Master Sourcing Strategies for Mesh Wiring: A Comprehensive
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mesh wiring
Navigating the global market for mesh wiring is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains and enhance product reliability. Mesh wiring serves a crucial role across various industries, including construction, automotive, and electronics, where it is utilized for everything from structural reinforcement to electrical connectivity. Understanding the nuances of mesh wiring—such as types, materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards—can significantly impact sourcing decisions and operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide will delve into critical aspects of mesh wiring, including an overview of the different types available, the materials commonly used, and the manufacturing and quality control practices that ensure product integrity. Furthermore, it will provide insights into reputable suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends. By addressing frequently asked questions, this guide aims to empower buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (such as Spain and Argentina), with the knowledge necessary to make informed sourcing decisions.
Equipped with this information, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the global mesh wiring market, ultimately leading to improved procurement strategies, reduced costs, and enhanced product performance. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your sourcing processes and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
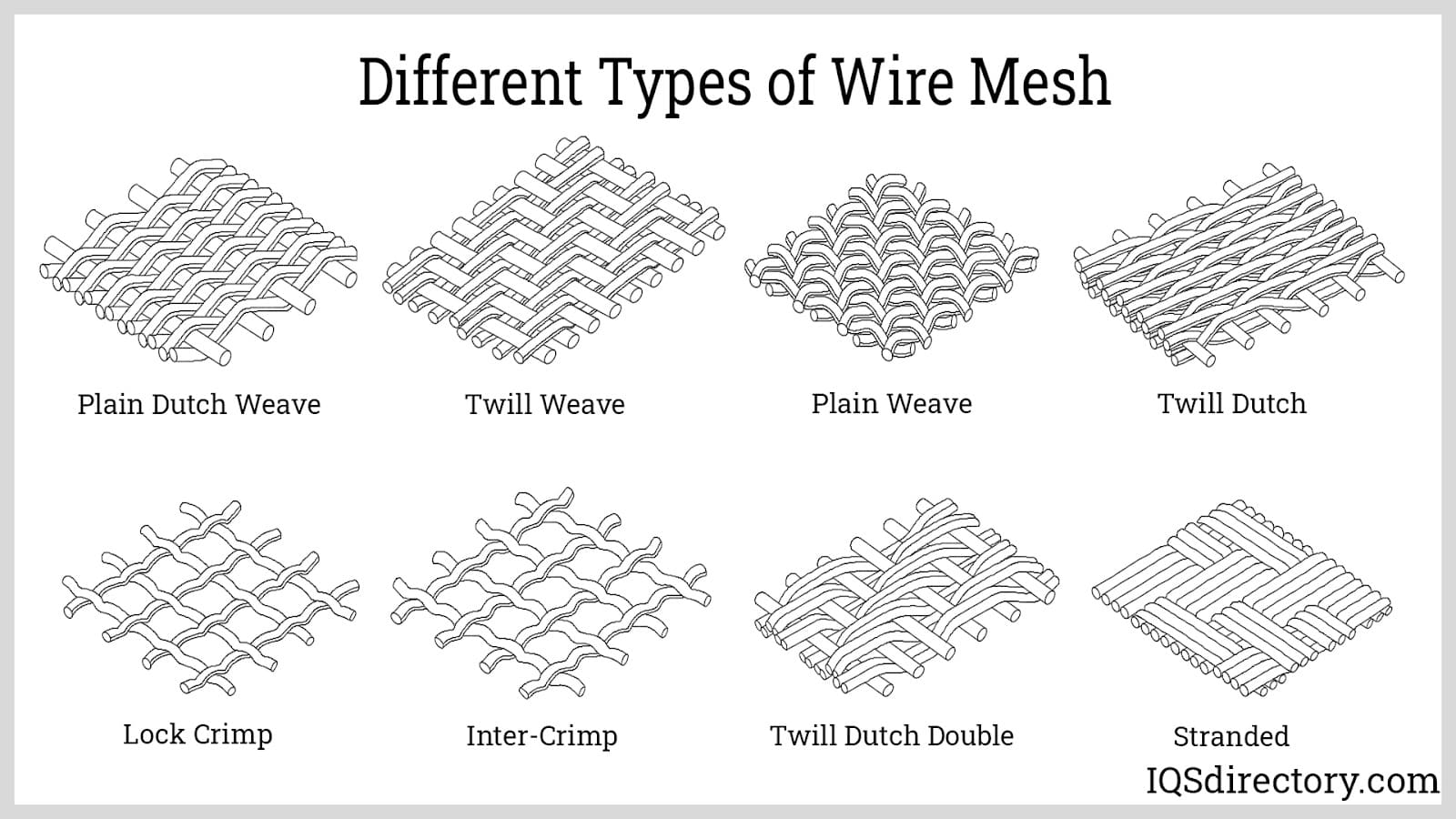
Understanding mesh wiring Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woven Mesh Wiring | Interlaced wires creating a flexible structure. | Automotive, aerospace, and textiles. | Pros: High durability; flexible. Cons: May require more maintenance. |
| Expanded Metal Mesh | Made from a single sheet of metal, expanded into a mesh. | Construction, safety barriers, and filtration. | Pros: Lightweight; cost-effective. Cons: Limited flexibility in design. |
| Wire Cloth Mesh | Consists of woven wire strands, often stainless steel. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. | Pros: Corrosion-resistant; easy to clean. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Knitted Wire Mesh | Made from interlocking wire loops, providing elasticity. | Medical devices and filtration systems. | Pros: Excellent flexibility; customizable. Cons: Can be less durable under stress. |
| Chain Link Mesh | Formed by interlocking zigzag wires, typically galvanized. | Fencing, security, and sports enclosures. | Pros: Affordable; quick installation. Cons: Less aesthetic appeal; limited privacy. |
Woven Mesh Wiring
Woven mesh wiring is characterized by interlaced wires that create a flexible and durable structure. This type is widely used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where lightweight yet strong materials are essential. When considering woven mesh, buyers should evaluate the material’s flexibility and maintenance requirements, as it may need regular inspections and repairs depending on the application.
Expanded Metal Mesh
Expanded metal mesh is produced by cutting and stretching a single sheet of metal, resulting in a lightweight yet robust mesh. It is commonly utilized in construction, safety barriers, and filtration systems. B2B buyers appreciate its cost-effectiveness and strength, but should be aware that its rigid structure may limit design flexibility for specific applications.
Wire Cloth Mesh
Wire cloth mesh is constructed from woven wire strands, often using stainless steel, making it an ideal choice for environments that require corrosion resistance, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Its ease of cleaning is a significant advantage for B2B buyers, though the initial investment can be higher compared to other types of mesh. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of durability and hygiene in their purchasing decisions.
Knitted Wire Mesh
Knitted wire mesh features interlocking wire loops that provide excellent elasticity and flexibility. This type is particularly suitable for medical devices and filtration systems, where adaptability is crucial. While it offers customization options, B2B buyers should weigh the potential trade-offs in durability under stress, as knitted mesh may not withstand heavy loads as effectively as other types.
Chain Link Mesh
Chain link mesh is formed by interlocking zigzag wires, typically galvanized for weather resistance. It is widely used in fencing, security applications, and sports enclosures due to its affordability and quick installation. However, buyers should consider the aesthetic aspects and the level of privacy it offers, as chain link mesh may not be suitable for applications requiring a more visually appealing or secure barrier.
Related Video: What are Transformer Models and how do they work?
Key Industrial Applications of mesh wiring
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mesh wiring | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Reinforcement in concrete structures | Enhances structural integrity and durability | Sourcing high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials |
| Telecommunications | Antenna mesh for signal distribution | Improves signal strength and coverage | Ensuring compatibility with existing network infrastructure |
| Agriculture | Crop protection and fencing solutions | Safeguards crops from pests and animals | Sourcing locally available materials to reduce costs |
| Automotive | Wiring harnesses for electrical systems | Increases safety and reliability of vehicles | Compliance with international safety standards |
| Mining | Safety barriers and equipment protection | Reduces accidents and enhances operational safety | Durability against harsh environmental conditions |
Construction
In the construction industry, mesh wiring is primarily used as reinforcement in concrete structures. It enhances the structural integrity and durability of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructures. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality, corrosion-resistant mesh is crucial due to varying environmental conditions that can affect longevity. Local sourcing options can also provide cost advantages while ensuring compliance with regional construction standards.
Telecommunications
Mesh wiring plays a critical role in telecommunications, particularly in the creation of antenna systems for signal distribution. By using mesh wiring, companies can improve signal strength and coverage, which is essential for maintaining robust communication networks. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the compatibility of mesh wiring with existing network infrastructure to ensure seamless integration and performance.
Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, mesh wiring is widely utilized for crop protection and fencing solutions. It serves as an effective barrier against pests and animals, thereby safeguarding crops and ensuring better yields. For B2B buyers in regions like South America and Africa, sourcing locally available materials can significantly reduce costs while addressing specific agricultural challenges. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding agricultural fencing can aid in compliance and operational efficiency.
Automotive
The automotive industry employs mesh wiring in wiring harnesses for electrical systems, which are crucial for vehicle safety and reliability. The use of mesh wiring helps manage the complex electrical systems found in modern vehicles, contributing to enhanced safety features. International buyers, especially from Europe, must ensure that the sourced materials comply with stringent safety standards to avoid liabilities and enhance vehicle performance.
Mining
In mining operations, mesh wiring is utilized for safety barriers and equipment protection. It reduces the likelihood of accidents by providing necessary safeguards around hazardous areas and machinery. For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, sourcing durable mesh that can withstand harsh environmental conditions is essential. Understanding the specific safety regulations of the mining sector in their region will help buyers select the appropriate mesh wiring solutions that meet compliance and operational safety requirements.
Related Video: Industrial Wiring Tips and Tricks
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mesh wiring
When selecting materials for mesh wiring, international B2B buyers must consider the unique properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. Here, we analyze four common materials used in mesh wiring: stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and nylon. This analysis will provide actionable insights for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C). It is also non-magnetic, making it suitable for applications where magnetic interference is a concern.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can endure harsh environments and has a long lifespan. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which may affect budget constraints. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for specialized tools and techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications involving corrosive environments, such as chemical processing and food production. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel. In regions like Europe, adherence to the EU’s REACH regulations is crucial.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and can be anodized for enhanced durability. It typically performs well at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which simplifies handling and installation. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be prone to deformation under high stress. Additionally, aluminum is more susceptible to corrosion in saline environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries, where weight reduction is critical. It is also used in environments that do not involve harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the relevant standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In Europe, compliance with EN 573 is important.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical applications. It has moderate corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 200°C.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which is essential for electrical mesh wiring. However, it is heavier than aluminum and more expensive than both aluminum and nylon. Additionally, copper can tarnish over time, which may impact aesthetics and performance.
Impact on Application: Copper is primarily used in electrical applications, including wiring and grounding systems. Its compatibility with electrical media makes it indispensable in the electronics industry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential. Buyers should also consider the implications of copper theft, which is a significant issue in some regions.
Nylon
Key Properties: Nylon is a synthetic polymer known for its flexibility, lightweight nature, and resistance to abrasion. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and is resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility and lightweight characteristics of nylon make it easy to handle and install. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to metals and can degrade under UV exposure, making it less suitable for outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: Nylon is often used in applications requiring flexibility, such as in automotive and consumer goods. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM D4066 for nylon materials. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for mesh wiring | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food production | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight, easy to handle | Less durable, prone to deformation | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical applications | Superior electrical conductivity | Heavy, susceptible to tarnishing | High |
| Nylon | Automotive, consumer goods | Flexible, lightweight | Lower tensile strength, UV degradation | Low |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding mesh wiring materials, considering both performance and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mesh wiring
The manufacturing of mesh wiring involves several critical stages, each of which is essential for ensuring high-quality end products. Understanding these processes and the corresponding quality assurance measures is vital for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes for Mesh Wiring
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of mesh wiring manufacturing focuses on selecting and preparing raw materials. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and high-strength polymers. The quality of these materials directly impacts the durability and performance of the mesh. Key steps in this stage include:
- Material Sourcing: Choose suppliers who provide certified materials to ensure compliance with international standards.
- Material Inspection: Conduct Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks to assess the physical and chemical properties of the materials before processing.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next step involves forming the mesh. This process can vary depending on the type of mesh being produced (e.g., welded, woven, or knitted). Key techniques include:
- Welding: For welded mesh, wires are cut to size and then welded at their intersections using electric resistance methods. This technique offers high strength and durability.
- Weaving: In woven mesh, wires are interlaced in a specific pattern. This method is often used for applications requiring flexibility.
- Knitting: This technique produces mesh that is lightweight and has excellent airflow properties, suitable for various industrial applications.
3. Assembly
After forming, the next step is assembly, where the individual mesh pieces are combined into larger sections or specific configurations as per customer requirements. This process may involve:
- Joining Techniques: Employ methods like crimping, sewing, or additional welding to achieve the desired mesh structure.
- Customization: B2B buyers often require customized mesh sizes and shapes, necessitating close collaboration with manufacturers during this phase.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the mesh’s performance and appearance. This may involve:
- Surface Treatments: Techniques such as galvanization, powder coating, or anodizing can provide corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Quality Checks: Conduct thorough inspections to ensure that the finished mesh meets specified tolerances and surface finish standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process for mesh wiring. International and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining quality throughout production.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries. Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For mesh used in oil and gas applications, adherence to API standards ensures that products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
QC Checkpoints
To maintain high quality throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing stages to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough examination of the finished products before they leave the facility, ensuring they meet all quality and regulatory requirements.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality and performance of mesh wiring, including:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and elasticity of the mesh.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Assesses the material’s durability against environmental factors.
- Mesh Opening Size Verification: Ensures that the openings in the mesh meet specified dimensions for their intended use.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality assurance practices is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their quality management systems, production capabilities, and adherence to international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation detailing the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes, as well as any certifications or compliance reports.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to conduct quality assessments, providing an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
QC/Cert Nuances for International B2B Buyers
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality certification and assurance:
- Regional Standards Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international standards, as regional regulations may differ significantly.
- Cultural Differences: Understand that manufacturing practices and quality expectations may vary across regions. Establish clear communication and expectations with suppliers to avoid misunderstandings.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Develop relationships with suppliers that promote transparency, allowing for better oversight of the production process and quality assurance practices.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for mesh wiring, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions and ensure the reliability and quality of their products.
Related Video: Top 5 Mass Production Techniques: Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mesh wiring Sourcing
When sourcing mesh wiring, understanding the cost structure and pricing influences is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis aims to break down the key cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in mesh wiring is the raw materials used, typically consisting of metal wires (such as stainless steel or aluminum) and coatings (like PVC or vinyl). Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and raw material availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Western Europe, the overall manufacturing expense will be higher. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs may offer savings but could impact quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production facilities with advanced technology can reduce overhead costs, thus affecting the pricing of mesh wiring.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for manufacturing mesh wiring requires specific tooling, which can be a significant investment. This cost is amortized over production volume, meaning larger orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specified standards involves costs related to testing and inspection. Certifications (like ISO) can add to expenses but may be necessary for certain markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on the distance, mode of transport, and volume. Buyers should consider the Incoterms applicable, as they define responsibilities and risks related to shipping.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit. This can vary based on market competition and supplier relationships.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often qualify for lower prices due to economies of scale. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also dictate pricing; negotiating lower MOQs can be beneficial for smaller businesses.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs may incur additional costs. Providing clear specifications can help avoid unexpected charges and delays.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials or specific certifications can increase costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in your contract can significantly impact total costs, as they dictate who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Always seek to negotiate prices, especially for larger orders. Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and logistics. A cheaper initial price may result in higher costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, buyers from Europe might find different price structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to varying economic conditions and labor costs.
-
Request Quotes from Multiple Suppliers: This practice helps in benchmarking prices and understanding the market rate for the required specifications.
-
Be Mindful of Currency Fluctuations: When dealing with international suppliers, currency exchange rates can impact costs. Locking in prices when rates are favorable can be advantageous.
Disclaimer
The prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.
Spotlight on Potential mesh wiring Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘mesh wiring’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mesh wiring
Key Technical Properties of Mesh Wiring
Understanding the technical specifications of mesh wiring is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating suppliers and making purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The grade of material used in mesh wiring, often stainless steel, aluminum, or coated wire, significantly influences durability and corrosion resistance. Buyers should assess the specific environment in which the wiring will be used to ensure optimal performance and longevity. -
Wire Diameter
The wire diameter directly affects the strength and flexibility of the mesh. Thicker wires provide greater strength and load-bearing capacity, while thinner wires offer more flexibility. Understanding the application requirements helps in selecting the appropriate diameter. -
Mesh Opening Size
This refers to the size of the openings between the wires in the mesh. The opening size is critical for applications that require specific filtering or containment properties. For example, smaller openings may be necessary for security fencing, while larger openings may suffice for agriculture. -
Tensile Strength
This property measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that the mesh can withstand before failure. High tensile strength is vital for applications subjected to heavy loads or harsh conditions, ensuring reliability and safety in use.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in dimensions of the mesh wiring. Accurate tolerances are essential for ensuring that the mesh fits properly in its intended application, reducing the risk of installation issues or structural failures. -
Finish and Coating
The finish (e.g., galvanized, PVC coated) provides additional protection against environmental factors. Different coatings can enhance corrosion resistance, UV protection, and overall aesthetics, making it essential for buyers to consider the specific requirements of their projects.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to mesh wiring:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure quality.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller businesses or those testing new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products. Buyers should use RFQs to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed comparisons and negotiations. -
Incoterms
These are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, EXW) is critical for managing shipping costs and responsibilities effectively. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Awareness of lead times helps in planning projects and managing expectations regarding delivery schedules. -
Certification Standards
Certifications (such as ISO, ASTM) indicate that a product meets specific industry standards for quality and safety. Buyers should verify certifications to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhancing their procurement processes and ensuring they select the best mesh wiring solutions for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the mesh wiring Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The mesh wiring sector is experiencing significant shifts driven by global demand for connectivity and efficiency in various applications, including telecommunications, construction, and agriculture. Key drivers include the increasing need for robust infrastructure in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, coupled with the push for smart technologies in developed regions like Europe and the Middle East. International B2B buyers are witnessing a surge in demand for lightweight yet durable materials that can withstand environmental challenges, which mesh wiring readily provides.
Emerging trends in sourcing include the adoption of advanced digital procurement solutions that enhance transparency and reduce lead times. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to identify optimal suppliers and to negotiate better terms, fostering a collaborative environment that supports innovation. Furthermore, as supply chains continue to evolve, there is a pronounced shift towards local sourcing to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and transportation disruptions. Buyers in regions such as Spain and Argentina are particularly focused on sourcing from suppliers who can offer competitive pricing without compromising quality.
The integration of IoT technologies within mesh wiring applications is also gaining traction. This trend is notable in sectors like agriculture, where smart mesh networks facilitate efficient resource management. As a result, buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers who are not only providing high-quality products but also embracing technological advancements that enhance product functionality.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of sourcing materials for mesh wiring cannot be overstated. As global attention shifts towards sustainable practices, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing standards and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This includes assessing the lifecycle of materials used in production, from extraction to disposal, and ensuring that they are sourced responsibly.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications into procurement processes is becoming essential. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for sustainable building practices are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should actively seek out mesh wiring products made from recycled materials or those that utilize eco-friendly manufacturing processes, as these options not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation.
Moreover, the emphasis on ethical supply chains extends to fair labor practices and community engagement. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their operations and contribute positively to local economies. This holistic approach to sustainability not only meets regulatory requirements but also resonates with increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Brief Evolution/History
The mesh wiring sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from traditional metal and wire frameworks to innovative solutions that incorporate advanced materials such as polymer and composite fibers. Initially, mesh wiring was primarily used in construction and security applications. However, advancements in technology have broadened its applications to include telecommunications, agriculture, and even art installations.
As the demand for connectivity and efficiency grew, manufacturers began to explore new production methods, including 3D printing and automated manufacturing processes, which have allowed for greater customization and efficiency. This evolution has positioned mesh wiring as a critical component in various industries, aligning with the global trend towards smart infrastructure and sustainable development. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with current market dynamics and future trends.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mesh wiring
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for mesh wiring?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, reputation, and compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients and check their certifications (ISO, CE, etc.). It’s beneficial to conduct a factory visit or utilize third-party inspection services to assess production capabilities and quality control processes. Additionally, evaluate their financial stability and ability to handle your order volume, especially if you’re sourcing from regions with varying economic conditions. -
Can I customize mesh wiring products to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for mesh wiring. Discuss your specific requirements regarding dimensions, materials, and coating finishes with potential suppliers. Ensure that the supplier has the capability to produce customized products without significantly affecting lead times or costs. It’s advisable to request samples before committing to a larger order to ensure that the final product meets your specifications. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for mesh wiring?
MOQs for mesh wiring can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs can range from 500 to 5,000 units. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the supplier’s production schedule and your customization requirements. Always confirm these details upfront and consider potential delays due to logistics or raw material availability, especially when sourcing internationally. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing mesh wiring?
Payment terms can differ by supplier and region. Common arrangements include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. It’s prudent to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions. Be aware of the implications of currency fluctuations, especially when dealing with suppliers across different continents. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for mesh wiring?
Request documentation proving that the mesh wiring complies with relevant international standards and certifications. Ask for test reports from accredited laboratories, including tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and safety compliance. Establish a clear quality assurance process with the supplier, including regular inspections and testing of raw materials and finished products to mitigate risks of defects or non-compliance. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing mesh wiring?
Logistics can significantly affect your supply chain efficiency. Understand the shipping terms (Incoterms) and the responsibilities of both parties regarding shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties. Consider working with a logistics partner who has experience in international shipping to navigate customs regulations and ensure timely delivery. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs or trade restrictions that may apply based on the origin of the mesh wiring. -
How should I handle disputes with my mesh wiring supplier?
To manage disputes effectively, establish a clear communication protocol with your supplier from the outset. Document all agreements and communications to provide a clear record if issues arise. If a dispute occurs, attempt to resolve it amicably through negotiation. If necessary, escalate the issue to mediation or arbitration as per the terms outlined in your contract. Always include a clause for dispute resolution in your agreements to safeguard your interests. -
What factors should I consider regarding the environmental impact of mesh wiring production?
Evaluate suppliers based on their commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste during production. Request information about their environmental certifications and adherence to regulations like REACH or RoHS. Understanding the environmental impact not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances your brand reputation, especially in markets where consumers prioritize eco-friendly products.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mesh wiring
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for mesh wiring presents an invaluable opportunity for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing a collaborative approach with suppliers, businesses can unlock significant cost savings while ensuring quality and reliability in their supply chains. Key takeaways include leveraging data-driven decision-making, fostering supplier relationships, and employing advanced procurement technologies to streamline operations and enhance value.
As the demand for mesh wiring continues to grow across diverse sectors, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, organizations must remain agile and proactive. Embracing a strategic sourcing mindset not only mitigates risks associated with price volatility and supply chain disruptions but also positions companies for sustainable growth in a competitive landscape.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should act now to reassess their sourcing strategies, seek innovative partnerships, and invest in long-term supplier collaborations. This forward-thinking approach will not only enhance operational efficiency but also drive profitability in the ever-evolving marketplace.