certifications, can be advantageous.
By aligning procurement strategies with regional requirements, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance supply chain resilience.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for ball bearings is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, production techniques, quality control standards, and supplier verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reliability in their applications. As the global market for ball bearings continues to evolve, staying abreast of these factors will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Related Video: Process of Making Ball Bearings. A Mechanical Parts Manufacturing Factory in Korea.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ball bering Sourcing
When sourcing ball bearings, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing landscape is crucial for B2B buyers. The cost of ball bearings can be broken down into several components, each influencing the final price.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects pricing. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, and ceramics. Each material has varying costs based on availability and demand in different regions. For instance, stainless steel is generally more expensive due to its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely based on geographic location and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Regions with lower labor costs can provide competitive pricing but may compromise on quality. It’s essential to assess labor practices, especially in countries with different labor regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, contributing to a more competitive price point.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often a significant upfront expense in the manufacturing of ball bearings. Custom tooling for specialized bearings can drive prices higher, particularly for low-volume production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes ensure the reliability and safety of ball bearings. While these processes can add to costs, they are crucial for long-term performance and should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can greatly influence pricing, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties must be considered. Incoterms will also dictate who bears these costs, affecting the overall price.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary by manufacturer and can depend on their market positioning and operational efficiencies. Understanding the typical markup in your region can help in negotiations.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of ball bearings:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. It’s essential to balance customization needs with budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Bearings that meet international quality standards or have specific certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices. However, investing in certified products can yield long-term savings through reduced failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can impact costs. Established suppliers may offer premium products but might also charge higher prices due to their track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, which can influence overall costs, including shipping and insurance.
Buyer Tips
To navigate the complexities of ball bearing pricing effectively:
-
Negotiate: Always engage in price negotiations. Suppliers often have flexibility, especially for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, replacements, and operational efficiencies over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, sourcing from a local supplier in Africa or South America may reduce logistics costs, whereas sourcing from Europe might offer higher quality but at a premium price.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and fluctuations in raw material prices to anticipate changes in pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices for ball bearings can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential ball bering Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘ball bering’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ball bering
Understanding the technical properties and terminology associated with ball bearings is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize procurement and ensure compatibility with their machinery and operational requirements. This section outlines essential specifications and commonly used terms that will empower decision-makers in their sourcing strategies.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Ball bearings are typically made from materials such as stainless steel, chrome steel, or plastic. The material grade determines the bearing’s durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific environments. For instance, stainless steel bearings are ideal for humid or corrosive settings, while chrome steel is better for high-load applications. Understanding material grades helps buyers select products that align with their operational conditions. -
Load Rating
– This specification refers to the maximum load a bearing can support while maintaining performance. Load ratings are expressed in pounds or kilograms and are critical for ensuring that the bearings can handle the demands of the application. Buyers must consider the dynamic (moving) and static (stationary) load ratings to avoid premature failure of the bearings in heavy-duty applications. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a bearing’s dimensions. It is crucial for ensuring that bearings fit properly within their assemblies. Tight tolerances are essential for high-speed applications, while looser tolerances may suffice for less demanding environments. Buyers should consult tolerance standards to ensure compatibility with their equipment specifications. -
Operating Temperature Range
– This property defines the temperature limits within which the bearing can function effectively. Exceeding these limits can lead to material degradation and failure. Buyers operating in extreme climates or high-temperature environments must prioritize bearings designed for such conditions to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Seal Type
– The type of seal (e.g., rubber, metal shield) affects the bearing’s protection against contaminants and lubrication retention. Sealed bearings reduce maintenance needs and extend service life, making them preferable for applications in dusty or wet environments. Buyers should assess the expected operating conditions to choose the right seal type.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is essential for buyers to ensure that they are sourcing compatible components that meet the original design standards of their equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their demand forecasts to optimize procurement costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific quantities and specifications. It is a vital step in the procurement process that allows buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple vendors, aiding in informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping, insurance, and risk management responsibilities, ultimately leading to smoother procurement processes. -
Lead Time
– This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. It is crucial for inventory planning and ensuring that operations are not disrupted due to delays. Buyers should factor in lead times when making procurement decisions, especially for critical components like ball bearings.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies, minimize risks, and ensure that they select the right ball bearings for their specific needs. This knowledge not only aids in procurement efficiency but also contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of their operational systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the ball bering Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global ball bearing market is experiencing a dynamic transformation driven by several key factors. Firstly, the rising demand for high-performance machinery across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing is propelling the growth of ball bearings. In regions like Africa and South America, infrastructural developments and increased industrialization are leading to a surge in manufacturing activities, thus elevating the demand for reliable ball bearing solutions.
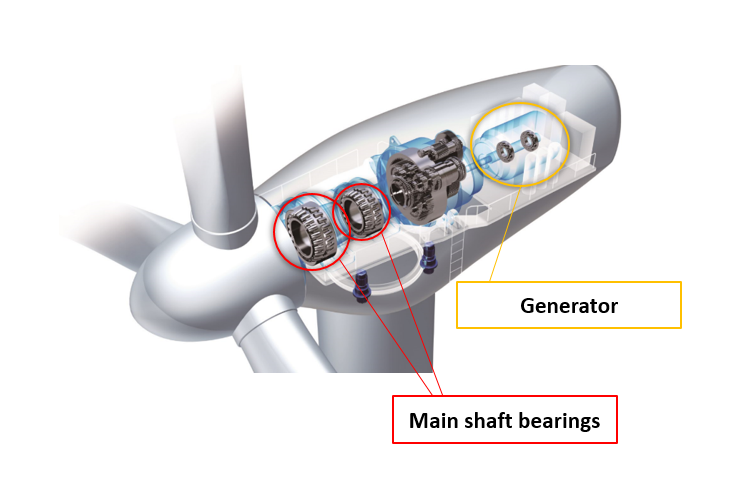
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Technological advancements also play a crucial role in shaping sourcing trends. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, enhances predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to streamline their supply chains, optimize inventory levels, and reduce costs. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in Europe, where advanced manufacturing practices are being adopted.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in procurement decisions. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices and ethical sourcing. The market is witnessing a shift towards the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. As buyers from diverse regions, including the Middle East and Europe, become more environmentally conscious, they are demanding transparency from suppliers regarding their sustainability practices.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it has become a necessity in the ball bearing sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning resource depletion and waste generation, is prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainability. The use of eco-friendly materials and practices not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances brand reputation among increasingly environmentally aware consumers.
Ethical supply chains are integral to this movement. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as benchmarks for evaluating supplier commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the adoption of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable metals and non-toxic lubricants, is gaining traction. These materials not only meet performance requirements but also align with corporate social responsibility goals. Buyers should actively engage with suppliers to understand their sustainability initiatives and seek partnerships that reflect shared values regarding environmental stewardship.
Brief Evolution/History
The ball bearing industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century. Initially developed to reduce friction in machinery, ball bearings have become critical components across various sectors. The introduction of precision engineering and advanced manufacturing techniques in the 20th century led to enhanced performance and reliability.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards not only performance but also sustainability and ethical sourcing. As global supply chains have become more complex, the demand for transparency and responsible sourcing has risen. Buyers today are not just looking for high-quality products but also for suppliers who align with their sustainability goals and ethical standards. This evolution underscores the growing importance of integrating environmental and social considerations into procurement strategies in the ball bearing sector.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ball bering
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for ball bearings?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, quality certifications (like ISO 9001), and production capabilities. Verify their reputation through references and reviews. Conduct site visits if possible, and assess their adherence to international standards, especially if your operations require compliance with specific regulations. Additionally, consider their financial stability and ability to support your long-term needs, including scalability and responsiveness to changes in demand. -
Can I customize ball bearings to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for ball bearings. This can include variations in size, material, or design to suit unique applications or environmental conditions. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications, including load capacity, environmental factors, and operational conditions. Be prepared for potential adjustments in lead times and costs, and ensure that the supplier has experience with similar custom projects. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for ball bearings?
MOQs can vary significantly based on supplier capabilities and the type of ball bearings needed. Generally, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times also depend on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production schedule, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss these factors upfront and consider the implications for your inventory management and cash flow. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for ball bearings?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common arrangements include letters of credit, advance payments, or net 30/60/90 days after delivery. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment, especially when dealing with new suppliers. Additionally, be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for ball bearings?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes and relevant certifications from suppliers. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO or industry-specific certifications (like ASTM for certain materials). Ask about their testing procedures, including load testing and durability assessments, to ensure the bearings will perform reliably in your application. Regular audits and inspections can further reinforce product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing ball bearings internationally?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Evaluate shipping methods, costs, and delivery times to ensure they align with your operational needs. Be aware of customs regulations and duties that may apply to your shipments. Collaborating with experienced freight forwarders can streamline the process and minimize delays. Additionally, ensure that your supplier has reliable logistics partners for timely deliveries. -
What should I do if there’s a dispute with my supplier regarding ball bearings?
In the event of a dispute, start by reviewing the contract terms to understand your rights and obligations. Communicate directly with the supplier to address the issue and seek resolution through negotiation. If needed, escalate the matter to a formal mediation process or arbitration, depending on the terms of your contract. Keeping thorough documentation of all communications and transactions will be beneficial in resolving disputes effectively.
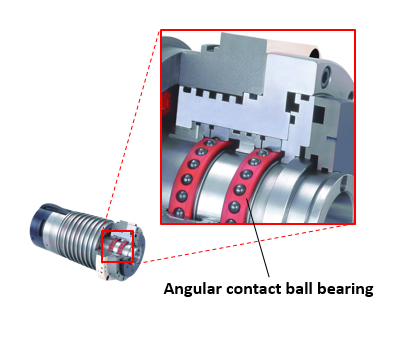
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- How can I stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations for ball bearings?
To stay informed, subscribe to industry publications, join relevant trade associations, and participate in conferences or webinars focused on ball bearing technology and market developments. Engage with suppliers and industry experts to gain insights into pricing trends and potential supply chain disruptions. Utilizing data analytics tools can also help you monitor market conditions and make informed purchasing decisions based on real-time information.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ball bering
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on ball bearings, it’s clear that strategic sourcing is paramount for B2B buyers navigating the diverse global landscape. Understanding the various types of ball bearings, their applications, and material considerations allows businesses to optimize operational efficiency and reduce costs. Key takeaways include recognizing the importance of quality standards, evaluating supplier reliability, and leveraging regional insights to make informed purchasing decisions.
The emphasis on responsible sourcing cannot be overstated, particularly as international buyers increasingly prioritize sustainability and ethical practices in their supply chains. By aligning sourcing strategies with local environmental conditions and compliance requirements, businesses can enhance their operational resilience.
Looking forward, the demand for high-quality ball bearings will continue to grow across industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. We encourage B2B buyers to actively engage with suppliers, explore innovative materials, and stay abreast of market trends to capitalize on emerging opportunities. By doing so, organizations can not only enhance their product offerings but also secure a competitive edge in an evolving marketplace.