Master Sourcing Strategies for Mesh and Wire in Global
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mesh and wire
In today’s interconnected world, the demand for mesh and wire products spans numerous industries, making them indispensable components in construction, manufacturing, and filtration processes. Whether it’s welded wire mesh for structural reinforcement or woven wire mesh for filtration applications, the versatility of these materials has cemented their role as foundational elements in both traditional and innovative projects. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of these products is critical for making informed sourcing decisions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the mesh and wire market, detailing the various types and materials available, the manufacturing processes and quality control standards that ensure product reliability, and insights into selecting the right suppliers. Furthermore, it addresses cost considerations and explores market trends to equip buyers with the necessary knowledge to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
By delving into frequently asked questions and practical tips, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make strategic decisions tailored to their specific needs, fostering successful partnerships and enhancing supply chain efficiency. Whether you are sourcing for a large-scale construction project in Brazil or seeking specialized mesh solutions in Poland, this guide will serve as your essential roadmap in the global market for mesh and wire.
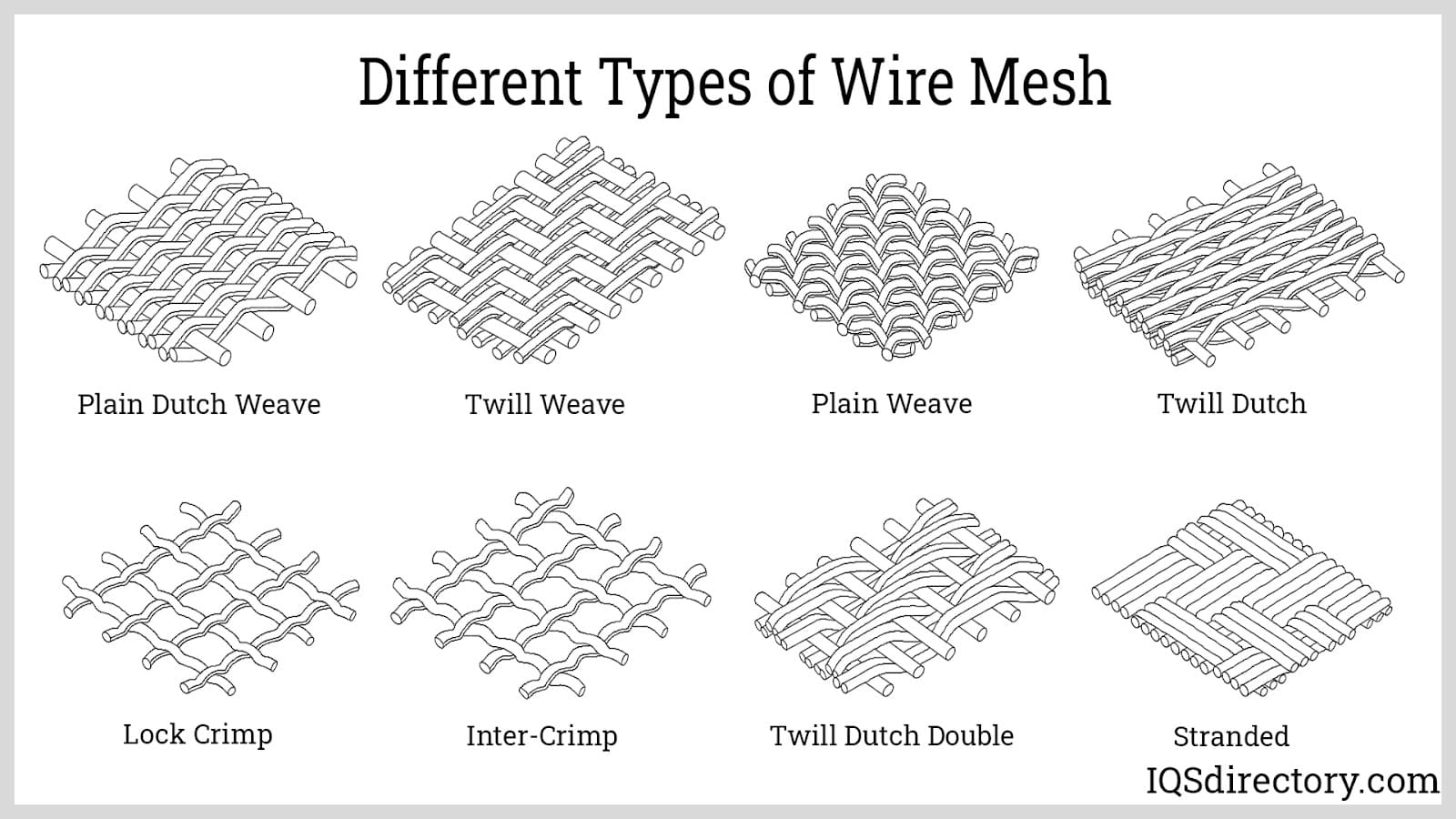
Understanding mesh and wire Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welded Wire Mesh | Rigid structure, welded intersections, high strength | Fencing, concrete reinforcement | Pros: High stability and durability; Cons: Less flexible, may require custom sizing. |
| Woven Wire Mesh | Interwoven pattern, flexible, various weave types | Filtration, sieving, architectural uses | Pros: Versatile applications; Cons: Weaker than welded mesh, may not withstand heavy loads. |
| Expanded Metal Mesh | Sheets with diamond-shaped openings, lightweight | Grating, security fencing, architectural | Pros: Lightweight and strong; Cons: Limited customization in mesh size. |
| Knitted Wire Mesh | Flexible, interlocking loops, various materials | Medical applications, filtration | Pros: High flexibility; Cons: May not provide structural support. |
| Crimped Wire Mesh | Wavy pattern, enhanced strength, thicker wires | Industrial applications, heavy-duty use | Pros: High strength and rigidity; Cons: Heavier, less suitable for lightweight applications. |
Welded Wire Mesh
Welded wire mesh is characterized by its rigid structure formed by welding wires at their intersections, providing exceptional strength and stability. This type is ideal for applications requiring high durability, such as fencing, concrete reinforcement, and industrial barriers. When purchasing, buyers should consider the material (e.g., galvanized steel for corrosion resistance) and the mesh size required for specific applications. Custom sizing may be necessary, which could impact lead times and costs.
Woven Wire Mesh
Woven wire mesh features an interwoven pattern that allows for flexibility and various opening sizes, making it suitable for filtration, sieving, and architectural applications. Buyers should assess the weave type—such as plain, twill, or Dutch weave—based on their specific needs. While this type of mesh is versatile, its tensile strength may not match that of welded wire mesh, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. Consideration should also be given to protective coatings to enhance durability.
Expanded Metal Mesh
Expanded metal mesh is created by cutting and stretching metal sheets, resulting in diamond-shaped openings. This type is lightweight yet strong, making it popular for grating, security fencing, and architectural applications. Buyers should evaluate the thickness of the sheet and the size of the openings based on their application requirements. While it offers excellent airflow and light passage, customization options may be limited compared to other mesh types.
Knitted Wire Mesh
Knitted wire mesh is formed using interlocking loops, offering high flexibility and adaptability for various applications, particularly in the medical field and filtration systems. When considering knitted wire mesh, buyers should focus on material selection and the specific properties required for their applications, such as biocompatibility for medical uses. However, its lack of structural support compared to welded or crimped types may limit its use in heavy-duty settings.
Crimped Wire Mesh
Crimped wire mesh is distinguished by its wavy pattern, which enhances its strength and rigidity, making it suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Buyers should consider wire thickness and mesh size when selecting crimped wire mesh for their projects. While it offers excellent durability, it tends to be heavier than other types, which may not be suitable for lightweight applications. Understanding the specific requirements of the intended use will help in making an informed purchasing decision.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of mesh and wire
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mesh and wire | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Reinforcement in concrete structures | Enhances structural integrity and load-bearing capacity | Material composition (e.g., galvanized vs. stainless steel), mesh size, and compliance with local building codes |
| Agriculture | Crop protection and fencing | Protects crops from pests and livestock, reducing losses | Durability against environmental factors, mesh size for specific crop types, and local availability |
| Mining | Filtration and safety barriers | Improves operational efficiency and worker safety | Compliance with safety regulations, mesh strength, and resistance to corrosion in harsh environments |
| Manufacturing & Processing | Filtration systems for liquids and gases | Ensures product quality and process efficiency | Mesh size and material compatibility with processed substances, ease of cleaning and maintenance |
| Architecture & Design | Decorative elements and architectural features | Enhances aesthetic appeal while providing functionality | Customization options, material selection for durability, and adherence to design specifications |
Construction
In the construction industry, mesh and wire are primarily used for reinforcing concrete structures, such as slabs, walls, and foundations. Welded wire mesh provides enhanced structural integrity, ensuring that buildings can withstand various loads and stresses. International buyers must consider the material composition, such as choosing between galvanized or stainless steel, depending on environmental conditions. Additionally, compliance with local building codes is crucial to ensure safety and durability.
Agriculture
Mesh and wire applications in agriculture include crop protection and fencing solutions. These materials help shield crops from pests and livestock, thereby reducing potential losses. For B2B buyers, sourcing durable mesh that can withstand harsh weather conditions is essential. The mesh size must also be suitable for the specific crops being protected, ensuring maximum effectiveness while considering local supply chains for timely availability.
Mining
In the mining sector, wire mesh is vital for filtration systems and safety barriers. It plays a crucial role in improving operational efficiency by separating materials and ensuring worker safety through effective containment. Buyers should focus on mesh strength and corrosion resistance, as mining environments can be particularly harsh. Compliance with safety regulations is also a critical consideration, ensuring that the selected mesh meets industry standards.
Manufacturing & Processing
Filtration systems in manufacturing and processing industries utilize mesh and wire to filter liquids and gases, ensuring product quality and operational efficiency. This application is particularly important in sectors such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. B2B buyers need to consider the compatibility of the mesh material with the substances being processed, as well as the mesh size for optimal filtration. Ease of cleaning and maintenance should also be factored into the sourcing process to minimize downtime.
Architecture & Design
In architecture and design, mesh and wire serve not only functional purposes but also aesthetic ones. They are used in decorative elements and architectural features, enhancing the visual appeal of structures while providing necessary functionality. Buyers should seek customization options that allow for unique designs, as well as durable materials that can withstand environmental factors. Adhering to design specifications is critical for ensuring that the final product meets both aesthetic and structural requirements.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mesh and wire
When selecting materials for mesh and wire applications, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that can significantly impact performance, durability, and cost. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in mesh and wire manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It is often rated for use in environments with extreme conditions, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and longevity, which can reduce replacement costs over time. However, it tends to be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel mesh is ideal for filtration applications, food processing, and environments where hygiene is critical. Its compatibility with various media, including corrosive substances, makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Europe, the preference for stainless steel is high due to stringent regulations regarding food safety and environmental impact.
Galvanized Steel
Key Properties:
Galvanized steel features a protective zinc coating that enhances corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. It can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, depending on the thickness of the steel.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of galvanized steel is its cost-effectiveness and decent durability. However, it may not perform well in highly corrosive environments, and the zinc coating can wear off over time, leading to rust.
Impact on Application:
Galvanized wire mesh is commonly used in fencing, construction, and agricultural applications where exposure to the elements is expected. Its affordability makes it a popular choice for large-scale projects.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of galvanized materials, especially in construction. Compliance with standards such as JIS and ASTM is crucial, particularly in regions like South America and Africa, where building codes may vary.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for applications where weight is a concern. It can withstand moderate temperatures but may not be suitable for high-pressure environments.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum is a significant advantage, facilitating easier handling and installation. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be more expensive than galvanized options.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum mesh is often used in architectural applications, such as decorative facades and screens, as well as in aerospace and automotive industries where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum in their region and any associated tariffs. Compliance with international standards is essential, particularly in Europe, where aluminum is widely used in construction and manufacturing.
Fiberglass
Key Properties:
Fiberglass mesh is non-metallic, offering excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. It can withstand a range of temperatures but is generally not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
Fiberglass is highly resistant to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for use in harsh environments. However, it may not be as strong as metal options and can be more susceptible to physical damage.
Impact on Application:
Fiberglass mesh is commonly used in applications such as pool enclosures, industrial filtration, and construction reinforcement, particularly in environments where metal corrosion is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure that fiberglass products meet local safety and performance standards, which can vary significantly between regions. Understanding the specific requirements of markets in Africa and the Middle East is crucial for successful procurement.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for mesh and wire | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Filtration, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Galvanized Steel | Fencing, construction | Cost-effective, decent durability | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Architectural, aerospace | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Fiberglass | Pool enclosures, industrial use | Chemical corrosion resistance | Susceptible to physical damage | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for mesh and wire, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mesh and wire
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for mesh and wire products is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of the typical stages involved in the production of mesh and wire, alongside the quality control measures essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance with international standards.
Manufacturing Process for Mesh and Wire
The manufacturing process for mesh and wire involves several key stages, which can vary slightly depending on the specific type of mesh being produced. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is selecting the appropriate raw materials. Common materials include galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and various alloys. The choice of material impacts the final product’s strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
- Wire Drawing: This involves reducing the diameter of the wire by drawing it through a series of dies. This process enhances the wire’s tensile strength and prepares it for subsequent stages.
- Coating: Depending on the intended application, wires may undergo surface treatments such as galvanization or coating with PVC to improve resistance against environmental factors.
2. Forming
The forming stage consists of converting prepared wires into mesh structures through either welding or weaving techniques.
- Welded Wire Mesh: In this method, wires are arranged in a grid pattern and welded at their intersections using automated welding machines. This process creates a rigid structure ideal for applications requiring strength and stability, such as in construction and fencing.
- Woven Wire Mesh: This technique interlaces wires using a loom, creating a flexible mesh suitable for filtration and architectural applications. The specific weave type (e.g., plain, twill, Dutch) can be customized to meet different needs.
3. Assembly
Once the mesh is formed, it may undergo assembly processes where larger panels are cut, stacked, or further processed into specific shapes or sizes. This stage may also include the integration of additional components, such as frames or support structures, depending on the product requirements.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves applying surface treatments to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. This may include:
- Surface Coating: Additional coatings or paints are applied to improve corrosion resistance and provide a protective layer.
- Quality Checks: Before the product is packaged and shipped, it undergoes several quality checks to ensure it meets specified standards.
Quality Assurance in Mesh and Wire Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, especially for B2B buyers who depend on consistent product quality. Several international and industry-specific standards guide QA practices, including ISO 9001, CE marking, and API standards.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is widely recognized across industries. Compliance indicates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: This certification demonstrates that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards, which is crucial for buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are vital for ensuring that products meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify issues early, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product is thoroughly inspected and tested before shipping to ensure it meets all relevant specifications and quality standards.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of mesh and wire products, including:
- Tensile Testing: To assess the strength and ductility of the wire.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: To evaluate how well the material withstands environmental factors.
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensures that products meet the specified dimensions and tolerances.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should implement strategies to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation of their quality control processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspection services to evaluate product quality before shipment, ensuring compliance with international standards.
Regional Considerations for B2B Buyers
When sourcing mesh and wire products from international suppliers, buyers must be aware of the nuances related to quality control and certification in their regions:
- Africa: Buyers should consider local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication about quality expectations.
- South America: Understanding local certifications and compliance requirements is essential. Buyers should verify that suppliers can meet both local and international standards.
- Middle East: Given the region’s diverse market, buyers must ensure that suppliers are familiar with the specific requirements of various industries, such as construction or oil and gas.
- Europe (e.g., Poland): Compliance with EU standards is crucial. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with CE marking and ISO certifications to ensure product quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for mesh and wire products, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Do You Know How Cable Made? Factory Wire Cable Manufacturing Process is Amazing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mesh and wire Sourcing
The sourcing of mesh and wire products involves a multifaceted cost structure and pricing dynamics that international B2B buyers must navigate effectively. Understanding these components can lead to better purchasing decisions and enhanced cost efficiency.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences costs. Common materials for wire mesh include galvanized steel, stainless steel, and low carbon steel. Prices fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with stable supply chains to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and impact the overall pricing of mesh products. In countries with higher labor costs, expect a premium on the final product. Conversely, regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but quality control may vary.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturers may have lower overhead costs, allowing them to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom mesh solutions often require specialized tooling, which can increase initial costs. However, investing in quality tooling can enhance production efficiency and product quality in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is essential to ensure product reliability. While this may add to the overall cost, it is crucial for preventing costly defects and maintaining customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and geopolitical stability. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital to clarify responsibilities and manage logistics expenses effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s positioning strategy.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. International buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs while maximizing cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products may incur additional costs due to specialized manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials often come at a premium but can provide long-term savings through durability and reduced failure rates. Certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can also influence pricing, as they assure compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of a supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their quality assurance processes, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for international transactions. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, impacting overall costs, especially in logistics and insurance.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to significant savings. Buyers should prepare by understanding market prices and being ready to discuss terms that can benefit both parties.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also shipping, installation, maintenance, and disposal costs. Evaluating TCO can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade tariffs that can affect pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers may provide insights into regional pricing trends and potential savings.
Disclaimer
Prices for mesh and wire products are indicative and can vary widely based on specific project requirements, regional market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential mesh and wire Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘mesh and wire’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mesh and wire
Key Technical Properties of Mesh and Wire
Understanding the essential technical properties of mesh and wire is crucial for international B2B buyers. Here are several key specifications that influence product selection and performance:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the quality and type of metal used in mesh and wire production, such as stainless steel, galvanized steel, or aluminum.
– Importance: The choice of material impacts durability, resistance to corrosion, and suitability for specific applications. For instance, stainless steel is preferred in environments prone to rust, while galvanized steel is often used for outdoor fencing due to its protective coating. -
Wire Diameter
– Definition: Wire diameter is the thickness of the wire used in the mesh, typically measured in millimeters or gauge.
– Importance: A thicker wire generally provides greater strength and load-bearing capacity, which is essential for structural applications. Buyers should align wire diameter with the intended use, such as heavy-duty fencing or lightweight sieving. -
Mesh Opening Size
– Definition: Mesh opening size refers to the dimensions of the gaps in the mesh, which can vary based on application requirements.
– Importance: This specification determines the flow of air, liquid, or solids through the mesh. For filtration applications, precise opening sizes are critical to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. -
Tensile Strength
– Definition: Tensile strength is the maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing.
– Importance: High tensile strength is vital in applications where the mesh will experience tension or heavy loads. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers select the right mesh for demanding environments, such as construction or industrial settings. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during the manufacturing process.
– Importance: Tighter tolerances ensure better fit and function, especially in critical applications like architectural designs or machinery components. Buyers should specify tolerance levels to avoid issues during installation or operation.
Common Trade Terminology
Navigating the trade terminology associated with mesh and wire is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Context: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify potential suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems or machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Context: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate favorable terms without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specified products or services.
– Context: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. It is a standard practice in procurement that fosters transparency. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Context: Incoterms clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms can prevent misunderstandings in international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Context: Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should confirm lead times with suppliers to ensure timely delivery and avoid project delays.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Certification Standards
– Definition: Industry standards that products must meet to ensure quality and safety, such as ISO or ASTM.
– Context: Certifications provide assurance regarding product quality and compliance with international regulations. Buyers should verify certifications to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize procurement processes, and foster successful international partnerships.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the mesh and wire Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global mesh and wire market is experiencing significant transformation driven by advancements in technology, rising demand for versatile applications, and an increasing emphasis on sustainability. Key market drivers include industrialization in emerging economies, particularly in Africa and South America, and an uptick in construction activities in the Middle East and Europe. For instance, Brazil and Poland are seeing increased investments in infrastructure, leading to a greater demand for durable wire mesh products for construction and fencing.
Current and emerging B2B technology trends include the adoption of automation and digital manufacturing processes, which enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. Automated welding and weaving technologies allow manufacturers to produce customized mesh solutions quickly, catering to the specific needs of diverse industries. Furthermore, the use of smart technology for inventory management and supply chain optimization is gaining traction, enabling international buyers to streamline sourcing processes and reduce lead times.
The market dynamics for international B2B buyers are shifting towards localized sourcing strategies. Many companies are seeking suppliers closer to their operational bases to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where logistical challenges can impact delivery timelines. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers that demonstrate commitment to environmentally friendly practices and materials.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As environmental concerns gain prominence, the mesh and wire sector is under pressure to adopt sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. The environmental impact of wire mesh production can be significant, particularly in terms of energy consumption and resource use. International B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, such as recycled metals and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ certifications and materials is on the rise. Buyers should actively seek products that are certified for sustainable sourcing, as this not only enhances their brand reputation but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. By integrating sustainability into their sourcing strategies, international buyers can contribute to a more responsible and sustainable mesh and wire market.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of wire mesh dates back to the 18th century, where its manufacturing was heavily influenced by advancements in textile technologies. Initially utilized for various industrial applications, the versatility of wire mesh expanded with the industrial revolution, particularly in the paper industry and mining safety equipment. The introduction of automated weaving and welding techniques in the early 20th century marked a significant leap forward, allowing for mass production and customization of wire mesh products. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers as it underscores the long-standing relevance and adaptability of wire mesh in meeting diverse industrial needs.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mesh and wire
-
How should I vet suppliers when sourcing mesh and wire internationally?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their certifications, reputation, and production capabilities. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications, as this indicates adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, request references from previous clients and seek feedback on their experiences. Conducting on-site visits or virtual audits can provide insights into their facilities and processes. Lastly, utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to assess supplier ratings and reviews. -
Can I customize my mesh and wire orders?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options based on your specific requirements. This can include variations in wire gauge, mesh opening size, material type (such as stainless steel or galvanized), and surface treatments (like coatings). When placing an order, provide detailed specifications and discuss any design nuances with your supplier to ensure they can meet your needs effectively. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for mesh and wire products?
MOQs can vary widely depending on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 square meters for standard items, while custom orders may have higher MOQs. Lead times typically range from 2 to 6 weeks, influenced by factors such as product complexity and production schedules. Always confirm these details upfront to align your procurement timelines with your project needs. -
What payment options should I consider when importing mesh and wire?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common options include wire transfers, letters of credit (LC), and PayPal. Wire transfers are standard for larger orders, while LCs provide added security for both parties. Ensure you discuss payment terms and conditions upfront, including any required deposits. Additionally, consider using escrow services to protect your funds until goods are received in satisfactory condition. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for my orders?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes and certifications from your supplier. This may include ISO certifications, material test reports, and compliance with industry standards relevant to your application. Some suppliers may offer third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipping. Establishing clear quality expectations and conducting inspections upon receipt can help mitigate risks. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping?
When planning logistics, consider factors such as shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery times. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in your supplier’s region to navigate these complexities. Ensure you understand the Incoterms being used, as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Additionally, plan for potential delays due to customs checks or local regulations that may affect the import process. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To manage disputes, maintain open and clear communication with your supplier from the outset. Document all agreements, specifications, and correspondences to have a clear record. If issues arise, address them promptly, focusing on collaborative solutions. Consider mediation or arbitration as a means to resolve conflicts without escalating to legal action. Familiarize yourself with the supplier’s dispute resolution policies to streamline the process. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with mesh and wire suppliers?
Building a strong partnership involves regular communication, timely payments, and providing constructive feedback. Engage in periodic reviews of product quality and service levels to ensure alignment with your expectations. Consider joint development projects or collaborative initiatives to foster innovation. Long-term relationships can lead to better pricing, priority production, and improved service, benefiting both parties in the long run.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mesh and wire
In navigating the dynamic landscape of mesh and wire sourcing, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic partnerships and informed decision-making. The diverse applications of wire mesh—from industrial filtration to architectural uses—underscore the importance of selecting the right type and specifications tailored to specific needs. Understanding the manufacturing processes, such as welding and weaving, is crucial for evaluating product quality and supplier capabilities.
Buyers should leverage local insights and supplier relationships, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By fostering these connections, businesses can not only reduce lead times but also optimize costs and enhance product availability. Investing in strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also empowers companies to innovate and stay competitive.
As we look ahead, the demand for customized and high-quality mesh solutions is expected to grow. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate flexibility, sustainability practices, and a commitment to quality. Seize this opportunity to enhance your supply chain by exploring partnerships that align with your strategic goals. Embrace the future of sourcing mesh and wire with confidence, ensuring that your business remains resilient and adaptive in an ever-evolving market.