Master the Art of Sourcing Bolt Heads: Key Insights for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bolt heads
In the intricate world of industrial fasteners, bolt heads play a pivotal role in ensuring structural integrity and operational efficiency across various applications. From supporting heavy machinery in bustling African factories to securing critical infrastructure in South American cities, the right bolt head selection is vital for performance and safety. With a myriad of designs, materials, and specifications, navigating the global market for bolt heads presents both challenges and opportunities for B2B buyers.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of bolt heads, exploring a range of types—from hexagonal to countersunk—each tailored for specific applications. It also covers the diverse materials that influence strength and corrosion resistance, such as steel, stainless steel, and titanium. Furthermore, the guide highlights manufacturing and quality control standards that ensure reliability and compliance in international sourcing.
B2B buyers will benefit from strategic insights into supplier selection, cost structures, and market trends, empowering them to make informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are operating in the Middle East or Europe, understanding these nuances will enable you to mitigate risks and enhance supply chain efficiency. With this guide, you can confidently navigate the complexities of bolt head procurement, ensuring that your operations remain robust and competitive in the global marketplace.
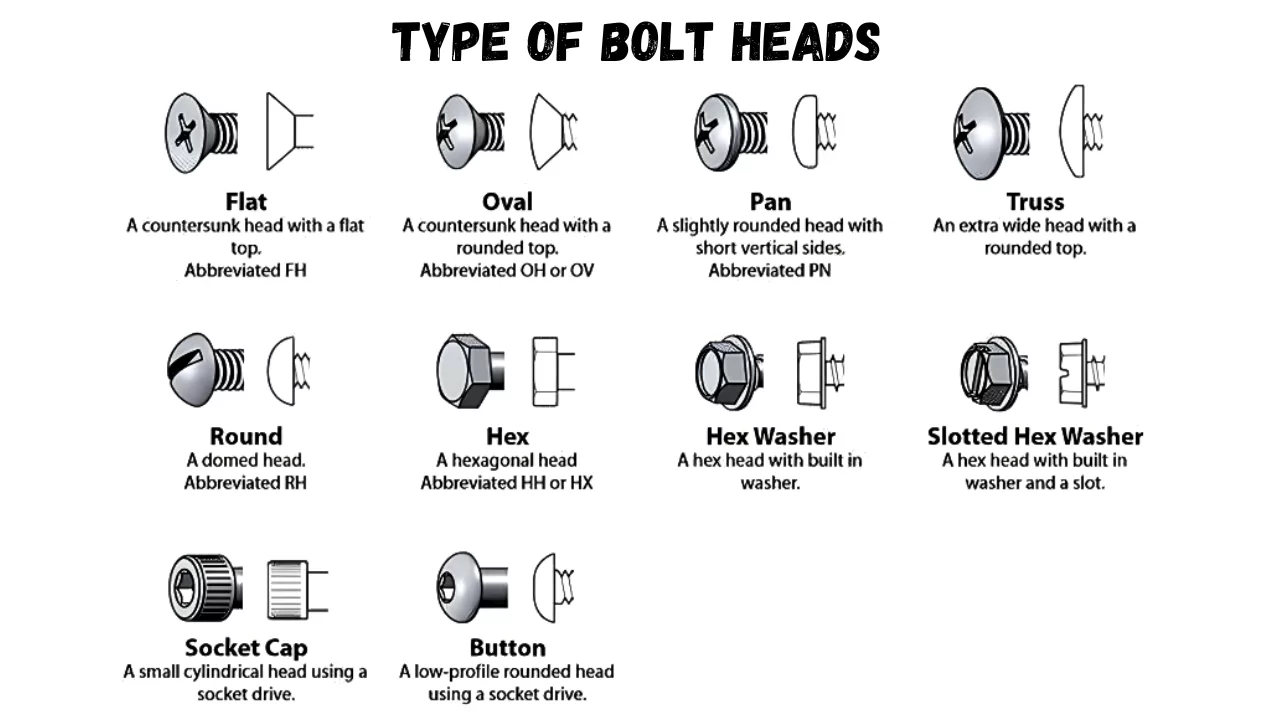
Understanding bolt heads Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hexagonal Head | Six-sided shape for easy wrench access | Construction, automotive, machinery | Widely available and versatile; risk of overtightening |
| Button Head | Rounded top for a smooth finish | Aesthetic applications, furniture | Offers a clean look; less torque transfer than hex |
| Countersunk Head | Sits flush with the surface, ideal for a smooth finish | Electronics, furniture, cabinetry | Provides a sleek appearance; may require precise installation |
| Socket Head | Cylindrical shape with internal hex drive | Aerospace, automotive, machinery | High torque capability; requires specific tools |
| Flange Head | Integrated flange acts as a washer | Heavy equipment, pipelines, automotive | Distributes load evenly; bulkier, may increase costs |
Hexagonal Head
Hexagonal head bolts are characterized by their six-sided shape, which allows for easy gripping with standard wrenches. They are available in a variety of sizes and material grades, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from construction to automotive assembly. For B2B buyers, it is essential to consider the local availability of these bolts, their grades, and compliance with international standards to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Button Head
Button head bolts feature a rounded top that provides a smooth finish, making them ideal for aesthetic applications such as furniture and decorative installations. While they offer a visually appealing solution, their design can limit torque transfer compared to hexagonal counterparts. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs for appearance versus functionality and consider the potential need for additional tools for installation.
Countersunk Head
Countersunk head bolts are designed to sit flush with the surface of the material they are fastened to, creating a sleek appearance. These bolts are commonly used in electronics and cabinetry where aesthetics are important. Buyers should be aware that precise installation is crucial to ensure a proper fit, and they may need to source specific types of drivers to install them effectively.
Socket Head
Socket head bolts feature a cylindrical shape with an internal hex drive, allowing for high torque applications. They are widely used in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where strength and reliability are paramount. When sourcing socket head bolts, B2B buyers should consider the availability of compatible tools and ensure that they meet the necessary quality and safety standards for their specific applications.
Flange Head
Flange head bolts come with an integrated flange that acts as a washer, distributing load evenly across the surface. This design makes them particularly useful in heavy equipment and pipeline applications, where load distribution is critical. Buyers should assess the flange dimensions and thickness to ensure they meet the requirements of their projects, as well as consider potential cost implications due to their bulkier design.
Related Video: Types of Bolts – Types of Bolt Heads
Key Industrial Applications of bolt heads
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bolt heads | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Fastening aircraft components | Ensures structural integrity and safety in aviation | Compliance with strict aerospace standards; lightweight materials |
| Construction | Securing structural frameworks | Enhances stability and longevity of buildings and bridges | Local availability of high-strength bolts; corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Assembling vehicle chassis and components | Facilitates efficient assembly and maintenance of vehicles | Compatibility with various materials and designs; quality certifications |
| Energy (Oil & Gas) | Connecting pipelines and drilling equipment | Prevents leaks and failures, ensuring operational efficiency | Resistance to harsh environments; compliance with safety regulations |
| Marine | Fixing components in ships and offshore platforms | Enhances durability against corrosion and extreme conditions | Sourcing corrosion-resistant materials; adherence to maritime standards |
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, bolt heads play a crucial role in fastening aircraft components such as wings, fuselage, and engines. The specific requirements for bolt heads in this sector include high strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to fatigue and corrosion. International buyers must ensure compliance with rigorous aerospace standards and certifications, such as AS9100, while also considering the sourcing of lightweight materials like titanium or high-strength steel to maintain performance and safety.
Construction
Bolt heads are essential in securing structural frameworks in construction projects, from residential buildings to large bridges. They provide the necessary strength and stability, ensuring that structures can withstand various loads and environmental conditions. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing high-strength bolts with corrosion-resistant coatings, especially in regions with high humidity or exposure to harsh weather, to enhance the longevity of the structures they are involved in.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, bolt heads are widely used for assembling vehicle chassis and other components. They facilitate efficient assembly and allow for easy maintenance and repair. Buyers should focus on sourcing bolts that meet specific automotive standards, such as ISO/TS 16949, and ensure compatibility with various materials used in vehicle manufacturing. Additionally, considering the impact of vibration and thermal cycling on bolt performance is crucial for ensuring vehicle safety and reliability.
Energy (Oil & Gas)
Bolt heads are critical in the energy sector, particularly for connecting pipelines and drilling equipment. They help prevent leaks and ensure operational efficiency in environments that can be harsh and unpredictable. For international buyers, sourcing bolts that comply with safety regulations and possess resistance to corrosive substances is essential. Understanding local regulations and environmental conditions will aid in making informed sourcing decisions that enhance project success.
Marine
In the marine industry, bolt heads are used to fix components in ships and offshore platforms, where they face extreme conditions, including saltwater exposure and high pressures. The durability of bolt heads against corrosion is paramount for the safety and longevity of marine vessels. Buyers should prioritize sourcing corrosion-resistant materials and ensure that all fasteners meet maritime standards, such as those set by the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) or the International Maritime Organization (IMO), to mitigate risks associated with marine operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bolt heads
When selecting materials for bolt heads, it is crucial to consider their properties, applications, and how they align with the specific needs of international B2B buyers. Below is an analysis of four common materials used for bolt heads, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Depending on the grade, steel can also offer varying levels of corrosion resistance, especially when galvanized or coated.
Pros & Cons: Steel is relatively low-cost and widely available, making it a go-to choice for many industries. However, it may not perform well in highly corrosive environments unless treated, which can add to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel bolt heads are commonly used in construction, automotive, and machinery applications. They are compatible with a variety of media, but extra care must be taken in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN. In regions with high corrosion risks, such as coastal areas in Africa or South America, opting for coated or stainless steel variants is advisable.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand extreme temperatures. It is less prone to rust and degradation, making it suitable for demanding environments, including marine and chemical applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and ability to maintain structural integrity under adverse conditions. However, it is typically more expensive than standard steel and can be more challenging to machine.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bolt heads are ideal for applications where exposure to moisture or corrosive substances is a concern, such as in the food processing or chemical industries.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers must verify that the stainless steel grade meets the specific requirements of their application and complies with local regulations. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures can affect material performance, selecting the right grade is crucial.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance. It performs well in high-temperature environments and is non-magnetic, making it suitable for specialized applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its lightweight nature, which is beneficial in aerospace and automotive applications where reducing weight is critical. However, titanium is significantly more expensive than both steel and stainless steel, and its machining can be complex.
Impact on Application: Titanium bolt heads are often used in aerospace, military, and high-performance automotive applications where strength and weight are critical factors.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider the high cost of titanium and ensure that the benefits justify the investment. Compliance with aerospace or military standards may also be necessary, particularly in regions with stringent regulations.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, making it an attractive option for applications where weight savings are essential. It has moderate strength compared to steel but is often used in non-structural applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight and resistance to corrosion, which can reduce overall project costs in terms of transportation and installation. However, its lower strength limits its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum bolt heads are commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries, particularly in components where weight reduction is crucial.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should assess whether the strength of aluminum meets their application needs. In regions with varying climates, such as the Middle East, the corrosion resistance of aluminum can be beneficial, but it may not be suitable for high-load applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for bolt heads | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Construction, automotive | High strength and low cost | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, chemical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, military | Lightweight with high strength | Very high cost and complex machining | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive, non-structural | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for bolt heads, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bolt heads
The manufacturing of bolt heads is a multi-faceted process that requires precision engineering and stringent quality control. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the manufacturing processes, quality assurance standards, and practical insights for verifying supplier capabilities.
Manufacturing Processes for Bolt Heads
The production of bolt heads involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets specified performance and safety standards.
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with selecting the appropriate raw materials, commonly steel, stainless steel, or specialized alloys. The chosen material is then subjected to various treatments to enhance its properties, such as:
- Heat Treatment: Increases hardness and strength through processes like quenching and tempering.
- Surface Treatment: Involves processes like galvanizing or coating to improve corrosion resistance.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming the bolt heads. This can be accomplished through several techniques:
- Cold Forging: This process involves shaping the metal at room temperature, which enhances the material’s strength through work hardening. It is often used for producing high-volume, precision bolt heads.
- Hot Forging: Used for larger bolt heads or when more complex shapes are required, this method involves heating the metal to a pliable state before shaping.
- Machining: For custom or high-precision bolt heads, machining may be employed after initial forming to achieve the desired dimensions and tolerances.
3. Assembly
In some cases, bolt heads may require additional components, such as washers or locking mechanisms. This stage involves assembling these parts using techniques that ensure they fit securely and function as intended.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the appearance and performance of bolt heads. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: Additional coatings or finishes may be applied to enhance aesthetic appeal or further improve corrosion resistance.
- Deburring: Removing sharp edges or burrs from the bolt head to ensure safety and compatibility with other components.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of bolt heads, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards can aid in selecting reliable suppliers.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is the most recognized quality management standard globally, ensuring consistent quality and continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
- ISO 898-1: Specifically pertains to mechanical properties of fasteners made of carbon steel and alloy steel, providing guidelines for tensile strength and hardness.
Industry-Specific Standards
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Specifications: Important for bolt heads used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they can withstand extreme conditions.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets all specifications. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing monitoring during production to identify and rectify any issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to verify compliance with relevant standards and specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the integrity and performance of bolt heads:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of the bolt head and its ability to withstand pulling forces.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the hardness of the material, which is crucial for determining its resistance to wear and deformation.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Evaluates the bolt head’s ability to withstand environmental factors that could lead to degradation.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those operating across diverse regulatory environments, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can reveal adherence to quality standards and production capabilities. Buyers should consider both internal and external audits to gauge compliance effectively.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide detailed documentation of their quality management systems, including certifications and quality control reports.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality and adherence to specifications.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must navigate various challenges regarding quality control and certifications:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local standards, especially when exporting goods.
-
Certification Validity: It is essential to verify that certifications are current and issued by recognized bodies. This can prevent sourcing from suppliers who might misrepresent their compliance status.
-
Cultural Considerations: In regions like Africa and South America, it may be beneficial to establish personal relationships with suppliers to foster transparency and trust regarding quality practices.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for bolt heads is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can ensure they select high-quality products that meet their specific needs, ultimately leading to greater operational success and reliability in their applications.
Related Video: How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bolt heads Sourcing
In the sourcing of bolt heads, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers operating across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis breaks down the cost components, pricing influencers, and offers actionable insights for effective procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in bolt head pricing. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialty alloys. Prices fluctuate based on global commodity markets, with stainless steel typically commanding a higher price due to its corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with higher wage standards, such as those in Europe, the labor component can be substantial. Conversely, regions like South America or Africa may offer lower labor costs, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can lower overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost for specialized bolt heads. Buyers should assess whether the supplier can absorb this cost or if it will be passed on through higher prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards, but they also add to manufacturing costs. Buyers should look for suppliers who balance quality with cost-effectiveness.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on destination, volume, and chosen logistics partners. Understanding Incoterms is essential for clarifying responsibilities and costs associated with transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition and supplier reputation. Established suppliers may charge a premium due to perceived reliability and quality.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes can lead to better pricing. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to align with their needs while capitalizing on volume discounts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom bolt heads require more complex manufacturing processes, increasing costs. Buyers must weigh the necessity of customization against its impact on pricing.
-
Materials: As previously mentioned, the choice of materials directly affects cost. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between material properties and budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Certifications such as ISO or ASTM can add to costs but are crucial for ensuring product quality and compliance. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their application.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and location can significantly impact pricing. Local suppliers might offer lower logistics costs, while international suppliers may provide a wider variety of products.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can help buyers anticipate additional costs. For instance, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may result in higher initial costs but simplifies the purchasing process.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms and pricing, especially when ordering in bulk. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and eventual disposal costs. This holistic view can lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of pricing variations due to geopolitical factors, currency fluctuations, and trade tariffs, especially when sourcing from different continents.
In conclusion, understanding the multifaceted cost structure and pricing dynamics of bolt heads is essential for international B2B buyers. By considering these components and influencers, buyers can make informed, strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that the prices provided in quotes are indicative and may vary based on market conditions and specific supplier circumstances.
Spotlight on Potential bolt heads Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘bolt heads’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bolt heads
In the world of fasteners, understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with bolt heads is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge ensures that procurement decisions align with project specifications and operational requirements across diverse industries. Below are critical specifications and commonly used terms that every buyer should be familiar with.
Key Technical Properties of Bolt Heads
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the classification of the material used to manufacture the bolt, which impacts its strength and corrosion resistance.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the bolt can withstand the operational stresses and environmental conditions it will face. For example, high-strength steel is ideal for heavy machinery, while stainless steel is preferred in corrosive environments. -
Tensile Strength
– Definition: The maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a bolt can withstand before failure.
– B2B Importance: Understanding tensile strength is crucial for safety and performance. In applications like construction or automotive manufacturing, bolts must meet specific tensile strength requirements to prevent structural failures. -
Diameter and Length
– Definition: The diameter refers to the thickness of the bolt, while the length measures how far the bolt extends from the head to the tip.
– B2B Importance: Accurate sizing ensures compatibility with corresponding nuts and the assembly’s overall integrity. Mismatched sizes can lead to assembly issues and increased downtime. -
Thread Pitch
– Definition: The distance between threads, which can be coarse or fine.
– B2B Importance: Thread pitch affects the bolt’s grip and ease of installation. Coarse threads are better for quick assembly, while fine threads provide a stronger hold but require more turns for tightening. -
Finish and Coating
– Definition: The surface treatment applied to the bolt, such as zinc plating or galvanization, which enhances corrosion resistance.
– B2B Importance: The choice of finish is critical for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. Buyers must consider the environmental conditions to select an appropriate finish that prolongs the life of the bolt. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a bolt’s dimensions, ensuring it fits correctly within its application.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are essential in precision applications, such as aerospace or automotive industries, where even minor deviations can lead to failures or safety hazards.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEMs helps buyers source quality components that meet specific manufacturer standards, ensuring compatibility and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. It can affect cash flow, especially for small businesses or projects requiring low volumes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific quantities of products.
– Importance: An RFQ is crucial for comparing costs and ensuring that buyers receive competitive pricing from multiple suppliers, enabling informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International Commercial Terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smoother logistics and compliance in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is vital for project scheduling and inventory management. It allows buyers to plan ahead and avoid delays in production or assembly. -
Quality Assurance (QA)
– Definition: A systematic process of ensuring that products meet specified requirements and standards.
– Importance: QA is essential for maintaining product reliability and safety, especially in high-stakes industries like aerospace and automotive, where failures can have severe consequences.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terminology, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they procure the right bolt heads for their specific applications and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the bolt heads Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global bolt heads market is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by advancements in technology, increasing industrialization, and the rising demand for high-performance fasteners across various sectors. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in infrastructure projects and manufacturing, significantly impacting the demand for reliable and efficient bolt heads.
One of the most notable trends is the integration of smart manufacturing technologies. Automation and data analytics are enhancing production efficiency and precision in bolt head manufacturing. For B2B buyers, this means sourcing products that not only meet traditional specifications but also incorporate advanced features that enhance performance and longevity. Additionally, the rise of digital procurement platforms is revolutionizing how buyers interact with suppliers, facilitating easier access to comprehensive product catalogs and enabling more competitive pricing.
Furthermore, sustainability is emerging as a critical factor influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to environmentally friendly practices and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This trend aligns with global regulatory pressures and consumer expectations for sustainable products, making it essential for international B2B buyers to consider the environmental implications of their sourcing choices.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it has become a crucial consideration in the sourcing of bolt heads. The environmental impact of fastener production, particularly concerning resource extraction and manufacturing processes, is significant. As such, B2B buyers must assess the sustainability credentials of their suppliers. This includes evaluating the materials used, energy consumption during manufacturing, and waste management practices.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction, with companies striving to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitative labor practices and that they promote fair trade. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and SA8000 for social accountability are becoming essential benchmarks for buyers looking to partner with responsible suppliers.
Moreover, the adoption of green materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly coatings, is on the rise. These materials not only reduce the environmental footprint but can also improve the overall durability and performance of bolt heads. For B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers that prioritize sustainability can enhance brand reputation and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of bolt heads is closely tied to advancements in engineering and manufacturing. Historically, the use of bolts can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where simple wooden or metal fasteners were utilized for construction and machinery. The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point, as mass production techniques emerged, allowing for standardized bolt head designs, such as hexagonal and square shapes.
In recent decades, innovations in materials science have led to the development of high-strength alloys and coatings that enhance corrosion resistance and performance under extreme conditions. This evolution not only reflects the growing complexity of modern machinery but also underscores the need for international B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in the fastener industry. Understanding this history can provide valuable insights into current sourcing strategies and the future direction of bolt head production.
Related Video: Exim Trade Conclave 2025 LIVE | Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman Delivers Keynote Address | N18L
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bolt heads
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for bolt heads?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, certifications (like ISO or ASTM), and product quality standards. Request samples to assess the quality of their bolt heads firsthand. Additionally, check their reputation through reviews and testimonials from other international buyers. It’s essential to verify their production capabilities, including the ability to meet your specific needs, such as customization or volume demands. Establish clear communication channels to ensure they understand your requirements and can respond promptly. -
Can I customize bolt heads to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for bolt heads, including variations in size, shape, material, and finish. When seeking customization, provide detailed specifications and drawings to avoid miscommunication. Be aware that customization may increase lead times and costs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs upfront and confirm the supplier’s ability to deliver the desired modifications without compromising quality. Always request prototypes or samples before placing large orders to ensure they meet your expectations. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for bolt heads?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly based on the supplier, the type of bolt head, and the level of customization. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 to several thousand units. Lead times also depend on factors such as the complexity of the order, supplier location, and production capacity. For standard items, lead times may be as short as two weeks, while custom orders could take several months. Always clarify these details during negotiations to plan your procurement timeline effectively. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted by international suppliers?
International suppliers typically accept various payment methods, including bank transfers, letters of credit, and online payment platforms like PayPal. The choice of payment method may depend on your relationship with the supplier and the size of the order. Letters of credit are often recommended for larger transactions, providing security for both parties. Ensure you discuss payment terms upfront, including any required deposits, payment schedules, and currency exchange considerations, to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for bolt heads?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications from your supplier, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or specific industry standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN). Ask about their quality control processes, including inspections and testing methods used during production. Some suppliers may offer third-party inspection services to validate product quality before shipment. It’s advisable to establish clear quality expectations in your contract, including penalties for non-compliance, to safeguard your interests. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing bolt heads internationally?
When sourcing bolt heads internationally, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling industrial components to ensure timely delivery. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country to avoid delays or additional costs. It’s also beneficial to negotiate Incoterms with your supplier, defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and risk during transit. Proper logistics planning can significantly reduce lead times and costs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding bolt head orders?
To handle disputes effectively, maintain open communication with your supplier and document all interactions related to the order. If a dispute arises, refer to your contract for resolution procedures and timelines. Mediation or arbitration can be effective for resolving conflicts without escalating to legal action. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations during disputes. If necessary, involve third-party arbitration to ensure an unbiased resolution. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with bolt head suppliers?
To maintain a long-term relationship with suppliers, prioritize clear communication and regular feedback on their products and services. Schedule periodic reviews to discuss performance, quality, and any emerging needs you may have. Building trust through timely payments and honoring contracts can strengthen your partnership. Consider collaborating on product development or joint marketing efforts, which can create mutual benefits and foster loyalty. Lastly, keep abreast of their capabilities and innovations to maximize your procurement strategy.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bolt heads
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, the strategic sourcing of bolt heads is paramount for ensuring operational efficiency and product reliability. Key considerations for B2B buyers include the selection of appropriate materials, understanding the nuances of various head designs, and aligning with suppliers who meet international quality standards. By prioritizing these factors, businesses can enhance assembly performance, minimize the risk of component failure, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction.
Actionable Insights:
- Evaluate Supplier Reliability: Ensure that potential suppliers can provide consistent quality and timely delivery to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
- Understand Regional Variations: Each market has unique climatic and regulatory challenges; tailor your sourcing strategy to meet local demands, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Leverage Expert Consultation: Engage with industry experts to stay updated on trends and innovations in bolt head technology.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced fastening solutions will continue to grow. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing and aligning with trusted partners, international B2B buyers can position themselves for success in an evolving marketplace. Embrace these insights to secure a competitive edge and drive your business forward.