Master Sourcing Strategies for Three Way Solenoid Valve
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for three way solenoid valve
In the dynamic landscape of industrial automation, the three-way solenoid valve stands out as a pivotal component that enhances operational efficiency and precision. These devices play a crucial role in controlling the flow of fluids in various applications, from manufacturing and water treatment to HVAC systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of three-way solenoid valves is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of three-way solenoid valves, their construction materials, manufacturing quality control standards, and key suppliers in the global market. We will also explore cost considerations and market trends, providing insights into how these factors influence purchasing decisions. With an emphasis on practical FAQs, buyers will be equipped with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of selecting the right valve for their specific needs.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide aims to facilitate better sourcing strategies and foster successful partnerships. Whether you are in Nigeria seeking reliable suppliers or in Argentina looking to optimize your operational processes, understanding the value and functionality of three-way solenoid valves can significantly impact your business’s success. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your procurement strategy and ensure your operations run smoothly with the right solutions.
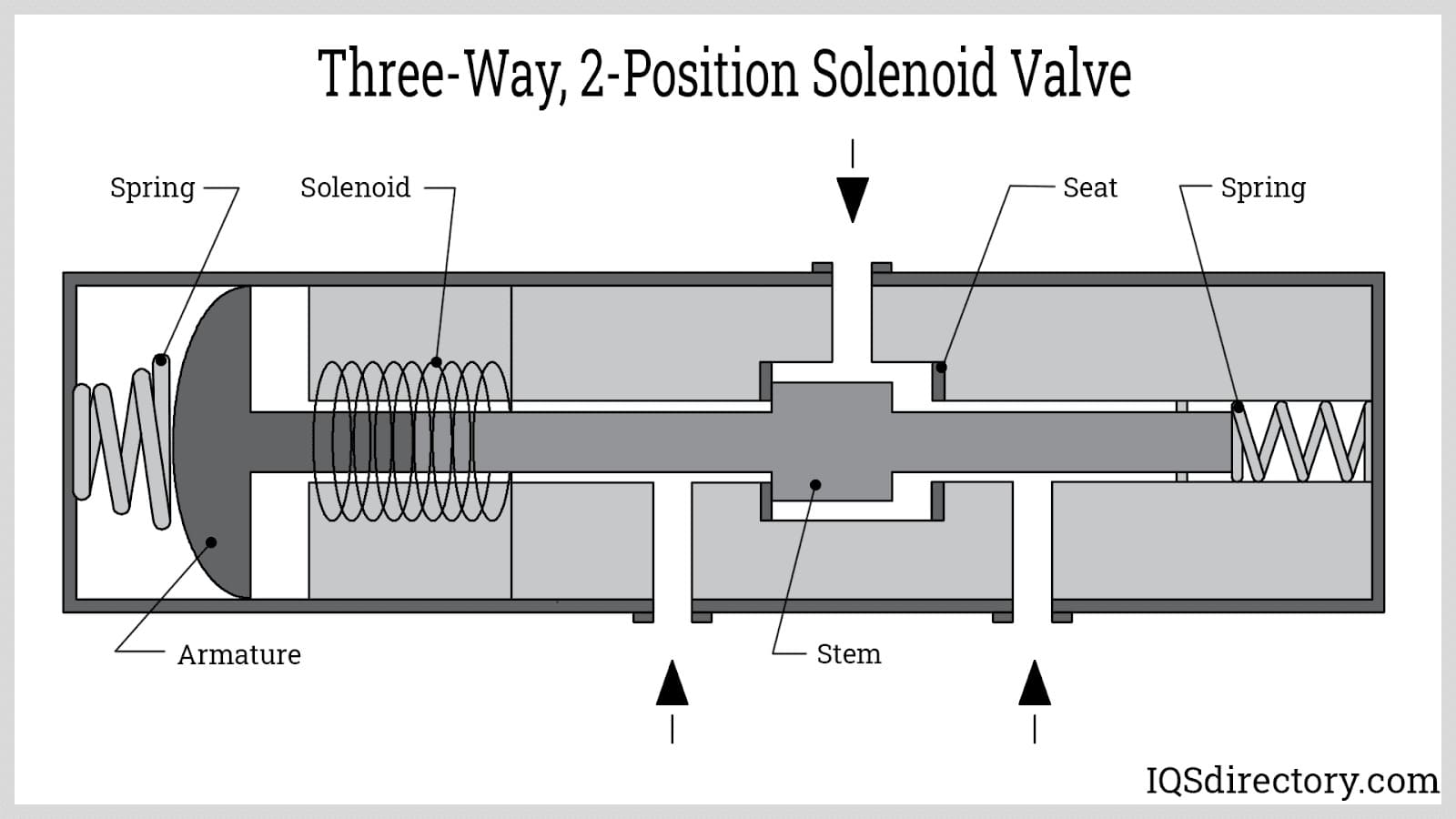
Understanding three way solenoid valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Acting Three-Way | Simple design, operates directly with electromagnetic coil | HVAC systems, water control | Pros: Quick response time, compact. Cons: Limited flow capacity. |
| Pilot-Operated Three-Way | Utilizes system pressure for operation | Industrial automation, high-pressure systems | Pros: Handles larger flow, efficient in high pressure. Cons: More complex and costly. |
| Normally Open Three-Way | Valve remains open until energized | Irrigation systems, cooling applications | Pros: Energy-efficient, ideal for continuous flow. Cons: May not suit all applications. |
| Normally Closed Three-Way | Valve remains closed until energized | Fuel systems, hydraulic controls | Pros: Safety in critical applications, prevents leaks. Cons: Slower response in emergencies. |
| Bistable Three-Way | Maintains its position until switched | Robotics, automated systems | Pros: Reduces energy consumption, stable in position. Cons: Requires precise control signals. |
Direct-Acting Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Direct-acting three-way solenoid valves are known for their straightforward design, where the electromagnetic coil directly operates the valve. These valves are typically used in applications such as HVAC systems and water control, where quick response times are essential. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the valve’s flow capacity and response speed, which makes them ideal for low-pressure environments but limits their use in high-flow applications.
Pilot-Operated Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Pilot-operated three-way solenoid valves leverage system pressure to assist in valve operation. This design is particularly advantageous for industrial automation and high-pressure systems, as it can manage larger flow rates without compromising performance. Buyers should consider the complexity and cost of these valves, as they require more intricate installation and maintenance compared to direct-acting types. However, their efficiency in handling high-pressure environments often justifies the investment.
Normally Open Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Normally open three-way solenoid valves remain open when not energized, making them suitable for applications such as irrigation systems and cooling processes. These valves promote energy efficiency by allowing continuous flow without constant electrical activation. However, buyers must ensure that this design fits their specific operational needs, as it may not be suitable for applications requiring frequent shut-off.
Normally Closed Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Normally closed three-way solenoid valves are designed to remain closed until energized, providing safety in critical applications like fuel systems and hydraulic controls. This feature helps prevent leaks and ensures controlled operation. Buyers should consider the response time in emergencies, as these valves may take longer to activate compared to normally open types. Their reliability in safety-critical systems often outweighs the potential downsides.
Bistable Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Bistable three-way solenoid valves maintain their position until switched, making them ideal for robotics and automated systems. This design reduces energy consumption since they do not require continuous power to maintain their state. Buyers should focus on the precision of control signals needed for operation, as any inaccuracies can lead to operational failures. The stability and energy efficiency of bistable valves make them a compelling choice for various applications.
Key Industrial Applications of three way solenoid valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of three way solenoid valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Enhances production speed and accuracy | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and pressure ratings. |
| HVAC Systems | Temperature control in heating/cooling units | Improves energy efficiency and reduces operational costs | Look for valves with robust materials to withstand varying temperatures. |
| Water Treatment | Flow regulation in filtration systems | Ensures consistent water quality and system reliability | Consider valves that meet local regulations and material compatibility with water. |
| Food and Beverage | Process control in bottling plants | Maintains product integrity and compliance with safety standards | Select FDA-approved materials to ensure food safety. |
| Oil and Gas | Control of fluid flow in pipelines | Increases operational safety and efficiency | Evaluate valves for pressure and temperature ratings suitable for harsh environments. |
In manufacturing, three-way solenoid valves are pivotal in automating assembly lines, facilitating the seamless transition of materials and components. By allowing for the quick switching between different pathways, these valves significantly enhance production speed and accuracy. International buyers should prioritize sourcing valves that are compatible with their existing systems and have appropriate pressure ratings to ensure optimal performance.
In HVAC systems, three-way solenoid valves play a crucial role in regulating temperature by controlling the flow of refrigerants or hot water. This functionality leads to improved energy efficiency, which can substantially reduce operational costs. Buyers should consider valves made from robust materials that can withstand varying temperatures and pressures typical in HVAC applications.
In the water treatment sector, these valves are essential for regulating flow in filtration systems, ensuring a consistent water quality and system reliability. The use of three-way solenoid valves helps in managing the distribution of water effectively. When sourcing, it is vital to consider local regulations and ensure material compatibility with water to avoid contamination.
In the food and beverage industry, three-way solenoid valves are used for process control in bottling plants. They maintain product integrity while ensuring compliance with safety standards. Buyers in this sector should select valves made from FDA-approved materials to guarantee food safety and avoid any regulatory issues.
In the oil and gas industry, three-way solenoid valves are critical for controlling fluid flow in pipelines. Their ability to manage flow efficiently increases operational safety and overall efficiency. Buyers should evaluate valves for their pressure and temperature ratings, ensuring they are suitable for the harsh environments typical in this sector.
Related Video: How a 3 Way Directional Control Solenoid Valve Operates
Strategic Material Selection Guide for three way solenoid valve
When selecting materials for three-way solenoid valves, it’s essential to consider the operational environment, the type of media being controlled, and the specific application requirements. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of these valves, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, and ability to withstand moderate pressure and temperature ranges (up to 250°C). It is often used in applications involving water and air.
Pros & Cons:
Brass is durable and relatively easy to machine, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. However, it can be more expensive than other options like plastic, and its performance may degrade in highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application:
Brass is suitable for applications with non-aggressive media, such as water and air. It is not ideal for harsh chemicals, which can lead to rapid degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B453 and consider local regulations regarding lead content in brass, especially in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations exist.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance, excellent strength, and can handle high-pressure applications (up to 300°C). It is particularly effective in environments where hygiene is critical, such as food processing.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, it is also more expensive and can be challenging to machine compared to brass. Its weight may also be a consideration in some applications.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive chemicals and high-temperature fluids, making it versatile for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should confirm compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 and consider the specific grade of stainless steel (e.g., 304 vs. 316) based on the application. In regions like Africa and South America, availability and cost may vary significantly.
3. Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties:
Plastic materials, such as PVC and PTFE, are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can handle a variety of chemical media. They typically operate effectively at lower temperature and pressure ranges compared to metals.
Pros & Cons:
Plastic valves are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, but they may not withstand high temperatures or pressures, limiting their application scope. They are also less durable than metal options.
Impact on Application:
Plastics are ideal for corrosive media and applications where weight is a concern. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM D1784 for PVC. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should also consider the local availability of specific plastic materials and their compatibility with regional media.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and can handle moderate pressures and temperatures (up to 150°C). It is often used in applications where weight savings are critical.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is easier to machine than stainless steel and is generally more affordable. However, it is less durable than brass or stainless steel and may not perform well in highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for air and gas applications but may not be ideal for liquid media, particularly those that are corrosive.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with standards like ASTM B221. In Europe, buyers should also consider the environmental impact of aluminum production and recycling.
| Material | Typical Use Case for three way solenoid valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Water and air applications | Good corrosion resistance | Not suitable for aggressive media | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and chemical handling | High strength and durability | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Plastic | Corrosive chemical applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited pressure and temperature range | Low |
| Aluminum | Air and gas applications | Lightweight and affordable | Less durable in corrosive environments | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for three way solenoid valve
Manufacturing Processes for Three-Way Solenoid Valves
The manufacturing of three-way solenoid valves involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure high-quality output that meets diverse operational needs. Understanding these processes is vital for B2B buyers aiming to procure reliable components for their systems.
1. Material Preparation
Material selection is fundamental in the production of three-way solenoid valves. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastics, chosen based on their compatibility with the intended application—whether for water, air, or corrosive fluids.
- Material Inspection: The initial step involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications. This may include checking the chemical composition and mechanical properties.
- Cutting and Shaping: Materials are then cut and shaped using precision machining techniques. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for their accuracy in creating valve bodies and components.
2. Forming
Forming processes are critical in shaping the valve components to their final designs.
- Casting: For metal valves, casting techniques such as sand or die casting are frequently used. This allows for complex shapes and high production rates.
- Molding: In the case of plastic valves, injection molding is a popular method, ensuring uniformity and precision in the final product.
- Machining: Post-forming, components undergo machining processes to ensure tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, which are essential for optimal sealing and performance.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form a complete solenoid valve.
- Component Assembly: This involves fitting the solenoid coil, plunger, and valve body. Careful alignment is crucial to ensure proper operation.
- Sealing: The use of gaskets or O-rings during assembly prevents leakage, enhancing the valve’s reliability.
- Testing During Assembly: Initial functional tests may be conducted to verify that each unit operates correctly before moving to the finishing stage.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic quality of the valves.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as anodizing, plating, or powder coating may be applied to improve corrosion resistance and wear properties.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection ensures that all components meet quality standards and that the valve operates within specified parameters.
Quality Assurance Practices
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process of three-way solenoid valves, ensuring that each product meets international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the key quality standards that govern manufacturing processes:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must comply with EU safety and health regulations, and obtaining CE marking is crucial for market access.
- API Standards: For valves used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is often required.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure that each valve meets stringent standards.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials upon arrival, ensuring they meet specified standards before use.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during production monitor critical parameters, such as dimensions and assembly integrity.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection assesses the complete valve for functionality, leakage, and adherence to specifications.
Common Testing Methods
A variety of testing methods are employed to validate the quality of the valves:
- Pressure Testing: Ensures the valve can withstand specified pressure levels without leaking.
- Electrical Testing: Verifies the solenoid’s operation, ensuring it activates and deactivates correctly.
- Flow Testing: Assesses the valve’s ability to control fluid flow, ensuring it meets performance specifications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is critical to ensuring product reliability.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This helps establish trust and ensures compliance with standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including testing results and compliance certifications, allows buyers to assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and product quality. This is particularly valuable when sourcing from regions with varying regulatory standards.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when dealing with international suppliers.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can help in negotiations and establishing mutual expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying requirements for certifications and quality standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
- Communication: Clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards is essential to mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that products meet buyer specifications.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for three-way solenoid valves equips international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on quality control, compliance with international standards, and effective supplier verification strategies, buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Related Video: How Solenoid Valves Work – Basics actuator control valve working principle
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for three way solenoid valve Sourcing
In sourcing three-way solenoid valves, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. The costs associated with these valves can be categorized into several key components, each influencing the final price.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing three-way solenoid valves include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. The choice of material significantly impacts the cost, with stainless steel typically being more expensive due to its durability and corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. Countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Western Europe, may yield higher prices compared to manufacturers in regions with lower labor costs, like parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can vary based on the efficiency of the production process and the location of the manufacturing facility.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are associated with the molds and machinery required for production. Custom tooling for specialized designs can increase initial costs but may lead to cost savings in large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures can incur additional costs, but this is crucial for ensuring reliability and compliance with international standards. Certificates such as ISO can also add to the cost but are often essential for market acceptance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. Factors such as fuel prices, shipping methods, and customs duties play a significant role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s business model, market competition, and perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of three-way solenoid valves:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger order volumes often lead to discounts per unit, as suppliers benefit from economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized valves tailored to specific applications may incur higher costs due to additional design and manufacturing requirements.
-
Material Choices: The choice of materials not only affects durability but also the price. High-performance materials may be necessary for certain applications but will increase costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with industry standards and certifications can add to the cost but is crucial for buyers in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to perceived quality.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) will affect the total landed cost, including shipping and insurance, which are critical for international transactions.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate prices, especially for large orders. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing that can benefit your bottom line.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Factors like energy efficiency and maintenance costs can significantly impact long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, suppliers in Africa or South America may offer more competitive pricing compared to those in Europe, but ensure that quality and service levels are comparable.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand typical pricing for three-way solenoid valves in your industry and region. This will equip you with the knowledge to negotiate effectively.
-
Supplier Relationships: Build long-term relationships with suppliers for better pricing and service. Loyal customers often receive preferential treatment and pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices for three-way solenoid valves can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and changes in material costs. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct a thorough analysis to make informed purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential three way solenoid valve Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘three way solenoid valve’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for three way solenoid valve
Understanding the key technical properties and terminology associated with three-way solenoid valves is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge not only enhances purchasing decisions but also ensures better integration into existing systems.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the type of materials used in the construction of the solenoid valve, such as brass, stainless steel, or plastic.
– B2B Importance: The choice of material affects durability, resistance to corrosion, and suitability for specific fluids or gases. For example, stainless steel is ideal for corrosive environments, while brass may suffice for less aggressive applications. -
Flow Rate
– Definition: Measured in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM), the flow rate indicates the volume of fluid that can pass through the valve in a given time.
– B2B Importance: Understanding flow rates helps buyers ensure that the valve meets the operational demands of their systems, preventing bottlenecks or inadequate fluid supply. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: This specification denotes the maximum pressure the valve can safely handle, typically expressed in psi (pounds per square inch) or bar.
– B2B Importance: Selecting a valve with an appropriate pressure rating is essential to avoid failures that could lead to system downtime and costly repairs. -
Electrical Specifications
– Definition: This includes voltage (e.g., 12V, 24V, 220V) and current ratings, as well as power consumption of the solenoid.
– B2B Importance: Buyers must ensure compatibility with their electrical systems to avoid issues with operation and energy efficiency. -
Tolerance
– Definition: This refers to the allowable variation in manufacturing dimensions, critical for ensuring a proper fit and function in the system.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are crucial for high-precision applications, impacting overall system reliability and performance. -
Actuation Time
– Definition: The time it takes for the valve to open or close after receiving an electrical signal.
– B2B Importance: Fast actuation times are vital in applications where quick response is necessary, such as in automation and control systems.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Buyers must be aware of MOQs to manage inventory effectively and ensure they meet supplier requirements without overcommitting. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to gather competitive pricing and terms, facilitating informed decision-making in procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications in global sourcing. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Knowing lead times is critical for project planning and can significantly impact the operational schedule, particularly in industries with tight deadlines. -
Warranty
– Definition: A guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the product and the terms of repair or replacement.
– Importance: Understanding warranty terms can protect buyers from unexpected costs and ensure long-term reliability of their investment.
By grasping these essential specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding the procurement and integration of three-way solenoid valves into their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the three way solenoid valve Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for three-way solenoid valves is witnessing significant growth, driven by advancements in automation and increasing demand for efficient fluid control systems across various industries. Key sectors such as manufacturing, oil and gas, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals are leading the charge in adopting these technologies to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several key trends shaping this market.
Firstly, the integration of smart technology and IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities into solenoid valves is revolutionizing their functionality. These smart valves enable real-time monitoring and control, providing operators with data analytics that optimize performance and predict maintenance needs. Secondly, there is a growing emphasis on customization, with manufacturers offering tailored solutions to meet specific operational requirements. This trend is particularly important for industries in emerging markets, where unique local challenges necessitate specialized products.
Moreover, regulatory frameworks and safety standards are becoming increasingly stringent, pushing manufacturers to innovate and enhance the reliability of their products. For B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with industry trends and compliance requirements. Engaging with suppliers who are at the forefront of these technological advancements can provide a competitive edge in the market.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B procurement strategies, particularly in the three-way solenoid valve sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in solenoid valves is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is critical in ensuring that materials used in the production of solenoid valves are obtained responsibly, minimizing harm to both the environment and local communities. Buyers should look for suppliers who offer certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other “green” certifications that indicate compliance with sustainability standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, the use of eco-friendly materials in valve construction is gaining traction. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of materials, such as recycled metals or biodegradable components, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of their operations. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers not only contribute to environmental conservation but also enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for responsible business practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of solenoid valves dates back to the early 20th century, with the initial designs focusing primarily on mechanical actuation. Over the decades, advancements in electromagnetic technology have transformed solenoid valves into sophisticated devices capable of precise fluid control. The introduction of three-way configurations allowed for more complex applications, enabling manufacturers to streamline processes in various industries.
Today, the integration of digital technologies has further refined the capabilities of three-way solenoid valves, making them essential components in modern automation systems. This historical progression highlights the importance of continuous innovation in meeting the ever-evolving demands of international B2B buyers, particularly as industries strive for greater efficiency and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of three way solenoid valve
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for three-way solenoid valves?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, technical capabilities, and customer reviews. Investigate their certifications, such as ISO or API, to ensure quality standards. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region, to assess reliability. Additionally, evaluate their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demand. It’s also beneficial to verify their after-sales support and warranty policies, which can be crucial for long-term partnerships. -
Can I customize three-way solenoid valves to suit my specific application?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for three-way solenoid valves. You can request specific materials, sizes, pressure ratings, and electrical specifications based on your application needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed technical requirements and operational conditions. Ensure that the supplier has the capability to produce custom solutions and inquire about any additional costs or lead times associated with these modifications. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for three-way solenoid valves?
MOQs for three-way solenoid valves can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the valve. Commonly, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 50 to 500 units. Lead times can also differ based on customization and supplier location, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid surprises and ensure that they align with your project timelines and inventory needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing three-way solenoid valves internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits ranging from 30-50% with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer payment upon delivery or letter of credit options, especially for larger orders. Always negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s trustworthiness. Be aware of any currency exchange risks and consider using escrow services for added security in international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and necessary certifications for my valves?
Request that your supplier provides detailed quality assurance processes and relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards. Ask for documentation proving compliance with international regulations, such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the USA. It’s wise to conduct periodic audits or inspections, especially for larger orders, to verify that the valves meet your quality requirements. Establishing a clear quality control agreement with your supplier can also mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing three-way solenoid valves?
Logistics involves understanding shipping methods, costs, and customs regulations in your country. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness based on your urgency and budget. Confirm with your supplier about shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) and ensure they provide necessary shipping documents. Collaborate with a reliable freight forwarder familiar with your region to navigate customs smoothly and avoid delays in delivery.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding three-way solenoid valves?
Dispute resolution should start with clear communication; address any issues directly with the supplier to seek an amicable solution. Always refer to your purchase agreement, which should outline terms for returns, refunds, or replacements. If informal discussions fail, consider mediation or arbitration, especially if stipulated in your contract. Maintaining detailed records of all communications and transactions can support your case should legal action become necessary. -
What should I know about the warranty and support for three-way solenoid valves?
When sourcing, inquire about the warranty period and what it covers, including defects in materials or workmanship. Most suppliers offer warranties ranging from 1 to 5 years. Understand the claims process and any conditions that may void the warranty, such as improper installation. Additionally, evaluate the supplier’s technical support and service capabilities, as having access to expert advice can be invaluable for troubleshooting and maintenance after purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for three way solenoid valve
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of three-way solenoid valves is pivotal for optimizing operational efficiency and enhancing automation capabilities across various industries. By understanding the diverse functionalities and applications of these valves, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. Key considerations include evaluating supplier reliability, assessing product specifications, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
The value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated; it allows businesses to secure high-quality components at competitive prices while fostering sustainable supplier relationships. As the demand for automation and efficiency continues to rise globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in reliable solenoid valve solutions becomes increasingly critical.
Looking ahead, we encourage B2B buyers to actively engage with reputable suppliers, conduct thorough market research, and leverage technology to streamline procurement processes. By doing so, organizations can not only enhance their operational capabilities but also position themselves for future growth in an ever-evolving industrial landscape. Embrace the potential of three-way solenoid valves today to drive your business forward.