Master Sourcing Strategies for Pneumatic and Hydraulic
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pneumatic and hydraulic
In today’s competitive global landscape, the significance of pneumatic and hydraulic systems cannot be overstated. These technologies are integral to various industries, from manufacturing and construction to automotive and aerospace. By harnessing the power of pressurized fluids, pneumatic and hydraulic systems enable efficient operation, precise control, and enhanced productivity. For international B2B buyers, understanding these systems is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of pneumatic and hydraulic systems, covering essential topics such as types, materials, manufacturing and quality control, suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends. It also addresses frequently asked questions, providing valuable insights to navigate the complexities of sourcing these critical components.
Particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this guide empowers decision-makers to identify reliable suppliers, evaluate product quality, and optimize procurement strategies. By leveraging this information, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Whether you are looking to upgrade existing systems or implement new solutions, understanding the nuances of pneumatic and hydraulic technologies will enable you to make strategic choices that drive your business forward. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your operations with informed decisions backed by this essential resource.
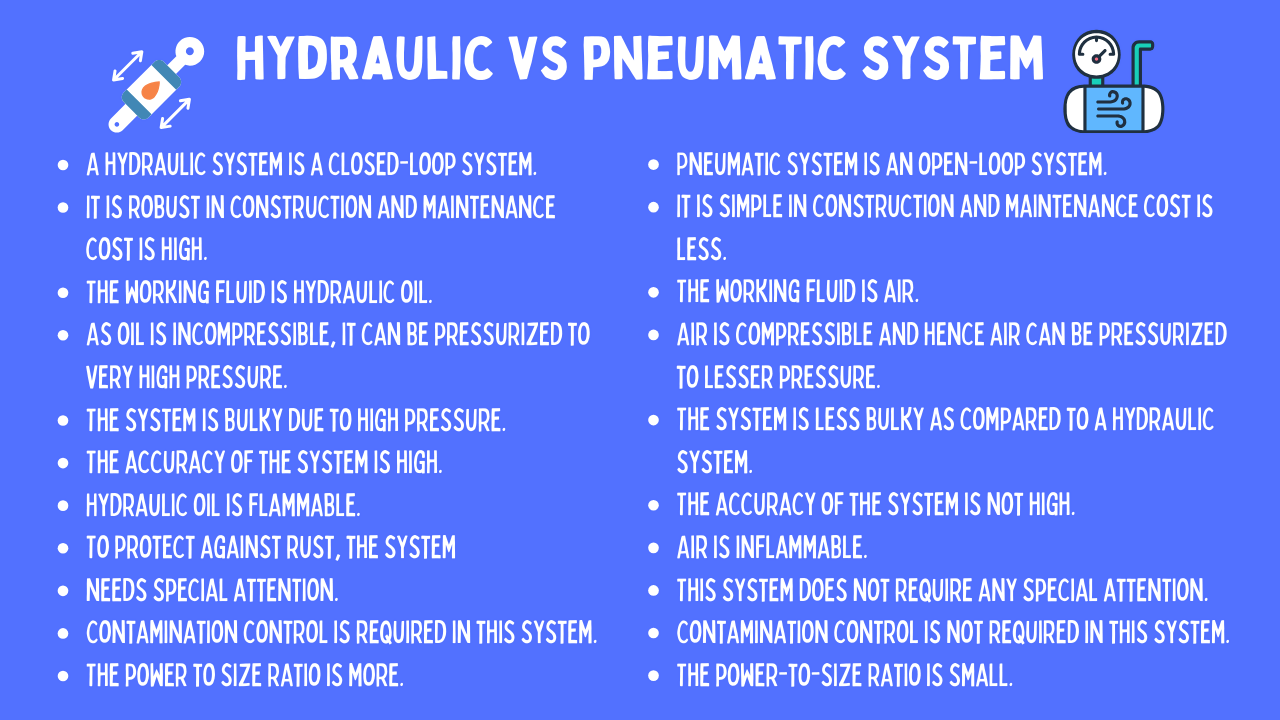
Understanding pneumatic and hydraulic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Cylinders | Utilize liquids for power transmission; offer high force and precision. | Construction equipment, automotive systems, aerospace. | Pros: High power density, precise control. Cons: Heavier, potential for leaks. |
| Pneumatic Cylinders | Use compressed air; typically lighter and faster than hydraulic systems. | Manufacturing automation, packaging, and assembly lines. | Pros: Quick response, cleaner operation. Cons: Limited force compared to hydraulics. |
| Hydraulic Pumps | Convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy; essential for system operation. | Industrial machinery, hydraulic presses, and lifts. | Pros: Efficient energy transfer, customizable pressure settings. Cons: Maintenance can be complex. |
| Pneumatic Actuators | Convert compressed air into mechanical motion; simpler design. | Robotics, material handling, and food processing. | Pros: Easy installation, low maintenance. Cons: Less powerful than hydraulic alternatives. |
| Hydraulic Power Units (HPUs) | Centralized units that supply hydraulic power to various components. | Oil and gas, manufacturing, and construction. | Pros: Versatile and scalable, can operate multiple systems. Cons: Requires careful installation and monitoring. |
Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders are robust devices that use pressurized liquid to generate force, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. They are commonly employed in construction equipment, automotive systems, and aerospace applications where high precision and power are critical. When considering hydraulic cylinders, buyers should assess the required force output, operating environment, and potential maintenance needs, including leak prevention and fluid management.
Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders operate using compressed air, providing a lighter and faster alternative to hydraulic systems. They are widely used in manufacturing automation, packaging, and assembly lines where quick actuation is essential. Buyers should evaluate the speed requirements, cycle frequency, and environmental conditions, such as cleanliness and temperature, to ensure pneumatic cylinders meet their operational needs.
Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps are crucial for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, serving as the heart of hydraulic systems. They are often found in industrial machinery, hydraulic presses, and lifts. When purchasing hydraulic pumps, businesses should consider factors such as flow rate, pressure capacity, and compatibility with existing systems to ensure efficient operation and longevity.
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to create mechanical motion, characterized by their simple design and ease of installation. They are commonly used in robotics, material handling, and food processing applications. Buyers should focus on the actuator’s speed, stroke length, and environmental compatibility to ensure optimal performance in their specific applications.
Hydraulic Power Units (HPUs)
Hydraulic Power Units (HPUs) are centralized systems that supply hydraulic power to various components, making them essential in industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, and construction. HPUs offer versatility and scalability, enabling them to support multiple systems simultaneously. Buyers should consider the unit’s power output, space requirements, and maintenance protocols to ensure reliable performance in demanding environments.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of pneumatic and hydraulic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pneumatic and hydraulic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines using pneumatic actuators | Increased efficiency and reduced labor costs | Quality of components, supplier reliability, and after-sales support |
| Construction | Hydraulic cranes for lifting heavy materials | Enhanced safety and productivity in lifting operations | Compliance with local safety regulations and certifications |
| Automotive | Hydraulic systems in braking and steering mechanisms | Improved vehicle safety and performance | Compatibility with existing systems and maintenance services |
| Food and Beverage | Pneumatic systems for packaging and bottling processes | Higher production rates and reduced contamination risks | Hygiene standards compliance and energy efficiency |
| Mining and Heavy Equipment | Hydraulic excavators for earth-moving tasks | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Equipment durability and local availability of parts |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, pneumatic systems are often deployed in automated assembly lines where precision and speed are critical. Pneumatic actuators enable fast and reliable movements, which enhance production rates while minimizing manual labor. For international buyers, it is essential to ensure that components meet stringent quality standards and that suppliers can provide robust after-sales support to maintain operational efficiency.
Construction
Hydraulic cranes are indispensable in the construction industry for lifting heavy materials such as steel beams and concrete blocks. These systems allow for safer and more efficient operations, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that comply with local safety regulations and offer equipment that meets the required certifications, especially in regions with stringent safety standards.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, hydraulic systems are critical for the functionality of braking and steering mechanisms. These systems enhance vehicle safety and performance by providing reliable and responsive control. International buyers must consider the compatibility of hydraulic components with existing systems and ensure that suppliers can provide ongoing maintenance services to avoid operational disruptions.
Food and Beverage
Pneumatic systems are widely used in the food and beverage industry for packaging and bottling processes. These systems help achieve higher production rates while minimizing contamination risks, which is crucial for maintaining product quality. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing equipment that complies with hygiene standards and offers energy efficiency to reduce operational costs.
Mining and Heavy Equipment
Hydraulic excavators are essential in the mining and heavy equipment sector for performing earth-moving tasks. These machines enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime, which is vital in industries where time is money. Buyers should prioritize the durability of equipment and the local availability of parts to ensure minimal disruption to operations, especially in remote locations.
Related Video: Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems – An Introduction
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pneumatic and hydraulic
When selecting materials for pneumatic and hydraulic systems, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance, durability, cost, and compliance with industry standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in these systems, providing insights into their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for specific markets.
1. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. It typically has a temperature rating up to 500°F (260°C) and excellent corrosion resistance when treated with coatings or stainless steel variants.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s main advantage is its strength and ability to withstand high pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, it can be heavier than other materials, which may increase manufacturing complexity and shipping costs. Additionally, untreated steel is susceptible to corrosion, necessitating protective measures.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of hydraulic fluids and gases, but care must be taken with corrosive media. Its robust nature makes it suitable for industrial machinery, construction equipment, and automotive applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and ISO. In Europe and the Middle East, adherence to EN standards is critical. Buyers should also consider sourcing from local suppliers to reduce costs and lead times.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C). It is also known for its excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce overall system weight and improve efficiency. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, making it less suitable for high-pressure applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel in some regions.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in pneumatic systems where weight savings are crucial, such as in aerospace and automotive applications. It is compatible with air and many non-corrosive hydraulic fluids.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of specific alloy grades that comply with regional standards. In Europe, for example, EN standards apply, while ASTM standards are relevant in North America. Understanding local market preferences for aluminum grades can also inform purchasing decisions.
3. Polyurethane
Key Properties:
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer with excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility. It can operate within a temperature range of -40°F to 200°F (-40°C to 93°C) and is resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The flexibility and lightweight nature of polyurethane make it ideal for pneumatic applications, particularly in seals and hoses. However, it may not withstand high pressures as effectively as metals, limiting its use in hydraulic systems. Additionally, it can be sensitive to UV light and may degrade over time if exposed.
Impact on Application:
Polyurethane is commonly used in pneumatic actuators, seals, and hoses. Its compatibility with various gases and non-aggressive fluids makes it suitable for many applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the selected polyurethane meets industry standards for chemical resistance and performance. In regions like South America and Africa, sourcing from local manufacturers can help mitigate import costs and ensure compliance with local regulations.
4. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It typically operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°F to 300°F (-40°C to 149°C).
Pros & Cons:
Brass offers good strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for fittings and connectors in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications due to lower tensile strength.
Impact on Application:
Brass is ideal for low to medium-pressure applications, particularly in pneumatic systems. It is compatible with air and various hydraulic fluids, making it a popular choice for fittings and valves.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of brass that meet local standards. Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is essential, especially in Europe and the Middle East, where regulations are stringent.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for pneumatic and hydraulic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty hydraulic systems | High strength and pressure resistance | Heavier, susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight pneumatic applications | Low weight, good corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength than steel | High |
| Polyurethane | Seals and hoses in pneumatic systems | Flexibility and abrasion resistance | Limited pressure capacity, UV sensitivity | Medium |
| Brass | Fittings and connectors in pneumatic systems | Excellent machinability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, lower pressure capacity | Medium |
This material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pneumatic and hydraulic
Manufacturing Processes for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
Understanding the manufacturing processes for pneumatic and hydraulic systems is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and reliability in their supply chains. The production of these systems typically involves several key stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages incorporates specific techniques and practices that significantly influence the final product’s performance.
Material Preparation
Material selection is fundamental to the durability and functionality of pneumatic and hydraulic components. Common materials used include high-strength alloys, stainless steel, and composite materials, chosen for their ability to withstand high pressures and corrosive environments.
Key Techniques:
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut and shaped using CNC machining or laser cutting, which provides precision and consistency.
– Surface Treatment: Components often undergo surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance and improve longevity.
Forming
The forming stage is where the basic shapes of components are created. This can involve various processes depending on the complexity and requirements of the part.
Key Techniques:
– Casting: Used for complex shapes, casting can produce intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve through machining.
– Forging: This technique enhances material properties by altering the grain structure, resulting in stronger components.
– Extrusion: Commonly used for producing long, continuous shapes like tubes, extrusion allows for uniformity in wall thickness and dimensions.
Assembly
Assembly is a critical stage where individual components are brought together to form a complete system. This stage requires precision and attention to detail to ensure that all parts fit and function correctly.
Key Techniques:
– Mechanical Assembly: Components are joined using fasteners, such as bolts or screws, ensuring strong connections.
– Welding: For parts that must endure high pressure, welding offers a permanent solution to create robust joints.
– Sealing: Gaskets and O-rings are used to prevent leaks, a vital consideration for both hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional aspects of the components. It often includes cleaning, polishing, and applying protective coatings.
Key Techniques:
– Cleaning: Components must be free from contaminants, often achieved through ultrasonic cleaning or chemical solvents.
– Inspection and Testing: Before final packaging, parts undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specified tolerances and operational standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of pneumatic and hydraulic systems, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA processes can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
International Standards
Several international standards govern the manufacturing and quality assurance processes in the pneumatic and hydraulic industry. Compliance with these standards is often a prerequisite for doing business globally.
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard focuses on consistent quality and customer satisfaction. It requires companies to demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides specifications for equipment used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before entering production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing ensure that processes are adhered to and that any deviations are corrected immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection verifies that the finished product meets all specifications and is ready for delivery.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are crucial for validating the performance and safety of pneumatic and hydraulic components. Common methods include:
- Pressure Testing: Evaluates the integrity of hydraulic systems under pressure to ensure there are no leaks or weaknesses.
- Functional Testing: Ensures that components operate correctly under simulated conditions.
- Durability Testing: Subjects components to extreme conditions to assess their longevity and reliability.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product quality.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and adherence to standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC practices and any historical performance data.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s processes and products.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
When sourcing pneumatic and hydraulic components, international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific regional nuances that can affect quality assurance.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding local regulations and cultural expectations can impact supplier relationships and compliance.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Consider the logistics of shipping and customs, which can introduce delays or additional costs. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about these factors is essential.
- Economic Conditions: Fluctuations in the local economy can affect supplier stability and reliability. It’s prudent to assess the financial health of potential suppliers.
In conclusion, B2B buyers should prioritize understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in the pneumatic and hydraulic industry. By focusing on supplier verification, compliance with international standards, and maintaining a proactive approach to quality control, buyers can ensure they source high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: BMW Car PRODUCTION ⚙️ ENGINE Factory Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pneumatic and hydraulic Sourcing
Cost Structure of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Sourcing
In the realm of pneumatic and hydraulic systems, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The total cost of sourcing these systems comprises several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality metals, specialized seals, and advanced polymers often command higher prices but may offer better performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can affect the overall price. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and testing, especially in custom applications.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running manufacturing facilities, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Buyers should consider suppliers with efficient operations to mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, particularly for custom components. This cost is often amortized over larger production runs, making volume purchases more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet specifications and certifications. While these processes add to costs, they are vital for safety and reliability, especially in critical applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Buyers should plan logistics carefully to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will influence final pricing. Buyers should be aware of the market rates and negotiate accordingly.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of pneumatic and hydraulic systems:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk purchases. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers gauge the feasibility of large orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs typically incur higher costs due to the unique tooling and labor required. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the increased costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and adherence to industry certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can significantly affect price. Investing in higher-quality components may reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence costs. Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs, while established suppliers may justify higher prices with proven quality.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
To ensure cost-effective sourcing, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Leverage volume discounts and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also yield favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs when making purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences and currency fluctuations, particularly when sourcing from suppliers in different continents. This knowledge can help in budgeting and cost forecasting.
-
Assess Quality vs. Cost: Sometimes, opting for the cheapest option can lead to higher costs in the long run due to failures or inefficiencies. Always balance quality with cost.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends and innovations in pneumatic and hydraulic technologies. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations and inform better purchasing decisions.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers, combined with strategic negotiation and evaluation of total costs, can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions in sourcing pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Disclaimer: Prices can vary significantly based on market conditions, currency fluctuations, and supplier negotiations, so always seek updated quotes before making purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential pneumatic and hydraulic Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘pneumatic and hydraulic’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pneumatic and hydraulic
Key Technical Properties for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
Understanding the technical specifications of pneumatic and hydraulic systems is essential for international B2B buyers. Here are several critical specifications that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the specific type of material used in components, such as aluminum, steel, or polymers.
– B2B Importance: The choice of material affects durability, weight, and resistance to corrosion or wear. Buyers must select materials that are suitable for their operational environment to ensure longevity and performance. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: The maximum pressure that a hydraulic or pneumatic system can safely handle, often measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the correct pressure rating is critical for safety and functionality. Systems operating above the rated pressure can fail, leading to costly downtime and potential injury. -
Flow Rate
– Definition: The volume of fluid that can pass through a component over a specific period, typically measured in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM).
– B2B Importance: Understanding flow rates is crucial for determining the speed and efficiency of operations. Buyers need to match flow rates with application requirements to avoid performance issues. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the manufacturing process.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances ensure that parts fit together properly, which is vital for system efficiency and reliability. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to stringent tolerance specifications to minimize defects and enhance performance. -
Actuator Type
– Definition: Refers to the mechanism that converts energy into motion, such as linear actuators or rotary actuators.
– B2B Importance: The choice of actuator type influences the system’s capability and suitability for specific applications. Buyers must consider the actuation requirements of their processes when selecting components.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is equally important for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several common terms used in the pneumatic and hydraulic sectors:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Identifying OEMs is essential for buyers seeking high-quality components that meet industry standards. OEM parts are often preferred for their reliability and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to optimize costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price proposals for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk management, which is vital for international transactions. -
Pneumatic Actuator
– Definition: A type of actuator that uses compressed air to produce motion.
– Relevance: Recognizing different actuator types helps buyers select the right equipment for their specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, improving their procurement processes and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the pneumatic and hydraulic Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The pneumatic and hydraulic sector is witnessing significant growth, driven by the global demand for automation and efficiency across industries. Key trends shaping this market include the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), which enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these trends is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
One emerging trend is the shift towards smart pneumatic and hydraulic systems that utilize sensors and data analytics to optimize performance and reduce downtime. This is particularly relevant for sectors like manufacturing, construction, and automotive, where operational efficiency is paramount. Additionally, suppliers are increasingly offering customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs, allowing buyers to achieve greater control and flexibility in their operations.
Buyers should also be aware of the regional dynamics affecting the market. In Africa and South America, infrastructure development projects are driving demand for hydraulic systems in construction and mining. Conversely, in Europe and the Middle East, the focus is on upgrading existing systems to meet stringent efficiency and sustainability standards. Recognizing these regional nuances can help buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing in the pneumatic and hydraulic market effectively.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the pneumatic and hydraulic sector. The environmental impact of hydraulic fluids and pneumatic systems can be significant; therefore, buyers must prioritize products that minimize ecological footprints. This includes selecting suppliers who utilize biodegradable hydraulic fluids and energy-efficient pneumatic components.
Moreover, ethical sourcing has gained traction, as companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. Buyers should seek suppliers that demonstrate commitment to fair labor practices, transparency, and sustainability. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to ethical practices.
Investing in “green” materials and technologies not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance a company’s brand reputation. Buyers should actively inquire about the sustainability initiatives of potential suppliers, including their use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. This focus on sustainability can lead to long-term cost savings and compliance with evolving regulations.
Brief Evolution/History
The pneumatic and hydraulic industries have evolved significantly since their inception. Early hydraulic systems, used in ancient civilizations for irrigation and lifting, laid the groundwork for modern applications. The industrial revolution further propelled advancements in pneumatic technology, leading to the development of air-powered tools that transformed manufacturing processes.
In recent decades, the integration of electronics and computer technologies has revolutionized these sectors. The introduction of automation and smart technologies has shifted the focus from merely mechanical systems to highly sophisticated, interconnected networks. This evolution is critical for B2B buyers, as it informs sourcing strategies that prioritize advanced, efficient, and sustainable solutions in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Understanding this historical context can help buyers appreciate the technological advancements that continue to shape the industry today.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pneumatic and hydraulic
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for pneumatic and hydraulic equipment?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation and experience in the industry. Request references and case studies from previous clients, particularly those in your region. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001. Assess their production capabilities and quality control processes to ensure they can meet your specific requirements. Additionally, consider their customer service responsiveness and support options, as these can significantly impact your procurement experience. -
Can I customize pneumatic and hydraulic components to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for pneumatic and hydraulic components. This can include alterations in size, pressure ratings, materials, and design features. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements and expectations. Inquire about the supplier’s design capabilities and whether they can provide prototypes or samples. It’s also essential to understand any additional costs and lead times associated with custom orders. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for pneumatic and hydraulic products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific components. Generally, MOQs for standard items may range from 50 to 100 units, while custom products might require higher quantities. Lead times also depend on factors such as product complexity and supplier location. Typical lead times can range from 4 to 12 weeks. Always confirm these details upfront to plan your procurement timeline effectively.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, especially in international transactions. Common options include advance payment, net 30 or net 60 terms, and letters of credit. To mitigate risks, consider using payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as escrow services or PayPal for smaller orders. Establishing a clear payment schedule can also help maintain a good relationship with your supplier and ensure timely delivery of goods. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification of the products I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards, such as CE marking or ISO certifications. Ask for quality control reports, including test results and inspection records. Consider conducting factory audits or inspections, especially for large orders or new suppliers. Additionally, inquire about warranty and return policies to safeguard your investment against defects or quality issues.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing pneumatic and hydraulic equipment?
Logistics plays a crucial role in international sourcing. Consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), costs, and transit times. Research customs regulations and duties applicable to your products in your country, as these can significantly affect overall costs. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling pneumatic and hydraulic equipment to ensure compliance and smooth delivery. It’s also advisable to track shipments and have contingency plans for potential delays. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and maintain thorough documentation of all agreements, including contracts, purchase orders, and correspondence. If a dispute arises, attempt to resolve it amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding conflict resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Having a legal advisor familiar with international trade can also be beneficial for navigating complex disputes. -
What industry trends should I be aware of when sourcing pneumatic and hydraulic equipment?
Stay informed about advancements in technology, such as the integration of IoT and automation in pneumatic and hydraulic systems, which can enhance efficiency and performance. Additionally, consider sustainability trends, as many manufacturers are now prioritizing eco-friendly materials and processes. Economic factors, such as currency fluctuations and trade policies, can also impact sourcing decisions. Regularly reviewing industry publications and attending trade shows can provide valuable insights into emerging trends.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pneumatic and hydraulic
In the dynamic landscape of pneumatic and hydraulic systems, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers. By understanding the unique advantages and applications of both systems, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Investing in quality components and reliable suppliers not only ensures optimal performance but also mitigates risks associated with equipment failures and downtime.
Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers and suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability. This approach not only aligns with global trends but also caters to the growing demand for environmentally friendly solutions across industries. Leveraging technology for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring can further optimize system performance and extend the lifespan of equipment.
As we look to the future, the integration of automation and smart technologies in pneumatic and hydraulic systems will redefine operational capabilities. International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are encouraged to stay ahead of these trends. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategies and invest in solutions that drive your business forward. The time to act is now—position your company as a leader in efficiency and innovation in this essential sector.