Master Sourcing Thermoforming Solutions: A Comprehensive
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermoforming
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, thermoforming stands out as a pivotal process for producing a wide range of plastic products, from food packaging to medical devices. Its versatility and cost-effectiveness make it an essential consideration for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of international sourcing. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their supply chains, understanding the nuances of thermoforming becomes crucial.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international buyers with the insights needed to make informed sourcing decisions. It covers a broad spectrum of topics, including the various types of thermoforming plastics, sustainable material options, and manufacturing processes. Additionally, the guide delves into quality control standards, leading suppliers in key regions, and essential cost considerations, providing a holistic view of the market.
By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring a balance between quality, cost, and sustainability. Whether you are looking to establish new supplier relationships, explore regional manufacturing hubs, or source eco-friendly materials, this guide serves as an authoritative tool to navigate the dynamic thermoforming market effectively. Equip yourself with the knowledge to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities in this vital sector.
Understanding thermoforming Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) | Clear, tough, excellent chemical resistance | Food packaging, medical trays, display units | Pros: Good clarity, durability, food-safe; Cons: Higher cost, moderate impact strength |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Versatile, available in rigid or flexible forms | Medical devices, packaging, signage | Pros: Cost-effective, chemical resistant; Cons: Environmental concerns, limited UV stability |
| HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) | Impact-resistant, easy to thermoform | Food trays, cosmetic packaging, point-of-sale displays | Pros: Cost-efficient, easy to process; Cons: Less chemical resistance, lower heat tolerance |
| PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | Rigid, strong, highly recyclable | Bottles, food containers, electronics enclosures | Pros: High clarity, recyclability; Cons: Brittle at low temperatures, more expensive |
| PP (Polypropylene) | Lightweight, flexible, high chemical resistance | Automotive parts, caps, containers, medical devices | Pros: Cost-effective, chemical resistant; Cons: Lower impact strength at low temps |
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG is known for its clarity and toughness, making it ideal for applications that require both transparency and durability, such as food packaging and medical trays. B2B buyers should weigh its higher cost against its benefits, including excellent chemical resistance and recyclability. This material aligns well with sustainability initiatives, making it a strong choice for companies focused on eco-friendly practices.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is a highly versatile thermoforming plastic, available in both rigid and flexible forms. Its excellent chemical and flame resistance makes it suitable for a variety of applications, including medical devices and packaging. However, buyers should consider the growing environmental concerns associated with PVC, particularly in Europe and parts of Africa and South America, as regulations may impact future sourcing decisions.
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
HIPS is favored for its impact resistance and ease of thermoforming, commonly used in food trays and retail displays. Its cost-effectiveness and straightforward processing make it appealing for large-scale production. However, buyers should be cautious of its lower chemical resistance and heat tolerance, which may limit its use in specific high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
PET is recognized for its rigidity and high recyclability, making it a popular choice for bottles and food containers. It offers excellent barrier properties and clarity, which are advantageous for consumer-facing products. However, its brittleness at low temperatures and higher cost compared to alternatives require buyers to carefully consider their application needs and operational conditions.
PP (Polypropylene)
PP stands out for its lightweight, flexible nature, and high resistance to chemicals and fatigue, making it suitable for automotive parts and medical devices. Its cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage, but buyers must be aware of its lower impact strength at low temperatures. Evaluating operational environments is crucial for ensuring that PP meets the specific demands of intended applications.
Related Video: 10 Mental Models Explained
Key Industrial Applications of thermoforming
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thermoforming | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Packaging | Custom trays and containers for perishable goods | Enhances product shelf life, reduces waste, and improves presentation | Material safety certifications, compliance with food regulations |
| Medical Devices | Sterile packaging and trays for surgical instruments | Ensures safety and sterility, reduces risk of contamination | Cleanroom manufacturing capabilities, ISO certifications |
| Automotive | Interior panels and components | Lightweight, cost-effective solutions that enhance design flexibility | Material strength, impact resistance, and compliance with safety standards |
| Consumer Products | Packaging for electronics and cosmetics | Provides aesthetic appeal and protection, improves user experience | Customization options, surface finish requirements, and durability |
| Industrial Containers | Storage bins and transport packaging | Optimizes space utilization, enhances durability, and reduces shipping costs | Sourcing robust materials, size specifications, and load capacity |
Food Packaging
Thermoforming plays a crucial role in the food packaging industry by creating custom trays and containers designed specifically for perishable goods. This process not only enhances the shelf life of products but also minimizes waste through optimized packaging designs. For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa and South America, it is essential to source materials that comply with local food safety regulations and certifications. Additionally, understanding the environmental impact of packaging materials is increasingly important, as consumers demand sustainable solutions.
Medical Devices
In the medical sector, thermoforming is utilized for producing sterile packaging and trays that house surgical instruments. This application is vital for ensuring the safety and sterility of medical devices, thereby reducing the risk of contamination during surgeries. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe must prioritize suppliers with cleanroom manufacturing capabilities and relevant ISO certifications. These factors are critical to maintaining high standards of quality and compliance in a highly regulated industry.
Automotive
The automotive industry benefits from thermoforming through the production of lightweight interior panels and components. This method offers cost-effective solutions that enhance design flexibility while maintaining the necessary strength and durability required in automotive applications. For B2B buyers in Europe and Africa, it is important to source materials that meet stringent safety standards and can withstand various environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and performance.
Consumer Products
Thermoforming is widely used for packaging in the consumer products sector, particularly for electronics and cosmetics. This technique allows for the creation of aesthetically appealing and protective packaging that enhances the overall user experience. Buyers, especially in regions like South America and the Middle East, should focus on suppliers that offer customization options and meet specific surface finish requirements to align with brand values and consumer expectations.
Industrial Containers
In the realm of industrial applications, thermoforming is employed to create storage bins and transport packaging that optimize space utilization and enhance durability. This is particularly beneficial for logistics and supply chain management, as robust packaging can reduce shipping costs and minimize product damage. International buyers must consider the sourcing of materials that can withstand heavy loads and meet specific size specifications to ensure functionality and reliability in diverse operational environments.
Related Video: How the THERMOFORMING PROCESS works? – Factories
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermoforming
When selecting materials for thermoforming, international B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors that influence product performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common thermoforming materials, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and relevant considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
Key Properties:
PETG is known for its excellent clarity, toughness, and chemical resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and is suitable for applications requiring sterilization. Its low moisture absorption makes it ideal for food packaging and medical applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of PETG is its durability and recyclability, aligning with sustainability trends. However, it tends to be more expensive than alternatives like HIPS and may not be suitable for high-temperature applications due to its lower heat tolerance.
Impact on Application:
PETG is particularly effective in applications involving food contact and medical devices due to its safety and compliance with FDA regulations. Buyers must ensure that the specific grade of PETG meets the required standards for their intended use.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of compliance with local regulations, especially in Europe where stringent environmental laws may affect the use of certain plastics. Understanding ASTM and DIN standards for food safety is crucial when sourcing PETG.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties:
PVC is versatile and can be formulated to be either rigid or flexible. It has excellent chemical resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F). Its flame retardant properties make it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The cost-effectiveness of PVC is a significant advantage, making it a popular choice for packaging and medical devices. However, environmental concerns regarding its production and disposal can pose challenges, particularly in regions with strict regulations.
Impact on Application:
PVC is commonly used in medical devices and packaging due to its durability and resistance to chemicals. However, buyers must consider the potential for leaching and the need for compliance with health and safety regulations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and parts of Africa should be cautious of the increasing restrictions on PVC due to environmental concerns. Familiarity with local regulations and standards, such as REACH in Europe, is essential for compliance.
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
Key Properties:
HIPS is characterized by its impact resistance and ease of thermoforming. It can withstand temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and is often used in applications requiring a smooth surface finish.
Pros & Cons:
HIPS is cost-effective and easy to process, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. However, it has lower chemical resistance and heat tolerance, which may limit its use in specific applications.
Impact on Application:
HIPS is widely used in food trays and cosmetic packaging. Its suitability for food contact applications is contingent on compliance with relevant safety standards.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that HIPS sourced meets local food safety standards, particularly in regions with strict regulations. Understanding the implications of using HIPS in high-temperature applications is crucial for product performance.
PP (Polypropylene)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is lightweight, flexible, and exhibits high chemical and fatigue resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F), making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polypropylene is its cost-effectiveness and resilience. However, its lower impact strength at low temperatures can be a limitation for certain applications.
Impact on Application:
PP is commonly used in automotive parts and medical devices, where flexibility and chemical resistance are prioritized. Buyers must consider the specific operational conditions when selecting PP.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of local standards and regulations regarding the use of polypropylene, particularly in food contact applications. Familiarity with relevant certifications can help ensure compliance and product safety.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermoforming | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PETG | Food packaging, medical trays | Excellent clarity and recyclability | Higher cost, lower heat tolerance | High |
| PVC | Medical devices, packaging | Cost-effective, versatile | Environmental concerns, limited UV stability | Low |
| HIPS | Food trays, cosmetic packaging | Cost-efficient and easy to process | Lower chemical resistance, heat tolerance | Low |
| PP | Automotive parts, medical devices | Lightweight and flexible | Lower impact strength at low temperatures | Medium |
This analysis provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions when selecting materials for thermoforming applications. Understanding the properties and implications of each material will facilitate better sourcing strategies tailored to specific market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermoforming
In the realm of thermoforming, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers aiming to procure high-quality products. This section delves into the typical stages of the thermoforming manufacturing process, the key techniques employed, and the quality control (QC) measures that ensure product reliability.
Manufacturing Processes in Thermoforming
The manufacturing process of thermoforming can be broken down into several key stages:
1. Material Preparation
Material preparation is the initial step, where thermoplastic sheets are selected based on the specific application requirements. Common materials include PETG, PVC, HIPS, PET, and PP, each offering unique properties suitable for different end uses. The preparation phase involves:
- Sheet Selection: Choosing the appropriate polymer type and thickness based on product specifications.
- Material Conditioning: Preheating the sheets to a specific temperature to enhance their malleability during forming. This step is critical as it affects the final product’s surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the prepared material is shaped into the desired form. Key techniques include:
- Vacuum Forming: A widely used method where the heated sheet is draped over a mold, and a vacuum is applied to pull the material into the mold’s shape.
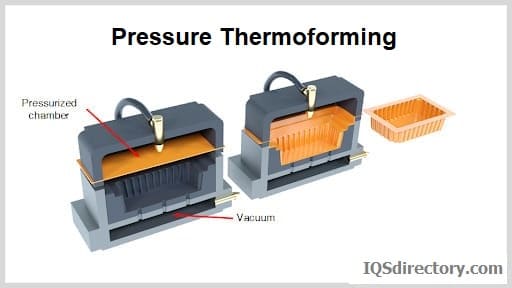
- Pressure Forming: Similar to vacuum forming but uses pressure to force the sheet into the mold, providing better detail and surface finish.
- Twin-Sheet Thermoforming: Involves heating and forming two sheets simultaneously, which are then fused together to create hollow parts.
This stage is crucial for achieving the desired product dimensions and ensuring that the material flows properly into all areas of the mold.
3. Assembly
After forming, the products may require assembly, especially if they consist of multiple parts. This can involve:
- Trimming: Removing excess material from the formed parts to meet precise specifications.
- Joining: Using techniques such as welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening to assemble components.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves surface treatments and quality checks. Common finishing processes include:
- Surface Treatment: Applying coatings or treatments to enhance aesthetics or improve functional properties such as UV resistance.
- Inspection and Testing: Conducting quality checks to ensure products meet specified tolerances and standards before shipment.
Quality Assurance in Thermoforming
Quality assurance is vital in maintaining the integrity and performance of thermoformed products. B2B buyers should be familiar with the relevant international standards and the specific QC processes employed by suppliers.
International Standards
Key quality standards relevant to thermoforming include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is widely recognized across industries. It ensures that suppliers maintain consistent quality in their processes and products.
- CE Marking: Particularly important for products sold within the European market, this certification indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as medical devices, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be required, particularly for components used in regulated applications.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is typically structured around several critical checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process in real-time to identify and rectify defects during production.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished products to ensure they meet all specifications and quality standards before dispatch.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of various testing methods employed to validate product quality:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that parts conform to specified dimensions using tools like calipers and gauges.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, color consistency, and overall appearance.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers adhere to high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take several proactive steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and manufacturing capabilities. This process should include reviews of documentation, production processes, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s historical performance regarding defect rates and compliance with quality standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality and supplier capabilities, particularly for high-stakes applications.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of various nuances in QC and certification:
- Regional Regulations: Different regions may have specific regulations that influence material choice and product safety. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local laws to avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across regions, impacting negotiations and quality expectations. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better understanding and alignment on quality requirements.
- Sustainability Standards: Increasingly, buyers are seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainability practices. Understanding the environmental certifications and sustainability measures in place can be a deciding factor in supplier selection.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in thermoforming, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality and supply chain reliability. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right suppliers but also fosters partnerships that align with strategic business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermoforming Sourcing
When sourcing thermoforming plastics, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis outlines the key cost components, price influencers, and provides actionable tips to optimize procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant portion of the total expense in thermoforming. Common materials like PETG, PVC, HIPS, PET, and PP vary in price based on market conditions, availability, and regional sourcing. Buyers should consider the long-term implications of material choices, especially as sustainability trends drive demand for eco-friendly options.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary greatly depending on the region. In regions like Africa and South America, labor may be more affordable, but this can be offset by the need for skilled workers and training. In contrast, European labor costs are generally higher, reflecting advanced skill levels and regulatory standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can mitigate overhead costs. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s operational efficiencies to understand how these might impact pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are critical, especially for custom parts. These costs can be amortized over production runs, affecting the per-unit price. Buyers should evaluate the tooling capabilities of suppliers and consider the potential for shared tooling arrangements to reduce initial investments.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. Suppliers with robust QC processes may charge higher prices, but this can lead to lower costs associated with defects and rework.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs should not be overlooked. They can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should assess logistics options that balance cost and delivery speed.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can fluctuate based on market competition, supplier reputation, and the perceived value of their offerings. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Prices often decrease with higher order volumes. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their production needs to take advantage of bulk pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized products typically incur higher costs due to unique tooling and material requirements. Clearly defining product specifications upfront can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences pricing. Premium materials with superior performance characteristics often come at a higher cost. Buyers should weigh the benefits against budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers offering higher quality products and certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA compliance) may command higher prices. However, investing in quality can yield long-term savings through reduced defects and improved customer satisfaction.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s market position, operational capabilities, and reputation can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better reliability but at a premium price.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms affect logistics costs and risk. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage total expenses effectively.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough negotiations with multiple suppliers to secure competitive pricing. Leverage your volume requirements as a bargaining chip.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond unit prices; consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) which includes all associated costs over the product lifecycle. This perspective can uncover more cost-effective options.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences, especially when sourcing from suppliers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Market conditions and local regulations can create significant variations.
-
Disclaimer on Prices: Always request detailed quotations that reflect current market conditions, as prices can fluctuate based on material costs and demand.
By understanding these components and employing strategic sourcing practices, international buyers can optimize their procurement processes in the thermoforming industry, ensuring they achieve the best balance of cost, quality, and service.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential thermoforming Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘thermoforming’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermoforming
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology in thermoforming is essential for B2B buyers aiming to make informed procurement decisions. This section outlines critical specifications to consider and explains key industry terms that will aid in navigating the thermoforming landscape.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The specific formulation of a plastic material that determines its performance characteristics, including strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and heat.
– Importance: Selecting the right material grade is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the required performance standards for its application. For instance, food packaging requires FDA-compliant grades, while automotive components may need materials that withstand higher temperatures. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable variation in a part’s dimensions, typically expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.5 mm).
– Importance: Tolerances are critical for ensuring that thermoformed parts fit together correctly in assemblies. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to assembly issues, increased costs, and product failures, making it vital for buyers to specify their tolerance requirements clearly. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: The texture and visual quality of the part’s surface, which can range from matte to glossy.
– Importance: The surface finish impacts both aesthetics and functionality. For example, a glossy finish may be preferred for consumer products, while a matte finish might be more suitable for industrial applications. Buyers should specify surface finish to meet branding or product requirements. -
Production Volume
– Definition: The quantity of parts produced within a specified timeframe, often annualized.
– Importance: Understanding production volume helps in determining the feasibility of sourcing, cost-effectiveness, and supplier capability. High-volume orders may allow for greater negotiation leverage on pricing and terms. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from order placement to delivery of the finished product.
– Importance: Lead times are critical for supply chain planning. Buyers must consider lead times to ensure that production schedules align with market demands and avoid potential disruptions in supply.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify suppliers who can provide high-quality components that meet specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Buyers need to be aware of MOQs to avoid excess inventory and ensure that their purchase aligns with production needs. Negotiating MOQs can also lead to better pricing structures. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ is a crucial step in the sourcing process, allowing buyers to gather competitive bids and assess supplier capabilities. Including detailed specifications in the RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process, including costs, risks, and logistics, which can significantly impact overall procurement costs. -
Secondary Operations
– Definition: Additional processes performed on thermoformed parts after the initial forming, such as trimming, drilling, or decorating.
– Relevance: Awareness of secondary operations is essential for buyers to fully understand the total cost of ownership and ensure that their supplier can meet all production requirements in a seamless manner.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies and make more informed decisions in the thermoforming market.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the thermoforming Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The thermoforming sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by global economic shifts and technological advancements. Key drivers include the growing demand for lightweight and cost-effective materials across industries such as food packaging, automotive, and healthcare. This has led to increased investment in automation and digital manufacturing technologies, allowing suppliers to enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times.
Emerging trends such as Industry 4.0 are reshaping sourcing strategies. International B2B buyers are leveraging advanced analytics and IoT (Internet of Things) to gain real-time insights into supply chain operations, which helps in optimizing inventory levels and minimizing waste. Additionally, there is a noticeable shift towards just-in-time manufacturing, allowing companies to respond swiftly to market demands while reducing excess stock.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional variations in supply chain dynamics is crucial. For instance, while European buyers may prioritize sustainability and compliance with stringent regulations, buyers in emerging markets might focus on cost-effectiveness and reliability of supply. Establishing partnerships with local suppliers can also mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions, ensuring a steady flow of materials and reducing shipping costs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it has become a critical component of sourcing strategies in the thermoforming sector. The environmental impact of plastics, particularly in terms of waste and pollution, has raised concerns among consumers and regulators alike. As a result, B2B buyers must prioritize ethical sourcing and consider the lifecycle of materials, from production to disposal.
Choosing suppliers that offer green certifications—such as ISO 14001 or certifications for recycled content—can enhance a company’s reputation and comply with increasing regulatory demands. Furthermore, opting for biodegradable or recyclable materials, such as certain grades of PET and PP, can significantly reduce environmental footprints.
Buyers should also engage with suppliers that adopt transparent supply chain practices, ensuring that their materials are sourced responsibly. This includes understanding the origins of raw materials and the sustainability practices employed by suppliers. By prioritizing ethical sourcing, companies can not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brief Evolution/History
The thermoforming process has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, it was primarily utilized for simple packaging solutions. However, advancements in polymer technology and processing techniques have expanded its applications across various sectors, including automotive and medical devices.
The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and automated machinery has revolutionized the industry, allowing for greater precision and customization in production. Today, thermoforming is recognized for its versatility and efficiency, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to balance cost, quality, and sustainability in their operations.
In summary, as B2B buyers navigate the complexities of the thermoforming market, understanding these dynamics, trends, and the importance of sustainability will be essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with their business goals.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermoforming
-
How do I effectively vet suppliers for thermoforming?
To vet suppliers, start by assessing their industry experience and expertise in thermoforming. Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge their reliability and performance. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or ISO 13485, especially for medical applications, to ensure compliance with quality standards. Additionally, visiting the facility (if feasible) can provide insights into their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. Utilize industry associations and trade shows to network and obtain referrals from trusted contacts in your region. -
Can I customize thermoformed products to meet specific requirements?
Yes, most thermoforming suppliers offer customization options. You can specify materials, dimensions, surface finishes, and even colors to align with your branding or functional needs. When engaging with suppliers, provide detailed product specifications, including any unique requirements for your application. It’s advisable to discuss potential design constraints early in the process to ensure that your customizations are feasible and cost-effective. Collaborating on prototypes can also help fine-tune the design before full-scale production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for thermoforming?
MOQs vary by supplier and depend on the complexity of the part and material costs, but they often range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times can also differ significantly based on factors like tooling requirements and production capacity, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify these parameters and discuss potential flexibility for smaller orders or faster turnaround times, especially for urgent projects. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications from suppliers?
Request comprehensive quality assurance documentation from suppliers, including their quality control processes and inspection protocols. Inquire about any relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 13485, or specific industry-related standards. It’s beneficial to establish clear quality expectations in your contract, including acceptable quality levels (AQL) and critical-to-quality (CTQ) characteristics. Periodic audits and inspections can also be arranged to ensure ongoing compliance with your quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing thermoformed products?
Logistics play a crucial role in the sourcing process. Consider factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and transportation modes. Understand the supplier’s shipping capabilities and whether they can accommodate your delivery schedules. Additionally, evaluate the potential for import duties and tariffs when sourcing internationally, as these can affect overall costs. Establishing a clear logistics plan, including inventory management strategies, can help streamline the supply chain and minimize delays. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with my supplier?
If a dispute arises, first attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication with the supplier. Clearly outline your concerns and provide evidence if necessary. If direct negotiations fail, refer to your contract for dispute resolution procedures, which may include mediation or arbitration. Maintaining detailed records of communications and agreements will be beneficial. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother resolutions in the future. -
Are there specific payment terms I should negotiate with thermoforming suppliers?
Yes, payment terms can significantly impact cash flow and project viability. Common practices include paying a percentage upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Negotiate terms that balance your financial situation with the supplier’s needs. Consider options like letter of credit or escrow services for larger orders to mitigate risks. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly stated in the contract to avoid misunderstandings later. -
How can I identify sustainable thermoforming materials?
To identify sustainable materials, inquire about the supplier’s material sourcing practices and their use of recycled or bio-based plastics. Look for certifications that indicate sustainability, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wood-based materials or the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) for recycled content. Engaging suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices can enhance your company’s sustainability profile. Consider collaborating with suppliers on research and development for innovative materials that meet both performance and environmental standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermoforming
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in the thermoforming sector is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their supply chain resilience and optimize costs. Understanding the diverse types of thermoforming plastics—such as PETG, PVC, HIPS, PET, and PP—allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific applications and sustainability goals. By defining product requirements, researching supplier capabilities, and analyzing total cost of ownership, buyers can establish robust relationships with manufacturers that not only meet quality standards but also foster innovation.
As the global market continues to evolve, it is crucial for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to stay ahead of industry trends and regulatory developments. Embracing sustainable practices and leveraging advanced materials will be pivotal in maintaining competitive advantage.
International B2B buyers are encouraged to engage actively with suppliers, explore new partnerships, and invest in technology that enhances manufacturing efficiency. The future of thermoforming is promising; seize the opportunity to transform your procurement strategy today and position your business for success in a dynamic market landscape.