Master Sourcing Strategies for Closed Cellular Foam: A B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for closed cellular foam
The global market for closed cellular foam is rapidly evolving, presenting a wealth of opportunities for international B2B buyers. This versatile material, characterized by its tightly packed cells, offers exceptional durability, moisture resistance, and insulation properties, making it essential across various sectors such as automotive, healthcare, and construction. Understanding the nuances of closed cellular foam can empower buyers to make informed sourcing decisions, ensuring they select the right type for their specific applications.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental aspects of closed cellular foam, covering key topics such as the various types and materials available, including polyethylene, neoprene, and polystyrene foams. Additionally, it explores the manufacturing processes and quality control measures that ensure the highest standards are met. Buyers will also find insights into cost considerations and market trends, equipping them with the knowledge to navigate pricing dynamics effectively.
Furthermore, the guide addresses common FAQs that can aid in clarifying uncertainties around sourcing and application. With a focus on the needs of B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in countries like Poland and the UK—this resource is designed to enhance your procurement strategy and foster successful partnerships with suppliers. Empower yourself with the insights necessary to leverage the potential of closed cellular foam in your business operations.
Understanding closed cellular foam Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Foam | Lightweight, water-resistant, and excellent shock absorption | Packaging, automotive, and healthcare | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Lower rigidity compared to other types. |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene | Enhanced durability, mildew resistance, and high density | Construction, flotation devices, industrial | Pros: Strong and resistant to wear. Cons: Higher cost than standard polyethylene. |
| Polystyrene Foam | Rigid structure, available in various densities | Storage, packaging, insulation | Pros: Excellent for protective applications. Cons: Less flexible, can be brittle. |
| Neoprene Rubber | Excellent insulation, resistant to mildew and bacteria | Flooring, wall paneling, medical equipment | Pros: Durable and hygienic. Cons: Higher price point. |
| Polypropylene Foam | High-density, strong rigidity for heavy-duty applications | Protective packaging, automotive parts | Pros: Outstanding protection and durability. Cons: Limited flexibility in design. |
Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a popular choice in various industries due to its lightweight nature and excellent shock absorption capabilities. Its water-resistant properties make it ideal for packaging fragile items, automotive applications, and healthcare products. When purchasing, buyers should consider the foam’s density and thickness, as these factors influence its performance. Additionally, its cost-effectiveness makes it an attractive option for bulk orders.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene
Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers enhanced durability and resistance to mildew and water, making it suitable for demanding applications like construction and flotation devices. This type of foam is available in various thicknesses and densities, providing versatility for different projects. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs for strength and moisture resistance, as this foam tends to be more expensive than standard polyethylene but offers superior performance.
Polystyrene Foam
Known for its rigid structure, polystyrene foam is available in multiple densities, making it an excellent choice for storage, packaging, and insulation applications. Its high resilience makes it particularly effective in protective packaging scenarios. When considering polystyrene foam, buyers should assess the specific density required for their applications, as higher density options may provide better protection but could also be more costly.
Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber foam is recognized for its excellent insulation properties and resistance to mildew and bacteria, making it suitable for flooring, wall paneling, and medical equipment. Its durability and hygienic qualities are essential for applications in healthcare and sports venues. Buyers should consider the thickness and density of neoprene foam to ensure it meets their specific insulation and cleanliness requirements, although it may come at a higher price point.
Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam stands out for its high density and rigidity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring strong protection, such as automotive parts and protective packaging. This foam type excels in providing robust support and cushioning. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs for durability and protection, keeping in mind that while polypropylene foam offers excellent performance, its rigidity may limit design flexibility.
Related Video: Health Belief and Transtheoretical Models – Fundamentals of Nursing | @LevelUpRN
Key Industrial Applications of closed cellular foam
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of closed cellular foam | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Insulation and soundproofing for buildings | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces noise pollution | Compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Automotive | Interior cushioning and insulation | Improves comfort and safety for passengers | Material density and flame resistance specifications |
| Marine | Buoyancy aids and flotation devices | Increases safety and reliability in water applications | Resistance to water absorption and UV degradation |
| Healthcare | Medical device padding and protective covers | Ensures comfort and hygiene in medical environments | Non-toxicity and ease of cleaning |
| Packaging | Protective packaging for fragile items | Reduces damage during transport and storage | Customization options for size and shape |
Detailed Applications of Closed Cellular Foam
Construction: Closed-cell foam is widely used in the construction industry for insulation and soundproofing applications. Its impermeable structure provides excellent thermal resistance, helping buildings maintain energy efficiency. Additionally, its sound-dampening properties contribute to quieter indoor environments. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the foam complies with local building codes and standards, particularly regarding fire safety and environmental impact.
Automotive: In the automotive industry, closed-cell foam is utilized for interior cushioning and insulation. It enhances passenger comfort by providing cushioning in seats and reducing road noise. The material’s durability and lightweight characteristics also contribute to vehicle efficiency. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing foams that meet specific density and flame resistance requirements to ensure safety and compliance with automotive standards.
Marine: Closed-cell foam plays a critical role in marine applications, particularly in buoyancy aids and flotation devices. Its water-resistant properties make it ideal for life jackets, buoys, and other safety equipment used in aquatic environments. This foam not only increases safety but also ensures reliability in harsh marine conditions. Buyers must consider the foam’s resistance to water absorption and UV degradation, especially in regions with intense sunlight and varying water conditions.
Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, closed-cell foam is employed for medical device padding and protective covers. Its cushioning properties help prevent pressure sores and provide comfort for patients. Additionally, the foam is easy to clean and maintain, which is crucial in medical settings. B2B buyers should prioritize non-toxic materials that meet hygiene standards to ensure safety and compliance in healthcare environments.
Packaging: Closed-cell foam is an excellent choice for protective packaging, particularly for fragile items. Its shock-absorbing capabilities reduce the risk of damage during transport and storage, making it invaluable in logistics and shipping. Buyers should look for customization options that cater to specific sizes and shapes of products, ensuring optimal protection and efficiency in their packaging solutions.
Related Video: Foam generator for cellular lightweight concrete production how it works
Strategic Material Selection Guide for closed cellular foam
When selecting closed cellular foam materials for various applications, international B2B buyers must consider several key factors, including the properties of the materials, their advantages and disadvantages, and how they align with specific industry standards and regional preferences. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in closed cellular foam, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Polyethylene Foam
Key Properties: Polyethylene foam is known for its excellent shock absorption, buoyancy, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. It typically has a temperature rating of -40°F to 180°F and offers moderate pressure resistance.
Pros & Cons: This material is lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to fabricate, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging and insulation. However, it can be less durable than other options, particularly in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: Polyethylene foam is compatible with various media, including water and certain chemicals, making it ideal for packaging sensitive items. Its buoyancy makes it a popular choice for flotation devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. In Europe, for example, adherence to REACH regulations is crucial.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam
Key Properties: Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam boasts superior durability, with a density range of 2 to 20 lb/cubic foot. It is resistant to mildew and has a temperature rating of -40°F to 200°F.
Pros & Cons: The enhanced durability and resistance to water absorption make XLPE foam ideal for demanding applications, such as automotive and construction. However, it tends to be more expensive and may require specialized fabrication techniques.
Impact on Application: XLPE foam is suitable for applications requiring high insulation values and moisture resistance, such as HVAC systems and refrigeration. Its robustness also makes it a good choice for protective packaging.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable in their region, such as ASTM or DIN, which may dictate material specifications for construction or automotive uses.
Neoprene Rubber Foam
Key Properties: Neoprene foam is known for its excellent thermal insulation and resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering. It can withstand temperatures from -40°F to 212°F.
Pros & Cons: This material is highly durable and provides good cushioning, making it suitable for applications in automotive and medical fields. However, it is generally more expensive than polyethylene options and may have limited availability in certain regions.
Impact on Application: Neoprene foam is particularly effective in environments where cleanliness and insulation are paramount, such as in hospitals and laboratories. Its resistance to mold and bacteria is a significant advantage in these settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the neoprene foam meets any specific health and safety standards relevant to their industry, particularly in the medical sector, where compliance with ISO standards is often required.
Polystyrene Foam
Key Properties: Polystyrene foam is rigid and provides excellent insulation properties, with a temperature rating of -40°F to 180°F. It is available in various densities, making it versatile for different applications.
Pros & Cons: This material is cost-effective and easy to mold, making it ideal for packaging and insulation. However, it is less resilient under impact compared to other closed-cell foams, which can be a limitation in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Polystyrene foam is widely used in food packaging and thermal insulation due to its lightweight nature and effective insulation properties.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards is critical for buyers in the food industry, particularly in Europe, where regulations such as the EU Food Contact Materials Regulation apply.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for closed cellular foam | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Foam | Packaging, insulation | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable in high-temperature environments | Low |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam | Automotive, construction | Superior durability and moisture resistance | More expensive, requires specialized fabrication | High |
| Neoprene Rubber Foam | Medical equipment, automotive | Excellent thermal insulation and durability | Higher cost, limited availability in some regions | Med |
| Polystyrene Foam | Food packaging, thermal insulation | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Less resilient under impact | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in closed cellular foam, offering actionable insights for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for closed cellular foam
The manufacturing process for closed cellular foam involves several critical stages, ensuring that the end product meets the rigorous demands of various applications. This section provides an in-depth look at these processes and the quality assurance measures that international B2B buyers should consider, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
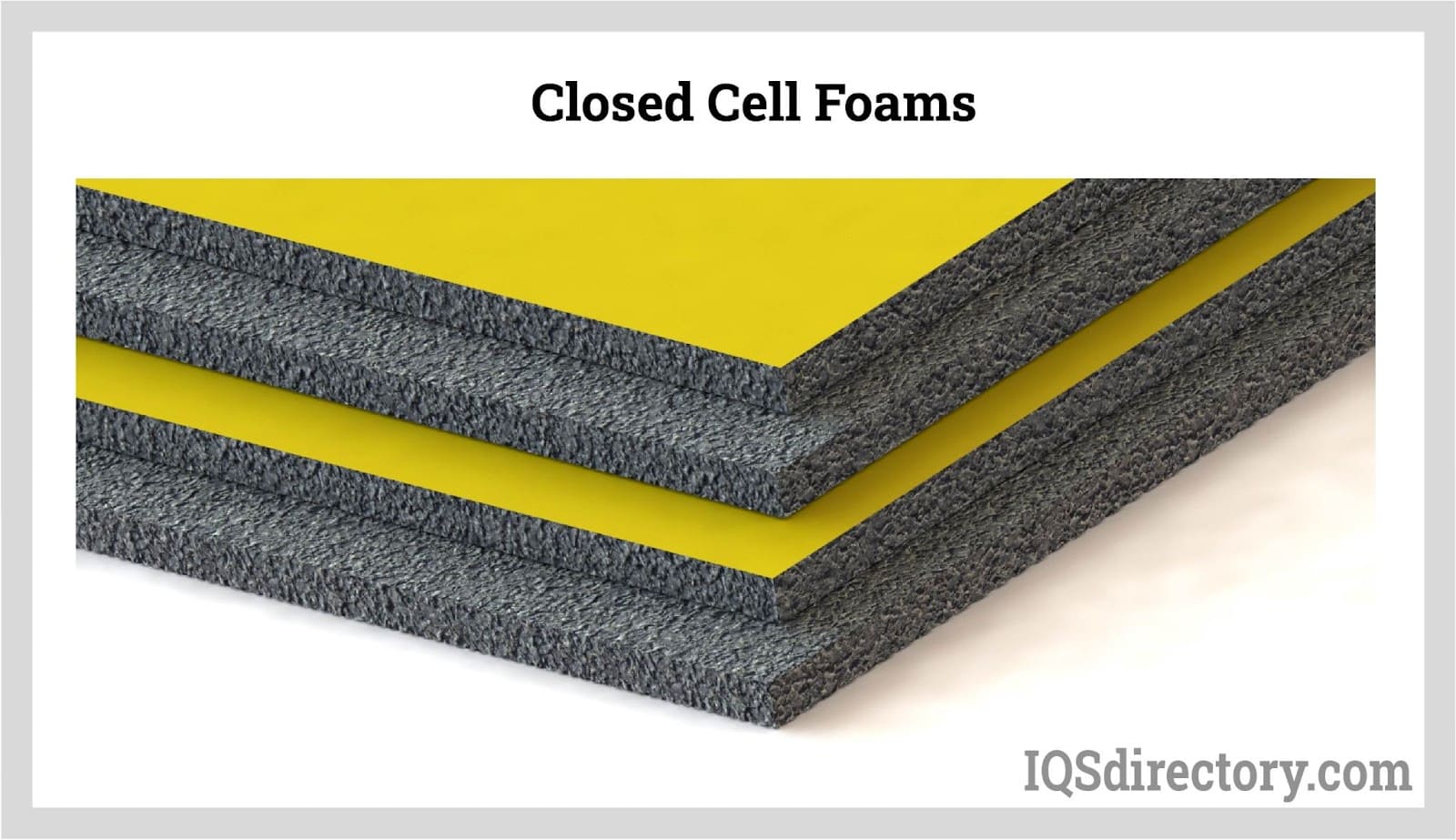

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Process
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in closed cellular foam production involves selecting and preparing the raw materials. Common materials include:
- Polyethylene: Known for its durability and resistance to moisture.
- Neoprene Rubber: Offers excellent insulation and is resistant to mildew.
- Cross-Linked Polyethylene: Provides enhanced strength and is suitable for various industrial applications.
These materials are often sourced from reputable suppliers, and it is crucial for buyers to verify the quality of these inputs through certifications or supplier audits.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the foam structure is created. This typically involves:
- Mixing: Raw materials are blended with blowing agents to create a foamable mixture.
- Heating and Pressurizing: The mixture is subjected to heat and pressure, causing it to expand and form closed cells. This process is vital for achieving the desired density and physical properties of the foam.
Key techniques in forming include:
- Batch Processing: Involves producing foam in large quantities, allowing for economies of scale.
- Continuous Processing: This method enables ongoing production, which can be more efficient for high-volume demands.
3. Assembly
Once the foam is formed, it may undergo various assembly processes depending on its intended use. This can involve:
- Cutting: The foam is cut to specific dimensions using precision cutting tools. CNC machines are often employed for accuracy.
- Laminating: In some applications, layers of foam may be laminated together to enhance properties such as sound insulation or thermal resistance.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves any additional treatments or coatings that enhance the foam’s performance. Common finishing processes include:
- Surface Treatment: This can involve applying adhesives or coatings to improve durability or aesthetics.
- Packaging: Proper packaging ensures that the foam retains its properties during transportation and storage.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of closed cellular foam is essential for ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key elements of the quality assurance process include:
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- CE Marking: This indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements, particularly important for buyers in Europe.
Industry-Specific Standards
- API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary.
- ASTM Standards: Various ASTM standards may apply, especially concerning testing methods for materials.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to detect and correct issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of finished products to verify that they meet quality specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is a critical aspect of the QC process. Common methods include:
- Density Testing: To ensure that the foam meets specified density requirements.
- Compression Testing: Evaluates the foam’s ability to withstand loads without deforming.
- Water Absorption Testing: Measures the foam’s resistance to moisture, crucial for applications in damp environments.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is paramount. Here are actionable steps to ensure compliance:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation that outlines their QC processes, including results from tests and inspections.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality practices, giving buyers peace of mind.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must also be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification. For instance:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications, which can complicate sourcing. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the regulations applicable in their regions.
- Documentation Requirements: Ensure that suppliers provide all necessary documentation for customs and compliance, especially for cross-border transactions.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother interactions with suppliers and enhance negotiation outcomes.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for closed cellular foam are complex yet vital to ensuring product performance and reliability. By understanding these processes and implementing rigorous verification practices, international B2B buyers can confidently source high-quality closed cellular foam that meets their specific needs. Investing time in supplier evaluation and quality assurance will ultimately lead to better product outcomes and enhanced business relationships.
Related Video: Inside the Molded Foam Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for closed cellular foam Sourcing
In sourcing closed cellular foam, understanding the comprehensive cost and pricing structure is critical for international B2B buyers. This analysis will outline the key cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in closed cellular foam production is the raw materials. Common materials include polyethylene, polystyrene, neoprene, and polypropylene, each varying in cost based on quality and sourcing location. Higher quality materials often command a premium, while cheaper alternatives may not meet specific application requirements.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with higher wage standards, such as those in Western Europe, labor costs may be substantial. Conversely, manufacturers in regions like Africa or South America may offer lower labor costs, which can influence overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility operations. Efficient production processes can help reduce overhead, thereby lowering the overall cost of the foam.
-
Tooling: For custom shapes and sizes, tooling costs can be significant. This expense is often amortized over large production runs, making it crucial to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) when negotiating prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the foam meets industry standards and specific buyer requirements incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes can increase the price but ensure product reliability, particularly in high-stakes applications like automotive or medical sectors.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the origin, destination, and chosen Incoterms. Buyers must consider freight, insurance, and customs duties when calculating total costs, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of the costs mentioned. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s position in the market, their reputation, and the competitiveness of their pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer better pricing for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better deals and lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications often lead to higher costs. Standardized products are typically less expensive than customized solutions due to reduced tooling and production complexity.
-
Materials and Quality: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Premium materials that offer enhanced durability or performance can significantly increase costs. Buyers should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of material selection.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their perceived value and quality assurance, while newer or less-known suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is vital. They dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect the final cost of goods delivered.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Transparency about your needs and expected volumes can lead to better terms and pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and potential replacement costs when selecting foam products.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, sourcing from local suppliers in Africa or South America may yield cost advantages due to lower transportation costs compared to sourcing from Europe or North America.
-
Certifications: Verify any quality certifications that may impact your purchasing decision. Products with recognized certifications may carry a higher price but can provide peace of mind regarding performance and compliance.
Disclaimer
Prices for closed cellular foam can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The information provided here serves as a guideline; actual prices should be confirmed with suppliers to reflect current market conditions and specific project requirements.
Spotlight on Potential closed cellular foam Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘closed cellular foam’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for closed cellular foam
When engaging with closed cellular foam, understanding its essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below are the key specifications and terms that will enhance your purchasing decisions.
Key Technical Properties of Closed Cellular Foam
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the quality and type of materials used in foam production, such as polyethylene, polystyrene, or neoprene.
– Importance: Different grades offer varying levels of durability, insulation, and resistance to environmental factors. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the foam meets specific application requirements, such as buoyancy for marine uses or sound absorption for acoustic applications. -
Density
– Definition: The mass per unit volume of the foam, typically measured in pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft³).
– Importance: Higher density foams provide better durability and support, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like packaging and insulation. Understanding density is essential for buyers to match the foam’s performance characteristics with their project needs. -
Compression Set
– Definition: The ability of foam to return to its original shape after being compressed, expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: A lower compression set indicates better resilience and longevity. This property is critical for applications where repeated compression occurs, such as in automotive seating or industrial gaskets. -
Thermal Conductivity
– Definition: A measure of the foam’s ability to conduct heat, typically expressed in units of watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K).
– Importance: For applications requiring insulation, such as HVAC systems or refrigeration, lower thermal conductivity values signify better insulating properties, leading to energy efficiency and cost savings. -
Water Absorption
– Definition: The percentage of water the foam can absorb when submerged, usually measured over a specific time.
– Importance: Closed cell foams are typically designed to have low water absorption, which is vital for applications in wet environments, like marine or outdoor uses. Buyers should verify this property to ensure durability and performance. -
Flame Retardancy
– Definition: The foam’s ability to resist ignition and slow down the spread of flames, often evaluated against industry standards.
– Importance: For applications in construction, automotive, and aerospace, flame retardancy is critical for safety compliance. Understanding this property helps buyers choose materials that meet regulatory requirements.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers for specialized foam products that meet specific application standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for buyers in regions where storage space is limited. -
RFQ (Request for Quote)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products.
– Relevance: This process is vital for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding terms of service, allowing buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers in negotiating shipping and delivery terms, crucial for managing costs and logistics in international trade. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the goods.
– Relevance: Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring that materials arrive on schedule, particularly in industries with tight deadlines.
By familiarizing yourself with these properties and terms, you can make more informed decisions when sourcing closed cellular foam, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness for your projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the closed cellular foam Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global closed cellular foam market is witnessing significant growth, driven by rising demand across various sectors such as automotive, healthcare, and construction. Key trends influencing this market include the increasing focus on lightweight materials for energy efficiency and the growing need for effective insulation solutions. International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several emerging trends.
Digital transformation is reshaping sourcing practices, with buyers leveraging advanced technologies like AI and blockchain to streamline procurement processes and enhance transparency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to suppliers, enabling buyers to compare products and negotiate better prices. The demand for customization is also on the rise, with manufacturers offering tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements.
Buyers should consider the competitive landscape, which is marked by a mix of established players and new entrants. This dynamic environment necessitates a strategic approach to sourcing, emphasizing the importance of evaluating suppliers based on their innovation capabilities and responsiveness to market demands. Understanding regional regulations and standards is crucial, particularly for buyers in Europe, where compliance with strict environmental and safety regulations can impact sourcing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of business strategy in the closed cellular foam sector. The environmental impact of foam production, particularly in terms of energy consumption and emissions, necessitates a commitment to sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a clear commitment to minimizing their carbon footprint through energy-efficient manufacturing processes and responsible sourcing of raw materials.
Ethical supply chains are increasingly important in the global marketplace. International B2B buyers should seek out suppliers that adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Oeko-Tex (Textile Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability and ethical practices.
Furthermore, the use of eco-friendly materials in closed cellular foam production is gaining traction. Biodegradable and recyclable foam products are becoming more prevalent, providing buyers with sustainable options that meet their performance needs while reducing environmental impact. By prioritizing suppliers with sustainable practices and materials, buyers can contribute to a greener supply chain and enhance their brand reputation.
Brief Evolution/History
The closed cellular foam sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for military and aerospace applications due to its lightweight and insulating properties, the use of closed cellular foam has expanded into various industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
In the 1980s and 1990s, advancements in polymer technology led to the development of more versatile and durable foam products, allowing for broader applications. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability in recent decades has further propelled innovation in this sector, with manufacturers increasingly focusing on eco-friendly materials and processes.
Today, closed cellular foam is recognized not only for its functional benefits but also for its potential to contribute to sustainable practices in diverse industries. As international B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into the future direction of the market.
Related Video: US-China Trade Truce Signed, Treasury Kills ‘Revenge Tax’ | Bloomberg The Pulse 06/27
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of closed cellular foam
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of closed cellular foam?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Look for companies with a proven track record in producing closed cellular foam that meets international standards. Request references from other B2B buyers in your region to assess reliability. Additionally, evaluate their production capabilities, quality control processes, and responsiveness to inquiries, as these factors significantly impact long-term partnerships. -
Can I customize closed cellular foam products to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for closed cellular foam, including size, density, thickness, and color. When seeking customized solutions, clearly communicate your specifications and intended application. Request samples to evaluate the foam’s performance before finalizing your order. This will ensure that the product meets your needs and reduces the risk of costly adjustments after production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for closed cellular foam?
MOQs for closed cellular foam can vary significantly by supplier and product type, often ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times typically depend on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity, generally falling between 2 to 6 weeks. It is advisable to confirm these details upfront to align your project timelines with supplier capabilities and avoid unexpected delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing closed cellular foam internationally?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers but commonly include options such as advance payment, partial payment upfront, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure methods like letters of credit or escrow services to minimize risks. Always review the supplier’s payment policies and negotiate terms that provide you with adequate protection while ensuring timely production. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for closed cellular foam?
Request documentation that verifies compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO certifications or specific industry-related certifications. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing methods for durability, density, and performance. Consider conducting a factory audit or using third-party inspection services to validate the supplier’s claims before placing a significant order. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping of closed cellular foam?
When planning logistics, factor in shipping costs, customs duties, and potential delays in transit. Choose reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling foam products to ensure safe transport. Clarify whether the supplier will handle shipping arrangements or if you will be responsible for logistics. Additionally, verify that the foam is packaged appropriately to prevent damage during transit. -
How should I handle disputes or quality issues with a supplier of closed cellular foam?
Establish clear communication channels with your supplier to address any issues promptly. Document all correspondence regarding disputes, including specifications and quality concerns. If a quality issue arises, refer to the agreed-upon terms in your contract, which should outline the process for addressing defects or discrepancies. Consider mediation or arbitration as a resolution strategy if direct communication fails. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with closed cellular foam suppliers?
Building a strong relationship with suppliers is crucial for consistent quality and service. Maintain open lines of communication and provide feedback on product performance. Regularly review contracts to ensure mutual satisfaction regarding pricing and delivery terms. Foster collaboration by involving suppliers in your product development process, which can lead to innovative solutions and shared growth opportunities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for closed cellular foam
As we conclude our exploration of closed cellular foam, it is crucial to recognize the strategic advantages it offers for various industries. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can leverage closed cellular foam’s unique properties—like moisture resistance, durability, and versatility—to enhance their product offerings.
Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right type of closed cellular foam for specific applications, understanding the manufacturing processes, and recognizing the diverse materials available, such as polyethylene and neoprene. Effective sourcing strategies will not only optimize costs but also ensure access to high-quality materials that meet regulatory standards and performance requirements.
Looking ahead, the demand for closed cellular foam is expected to grow, driven by trends in sustainability and innovation across industries. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with established suppliers and explore collaborations that can foster innovation and efficiency. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can not only secure a competitive edge but also contribute to the development of sustainable solutions that meet the evolving needs of the marketplace.