Master the Infrared Heating System: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for infrared heating system
In an increasingly competitive global marketplace, infrared heating systems have emerged as a vital solution for industries seeking efficiency, sustainability, and precision. These systems, known for their energy efficiency and ability to target specific heating applications, are transforming manufacturing processes across various sectors, including automotive, textiles, and food processing. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of infrared heating technology is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the diverse types of infrared heating systems, including short-wave, medium-wave, and long-wave options, along with the materials and technologies that underpin their effectiveness. We will explore critical aspects of manufacturing and quality control, ensuring that buyers are equipped to evaluate suppliers effectively. Additionally, the guide will cover cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions, providing a holistic view of the infrared heating landscape.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and detailed knowledge, this guide aims to facilitate strategic procurement processes, enabling companies to harness the full potential of infrared heating systems. Whether you are looking to enhance operational efficiency or reduce energy costs, understanding this technology will be a cornerstone of your success in the global market.
Understanding infrared heating system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Wave Infrared Heaters | High-intensity, rapid warm-up, quartz construction | Automotive, food processing, plastics | Pros: Fast heating; Cons: Higher energy consumption |
| Medium-Wave Infrared Heaters | Versatile, good for larger areas, slower warm-up | Textile drying, curing, and heating | Pros: Energy-efficient; Cons: Longer warm-up time |
| Gas Catalytic Infrared Heaters | Low emissions, water vapor as a byproduct, modular design | Greenhouses, industrial heating | Pros: Eco-friendly; Cons: Lower output compared to electric |
| Electric Infrared Panels | Flat design, customizable sizes, energy-efficient | Commercial spaces, residential heating | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Initial installation cost |
| Infrared Heating Tubes | Flexible installation, high output, discrete zone control | Heat treating, curing, and drying applications | Pros: Targeted heating; Cons: Requires careful placement |
Short-Wave Infrared Heaters
Short-wave infrared heaters are known for their high-intensity output and rapid warm-up capabilities, making them ideal for applications requiring quick heat. These heaters utilize quartz construction, allowing for focused heating of specific areas. They are particularly suitable for industries like automotive and food processing, where precision and speed are critical. When considering short-wave heaters, buyers should evaluate the energy consumption and the intensity of heat required for their specific application.
Medium-Wave Infrared Heaters
Medium-wave infrared heaters provide a balance between efficiency and coverage. They are versatile and suitable for larger areas, making them ideal for applications such as textile drying and curing. These heaters have a slower warm-up time compared to their short-wave counterparts, but they offer greater energy efficiency and are cost-effective for prolonged use. B2B buyers should assess the size of the area to be heated and the required heating duration when selecting medium-wave heaters.
Gas Catalytic Infrared Heaters
Gas catalytic infrared heaters stand out due to their low emissions, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. Their modular design allows for flexibility in installation, making them suitable for greenhouses and various industrial heating applications. While they are eco-friendly, buyers should be aware that their output may be lower compared to electric heaters. Evaluating the environmental impact and desired heating output is crucial for businesses considering gas catalytic options.
Electric Infrared Panels
Electric infrared panels are designed for space efficiency and can be customized to fit various sizes and applications. They are commonly used in commercial and residential settings for heating. While they are energy-efficient and easy to install, the initial cost can be a consideration for buyers. Businesses should weigh the long-term energy savings against the upfront investment when considering electric panels.
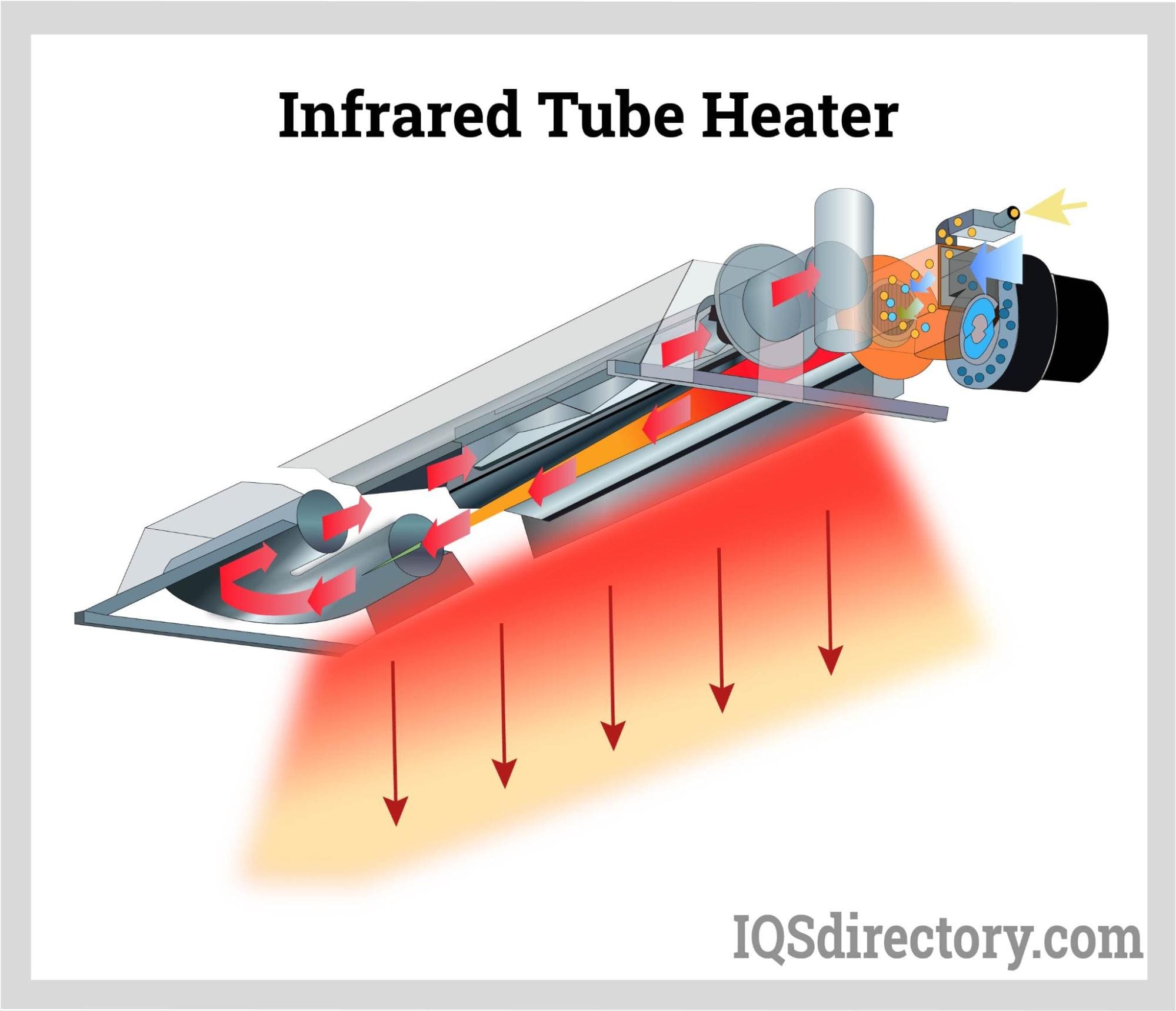
Infrared Heating Tubes
Infrared heating tubes offer flexible installation options and are capable of high output, making them ideal for applications requiring discrete zone control, such as heat treating and curing. Their targeted heating ability allows for efficient energy use, but careful placement is essential to maximize effectiveness. Buyers should consider the specific heating requirements of their processes and the installation environment when opting for heating tubes.
Key Industrial Applications of infrared heating system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Infrared Heating System | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Cooking and Drying of Food Products | Enhanced cooking efficiency and reduced energy costs | Compliance with food safety standards, energy efficiency ratings |
| Textile Manufacturing | Drying and Curing of Fabrics | Faster drying times leading to increased production rates | Material compatibility, temperature control capabilities |
| Automotive Industry | Paint Curing and Surface Treatment | Improved finish quality and reduced cycle times | Equipment scalability, reliability under heavy use |
| Plastic Manufacturing | Preheating for Molding and Forming Processes | Consistent product quality and reduced waste | Customization options, energy consumption efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization and Drying of Medical Equipment | Enhanced product safety and compliance with regulations | Certification requirements, compatibility with various materials |
Food Processing
Infrared heating systems are extensively used in the food processing industry for cooking and drying applications. These systems provide rapid, uniform heating which enhances cooking efficiency and reduces energy costs. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing infrared heaters that comply with local food safety standards is crucial. Buyers should also consider energy efficiency ratings to ensure long-term operational savings.
Textile Manufacturing
In the textile industry, infrared heating is utilized for drying and curing fabrics. The technology allows for faster drying times compared to traditional methods, significantly increasing production rates. For B2B buyers, particularly in Europe, it’s essential to ensure that the infrared systems are compatible with various fabric types and provide precise temperature control to prevent damage to delicate materials.
Automotive Industry
Infrared heating systems play a vital role in paint curing and surface treatment within the automotive sector. By using infrared technology, manufacturers can achieve an improved finish quality while reducing cycle times, thereby enhancing overall productivity. Buyers from the Middle East should focus on sourcing equipment that is scalable to accommodate varying production volumes and reliable under heavy use, ensuring continuous operation.
Plastic Manufacturing
In plastic manufacturing, infrared heating is employed for preheating materials before molding and forming processes. This application ensures consistent product quality and minimizes waste due to uneven heating. For buyers in regions like Europe and Africa, it is important to consider customization options that meet specific production requirements, as well as the energy consumption efficiency of the heating systems to optimize operational costs.
Pharmaceuticals
Infrared heating systems are also utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for sterilization and drying of medical equipment. This application is critical for ensuring enhanced product safety and compliance with stringent health regulations. International buyers must pay attention to certification requirements and the compatibility of infrared systems with various materials to ensure they meet industry standards and maintain operational integrity.
Related Video: Basics of Infrared Heating
Strategic Material Selection Guide for infrared heating system
When selecting materials for infrared heating systems, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in infrared heating systems, tailored for international B2B buyers from diverse regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Quartz
Key Properties: Quartz is known for its excellent thermal stability and high temperature resistance, typically handling temperatures up to 1,800°F (982°C). It also has good optical properties, allowing for effective infrared radiation.
Pros & Cons: Quartz is durable and resistant to thermal shock, making it suitable for high-intensity applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its fragility may pose manufacturing challenges, particularly in regions with less advanced production capabilities.
Impact on Application: Quartz is ideal for applications requiring rapid heating and cooling cycles, such as in the food processing and manufacturing sectors. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, is essential for ensuring product quality. Buyers should also consider the availability of quartz manufacturing facilities in their region to mitigate shipping costs and lead times.
Ceramic
Key Properties: Ceramics can withstand high temperatures (up to 2,400°F or 1,316°C) and exhibit excellent corrosion resistance. They are also known for their insulating properties, which can help improve energy efficiency.
Pros & Cons: The durability of ceramic materials makes them suitable for long-term applications. However, their brittleness can lead to breakage during handling and installation, and they may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are particularly effective in applications involving harsh chemicals or high humidity, such as in the chemical processing industry. Their insulating properties can also enhance energy efficiency in heating systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that ceramic products meet local and international safety standards. Additionally, the sourcing of raw materials for ceramics may vary by region, impacting cost and availability.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of industrial applications. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,500°F or 815°C) and is easy to clean.
Pros & Cons: The longevity and robustness of stainless steel make it a popular choice for infrared heating systems. However, it can be more expensive than other metals, and its thermal conductivity is lower than that of other materials, potentially affecting heating efficiency.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in food processing and medical applications where cleanliness and durability are paramount. Its resistance to corrosion is particularly beneficial in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with relevant standards (e.g., ASTM, JIS) to guarantee quality. Additionally, understanding the local market for stainless steel can help in negotiating better pricing.
Carbon Fiber
Key Properties: Carbon fiber materials are lightweight and can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,800°F or 982°C). They also offer excellent thermal conductivity, making them efficient for infrared heating applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of carbon fiber allows for easier installation and reduced structural load. However, it is generally more expensive than traditional materials, and sourcing may be limited in certain regions.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is particularly useful in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Its high thermal efficiency makes it suitable for rapid heating processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of carbon fiber suppliers in their region, as well as the associated costs. Compliance with international standards is also crucial for ensuring product integrity.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for infrared heating system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Food processing, manufacturing | High thermal stability | Fragile, higher cost | High |
| Ceramic | Chemical processing, energy-efficient systems | Excellent corrosion resistance | Brittle, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical applications | Durable and easy to clean | Higher cost, lower thermal conductivity | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | Aerospace, automotive industries | Lightweight and efficient | Higher cost, limited sourcing | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in infrared heating systems, equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for infrared heating system
The manufacturing of infrared heating systems involves a series of precise and methodical stages, complemented by rigorous quality assurance protocols to ensure product reliability and performance. This section provides a detailed examination of the typical manufacturing processes and quality control measures that international B2B buyers should consider when sourcing infrared heating systems.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of manufacturing infrared heating systems involves sourcing and preparing high-quality materials. Common materials include:
- Quartz Glass: Used in short-wave infrared heaters for its excellent thermal properties.
- Metal Alloys: Employed in the construction of heating elements due to their durability and heat resistance.
- Insulation Materials: Essential for ensuring safety and efficiency by preventing heat loss.
Key Techniques: Material selection is critical, and suppliers should provide documentation on material specifications, including certifications that meet international standards.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the components necessary for the heating systems. Techniques include:
- Molding: For creating quartz glass components, ensuring uniform thickness and structural integrity.
- Machining: Metal parts are cut and shaped using CNC machines for precision.
- Coating: Application of reflective coatings on heating elements to enhance efficiency.
Key Techniques: Advanced technologies such as laser cutting and precision molding are often employed to achieve high tolerances.
3. Assembly
The assembly phase involves integrating various components into a complete infrared heating system. This process typically includes:
- Component Integration: Assembly of heating elements, reflectors, and electrical components.
- Wiring: Ensuring safe and effective electrical connections.
- Quality Checks: At this stage, initial quality checks are performed to identify any defects.
Key Techniques: Automated assembly lines may be used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error, while skilled technicians oversee critical assembly tasks.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on the final touches that ensure the product is ready for market. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: Application of coatings that improve durability and aesthetics.
- Calibration: Adjusting the system to ensure optimal performance according to specifications.
- Packaging: Ensuring safe transportation of the finished products.
Key Techniques: Advanced testing equipment is often used for calibration, ensuring that each unit meets precise performance standards before leaving the factory.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical component in the manufacturing process of infrared heating systems. Buyers should be aware of the standards and practices that ensure product reliability.
International Standards
International quality standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to ensure product quality and continuous improvement.
Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO, other certifications relevant to infrared heating systems include:
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Particularly important for industrial applications, ensuring that products meet specific performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically segmented into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessment of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during production to monitor processes and detect defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all specifications and performance metrics.
Common Testing Methods
Buyers should inquire about the testing methods employed by manufacturers, which may include:
- Thermal Performance Testing: Verifying the efficiency and effectiveness of heating elements.
- Electrical Safety Testing: Ensuring that all electrical components meet safety standards.
- Durability Testing: Simulating long-term use to identify potential failure points.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Schedule regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Request Documentation: Ask for quality control reports, including test results and compliance certificates.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilize third-party inspection services to conduct independent assessments of product quality and compliance.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification processes:
- Regional Compliance: Understand the local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms.
- Import Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the import requirements in your country, including necessary certifications for infrared heating systems.
- Supplier Relations: Establish strong relationships with suppliers who are knowledgeable about international standards and can navigate complex compliance landscapes.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in infrared heating systems, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source reliable, high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Most Satisfying Factory Production Processes And Heavy-Duty Factory Machines!
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for infrared heating system Sourcing
Cost Structure of Infrared Heating Systems
When sourcing infrared heating systems, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly affects costs. High-quality materials, such as specialized quartz or advanced alloys, enhance performance but come at a premium. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in superior materials that offer better efficiency and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Countries with higher labor costs may influence overall pricing, especially if intricate assembly or skilled craftsmanship is required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory space costs. Efficient manufacturing facilities often pass on lower overhead costs to buyers, making it beneficial to assess suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront expense for bespoke infrared heating solutions. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customized designs against standard options, as the latter may offer cost savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure product reliability and performance, which can add to costs. However, investing in stringent QC practices can mitigate the risk of defects and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by the weight and size of the heating systems, as well as the distance to the destination. Understanding logistics costs is essential for accurate budgeting, particularly for buyers in remote locations.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. The margin can vary based on the supplier’s brand reputation, market demand, and competition.
Influencers on Pricing
Several factors can influence the pricing of infrared heating systems:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to secure better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define requirements and consider whether standard products can meet their needs without incurring additional costs.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials affects pricing. Buyers should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of high-performance materials versus standard options.
-
Quality/Certifications: Systems that come with certifications (e.g., energy efficiency, safety) may command higher prices. Buyers should ensure that the certifications align with their operational standards and regulatory requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service offerings (like warranty and support) can influence pricing. Establishing a relationship with reputable suppliers can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify total costs and avoid unexpected expenses.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
To optimize sourcing strategies for infrared heating systems, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate: Engage in open negotiations with suppliers. Discuss volume discounts, payment terms, and potential for long-term partnerships to secure better pricing.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, evaluate operational costs, maintenance, and energy efficiency. A system with a higher upfront cost may offer lower TCO due to energy savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of market variations. Prices may fluctuate based on regional demand, currency exchange rates, and local economic conditions. Conduct market research to make informed decisions.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships can lead to preferential pricing, better support, and access to new technologies.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Local sourcing may reduce logistics costs and lead times. It can also simplify compliance with regional regulations.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and may vary based on specific product requirements, supplier conditions, and market dynamics. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to ensure accurate budgeting and sourcing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential infrared heating system Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘infrared heating system’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for infrared heating system
Essential Technical Properties
When considering infrared heating systems, international B2B buyers should focus on several critical technical properties that directly influence performance, efficiency, and compatibility with industrial applications. Here are the key specifications:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in infrared heaters, such as quartz or specialized alloys, determine their durability and thermal efficiency. High-grade materials ensure longevity and resistance to thermal shock, which is vital for maintaining operational efficiency in demanding environments. Buyers should verify material specifications to ensure they meet their operational needs. -
Watt Density
This refers to the amount of power (watts) delivered per square inch of the heating element. A higher watt density indicates a more intense heat output, essential for applications requiring rapid heating. Understanding watt density helps buyers select the appropriate heaters for their specific manufacturing processes, ensuring effective heat transfer and reduced cycle times. -
Wavelength Range
Infrared heaters operate across different wavelengths (short, medium, or long). Short-wave heaters are ideal for fast heating processes, while medium-wave heaters provide a balance of speed and penetration. Buyers must assess their heating requirements to choose the correct wavelength, optimizing energy use and process efficiency. -
Warm-up Time
This specification indicates how quickly the heater reaches its operating temperature. Fast warm-up times (typically under 60 seconds) are crucial for industries needing quick transitions between production cycles. Buyers should consider warm-up times to minimize downtime and increase productivity.
-
Temperature Range
The maximum operating temperature is vital for determining the heater’s applicability in various processes. Infrared heaters can range from moderate temperatures (around 800°F) to high outputs (up to 5000°F). Buyers need to match the heater’s temperature capabilities with their specific application requirements to avoid overheating or inadequate heating. -
Operating Environment
Infrared heaters are designed for different environments, including high-humidity or high-dust settings. Knowing the heater’s suitability for specific conditions can prevent premature failure and ensure long-term reliability. Buyers should inquire about environmental ratings and certifications to ensure compatibility.
Common Trade Terminology
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiations in the procurement process. Here are essential trade terms relevant to infrared heating systems:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components that are used in another company’s end products. Buyers often work with OEMs to source specific heating elements tailored to their requirements, ensuring compatibility and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for smaller companies or those entering new markets. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific products or services. It is critical for buyers to clearly outline their needs in an RFQ to receive accurate and competitive pricing, facilitating better negotiation outcomes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which is vital when importing heating systems across borders. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for production planning and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight schedules. -
After-Sales Support
This encompasses services provided post-purchase, including installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Strong after-sales support can significantly influence buyer satisfaction and operational efficiency, making it a key consideration when selecting suppliers.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes and align with their operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the infrared heating system Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The infrared heating system sector is witnessing robust growth driven by increasing energy efficiency demands and advancements in technology. Globally, the transition towards renewable energy sources is reshaping the market landscape. B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking solutions that not only enhance productivity but also minimize energy consumption.
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled infrared systems that allow for real-time monitoring and control of heating processes. This capability is particularly valuable in industrial settings where precision and efficiency are paramount. Additionally, the demand for customized heating solutions is on the rise. Buyers are looking for systems tailored to specific applications, whether in manufacturing, agriculture, or commercial settings.
Moreover, the market is seeing a shift towards sustainable sourcing practices. As international regulations tighten around carbon emissions, suppliers are adapting by using eco-friendly materials and technologies. Buyers should be aware of the certifications that validate a supplier’s commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Energy Star ratings.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the infrared heating systems market. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste production, is under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprints, pushing them to adopt cleaner technologies and sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wood products and the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) for textiles are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable components and non-toxic coatings, is gaining traction. Infrared heating systems that incorporate these materials not only appeal to environmentally conscious buyers but also often result in lower operating costs due to increased energy efficiency.
Brief Evolution/History
The infrared heating technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially used in small-scale applications, advancements in materials science and engineering have transformed it into a robust solution for various industrial processes. The introduction of high-efficiency infrared emitters and smart control systems has further enhanced the utility of infrared heating systems.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and energy efficiency, influenced by global climate change initiatives. As a result, infrared heating systems are now recognized not only for their effectiveness in heating but also for their potential to reduce overall energy consumption and environmental impact. This evolution is pivotal for B2B buyers aiming to align their operations with modern sustainability standards while maintaining high productivity levels.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of infrared heating system
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of infrared heating systems?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, reputation, and product range. Look for companies with proven track records in manufacturing infrared heating systems and check for client testimonials or case studies. Verify their certifications, such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, assess their customer service and support capabilities, as ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
Can I customize infrared heating systems to meet specific application needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for infrared heating systems. Discuss your specific requirements, such as size, power output, and heating intensity, with potential suppliers. They can often design systems tailored to your operational needs, whether for industrial processes or commercial applications. Ensure that the customization aligns with your production timelines and performance expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for infrared heating systems?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly among suppliers. Generally, MOQs range from a few units to several hundred, depending on the manufacturer and product type. Lead times can span from a few weeks to several months, influenced by production schedules and customization requests. It’s advisable to negotiate these terms upfront and establish clear timelines to avoid delays in your procurement process. -
What payment options are available when sourcing infrared heating systems?
Payment options vary by supplier but typically include wire transfers, letters of credit, and credit terms for established partners. Some suppliers may offer financing solutions or installment payments for larger orders. Always ensure that the payment terms are documented in your contract to protect your interests. Additionally, consider using escrow services for high-value transactions to mitigate risks.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What quality assurance measures should I look for in infrared heating systems?
Ensure that the supplier implements rigorous quality assurance (QA) processes throughout the manufacturing cycle. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which signify a commitment to quality management. Request documentation on product testing, including performance metrics and safety standards. Additionally, inquire about warranty policies and post-sale support to address any potential issues after delivery. -
How can I manage logistics when importing infrared heating systems?
Logistics management is crucial for timely delivery and cost efficiency. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure compliance with customs regulations in your country. Consider partnering with a freight forwarder to handle shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. It’s also wise to discuss delivery terms (like Incoterms) with your supplier to clarify responsibilities regarding shipping costs and risks. -
What steps should I take in case of disputes with suppliers?
To manage disputes effectively, first, ensure that your contracts clearly outline terms, conditions, and dispute resolution processes. Maintain open lines of communication with your supplier to address issues as they arise. If a dispute escalates, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative resolution methods before pursuing legal action. Document all communications and agreements to support your case, if necessary. -
What certifications should I verify when sourcing infrared heating systems?
When sourcing infrared heating systems, check for relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with safety and environmental standards. Common certifications include CE marking for European markets, UL listing for safety in North America, and ISO certifications for quality management. These certifications not only ensure product safety but also enhance your credibility when presenting to your own clients. Always request copies of these certifications as part of your procurement process.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for infrared heating system
The strategic sourcing of infrared heating systems presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and precision in heating applications, infrared systems have emerged as a viable solution, offering rapid heating capabilities and reduced energy consumption.
When considering suppliers, it is crucial to assess their technological expertise and customization options. Buyers should focus on vendors who provide tailored solutions that align with specific industrial needs, as this can enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. Additionally, understanding regional regulations and incentives can further optimize sourcing strategies.
Looking ahead, the demand for infrared heating systems is expected to grow, driven by the ongoing transition towards sustainable manufacturing practices. International buyers are encouraged to engage with reputable suppliers, explore innovative technologies, and take advantage of strategic partnerships that can facilitate successful procurement. By doing so, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of this evolving market, ensuring they meet both current and future heating demands effectively.