Master the Art of Sourcing Plastic Tubing for Global B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic tubing
Flexible plastic tubing is an essential component in a myriad of industries, acting as a critical medium for the transfer of fluids, gases, and materials. Its versatility makes it indispensable in sectors such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and manufacturing. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of plastic tubing sourcing is crucial for operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the global market for plastic tubing, focusing on key aspects that influence purchasing decisions. Buyers will gain insights into various types of tubing, including PVC, polyurethane, and silicone, along with their specific applications. We delve into the materials used, examining how they impact performance and suitability for diverse operational environments.
Furthermore, the guide outlines essential manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable suppliers who meet their stringent requirements. Cost considerations, including total cost of ownership, are critically analyzed, allowing procurement teams to make economically sound decisions.
Additionally, we will highlight regional market trends and regulatory frameworks pertinent to different international markets, ensuring that buyers are well-informed about compliance. With expert answers to frequently asked questions, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing plastic tubing, empowering them to forge resilient supplier partnerships and enhance their competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding plastic tubing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Tubing | Cost-effective, flexible, and transparent | Food & beverage processing, medical devices | Economical but limited temperature range; check chemical compatibility. |
| Polyurethane (PU) Tubing | High abrasion resistance, excellent flexibility | Pneumatics, industrial automation | Durable and kink-resistant; higher cost and limited chemical resistance. |
| Silicone Tubing | High temperature tolerance, biocompatible | Pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food processing | Superior purity and heat tolerance; premium cost and less abrasion-resistant. |
| Polyethylene (PE) Tubing | Lightweight, good chemical resistance, semi-rigid | Chemical processing, agriculture | Cost-effective but lower pressure rating and flexibility. |
| Fuel & Oil Flexible Tubing | Formulated for fuel/oil resistance, reinforced options | Automotive, machinery lubrication | Specialized for fuels/oils; not suitable for food or medical applications. |
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Tubing
PVC tubing is one of the most commonly used types of plastic tubing due to its affordability and versatility. It is characterized by its flexibility and clarity, making it suitable for applications in food and beverage processing, as well as medical device assembly. B2B buyers should ensure that the PVC tubing meets necessary certifications for food-grade use, evaluate its temperature range suitability, and assess compatibility with cleaning agents and transported fluids. Its cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice, but buyers must be mindful of its limitations regarding temperature and chemical compatibility.
Polyurethane (PU) Tubing
Polyurethane tubing stands out for its exceptional durability and resistance to abrasion and kinking, making it ideal for pneumatic applications and industrial automation. Its elasticity allows it to withstand repeated movement without compromising performance. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific chemical resistance of PU tubing is crucial, as it may not be suitable for all fluid types. Additionally, while it offers superior mechanical properties, its higher price point compared to PVC could impact budget considerations. Buyers should weigh the benefits of long-term durability against initial costs.
Silicone Tubing
Silicone tubing is renowned for its high-temperature tolerance and biocompatibility, making it a preferred choice in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Its inert properties ensure that it does not leach harmful substances, making it ideal for applications where product purity is critical. B2B buyers should consider the regulatory approvals required for their specific applications, as well as the higher cost associated with silicone tubing. While it provides excellent heat resistance, its lower abrasion resistance may limit its use in high-wear environments.
Polyethylene (PE) Tubing
Polyethylene tubing is lightweight and offers good chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications in chemical processing and agriculture. It is available in various densities, including high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE), with the latter providing greater flexibility. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their applications, including pressure ratings and environmental conditions, as PE tubing may have limitations in flexibility compared to other materials. Its cost-effectiveness makes it a viable option for many industries, but careful consideration of its mechanical properties is essential.
Fuel & Oil Flexible Tubing
Fuel and oil flexible tubing is specifically designed to withstand exposure to hydrocarbons, making it essential for automotive and machinery lubrication applications. Reinforced options provide additional strength and durability. For B2B buyers, it is critical to ensure that the tubing is not used in food or medical applications due to potential contamination issues. While it offers specialized resistance to fuels and oils, buyers must consider the specific requirements of their applications, including temperature and pressure ratings, to ensure optimal performance.
Related Video: HOW TO JOIN PLASTIC PIPE AND LEAD PIPE.
Key Industrial Applications of plastic tubing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plastic tubing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Beverage transfer systems | Ensures safe and hygienic transport of liquids | Certification for food safety (e.g., FDA, NSF), flexibility in design |
| Pharmaceuticals | Medical device manufacturing | High purity and compliance with health regulations | Compliance with medical standards, biocompatibility, and temperature resistance |
| Agriculture | Irrigation and fluid delivery systems | Efficient water management and nutrient delivery | Durability against environmental factors, chemical compatibility |
| Automotive | Fuel and oil transfer lines | Specialized resistance to fuels and oils | Material compatibility with specific fuels, pressure ratings |
| Industrial Automation | Pneumatic control systems | Enhanced operational efficiency and reliability | Kink resistance, abrasion resistance, and chemical compatibility |
Food & Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, plastic tubing is crucial for beverage transfer systems, ensuring safe and hygienic transport of liquids. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing tubing that meets stringent food safety certifications, such as FDA or NSF standards. Additionally, the flexibility in design can help accommodate various processing environments, making it essential to understand the specific requirements of each application to prevent contamination and ensure product integrity.
Pharmaceuticals
Plastic tubing plays a vital role in the manufacturing of medical devices, where high purity and compliance with health regulations are paramount. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the tubing material is biocompatible and meets medical standards like USP Class VI. Moreover, the tubing must withstand specific temperature ranges and chemical exposures, making it critical for international buyers to verify supplier capabilities and certifications to avoid costly compliance issues.
Agriculture
In agriculture, plastic tubing is used for irrigation and fluid delivery systems, facilitating efficient water management and nutrient delivery to crops. Buyers should consider the tubing’s durability against environmental factors such as UV exposure and temperature fluctuations. Additionally, compatibility with fertilizers and other chemicals is essential to prevent degradation. Understanding local agricultural practices can also inform sourcing decisions, ensuring that the tubing meets regional needs.
Automotive
Plastic tubing is extensively utilized in automotive applications, particularly for fuel and oil transfer lines. This tubing must possess specialized resistance to fuels and oils to prevent leaks and ensure safety. B2B buyers need to focus on sourcing materials that are compatible with specific fuels used in their vehicles, as well as ensuring that the tubing can withstand varying pressure ratings. Awareness of local automotive regulations and standards is vital for compliance and safety.
Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, plastic tubing is integral to pneumatic control systems, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability. The tubing must be kink-resistant and abrasion-resistant to withstand the rigors of industrial environments. Buyers should prioritize sourcing tubing that is chemically compatible with the fluids being transported, as well as evaluating the tubing’s performance under high-pressure conditions. Understanding the specific operational needs of the automation systems can help in selecting the most suitable tubing solutions.
Related Video: How to install Compression Fittings on plastic tubing
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic tubing
Flexible plastic tubing is a crucial component across various industries, and selecting the right material can significantly impact operational efficiency and compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in plastic tubing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Tubing
Key Properties: PVC tubing is known for its excellent flexibility, transparency, and chemical resistance. It typically operates effectively within a temperature range of -10°C to 60°C and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons: One of the main advantages of PVC is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, it has limitations in temperature resistance and can become brittle over time, especially under UV exposure. Additionally, while PVC is versatile, its chemical compatibility can be a concern, particularly with solvents.
Impact on Application: PVC is widely used in food and beverage processing, medical devices, and general fluid transport. Buyers must ensure that the tubing meets necessary certifications, such as FDA or NSF for food-grade applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional compliance standards like ASTM or DIN. In markets like South Africa and the UK, regulatory compliance is critical, and buyers should verify that suppliers provide relevant certifications.
Polyurethane (PU) Tubing
Key Properties: PU tubing boasts superior abrasion resistance, elasticity, and kink resistance. It can withstand temperatures from -40°C to 90°C and has a high-pressure rating, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PU tubing is its durability and flexibility, which makes it ideal for pneumatic applications and environments with repeated movement. However, it is generally more expensive than PVC and may have limited chemical resistance against certain solvents.
Impact on Application: PU tubing is commonly used in industrial automation, pneumatic lines, and applications involving abrasive fluids. Its resilience ensures a longer service life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the higher upfront costs of PU tubing against its longevity and reduced maintenance needs. Compliance with international standards such as ISO and ASTM is essential, particularly in regulated industries.
Silicone Tubing
Key Properties: Silicone tubing is characterized by its high-temperature tolerance (up to 200°C), biocompatibility, and chemical inertness. It is flexible and can handle a variety of pressures, though it is less robust in high-wear situations.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of silicone is its purity and ability to maintain performance in extreme temperatures, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and food processing applications. However, it tends to be more expensive and less resistant to abrasion than other materials.
Impact on Application: Silicone is favored in industries where product purity is critical, such as biotech and pharmaceuticals. Its biocompatibility makes it suitable for medical applications, but its cost may be a barrier for some buyers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that silicone tubing meets specific regulatory approvals, such as USP Class VI or ISO 10993. Understanding local regulations regarding medical and food-grade materials is vital for compliance.
Polyethylene (PE) Tubing
Key Properties: PE tubing is lightweight, chemically stable, and available in both high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE) variants. It typically operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 60°C.
Pros & Cons: PE is cost-effective and offers good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various applications, including agriculture and chemical processing. However, it has a lower pressure rating and flexibility compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: PE tubing is commonly used in water lines, chemical processing, and agricultural applications. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to handle and install, but buyers should consider its limitations in high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the specific type of PE tubing required for their applications, as well as compliance with regional standards. In Europe and the Middle East, adherence to chemical safety regulations is particularly important.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic tubing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Food & beverage, medical devices | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited temperature range | Low |
| Polyurethane | Pneumatics, industrial automation | Superior durability and flexibility | Higher cost than PVC | Med |
| Silicone | Pharmaceuticals, food processing | High purity and temperature tolerance | Higher price and less abrasion-resistance | High |
| Polyethylene | Chemical processing, agriculture | Lightweight and chemically stable | Lower pressure rating | Low |
This guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into material selection for plastic tubing, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic tubing
Overview of Plastic Tubing Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing plastic tubing involves several distinct stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the required specifications for quality and performance. Understanding these processes will help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing plastic tubing, particularly in compliance with international standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of the manufacturing process involves selecting and preparing the raw materials. Common materials used in plastic tubing include PVC, polyurethane (PU), and polyethylene (PE).
- Material Selection: Buyers must consider the specific properties required for their applications—such as chemical resistance, flexibility, or temperature tolerance. For example, PU is preferred for its abrasion resistance, while PVC is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness.
- Compounding: Raw materials are often compounded with additives to enhance performance characteristics, such as UV stabilization or anti-microbial properties. This stage is crucial as it directly affects the tubing’s performance in its intended application.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming the tubing. This process typically employs one of two main techniques:
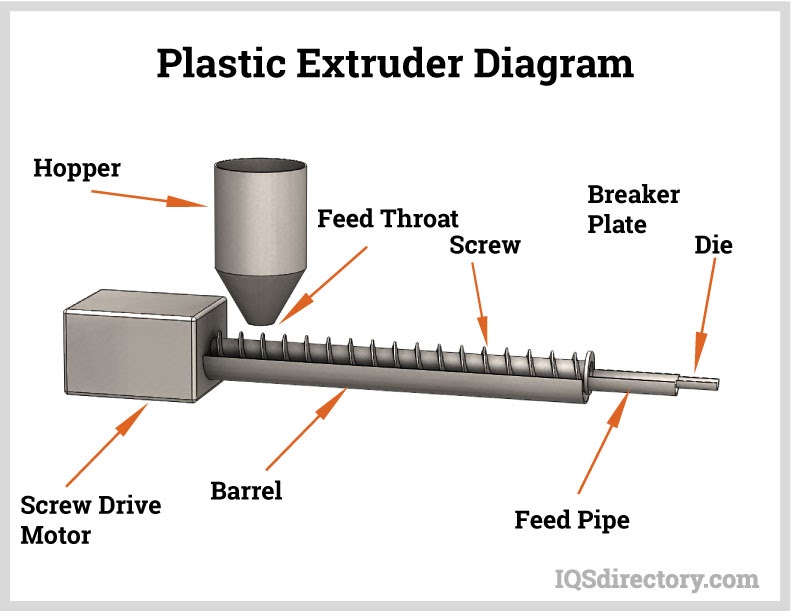
- Extrusion: The most common method, where the compounded material is fed into an extruder. The material is heated, melted, and forced through a die to form continuous tubing of the desired diameter. Adjusting the temperature and pressure settings during extrusion is essential to ensure uniformity and quality.
- Blow Molding: Used for creating hollow tubing, where air is blown into a pre-formed tube to expand it into the desired shape. This method is less common but useful for specific applications requiring thicker walls or more complex shapes.
3. Assembly
In some cases, tubing may require additional components to be assembled, such as fittings or connectors. This stage often involves:
- Cutting and Joining: Tubing is cut to specified lengths and may be joined with other components using techniques such as welding, adhesives, or mechanical fasteners.
- Customization: Buyers can often request custom colors, sizes, or additional features (like printed markings) to meet specific operational needs.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the product’s characteristics and prepare it for shipping. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Tubing may undergo treatments to improve its surface properties, such as making it smoother for fluid flow or adding coatings for enhanced chemical resistance.
- Quality Inspections: Before packaging, the tubing is thoroughly inspected to ensure it meets all specifications and standards.
Quality Assurance in Plastic Tubing Production
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring that plastic tubing meets both regulatory and customer specifications. B2B buyers should be aware of the key standards and practices that manufacturers implement to guarantee quality.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This international standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For tubing used in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral at various stages of production to ensure compliance with specifications:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet the specified requirements before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps detect any deviations from standards early, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed products undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet all specifications before being shipped to customers.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods for quality assurance can include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensuring the tubing meets specified diameters and lengths.
- Burst Pressure Testing: Assessing the tubing’s ability to withstand pressure without failure, which is crucial for applications involving high fluid pressures.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Evaluating how well the tubing performs against various chemicals it may encounter in its application.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing processes and quality management systems can provide insights into their commitment to quality.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports and certifications from suppliers, which outline testing methodologies and results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional regulations and standards is crucial.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements for plastic tubing, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with relevant local regulations.
- Cultural and Operational Differences: Buyers must be aware of potential cultural differences in business practices, which can affect communication and quality expectations. Establishing clear contracts and specifications is essential to mitigate misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in plastic tubing production, B2B buyers can make more informed sourcing decisions, ensuring that they select high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Plastic bottle manufacturing process – explained by UpSkul
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic tubing Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics for plastic tubing sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers. The complexity of these factors can significantly impact procurement decisions, especially for businesses operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Plastic Tubing
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials varies significantly based on the type of tubing. For instance, PVC is generally more economical compared to specialized materials like silicone or polyurethane, which often carry a premium due to their enhanced properties. Fluctuations in polymer prices due to global oil prices can also affect costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the region of manufacturing. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia, buyers may find more competitive pricing. However, in Europe and North America, labor costs are typically higher, which can be reflected in the final product price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with advanced machinery and automation may have lower overhead costs, allowing them to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom or specialized tubing can be significant. This cost is often amortized over the production run, impacting the price per unit. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs when considering custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that tubing meets industry standards and certifications (e.g., FDA, NSF) incurs additional costs. Manufacturers that prioritize stringent QC processes may charge higher prices, but this can lead to better reliability and compliance.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including freight and insurance, can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding these logistics costs is essential to evaluate the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely based on market positioning, brand reputation, and service offerings. Established suppliers with strong reputations may command higher prices, justified by their reliability and quality assurance.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence pricing strategies in the plastic tubing market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) often dictate pricing. Higher volumes typically lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to specialized tooling and production processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of material has a direct impact on cost. For example, food-grade silicone will generally be more expensive than standard PVC. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher-cost materials against their specific application needs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet rigorous industry standards or certifications may come at a premium. However, investing in high-quality tubing can mitigate risks related to compliance and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the cost structure of international shipments. Buyers should be aware of who bears the risk and responsibility for shipping, as this can influence overall costs.
Buyer Tips
To navigate the complexities of pricing in the plastic tubing market, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly when placing large orders or establishing long-term partnerships. Leverage competitive quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership rather than just the unit price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and compliance to ensure long-term value.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For example, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to labor and material costs.
-
Request Quotes with Transparency: Ensure that suppliers provide detailed quotes that break down costs. This transparency helps in making informed comparisons and decisions.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keep abreast of global market trends, including material costs and regulatory changes, to anticipate pricing shifts and plan procurement strategies accordingly.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific supplier quotes, market conditions, and negotiation outcomes. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to confirm current pricing and terms.
Spotlight on Potential plastic tubing Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘plastic tubing’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic tubing
Key Technical Properties of Plastic Tubing
When sourcing plastic tubing, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Material grade defines the composition and quality of the plastic used in the tubing. Common materials include PVC, polyurethane, and polyethylene. Each material has unique properties, such as chemical resistance, flexibility, and temperature tolerance. Selecting the correct material grade is vital for ensuring that the tubing meets the specific demands of your application, such as compliance with health and safety regulations in food or medical sectors. -
Diameter and Wall Thickness
– The diameter and wall thickness of tubing are critical for determining flow rates and pressure handling capabilities. Standard diameters range from a few millimeters to several inches, while wall thickness can vary based on the intended application. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the tubing can accommodate the necessary flow rates and withstand operational pressures is essential for maintaining system efficiency and safety. -
Temperature Tolerance
– Temperature tolerance indicates the range of temperatures the tubing can withstand without degrading. For example, silicone tubing offers high-temperature resistance, while PVC is more suitable for lower temperatures. This specification is particularly important for applications involving hot liquids or environments with extreme temperature fluctuations, as using inappropriate tubing can lead to failure or leakage. -
Chemical Resistance
– Different tubing materials exhibit varying levels of resistance to chemicals and solvents. For instance, polyurethane tubing is known for its abrasion resistance but may have limitations regarding certain chemicals. Understanding the chemical compatibility of the tubing with the substances it will encounter is crucial to prevent premature failure and ensure long-term durability. -
Flexibility and Kink Resistance
– Flexibility refers to how easily the tubing can bend without breaking, while kink resistance indicates its ability to maintain flow under bending stress. Tubing that is too rigid may not be suitable for applications requiring tight bends or movement. B2B buyers should assess these properties to ensure the tubing performs reliably in dynamic environments. -
Certifications and Compliance
– Certifications like FDA, NSF, or ISO indicate that the tubing meets specific safety and quality standards. These certifications are particularly important in regulated industries such as food and beverage or pharmaceuticals. Buyers should verify that the tubing complies with relevant standards to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can streamline the procurement process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality components that fit their specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and manage inventory effectively, particularly when sourcing specialized tubing. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best value for their procurement needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, covering aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations and manage risks associated with international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning and ensuring that supply chains remain uninterrupted, particularly in industries with tight deadlines. -
Customization
– Customization refers to the ability to tailor products to meet specific requirements, such as color, size, or material properties. For B2B buyers, leveraging customization options can lead to enhanced product performance and differentiation in competitive markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing plastic tubing, ensuring that their procurement aligns with operational needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the plastic tubing Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global plastic tubing market is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting buyer preferences. International B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must stay attuned to these dynamics. One major driver is the increasing demand for customized solutions tailored to specific applications across various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. This customization trend is facilitated by advancements in manufacturing techniques such as extrusion and blow molding, enabling suppliers to offer a wider range of sizes, colors, and material compositions.
Additionally, sustainability concerns are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize environmental responsibility, leading to a rise in the use of recycled materials and bio-based polymers. Emerging technologies, such as digital platforms for supplier discovery and procurement, are also enhancing transparency in the supply chain, allowing buyers to make informed decisions based on supplier reliability and compliance records.
Furthermore, regulatory frameworks are becoming stricter, especially in sectors like healthcare and food processing, necessitating that buyers understand local and international compliance standards. As a result, engaging with suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to these regulations is crucial. In summary, international buyers must navigate a complex landscape characterized by customization, sustainability, and compliance to optimize their sourcing strategies in the plastic tubing sector.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral concern but a central tenet in the sourcing of plastic tubing. The environmental impact of plastic production and waste has prompted businesses to rethink their procurement strategies. International B2B buyers must evaluate the lifecycle of plastic tubing products, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal. Opting for suppliers who utilize recycled materials or bio-based alternatives can significantly reduce the ecological footprint of operations.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for sustainable sourcing are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. In the context of plastic tubing, buyers should also look for products that are certified as food-safe (e.g., NSF, FDA) or compliant with environmental regulations (e.g., RoHS, REACH). This not only ensures compliance but also enhances brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of plastic tubing has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market needs. Initially, materials like rubber and metal dominated the industry, but the introduction of synthetic polymers in the mid-20th century revolutionized tubing applications. The development of flexible plastics such as PVC, polyurethane, and polyethylene led to increased versatility and performance in various sectors, including healthcare and manufacturing.
As industries grew more complex, the demand for specialized tubing solutions emerged, driving innovation in manufacturing processes and material science. Today, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and customization, reflecting broader societal trends and regulatory requirements. Understanding this historical context allows B2B buyers to appreciate the advancements in product offerings and the importance of aligning sourcing strategies with contemporary market demands.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic tubing
-
What key factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for plastic tubing?
When vetting suppliers for plastic tubing, prioritize their industry experience, product range, and certifications. Verify compliance with international standards such as ISO, FDA, or NSF, which indicate quality and safety. Request samples to assess product quality and performance in your specific application. Additionally, evaluate their responsiveness and customer support, as these can significantly impact your procurement process. It’s also beneficial to check references from other clients in your region or industry to gauge reliability and service levels. -
Can I customize plastic tubing to fit my specific application needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for plastic tubing. This can include variations in diameter, thickness, material composition, color, and mechanical properties. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers, including any regulatory compliance needs relevant to your industry. Customization can enhance performance and efficiency, particularly in specialized applications such as pharmaceuticals or food processing. Ensure you understand the implications of customization on lead times and costs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for plastic tubing?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plastic tubing can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the customization involved. Generally, standard products may have lower MOQs, while customized tubing may require larger orders. Lead times can range from a few days for stock items to several weeks for custom orders, influenced by factors such as production schedules and shipping logistics. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for the plastic tubing I source?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications from suppliers, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or specific compliance certificates relevant to your industry. Establish a clear understanding of their quality control processes, including testing methods and frequency. Consider conducting third-party audits or inspections, particularly for high-stakes applications. Building a relationship with suppliers who prioritize transparency in their QA processes can enhance your confidence in the materials sourced. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing plastic tubing internationally?
When sourcing plastic tubing internationally, consider shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. Understand the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) that will govern the transaction, as these define responsibilities for shipping and risk. Additionally, evaluate the supplier’s ability to manage logistics effectively, including their experience with international shipping and customs clearance. Partnering with a supplier who has robust logistics capabilities can help mitigate potential delays and unforeseen costs. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier regarding plastic tubing orders?
In the event of a dispute with a supplier, start by reviewing the contract terms to understand your rights and obligations. Communicate your concerns clearly and attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct dialogue. If resolution is not possible, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation. Document all communications and agreements, as this can be critical in any formal dispute resolution process. Establishing a clear dispute resolution process in your contracts can also help manage future conflicts. -
How can I assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) for plastic tubing?
To assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) for plastic tubing, consider not just the purchase price but also factors such as shipping costs, storage, and handling. Evaluate the expected lifespan and durability of the tubing, as longer-lasting products can reduce replacement frequency and associated costs. Additionally, factor in compliance costs related to regulations in your industry. A comprehensive understanding of TCO can help you make more informed purchasing decisions that align with your budget and operational goals. -
Are there specific regulatory considerations for sourcing plastic tubing in different regions?
Yes, regulatory considerations can vary significantly by region. In Europe, for example, compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) is crucial, while in the U.S., FDA regulations may apply for food-grade tubing. In Africa and South America, local regulations may differ, necessitating thorough research. Ensure your supplier is knowledgeable about and compliant with the relevant regulations in your target market. This diligence can help avoid costly penalties and ensure product acceptance in your region.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic tubing
In the rapidly evolving landscape of flexible plastic tubing, strategic sourcing is imperative for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains and meet compliance standards. By understanding the various types of tubing available—such as PVC, polyurethane, silicone, and polyethylene—buyers can align their selections with specific application needs, ensuring quality and durability. It is essential to evaluate suppliers not only on cost but also on their ability to provide reliable, certified products that adhere to regional regulations.
As international markets grow more interconnected, the importance of sustainability and customization in sourcing cannot be overstated. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively seek out suppliers who prioritize these aspects, as they can significantly enhance operational efficiency and long-term value.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and compliant plastic tubing solutions will continue to rise. Now is the time for B2B buyers to leverage insights from this guide to establish resilient partnerships with suppliers, ensuring they remain competitive in their respective industries. Engage with your suppliers, explore customization options, and invest in quality to secure a sustainable future for your business.