Master the Art of Sourcing Pump Vacuum Pressure Solutions
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pump vacuum pressure
In today’s competitive global market, pump vacuum pressure technologies play a pivotal role across various industries, from pharmaceuticals to food processing. These systems are essential for maintaining precise environmental conditions, ensuring product quality, and optimizing operational efficiency. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their operational capabilities, understanding the intricacies of pump vacuum pressure becomes increasingly critical.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of vacuum pumps, including oil rotary, dry screw, and liquid ring variants, providing insights into their specific applications and advantages. Buyers will gain an understanding of the materials used in pump construction, ensuring they select equipment that meets their operational needs while adhering to quality standards.
Additionally, the guide covers essential aspects of manufacturing and quality control processes, helping buyers evaluate suppliers effectively. With insights into market trends and cost considerations, it empowers decision-makers to navigate the complexities of sourcing.
Whether you are in Argentina looking for reliable suppliers or in the Middle East assessing the latest technologies, this guide is tailored to equip you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions. By leveraging this information, international buyers can enhance their operational efficiencies and drive sustainable growth in their respective markets.
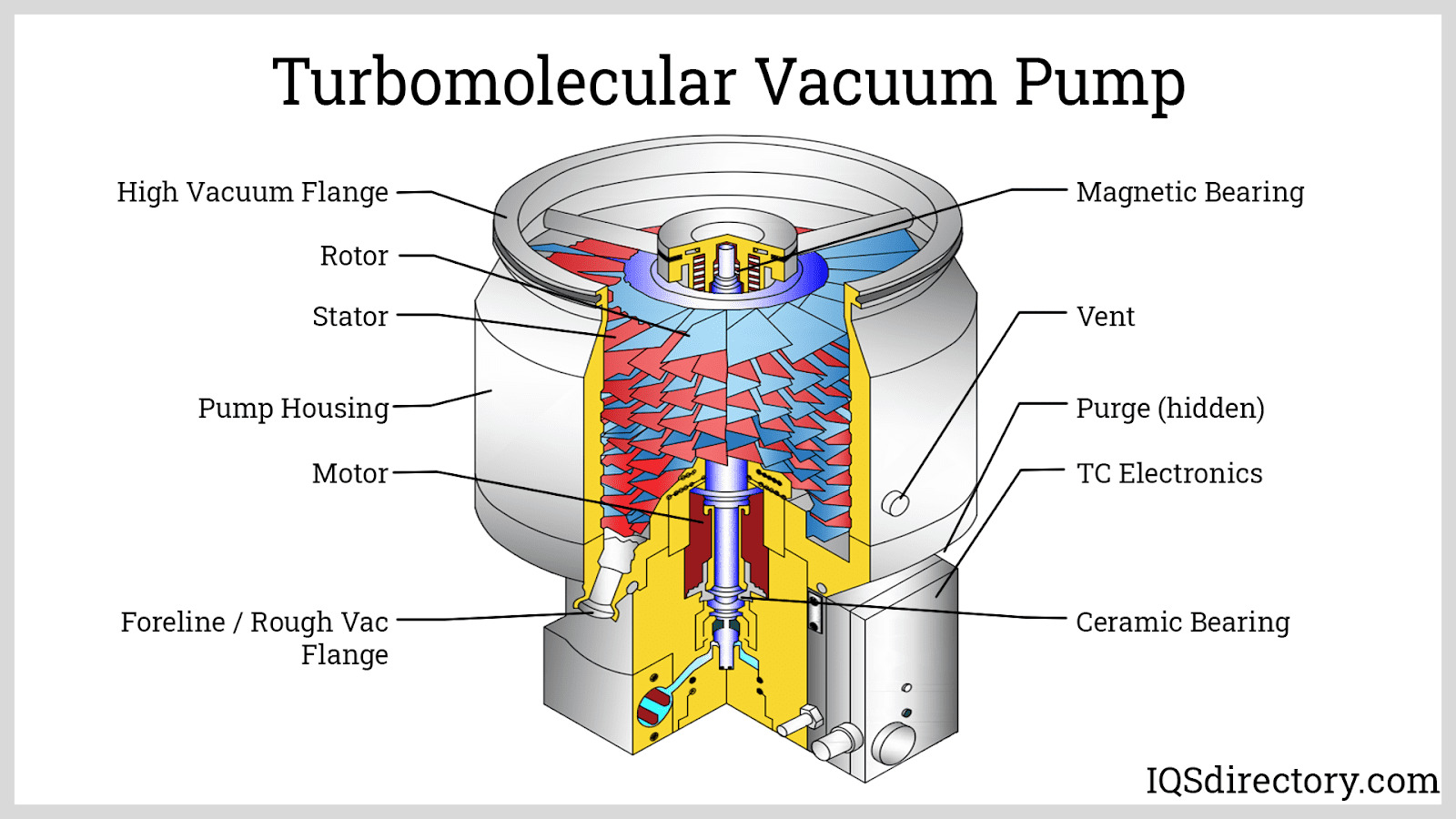
Understanding pump vacuum pressure Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump | Utilizes rotating vanes to create a vacuum; oil-lubricated or oil-free options available. | Pharmaceutical, food processing, electronics | Pros: High efficiency, reliable; Cons: Requires regular maintenance, oil management needed for lubricated types. |
| Dry Screw Vacuum Pump | Features two intermeshing screws; oil-free operation, minimal maintenance. | Semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing | Pros: Low maintenance, energy efficient; Cons: Higher initial cost, noise levels can be significant. |
| Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump | Uses liquid to form a ring that traps gas; operates at low to medium vacuum levels. | Chemical processing, paper manufacturing | Pros: Simple design, effective for wet applications; Cons: Liquid management required, lower efficiency than others. |
| Roots Blower | Positive displacement pump; utilizes two rotors to move air/gas without compressing it. | Wastewater treatment, pneumatic conveying | Pros: High flow rates, robust design; Cons: Limited vacuum levels, requires additional components for deep vacuum. |
| Claw Vacuum Pump | Combines claw technology with a compact design; oil-free operation. | Packaging, wood processing, recycling | Pros: Compact, low maintenance; Cons: Limited performance in extreme conditions, initial cost may be higher. |
Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump
Rotary vane vacuum pumps are highly regarded in various industries for their reliability and efficiency. They can be categorized into oil-lubricated and oil-free variants, allowing businesses to select based on their operational needs. These pumps excel in applications requiring consistent vacuum levels, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing and food processing. Buyers should consider the maintenance requirements and oil management, particularly with oil-lubricated models, which may incur additional operational costs.
Dry Screw Vacuum Pump
The dry screw vacuum pump is known for its oil-free operation and minimal maintenance needs. It consists of two intermeshing screws that create a vacuum without the use of any lubricants, making it ideal for sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing and chemical processing. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings on maintenance and energy efficiency can be substantial. Buyers should assess the noise levels and ensure compatibility with their processes before purchasing.
Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump
Liquid ring vacuum pumps utilize a rotating liquid to create a vacuum, making them suitable for low to medium vacuum applications. They are commonly used in industries like chemical processing and paper manufacturing, where wet applications are prevalent. The simplicity of their design makes them easy to operate; however, they require careful management of the operating liquid, which can add to operational complexity. Buyers should evaluate the efficiency needs of their processes against the operational costs associated with liquid management.
Roots Blower
Roots blowers are unique in that they are positive displacement pumps that move air or gas without compressing it. They are widely used in applications such as wastewater treatment and pneumatic conveying. Their robust design allows for high flow rates, which is beneficial in large-scale operations. However, they are limited in the vacuum levels they can achieve and often require additional components to reach deeper vacuums. Buyers should consider their specific flow requirements and the potential need for supplementary equipment.
Claw Vacuum Pump
Claw vacuum pumps are characterized by their compact design and oil-free operation, making them a popular choice for applications like packaging and recycling. They utilize claw technology to efficiently generate vacuum pressure while minimizing maintenance needs. However, their performance can be limited in extreme conditions, and the initial cost may be higher compared to other types. Buyers should assess the specific operational demands and environmental conditions to determine the suitability of claw vacuum pumps for their applications.
Related Video: Pump Chart Basics Explained – Pump curve HVACR
Key Industrial Applications of pump vacuum pressure
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pump vacuum pressure | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Vacuum drying and distillation processes | Ensures product purity and consistency, crucial for compliance | Need for high reliability and adherence to regulatory standards |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and preservation techniques | Extends shelf life, enhances quality, reduces spoilage | Consider energy efficiency and compatibility with food safety standards |
| Semiconductor | Etching and coating in chip manufacturing | Critical for achieving high precision in component fabrication | Must meet stringent technical specifications and support automation |
| Chemical Processing | Crystallization and solvent recovery | Improves yield and reduces waste, enhancing profitability | Focus on durability and maintenance ease, especially in harsh environments |
| Plastics Manufacturing | Degassing of resins and materials | Enhances quality of final products by reducing defects | Evaluate the pump’s capacity to handle varying material viscosities |
In the pharmaceutical industry, pump vacuum pressure is integral to processes such as vacuum drying and distillation. These applications ensure the removal of solvents while maintaining the integrity of sensitive compounds, crucial for producing high-quality pharmaceuticals. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that guarantee compliance with stringent regulatory standards, ensuring reliability and performance under varying operational conditions.
For the food and beverage industry, vacuum pumps are used extensively in packaging and preservation techniques. By removing air from packaging, these pumps help extend the shelf life of products while maintaining quality. International buyers should focus on energy-efficient models that align with food safety standards, as well as those capable of integrating into existing packaging systems.
In the semiconductor sector, vacuum pumps play a vital role in etching and coating processes. These processes require high precision to manufacture components that meet the growing demands of technology. Buyers must ensure that the pumps they source can handle automation and meet the specific technical requirements essential for semiconductor manufacturing.
In chemical processing, vacuum pumps are crucial for crystallization and solvent recovery. By maintaining optimal conditions for these processes, they improve yield and minimize waste, directly impacting profitability. Buyers should consider the durability of the pumps and ease of maintenance, especially when operating in harsh chemical environments.
Lastly, in plastics manufacturing, pump vacuum pressure is employed for degassing resins and materials. This application is essential for enhancing the quality of final products by reducing defects caused by trapped air. Buyers in this industry should evaluate pumps based on their capacity to handle varying viscosities and the specific requirements of their production processes, ensuring they select equipment that can adapt to their needs.
Related Video: NASH Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump – How It Works
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pump vacuum pressure
When selecting materials for pump vacuum pressure applications, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific industry requirements. Below, we analyze four common materials used in vacuum pumps, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C). It maintains structural integrity under varying pressures, making it suitable for vacuum applications.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is durable and can handle harsh environments, which is vital for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. However, its higher cost compared to other materials can be a barrier for some businesses. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires specialized welding and machining techniques.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for applications in chemical processing and food preservation. Its non-reactive nature ensures product purity.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing stainless steel components may be challenging due to supply chain issues.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good corrosion resistance, and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 300°C. Its low density makes it an attractive choice for portable vacuum systems.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can deform under high pressure, limiting its use in high-demand applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for less aggressive media and applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in mobile vacuum systems. However, it may not be suitable for environments with corrosive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards for aluminum in different regions. Compliance with local regulations is essential, especially in Europe, where stringent material standards are enforced.
3. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
Key Properties:
PTFE is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance and ability to operate at temperatures up to 260°C. It is non-stick and has low friction properties.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of PTFE is its excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals, making it ideal for aggressive environments. However, it is relatively expensive and can be challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
PTFE is particularly effective in applications involving harsh chemicals, such as in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not contaminate the media being processed.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that PTFE components meet relevant compliance standards, such as FDA regulations for food contact applications. In regions like the Middle East, where chemical processing is prevalent, ensuring proper sourcing of PTFE is crucial.
4. Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron is characterized by its high wear resistance and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures (up to 400°C). It is also cost-effective and has good machinability.
Pros & Cons:
The durability and strength of cast iron make it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is prone to corrosion and may require protective coatings, which can add to maintenance costs.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is often used in industrial settings where high durability is required, such as in manufacturing and construction. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile, although care must be taken with corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of cast iron components in their region. Compliance with local standards is critical, particularly in Europe, where material specifications are rigorously enforced.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for pump vacuum pressure | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Pharmaceutical and food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Portable vacuum systems | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| PTFE | Chemical and pharmaceutical industries | Exceptional chemical resistance | Expensive and challenging to machine | High |
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High durability and wear resistance | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
This guide provides essential insights into material selection for pump vacuum pressure systems, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pump vacuum pressure
Manufacturing Processes for Pump Vacuum Pressure
The manufacturing of pump vacuum pressure systems involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent performance and reliability standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Key materials used in pump vacuum pressure systems typically include:
- Metals: Commonly used metals include stainless steel, aluminum, and cast iron, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Polymers: High-performance polymers are often employed for seals and gaskets due to their flexibility and chemical resistance.
During this phase, materials undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Buyers should look for suppliers who provide certificates of compliance or material test reports to confirm material quality.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Forming
The forming process involves shaping raw materials into components that will eventually comprise the pump. Key techniques include:
- Machining: Techniques such as milling, turning, and grinding are used to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly employed for high accuracy.
- Casting: For complex shapes, metal casting techniques may be utilized. This is particularly relevant for pump housings and casings.
- Injection Molding: For polymer components, injection molding allows for efficient production of consistent and complex parts.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming technologies used by suppliers, as these can significantly impact the quality and performance of the final product.
3. Assembly
After forming, the next step is assembly, where various components are integrated to create the pump. This stage may involve:
- Component Integration: Assembly of motor, housing, impellers, and other critical components.
- Sealing and Testing: Proper sealing is essential to ensure vacuum integrity. Each unit is typically assembled with quality control measures in place, including torque specifications and alignment checks.
Buyers should consider suppliers that utilize automated assembly processes, as these often lead to improved consistency and reduced human error.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the performance and appearance of the pump. Key activities include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Final Inspection: This includes a thorough visual and dimensional inspection to ensure all components meet required specifications.
It’s advisable for B2B buyers to request detailed information about the finishing processes and any protective coatings used, as these can affect the longevity and performance of the pump in various environments.
Quality Assurance in Pump Manufacturing
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of pump vacuum pressure systems, as failures can lead to significant operational downtime and financial loss. Adhering to international standards and industry-specific certifications is essential for buyers looking to mitigate risks.
Relevant International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to quality management.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards. CE marking indicates compliance with EU regulations, which is crucial for buyers in European markets.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards specific to the oil and gas sector, including performance and safety requirements for pumps.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated into multiple stages of the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes comprehensive testing and inspection to verify performance against specifications.
B2B buyers should engage with suppliers to understand their quality control processes and request documentation of inspections and tests performed at each checkpoint.
Common Testing Methods
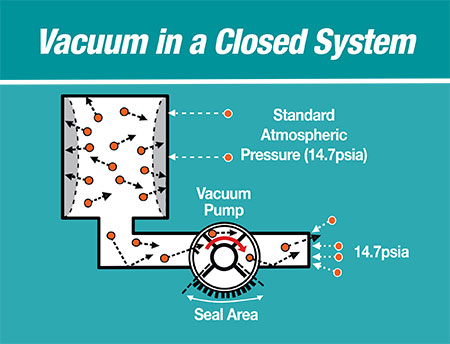
Several testing methods are commonly employed to verify the performance and reliability of pump vacuum pressure systems:
- Performance Testing: Pumps are tested under simulated operational conditions to ensure they meet flow and pressure specifications.
- Leak Testing: Vacuum integrity is crucial; therefore, leak tests are conducted to identify any potential failures.
- Durability Testing: Stress testing under extreme conditions helps ensure the pump’s long-term reliability.
Buyers should consider requesting test reports to confirm that the pumps have undergone these essential evaluations.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can adopt several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their performance trends and adherence to quality standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for pump vacuum pressure systems is critical for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, as well as ensuring compliance with international standards and robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. This knowledge is particularly valuable for international buyers from diverse regions, enabling them to navigate the complexities of sourcing and ensure the reliability of their equipment.
Related Video: Vacuum Pumps Explained – Basic working principle HVAC
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pump vacuum pressure Sourcing
When sourcing pump vacuum pressure systems, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section explores the various cost components, price influencers, and provides actionable tips for negotiating and optimizing purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor in the overall pricing of pump vacuum systems. Key materials include metals for the pump casing, seals, and various components. Prices can fluctuate based on global supply chains, which may be impacted by geopolitical factors.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region of manufacturing. For instance, labor may be cheaper in certain South American or African countries compared to Europe, affecting the overall price of the vacuum pumps. Additionally, skilled labor is often required for assembly and quality control, which can add to costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operation, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Manufacturers in regions with higher operational costs may pass these expenses onto buyers, resulting in higher prices.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary based on the complexity of the pump design. Custom tooling for specialized applications will increase upfront costs but may be necessary for specific operational requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust quality control measures ensures the reliability and safety of vacuum pumps. High QC standards may increase initial costs but can lead to long-term savings by reducing the likelihood of failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping and logistics play a critical role in the overall cost. International buyers need to consider freight charges, customs duties, and local transportation costs. Effective logistics management can mitigate some of these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the typical margin for the industry can help buyers gauge whether they are receiving a fair price.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly impact pricing. Ordering larger volumes typically leads to lower per-unit costs. B2B buyers should assess their demand forecast to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs due to the additional engineering and production time required. Clearly defining needs upfront can help control costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both performance and price. High-quality materials may increase costs but can enhance durability and efficiency, providing better long-term value.
-
Quality/Certifications: Pumps that meet specific industry certifications (like ISO) often command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) is essential. Different terms can shift costs and responsibilities between the buyer and seller, impacting the total price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations to secure better pricing, especially for larger orders. Understanding the cost structure can provide leverage in discussions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may not always equate to lower overall costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and economic conditions that may affect pricing. Additionally, regional trade agreements can provide opportunities for better pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices for pump vacuum pressure systems can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The content provided here serves as an indicative guide and should not be considered as fixed pricing or financial advice. Buyers are encouraged to conduct comprehensive market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential pump vacuum pressure Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘pump vacuum pressure’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pump vacuum pressure
Key Technical Properties of Pump Vacuum Pressure
Understanding the technical specifications of pump vacuum pressure is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Below are some essential technical properties that you should consider:
-
Material Grade: The materials used in vacuum pumps, such as aluminum, stainless steel, or polymer composites, determine their durability and resistance to corrosion. High-grade materials enhance the pump’s lifespan and reliability, which is critical for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing that require stringent hygiene standards.
-
Tolerance Levels: This refers to the acceptable limits of deviation from a specified value in the pump’s manufacturing process. High tolerance levels ensure that the pump operates efficiently under varying conditions, which is vital for maintaining consistent vacuum pressure in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing.
-
Pressure Range: Pumps are categorized based on their pressure capabilities, such as low vacuum (10^5-10^2 Pa) and medium vacuum (10^2 -10^-1 Pa). Understanding the pressure range is essential for selecting a pump that meets specific operational needs, such as drying or packaging processes in the food industry.
-
Flow Rate: This specification indicates the volume of air or gas that the pump can move within a specified time. A higher flow rate is advantageous for processes requiring rapid evacuation of air, making it a critical factor for production efficiency in sectors like plastics and composites.
-
Noise Level: The sound generated by vacuum pumps can impact workplace environments. Buyers should consider noise levels, especially in industries where worker comfort is paramount. Quiet operation can also be a selling point in markets sensitive to environmental regulations.
-
Energy Efficiency: Pumps with high energy efficiency ratings can significantly reduce operational costs. This is increasingly important for businesses in regions facing energy supply challenges, as well as those committed to sustainability practices.
Common Trade Terminology in Pump Vacuum Pressure
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce components or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are purchasing genuine parts.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for smaller businesses that may not require large quantities.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. Crafting a clear RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, ensuring that buyers receive competitive offers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and manage risks in international trade.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and ensuring timely delivery of goods.
-
Warranty: A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition and functionality of the pump over a specified period. Understanding warranty terms is essential for risk management and long-term budgeting.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, negotiate better deals, and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency in the competitive landscape of industrial vacuum pumps.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the pump vacuum pressure Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global pump vacuum pressure market is positioned for significant growth, driven by various factors including increased industrial automation, a surge in demand from the semiconductor and electronics sectors, and advancements in energy-efficient technologies. According to recent analyses, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2025 to 2034, with the market value projected to reach approximately USD 7.5 billion by 2024.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note the rising importance of IoT-enabled vacuum pumps that facilitate predictive maintenance and real-time performance monitoring. These innovations are crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Additionally, energy efficiency is becoming a key purchasing criterion, influenced by regulatory standards and sustainability goals. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights potential energy consumption reductions of up to 25% when utilizing advanced vacuum pump technologies.
Furthermore, the market is seeing a shift towards customization and modular systems, allowing companies to adapt solutions to their specific operational needs. This trend is particularly relevant for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in emerging markets, where flexible sourcing strategies can mitigate the high capital costs associated with industrial vacuum systems.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In the context of increasing environmental awareness, the significance of sustainability in the pump vacuum pressure sector cannot be overstated. The manufacturing and operation of vacuum pumps can have considerable environmental impacts, particularly concerning energy consumption and emissions. Therefore, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices and ethical sourcing.
To align with global sustainability goals, B2B buyers should look for suppliers offering green certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and those utilizing recyclable materials in their products. The adoption of energy-efficient technologies not only reduces operational costs but also positions companies favorably in a market that is progressively leaning towards sustainability.
Moreover, buyers should evaluate the entire supply chain to ensure ethical practices are upheld, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing processes. This scrutiny not only enhances corporate responsibility but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. By prioritizing suppliers who adhere to these principles, businesses can foster a positive brand image while contributing to global sustainability efforts.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of the pump vacuum pressure sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in industrial needs. Initially developed for simple applications, vacuum pumps have transitioned to complex systems that serve critical roles in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and electronics.
The introduction of oil-sealed rotary pumps in the mid-20th century revolutionized the industry, offering enhanced performance and reliability. As industries became more automation-driven, the integration of digital technologies and IoT capabilities in vacuum systems emerged, paving the way for smarter, more efficient operations. This historical trajectory illustrates how technological progress continues to shape the market, underscoring the importance for international buyers to stay informed about innovations that can enhance operational effectiveness and sustainability.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pump vacuum pressure
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of vacuum pressure pumps?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation in the market. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management practices. Request references from existing clients, preferably within your industry. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn for insights into their business relationships and customer feedback. Additionally, consider conducting on-site visits or virtual assessments to evaluate their production capabilities and quality control processes. -
Are customization options available for vacuum pressure pumps?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific operational needs. When discussing customization, clarify your requirements regarding size, pressure range, materials, and any additional features such as energy efficiency or noise reduction. Ensure that the supplier can provide prototypes or samples prior to full-scale production. Establish clear communication regarding design specifications to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to delays. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the vacuum pressure pump. Generally, MOQs for industrial equipment range from 5 to 50 units. Lead times can also differ; standard orders might take 4-8 weeks, while customized solutions could extend to 12 weeks or more. Discuss these factors upfront to align your production schedules and avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing vacuum pressure pumps internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the remainder upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using letters of credit (LC) to protect both parties. Always clarify currency exchange rates and any additional fees associated with international payments. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that ensure security while maintaining cash flow.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What quality assurance measures should I look for in suppliers?
Look for suppliers who have a robust quality assurance (QA) system in place. This includes regular testing of products at various stages of production, adherence to international standards, and certifications such as CE marking for European markets. Request documentation of their QA processes and any third-party inspections. Additionally, inquire about warranties and support for defective products to ensure long-term reliability. -
How can logistics and shipping be managed for international orders?
Effective logistics management is crucial for international orders. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight forwarders who can handle customs clearance and delivery. Understand the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) used in your agreement to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risks. Ensure that your supplier provides tracking information and maintains clear communication throughout the shipping process to address any potential delays. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with a supplier?
If a dispute arises, maintain open communication to resolve issues amicably. Document all correspondence and agreements to reference during discussions. If direct negotiation fails, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract. Familiarize yourself with the legal framework governing international trade in your supplier’s country, as this can impact dispute resolution. Engaging legal counsel may be necessary for significant disputes to protect your interests. -
What certifications should I look for in vacuum pressure pumps?
When sourcing vacuum pressure pumps, key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and CE marking for compliance with European regulations. For specific industries, additional certifications like ATEX for explosive environments or FDA approval for food processing may be relevant. Ensure that the certifications are up-to-date and applicable to the specific pumps you intend to purchase to guarantee safety and performance standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pump vacuum pressure
In summary, the strategic sourcing of pump vacuum pressure technology is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and maintain competitive advantage. With the industrial vacuum pump market projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% through 2034, sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and electronics are poised to drive demand. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right pump type based on specific application needs and the benefits of investing in energy-efficient models that align with sustainability goals.
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates costs but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who can provide advanced technology and support. As regulatory pressures increase and industries evolve, leveraging innovative vacuum pump solutions will be critical for maintaining productivity and compliance.
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to assess your vacuum pump requirements and engage with reputable suppliers. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing, you can position your business for future growth and success in a rapidly changing market landscape. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and enhance your operational capabilities today.