Master the Art of Sourcing the Right IR Oven for Your
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ir oven
In today’s increasingly interconnected global marketplace, the ir oven has emerged as a vital component for industries ranging from automotive to electronics and food processing. This sophisticated equipment plays a crucial role in various heat processing applications, including curing, drying, and annealing. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of selecting the right ir oven is essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring product quality.
This comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with actionable insights into the ir oven market. It covers a wide array of topics, including types of ovens available, materials used in their construction, manufacturing and quality control processes, and an overview of leading suppliers. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations, emerging market trends, and address frequently asked questions to enhance your sourcing strategy.
By delving into these critical areas, you will gain the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the global market, ultimately leading to improved procurement strategies and operational outcomes. Whether you are seeking a custom-engineered solution tailored to your specific needs or a standard model that fits your budget, this guide will empower you to make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Understanding ir oven Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Oven | Processes items in discrete batches; flexible loading options | Aerospace, automotive, electronics | Pros: Versatile, customizable; Cons: Longer cycle times. |
| Continuous Conveyor Oven | Allows uninterrupted flow of products; multi-zone capabilities | Food processing, coating, metal finishing | Pros: High throughput, efficient; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
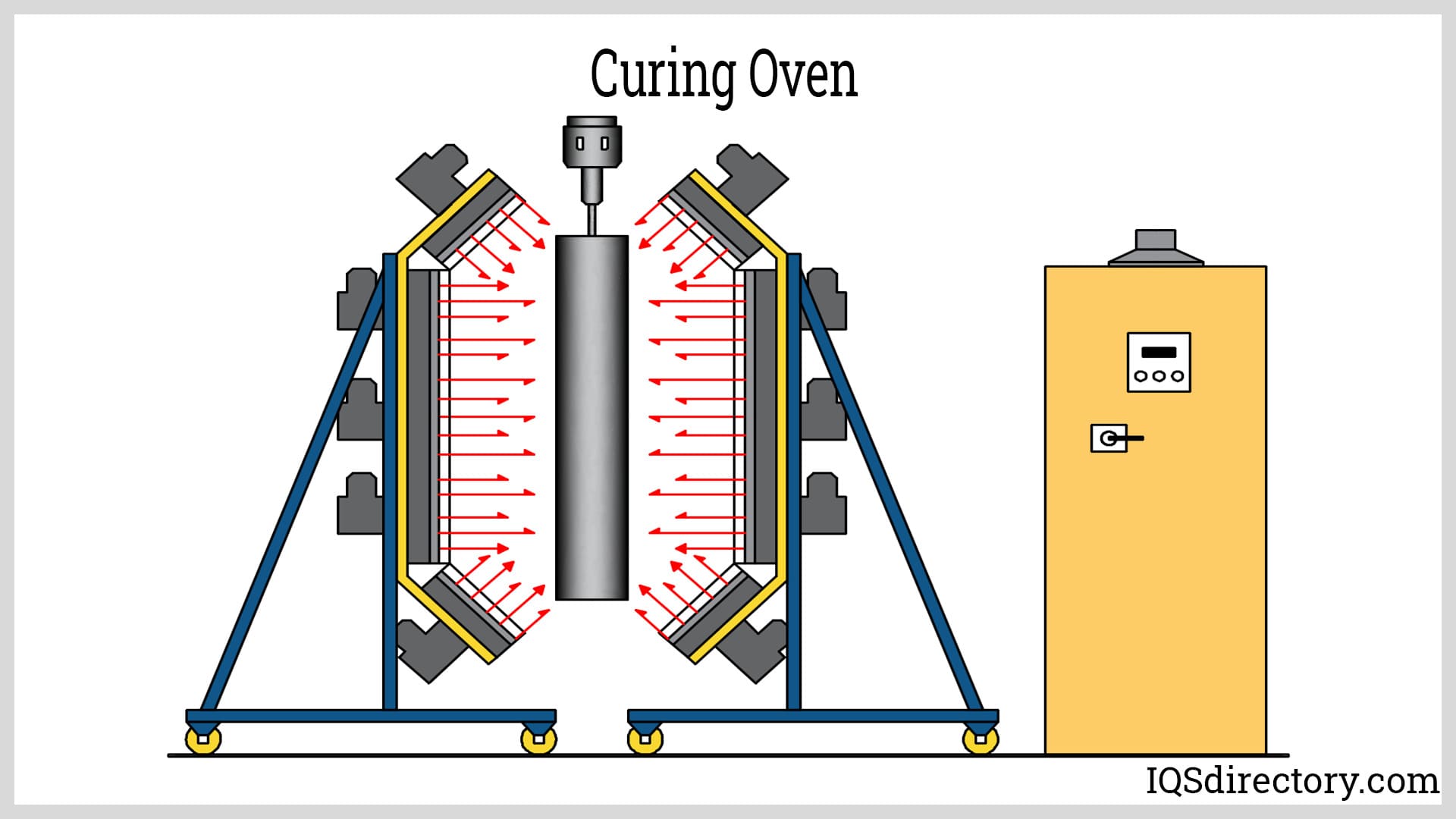
| Curing Oven | Designed for curing processes; precise temperature control | Composite materials, adhesives | Pros: Accurate temperature management; Cons: Limited versatility. |
| Drying Oven | Focused on moisture removal; often features forced air circulation | Textiles, pharmaceuticals, food products | Pros: Effective moisture removal; Cons: Maintenance intensive. |
| Preheating Oven | Quick heating times; prepares materials for subsequent processes | Welding, coating, forming | Pros: Enhances efficiency; Cons: Often part of a line. |
Batch Oven
Batch ovens are versatile industrial heating solutions that process items in discrete groups or batches. They are particularly suited for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where flexibility in loading and processing is essential. Buyers should consider the cycle times, as batch ovens may not be as efficient for high-volume operations compared to continuous systems. Customization options can enhance their utility, enabling specific heating profiles tailored to various applications, which is crucial for meeting diverse production needs.
Continuous Conveyor Oven
Continuous conveyor ovens are engineered for high-volume production, allowing products to flow seamlessly through multiple heating zones. This type is ideal for applications in food processing, coating, and metal finishing, where consistent throughput is vital. While these ovens offer significant labor savings and efficiency, buyers must weigh the higher initial investment against the long-term productivity benefits. The ability to control multiple zones with precise temperature settings accommodates diverse processing needs, making them a valuable asset for manufacturers focusing on scale and efficiency.
Curing Oven
Curing ovens are specialized units designed to provide controlled heating for curing processes, such as those used in composite materials and adhesives. Their capability to maintain precise temperature and time settings makes them indispensable for industries requiring high-quality finishes. When considering a curing oven, buyers should evaluate the specific curing requirements of their materials, as these ovens are often tailored for particular applications. This specialization can limit their versatility, so understanding the intended use is crucial for maximizing investment.
Drying Oven
Drying ovens are focused on the effective removal of moisture from products, utilizing forced air circulation to enhance drying efficiency. Commonly used in textiles, pharmaceuticals, and food production, these ovens are essential for ensuring product quality and stability. Buyers should consider the maintenance requirements and energy consumption of drying ovens, as these factors can impact operational costs significantly. While effective for moisture removal, their application may be limited if not integrated into a larger production line, making it essential to assess overall process compatibility.
Preheating Oven
Preheating ovens serve to prepare materials for subsequent processes, such as welding, coating, or forming. They are characterized by quick heating times, which can significantly enhance overall process efficiency. However, these ovens are often part of a larger manufacturing line and may not be suitable for standalone applications. Buyers should assess how a preheating oven fits into their existing processes, considering factors such as space limitations and integration with other equipment to ensure optimal workflow and productivity.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of ir oven
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ir oven | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Curing of paint and coatings | Enhances durability and finish quality | Temperature control, energy efficiency, size options |
| Electronics | Soldering and drying of circuit boards | Improves reliability and performance | Precision temperature management, batch vs. continuous |
| Food Processing | Drying fruits and vegetables | Extends shelf life and preserves quality | Compliance with food safety standards, moisture control |
| Aerospace | Annealing of metal components | Reduces stress and enhances material properties | Customization for specific alloys, operational costs |
| Textiles | Heat setting of fabrics | Ensures dimensional stability and colorfastness | Material compatibility, processing speed, maintenance |
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, IR ovens are primarily utilized for curing paint and coatings on vehicles. This process enhances the durability and aesthetic quality of finishes, ensuring that the vehicles meet stringent quality standards. Buyers must consider the oven’s temperature control and energy efficiency, as these factors directly impact operational costs. Additionally, understanding the size requirements based on production line configurations is crucial for optimizing space and throughput.
Electronics Industry
Within electronics manufacturing, IR ovens play a vital role in soldering and drying circuit boards. These ovens provide precise temperature management, essential for ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic components. International buyers should evaluate whether a batch or continuous processing setup aligns better with their production needs. Furthermore, sourcing ovens that can accommodate varying board sizes and configurations is critical for flexibility in production.
Food Processing Industry
The food processing industry employs IR ovens for drying fruits and vegetables, a process that significantly extends shelf life while preserving nutritional quality. For B2B buyers, compliance with food safety standards is paramount, necessitating ovens that can effectively control moisture levels. Understanding the energy consumption and maintenance needs of these ovens can help businesses enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, IR ovens are essential for annealing metal components, a process that reduces internal stresses and improves material properties. This application requires ovens that can be customized for specific alloys and processing requirements. Buyers should consider the operational costs associated with high-precision heating, as well as the durability and reliability of the equipment to withstand rigorous production demands.
Textiles Industry
The textiles sector utilizes IR ovens for heat setting fabrics, ensuring dimensional stability and colorfastness. This application is critical for maintaining product quality in a competitive market. Buyers should focus on material compatibility and processing speed when selecting an oven. Additionally, understanding the maintenance requirements can help businesses minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
Related Video: Infrared Powder Coating Oven Gas fired Infrared Industrial Oven
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ir oven
When selecting materials for an infrared (IR) oven, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. The right material can significantly impact the performance, durability, and overall efficiency of the oven, especially in diverse international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and structural integrity. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°F (649°C) without losing its properties, making it suitable for IR ovens.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is durable and easy to clean, which is crucial for maintaining hygiene in food processing applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex fabrication techniques, which can increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel’s compatibility with food-grade processes makes it ideal for food processing IR ovens, ensuring compliance with health and safety standards.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used meets international standards such as ASTM A240 for corrosion resistance. In regions like Europe, compliance with EU regulations regarding food contact materials is also vital.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has a good thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 1,000°F (538°C), making it suitable for various IR applications.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is generally less expensive than stainless steel and easier to machine, which can reduce manufacturing complexity. However, it is less durable and more prone to corrosion, particularly in humid environments, which may limit its lifespan.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in automotive or aerospace sectors. Its thermal properties make it suitable for quick heating processes.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that the aluminum meets relevant standards such as ASTM B221 for structural applications. In humid climates like parts of Africa and South America, additional protective coatings may be necessary to enhance corrosion resistance.
3. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel offers high strength and durability, with temperature ratings typically around 1,000°F (538°C). It is often used in applications where structural integrity is critical.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and strength. However, it is susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly coated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is suitable for industrial applications where the oven is not exposed to corrosive environments, such as in manufacturing settings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings to prevent rust, particularly in humid regions like the Middle East. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is also important.
4. Ceramics
Key Properties:
Ceramic materials can withstand extremely high temperatures (up to 2,500°F or 1,371°C) and have excellent thermal insulation properties. They are also resistant to chemical corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
Ceramics provide outstanding durability and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. However, they can be brittle and may require careful handling during manufacturing and installation.
Impact on Application:
Ceramics are particularly suited for specialized applications, such as in the aerospace industry, where high thermal resistance is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure that ceramics meet relevant standards for thermal insulation and safety, such as ASTM C21 for ceramic materials. Additionally, the fragility of ceramics may necessitate special shipping and handling considerations.
| Material | Typical Use Case for ir oven | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Industrial manufacturing | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to rust | Low |
| Ceramics | Aerospace and high-temp applications | Outstanding thermal resistance | Brittle and fragile | High |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, providing insights into the properties and considerations of various materials used in IR ovens. Understanding these factors can lead to more informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that the selected oven meets operational needs while adhering to regional standards and regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ir oven
Manufacturing Processes for IR Ovens
The manufacturing of infrared (IR) ovens involves several crucial stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer requirements. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing IR ovens.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing IR ovens is the preparation of materials. High-quality materials are essential for durability and performance. Common materials used include:
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for oven chambers.
- Insulation Materials: Such as ceramic fiber or mineral wool, which help maintain temperature and reduce energy consumption.
- Heating Elements: Typically made from high-grade nickel-chromium alloys that can withstand high temperatures.
During this phase, suppliers must ensure that all materials comply with relevant international standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Buyers should verify that suppliers maintain proper material certifications and traceability.
2. Forming
In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into the components of the IR oven. Key techniques include:
- Laser Cutting: Provides precision in cutting metal sheets, reducing waste and ensuring accurate dimensions.
- Bending and Stamping: These processes shape the metal into the desired forms for the oven’s body and structural components.
- Welding: Commonly used to join metal parts together, ensuring structural integrity.
Buyers should inquire about the technologies used in the forming processes, as advanced techniques can lead to better quality and performance.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves putting together the various components of the IR oven. This includes:
- Integration of Heating Elements: Proper placement and wiring of the heating elements are crucial for effective heat distribution.
- Installation of Control Systems: Advanced IR ovens may have digital controls, timers, and sensors for precise temperature management.
- Sealing and Insulation: Ensuring that all joints are sealed and that the insulation is correctly installed to enhance energy efficiency.
Quality control measures during assembly are vital. Suppliers should conduct in-process inspections to ensure that assembly meets specified standards.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage is where the IR oven is prepared for final inspection and packaging. Key activities include:
- Surface Treatment: Applying coatings or finishes that enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Final Assembly Checks: Inspecting all components to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Calibration of Control Systems: Ensuring that temperature settings and timers are accurate.
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that conduct comprehensive finishing checks and provide documentation of the processes used.
Quality Assurance for IR Ovens
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of IR ovens, as it directly impacts performance, safety, and customer satisfaction. Key components of a robust quality assurance program include adherence to international standards, inspection checkpoints, and testing methodologies.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with relevant international quality standards. Some of the most pertinent include:
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for industries like oil and gas, ensuring that products meet specific performance and safety criteria.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility of their suppliers.
Quality Control Checkpoints
A comprehensive quality control system should include several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch any defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all operational specifications.
Buyers should inquire about the frequency and rigor of these checks to gauge the reliability of their suppliers.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are essential for verifying the performance and safety of IR ovens. Common practices include:
- Temperature Uniformity Testing: Ensures even heat distribution within the oven.
- Energy Efficiency Tests: Evaluate how effectively the oven uses energy, which is critical for operational cost considerations.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to identify potential failures or weaknesses in the design.
B2B buyers should request documentation of testing results to confirm compliance with industry standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess manufacturing practices, quality control processes, and compliance with standards.
- Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports outlining their quality control measures and results from testing.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality assurance processes.
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional nuances in quality assurance practices is crucial. Buyers should be aware of local regulations and standards that may impact product quality and safety.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for IR ovens is essential for B2B buyers seeking to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with robust quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs. Engaging in due diligence regarding international standards and verification processes will further enhance procurement strategies, leading to improved operational outcomes.
Related Video: Business English Vocabulary : VV 47 – Manufacturing & Production Process (1) | English Vocabulary
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ir oven Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing of industrial ovens is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The financial implications of sourcing an industrial oven can vary significantly based on multiple factors, including materials, labor, and customization. Below is a breakdown of the key cost components and pricing influencers, along with actionable buyer tips.
Cost Components
-
Materials
– The choice of materials directly impacts the oven’s durability and performance. High-quality metals and insulation materials will increase the initial cost but may lead to lower maintenance and operational costs over time. For instance, stainless steel is commonly used for its corrosion resistance but is more expensive than standard steel. -
Labor
– Labor costs can vary by region and manufacturer. Skilled labor is essential for the assembly and quality control of industrial ovens. Buyers should consider the labor rates in the supplier’s country, as well as the expertise of the workforce, which can affect the overall quality and reliability of the product. -
Manufacturing Overhead
– This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Understanding the manufacturer’s operational efficiency can help buyers gauge how much of this cost is passed on to them.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tooling
– Customization often requires specialized tooling, which can add to the upfront costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the benefits of a custom solution justify these expenses. -
Quality Control (QC)
– Robust QC processes ensure the oven meets industry standards and specifications. Investing in quality assurance can lead to higher initial costs but reduces the risk of operational failures and costly repairs later. -
Logistics
– Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the oven’s size and weight, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should factor in these costs when evaluating total expenses. -
Margin
– Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding industry standards for margins can help buyers negotiate better terms.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases typically lead to lower unit costs. Buyers should consider their production needs and negotiate for better pricing based on order volume.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can significantly increase costs. Buyers should define essential requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality: The choice of materials affects both performance and price. Buyers should balance the need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer greater reliability and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for managing logistics costs and risks. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers anticipate additional fees related to shipping and customs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Use the insights gained from understanding cost components to negotiate better prices. Highlighting volume potential and long-term partnerships can strengthen your bargaining position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider not just the purchase price but the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and local economic conditions that may affect pricing. Engage with suppliers who are familiar with the regional markets to ensure transparent and fair pricing.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication and feedback can help maintain a mutually beneficial partnership.
In summary, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of industrial ovens can empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By considering the outlined cost components and price influencers, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency.
Spotlight on Potential ir oven Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘ir oven’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ir oven
Key Technical Properties of IR Ovens
Understanding the technical properties of infrared (IR) ovens is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Wavelength Range
The wavelength of infrared radiation typically ranges from 700 nm to 1 mm. IR ovens operate within specific ranges (shortwave, midwave, or longwave) to achieve desired heating effects. Buyers must assess the wavelength compatibility with their materials to ensure effective heating without damage. -
Temperature Control Range
IR ovens can operate at various temperature ranges, often exceeding 1,000°F (538°C). Precise temperature control is vital for applications such as curing and drying. Understanding the temperature requirements of your processes will help in selecting an oven that meets operational needs without compromising product quality. -
Heating Efficiency
Efficiency ratings indicate how effectively an IR oven converts energy into heat. Higher efficiency translates to lower operational costs and reduced energy consumption. B2B buyers should evaluate the heating efficiency to ensure long-term savings and a lower carbon footprint. -
Material Grade
The construction materials of the oven, such as stainless steel or high-temperature alloys, influence durability and performance. High-grade materials resist corrosion and thermal stress, ensuring longevity. Buyers should prioritize ovens constructed from durable materials to minimize maintenance and replacement costs. -
Cooling Mechanism
Many IR ovens incorporate cooling zones or mechanisms to manage temperature fluctuations and protect sensitive components. The presence of effective cooling systems is critical for maintaining consistent performance and extending the lifespan of the equipment. -
Size and Footprint
The physical dimensions of the oven, including floor space requirements and ceiling height, are important for integration into existing facilities. Buyers should consider these factors to avoid potential logistical challenges during installation and operation.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are several key terms relevant to IR ovens:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially for companies that may not require large quantities but still want to establish a supply relationship. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs that outline their needs, including technical specifications and delivery timelines, to receive accurate and competitive bids. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is essential for international transactions, as they dictate who bears the risk and cost at various stages of shipping. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Buyers should inquire about lead times to plan production schedules effectively and manage inventory levels. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates the duration for which the manufacturer will cover repairs or replacements due to defects. It is essential for buyers to understand warranty terms to safeguard their investment and ensure long-term operational reliability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhancing procurement strategies and operational outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the ir oven Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for industrial ovens, particularly infrared (IR) ovens, is witnessing significant growth driven by technological advancements and evolving manufacturing needs. Key factors influencing this market include increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions and the push for automation in production processes. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on modernizing their manufacturing capabilities, which is fostering a robust demand for IR ovens that offer precise heating and reduced energy consumption.
Emerging trends include the integration of IoT and Industry 4.0 technologies into oven systems. This allows for enhanced monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analytics, which can greatly improve operational efficiency. Furthermore, manufacturers are increasingly opting for customized solutions that align with specific processing requirements, leading to a rise in demand for bespoke IR ovens. International B2B buyers should be aware of these trends to ensure that their procurement strategies are aligned with technological advancements and market demands.
Additionally, sustainability is becoming a key consideration in purchasing decisions. Companies are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices, which includes energy-efficient equipment and sustainable materials. As a result, the sourcing process is evolving to favor vendors who can prove their compliance with international environmental standards.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In the context of IR ovens, sustainability is not merely an option; it is becoming a necessity. The environmental impact of industrial ovens can be substantial, particularly regarding energy consumption and emissions. As a response, many manufacturers are focusing on developing ovens that utilize less energy and produce fewer emissions during operation. This shift is crucial for international buyers who are increasingly held accountable for their environmental footprint.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, especially as global supply chains become more complex. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who uphold ethical labor practices and ensure transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable components and non-toxic coatings, is gaining traction in the industry. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide documentation of such certifications and practices, ensuring their procurement aligns with both sustainability goals and corporate social responsibility standards.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of industrial ovens, particularly IR ovens, can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for more efficient heating processes became apparent in manufacturing sectors. Initially, traditional convection ovens dominated the market; however, the introduction of infrared technology revolutionized heat processing by providing faster and more uniform heating.
Over the years, advancements in materials and technology have enabled the design of more sophisticated IR ovens that cater to diverse applications, from food processing to automotive manufacturing. The focus has shifted from simply meeting heating requirements to integrating features that enhance energy efficiency and process control. As global manufacturing continues to evolve, the IR oven sector is expected to adapt further, embracing innovations that address both operational efficiency and sustainability challenges.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ir oven
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of industrial ovens?
When vetting suppliers for industrial ovens, consider their experience in the industry, reputation, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients and evaluate their track record in meeting delivery timelines and quality standards. Additionally, assess their manufacturing capabilities, certifications (ISO, CE), and compliance with international safety standards. Engaging in discussions about their customer service approach and technical support can also provide insights into their reliability as a long-term partner. -
Can I customize the specifications of the industrial oven to suit my needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor industrial ovens to specific requirements. Buyers should clearly define their processing needs, including temperature ranges, dimensions, and special features like multi-zone heating or automation capabilities. Discussing customization during initial conversations with suppliers can ensure that the final product aligns with operational needs. Be prepared for potential lead times associated with custom orders, which may vary by manufacturer. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for industrial ovens?
MOQs for industrial ovens can vary widely depending on the supplier and the type of oven. Some manufacturers may accommodate small orders, while others may require larger quantities to justify production costs. Lead times generally range from a few weeks to several months, influenced by factors like customization, production schedules, and shipping logistics. It’s advisable to confirm these details upfront and factor them into your procurement planning.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for my industrial oven?
To ensure quality assurance, verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and CE marking for compliance with European safety regulations. Request documentation of the oven’s manufacturing process, including materials used and testing protocols. Many suppliers will provide a quality assurance plan detailing how they maintain standards throughout production. Conducting audits or site visits can further bolster your confidence in their quality control measures. -
What are the logistics considerations when sourcing an industrial oven internationally?
Logistics is a critical factor when sourcing industrial ovens internationally. Consider the shipping methods available, estimated transit times, and associated costs, including customs duties and tariffs. Ensure that the supplier can facilitate international shipping and understand your country’s import regulations. Additionally, plan for the handling and installation of the oven upon arrival, which may require specialized equipment or personnel, especially for larger units. -
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively managed?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear contractual agreements outlining terms of sale, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions. Include clauses for dispute resolution, such as arbitration or mediation, to provide a structured approach for resolving conflicts. Maintain open communication with suppliers throughout the procurement process to address issues proactively. Document all communications and agreements to ensure clarity and facilitate resolution if disputes arise. -
What payment options are typically available when purchasing industrial ovens?
Payment options for industrial ovens can include upfront payments, payment upon delivery, or financing arrangements. Many suppliers accept various methods such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment through trade finance solutions. It’s crucial to discuss payment terms early in negotiations to understand any deposit requirements and the overall payment schedule. Ensure that the payment method aligns with your risk management strategy and provides adequate protection against potential issues. -
What post-purchase support can I expect from oven suppliers?
Post-purchase support is vital for maintaining the operational efficiency of your industrial oven. Reputable suppliers typically offer technical support, training for your staff, and warranty services for repairs. Discuss the specifics of the support package during the negotiation phase, including response times for service calls and availability of spare parts. Additionally, inquire about ongoing maintenance services or contracts that can help extend the lifespan of your equipment and minimize downtime.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ir oven
The importance of strategic sourcing for industrial ovens cannot be overstated. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of selecting the ideal ir oven, understanding the nuances of heat processing requirements, production capabilities, and customization options is critical.
Key takeaways include recognizing the distinct advantages of batch versus continuous processing based on your operational needs, and the significance of engaging with experienced manufacturers who can ensure durability and efficiency. Additionally, considering factors such as energy consumption, maintenance, and integration within existing production lines will enhance your procurement strategy.
Looking ahead, the global demand for high-quality industrial ovens is expected to grow, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and increasing quality standards across industries. International buyers are encouraged to leverage this opportunity by conducting thorough market research and establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers. By doing so, you will not only enhance your operational efficiency but also position your business for sustainable growth in an ever-evolving marketplace. Embrace the future of heat processing solutions and make informed sourcing decisions today.