Master the Sourcing of Solenoid Control Valves for Optimal
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solenoid control valve
In today’s dynamic industrial landscape, solenoid control valves stand out as essential components for automating fluid and gas management processes. These electro-mechanical devices not only ensure precision in flow control but also enhance operational efficiency across various sectors, including manufacturing, HVAC, and agricultural systems. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable solutions, understanding the intricacies of solenoid control valves becomes critical.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of solenoid control valves, covering key aspects such as types, materials, manufacturing quality control, supplier selection, cost considerations, and market trends. By exploring the various designs—from direct-acting to pilot-operated valves—buyers will gain insights into which products best meet their operational needs.
Additionally, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, providing clarity on common concerns that can affect sourcing decisions. With a focus on actionable insights and practical applications, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make informed choices, ensuring they select the most suitable solenoid control valves for their specific requirements. Whether navigating the complexities of international sourcing or seeking to optimize their operations, readers will find invaluable information to enhance their procurement strategies and drive business success.
Understanding solenoid control valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Acting Solenoid | Operates directly via the solenoid coil; ideal for small flow rates. | HVAC systems, medical devices | Pros: Simple design, fast response. Cons: Limited flow capacity. |
| Pilot-Operated Solenoid | Uses a small pilot valve to control a larger main valve; efficient for high flow. | Industrial automation, water treatment | Pros: Higher flow rates, energy efficient. Cons: More complex installation. |
| 3-Way Solenoid Valve | Can direct flow between two outlets; versatile in applications. | Pneumatic systems, mixing applications | Pros: Flexible operation, space-saving. Cons: Potentially complex control. |
| Proportional Solenoid | Adjusts flow based on the input signal; offers variable control. | Process control, robotics | Pros: Precise flow control, adaptable. Cons: Higher cost and complexity. |
| Pneumatic Solenoid | Specifically designed for controlling air or gas flow; often used in automation. | Manufacturing, automotive systems | Pros: Quick actuation, reliable. Cons: Limited to pneumatic applications. |
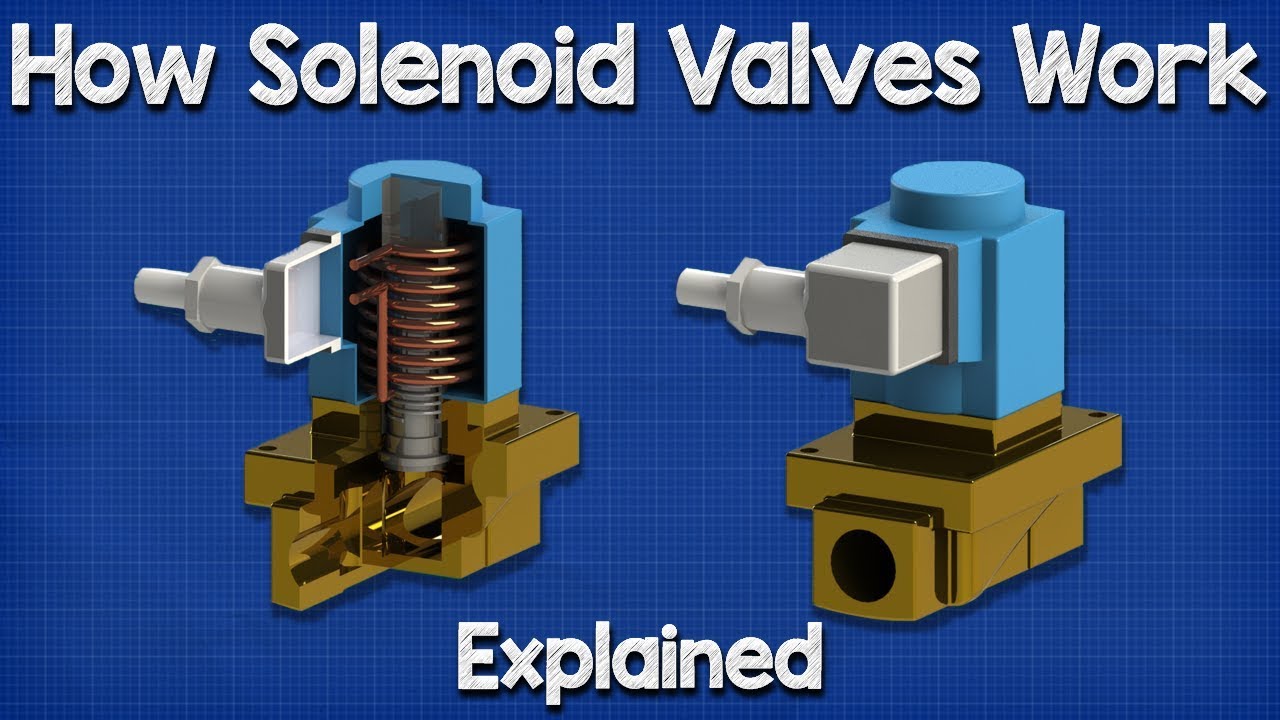
Direct-Acting Solenoid
Direct-acting solenoid valves are straightforward devices that use the electromagnetic field generated by the solenoid coil to directly operate the valve. They are particularly suited for applications requiring small flow rates, such as HVAC systems and medical devices. Buyers should consider the simplicity of installation and fast response times; however, the limited flow capacity may not be suitable for larger systems.
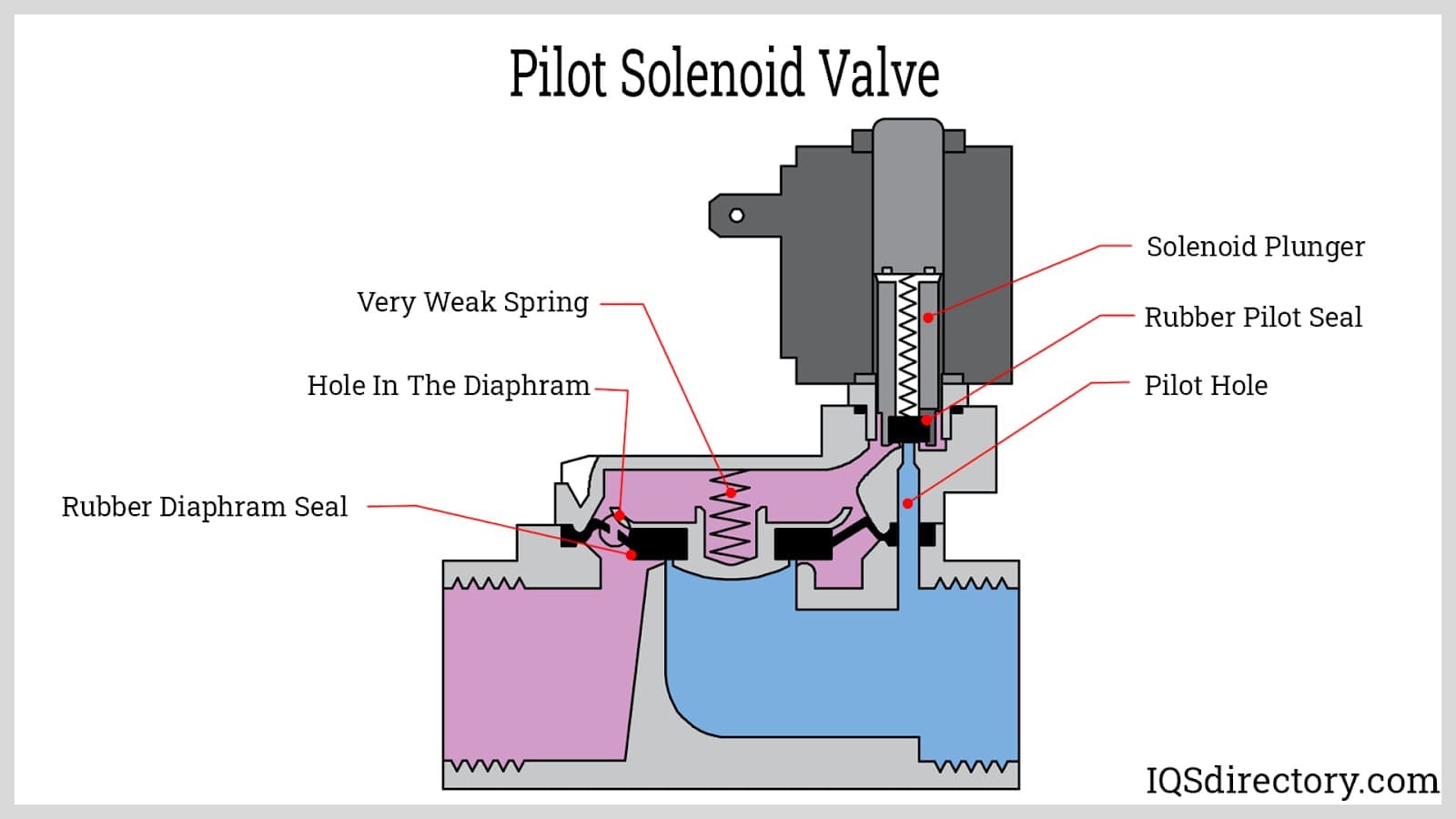
Pilot-Operated Solenoid
Pilot-operated solenoid valves utilize a small pilot valve to control a larger main valve, making them highly efficient for high flow applications. They are commonly used in industrial automation and water treatment systems. B2B buyers should note their energy efficiency and ability to handle larger flow rates, though the complexity of installation and maintenance can be a drawback.
3-Way Solenoid Valve
3-way solenoid valves can direct flow between two outlets, making them highly versatile for various applications, including pneumatic systems and mixing processes. They allow for flexible operation and can save space in installations. Buyers should weigh the benefits of adaptability against the potential complexity in control and installation, which may require additional expertise.
Proportional Solenoid
Proportional solenoid valves provide variable control of fluid flow based on an input signal, making them ideal for process control and robotics applications. Their ability to adjust flow rates precisely is a significant advantage for many industries. However, buyers should be aware that the increased precision comes at a higher cost and complexity in setup compared to simpler valve types.
Pneumatic Solenoid
Pneumatic solenoid valves are specifically designed to control the flow of air or gas, making them essential in manufacturing and automotive systems. They are known for their quick actuation and reliability in high-speed applications. Buyers should consider their suitability for pneumatic applications, but note that they are limited to controlling gases rather than liquids, which may restrict their usability in certain processes.
Related Video: How Solenoid Valves Work – Basics actuator control valve working principle
Key Industrial Applications of solenoid control valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solenoid control valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Automated control of chemical dosing systems | Ensures precise chemical mixing, improving water quality and compliance with safety standards | Material compatibility with chemicals, pressure ratings, and regulatory certifications |
| HVAC and Refrigeration | Temperature control in air conditioning systems | Enhances energy efficiency and comfort in residential and commercial buildings | Voltage specifications, response time, and durability in varying temperatures |
| Agriculture | Irrigation control systems for precision farming | Optimizes water usage and boosts crop yields | Resistance to environmental factors, flow rates, and automation compatibility |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Fuel injection systems in combustion engines | Increases fuel efficiency and reduces emissions | Compatibility with fuel types, temperature tolerances, and reliability under stress |
| Industrial Automation | Process control in manufacturing lines | Improves operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Sizing for flow capacity, integration with existing systems, and maintenance requirements |
Water Treatment
In water treatment facilities, solenoid control valves play a crucial role in the automated control of chemical dosing systems. These valves ensure the precise mixing of chemicals such as chlorine or coagulants, which is vital for maintaining water quality and meeting regulatory compliance. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing valves that are compatible with various chemicals and have certifications for safety and environmental regulations is essential.
HVAC and Refrigeration
In HVAC systems, solenoid control valves are utilized to regulate refrigerant flow and control temperature settings. This automation leads to enhanced energy efficiency and improved comfort levels in both residential and commercial environments. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on selecting valves that meet specific voltage and response time requirements to ensure optimal performance in diverse climates.
Agriculture
Solenoid control valves are integral to modern irrigation systems, allowing for precise control over water flow in agricultural applications. This precision helps optimize water usage, which is increasingly important for sustainability and maximizing crop yields. Buyers from regions like Africa, where water scarcity can be a significant issue, should consider valves that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and offer compatibility with advanced irrigation technologies.
Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive sector, solenoid control valves are essential for fuel injection systems in combustion engines. These valves improve fuel efficiency and help reduce harmful emissions, aligning with global sustainability trends. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Argentina, it is critical to ensure that the valves are compatible with various fuel types and can withstand high temperatures typical of engine environments.
Industrial Automation
In manufacturing lines, solenoid control valves are used for process control, enabling automated operations that enhance efficiency and reduce downtime. The ability to quickly open and close fluid pathways makes these valves indispensable for industries that rely on precise fluid management. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing valves that can be easily integrated into existing systems, have adequate flow capacity, and require minimal maintenance to ensure continuous operation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solenoid control valve
When selecting materials for solenoid control valves, it is essential to consider the specific application requirements, environmental factors, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of solenoid control valves, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength. It typically operates well in temperatures up to 200°C and pressures around 20 bar.
Pros & Cons: Brass is relatively easy to machine and has good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications involving hot fluids. However, it can be susceptible to dezincification in aggressive environments, which may compromise its integrity over time. Additionally, while brass is cost-effective, it may not be suitable for highly corrosive media.
Impact on Application: Brass valves are commonly used in water and air applications but may not be appropriate for aggressive chemicals or high-temperature steam. Buyers must assess the chemical compatibility of brass with the intended media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B36 for brass alloys is crucial. Buyers in regions like the Middle East and Africa should be aware of local corrosion rates and environmental conditions that may affect brass performance.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers superior corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 400°C) and pressures (up to 50 bar). Its durability makes it ideal for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including those involving aggressive chemicals. However, it is more expensive than brass and can be more challenging to machine, potentially increasing manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for chemical processing, food and beverage applications, and marine environments. Buyers must ensure that the selected grade of stainless steel is compatible with the specific media being controlled.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards like ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes and fittings. In Europe, adherence to EN standards is also essential, particularly for food-related applications.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is a thermoplastic polymer known for its lightweight and chemical resistance. It operates effectively within a temperature range of -10°C to 60°C and pressures up to 10 bar.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective, easy to fabricate, and resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for various applications. However, its lower temperature and pressure ratings limit its use in high-stress environments. Additionally, PVC can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: PVC valves are commonly used in water treatment, irrigation, and chemical handling applications. Buyers must consider the temperature and pressure limits when selecting PVC valves for their systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D1784 for PVC materials is important. Buyers in South America and Africa should also consider local regulations regarding plastic materials in industrial applications.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with operational capabilities up to 150°C and pressures around 20 bar. It is often anodized to enhance its protective qualities.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which reduces shipping costs and installation complexity. However, it is not as strong as stainless steel and may not perform well in highly corrosive environments, leading to potential failures.
Impact on Application: Aluminum valves are suitable for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in mobile equipment or HVAC systems. However, they may not be ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like Europe, adherence to REACH regulations regarding chemical safety is essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for solenoid control valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Water and air applications | Good corrosion resistance | Susceptible to dezincification | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food applications | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| PVC | Water treatment, irrigation | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited temperature and pressure rating | Low |
| Aluminum | Mobile equipment, HVAC systems | Lightweight and easy to install | Not suitable for corrosive environments | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in solenoid control valves, facilitating informed decision-making for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solenoid control valve
Manufacturing Processes for Solenoid Control Valves
The manufacturing of solenoid control valves involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating potential suppliers.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Material Selection: The first step is selecting the appropriate materials based on the valve’s intended application. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and specialized plastics, depending on factors like chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and pressure ratings.
– Material Inspection: Before processing, raw materials undergo inspection to verify compliance with specifications. This includes checking for defects and ensuring proper certifications are in place. -
Forming
– Machining: Key components such as the valve body, plunger, and coil are machined to precise specifications. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often utilized for high accuracy and repeatability.
– Coil Winding: The solenoid coil is wound using high-purity copper wire. The winding process must ensure uniform tension to avoid performance issues later.
– Casting and Forging: Some manufacturers may employ casting or forging for the valve body, which can enhance strength and durability. -
Assembly
– Component Assembly: After machining, components are assembled in a controlled environment. This includes fitting the plunger, valve seat, and other internal parts into the valve body.
– Sealing and Testing: Seals are installed to ensure leak-tightness. This is critical, especially for valves that will handle hazardous or high-purity fluids. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Valves may undergo surface treatments like anodizing or plating to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
– Final Inspection: Each valve is subjected to a final inspection to ensure it meets specifications and quality standards before packaging and shipment.
Quality Assurance Practices
Quality assurance in solenoid control valve manufacturing is vital to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. For international B2B buyers, understanding these practices can aid in selecting reputable suppliers.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: This indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA).
- API Standards: For valves used in oil and gas applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before they enter the production process. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During manufacturing, regular checks are performed at various stages. This can include dimensional checks and functional tests to ensure components meet design specifications. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– After assembly, each valve undergoes comprehensive testing, including pressure tests and functional tests, to ensure it operates correctly.
Common Testing Methods
- Pressure Testing: Verifies that the valve can withstand specified pressure without leaking.
- Electrical Testing: Ensures the solenoid operates correctly under various conditions.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to confirm that the valve will perform reliably over time.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits
– Regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facility can provide insights into their quality management processes and compliance with international standards. -
Request Quality Reports
– Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports, test results, and compliance certificates. -
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services
– Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product reliability. -
Assess Quality Certifications
– Verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) and understand the scope of these certifications to ensure they cover the products being sourced.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact. Understanding these can help in selecting compliant suppliers.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices may vary; fostering good relationships with suppliers can enhance clarity in quality expectations.
- Logistics and Lead Times: Quality assurance processes may affect lead times. It’s essential to factor in testing and inspection periods when planning orders.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in solenoid control valve production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet both their operational and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solenoid control valve Sourcing
In the sourcing of solenoid control valves, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. The cost components can broadly be categorized into several key areas:
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost of solenoid control valves. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and various plastics, each with different price points based on their properties and applications. For high-temperature or corrosive environments, specialized materials may be required, which can further increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia, may offer competitive pricing, while European and North American manufacturers might charge more due to higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, but any inefficiencies can lead to higher costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom solenoid valves can be significant, particularly for specialized applications. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating quotes, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures ensure that products meet industry standards and specifications. While higher QC costs can increase the upfront price, they often lead to lower failure rates and reduced warranty claims in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the supplier’s location, shipping methods, and destination. International buyers should factor in customs duties, taxes, and potential delays associated with logistics.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary significantly based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the typical margins in your industry can help you negotiate better pricing.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the final price of solenoid control valves:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers optimize their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clarify their needs upfront to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used directly impact pricing. For example, valves made from high-grade stainless steel will typically cost more than those made from brass.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO, ANSI) may command higher prices. Ensure that the quality level aligns with your application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers, their reputation, and their production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer better reliability but at a premium price.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can influence the overall cost. For instance, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) includes shipping and duties, which can simplify budgeting but may come with a higher upfront cost.
Buyer Tips
To navigate the complexities of pricing in the solenoid control valve market, consider these actionable insights:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Always approach suppliers with a clear understanding of the market rates and your budget. Leverage volume commitments for better pricing.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with valve failures.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of regional pricing differences, currency fluctuations, and economic conditions that might impact supplier pricing.
-
Research Suppliers Thoroughly: Evaluate suppliers based on their production capabilities, lead times, and customer service. A reliable supplier can save costs in the long run through efficient service.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed are indicative and can vary widely based on supplier, order size, customization, and other factors. Buyers should obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential solenoid control valve Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘solenoid control valve’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solenoid control valve
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with solenoid control valves is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Below, we outline key specifications that define solenoid control valves and explain common industry jargon that facilitates effective communication between suppliers and buyers.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Solenoid control valves are constructed from various materials such as brass, stainless steel, or reinforced plastics. The choice of material is crucial as it impacts the valve’s compatibility with different fluids, resistance to corrosion, and operational longevity. For example, stainless steel is often preferred for corrosive environments, while brass may suffice for neutral fluids. Understanding the material grade helps buyers select valves suited for their specific application, ensuring reliability and reducing maintenance costs. -
Pressure Rating
– This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle during operation. Common ratings range from low-pressure (under 1 bar) to high-pressure (up to 10 bar or more). Buyers must match the pressure rating with their system’s requirements to prevent valve failure and ensure safety. This is particularly important in industries like oil and gas, where pressure fluctuations are common. -
Flow Coefficient (Cv)
– The flow coefficient measures the valve’s capacity to allow fluid flow. A higher Cv value indicates a greater flow capacity, which is essential for applications requiring rapid fluid movement. B2B buyers should evaluate the Cv rating based on their system’s flow requirements to optimize performance and efficiency. -
Operating Temperature Range
– This specification defines the temperature limits within which the valve can operate effectively. For instance, some solenoid valves can function in extreme temperatures, from -40°C to +150°C. Buyers in industries such as food processing or chemical manufacturing must select valves that can withstand their operating conditions to ensure durability and compliance with industry standards. -
Wattage of the Solenoid Coil
– The wattage indicates the power consumption of the solenoid coil, which affects operational costs and energy efficiency. A lower wattage coil can reduce electricity costs, making it an important consideration for long-term operational budgets. Buyers should assess their energy needs against the solenoid’s power requirements. -
Response Time
– This is the time it takes for the valve to open or close after being energized. Response time is critical in applications requiring rapid actuation, such as in automation systems. Buyers should look for valves with shorter response times to enhance operational efficiency and responsiveness in their systems.
Common Industry Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are used as components in another company’s product. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source components that meet specific quality and compatibility standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to negotiate better pricing and inventory management. Buyers should assess their needs against the MOQ to ensure cost-effectiveness.
-
RFQ (Request for Quote)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. This process allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms effectively. A well-structured RFQ can streamline the procurement process and lead to better pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized trade terms used in international sales contracts that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers navigate international transactions and clarify their cost obligations. -
Pilot-Operated vs. Direct-Acting
– These terms describe two types of solenoid valve operation. Pilot-operated valves use a small pilot flow to control a larger flow, making them suitable for high-pressure applications. In contrast, direct-acting valves rely solely on the solenoid to operate, which is ideal for low-pressure scenarios. Knowing the differences allows buyers to select the appropriate valve type for their applications.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and terminologies, international B2B buyers can make better purchasing decisions, ensuring they choose the right solenoid control valves for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the solenoid control valve Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The solenoid control valve market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing automation across various industries, including manufacturing, oil and gas, and HVAC systems. Global demand is being propelled by the need for precise control in fluid handling processes and the rising adoption of smart technologies. Notably, regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing substantial investments in infrastructure and industrialization, creating significant opportunities for B2B buyers.
Emerging trends indicate a shift toward digitalization, with the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in solenoid valve systems. This advancement allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is encouraging manufacturers to develop more intelligent solenoid valves that can communicate with other devices in the network, providing more comprehensive data analytics for better decision-making.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
International buyers should also be aware of the growing importance of local sourcing. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that can offer shorter lead times and reduced transportation costs, particularly in regions like the UAE and Argentina, where logistical challenges can impact project timelines. Moreover, buyers are seeking manufacturers that demonstrate flexibility in customization to meet specific application requirements, ensuring optimal performance in diverse operational environments.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the solenoid control valve sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and product lifecycle management is under scrutiny, with companies striving to reduce their carbon footprint. Ethical sourcing practices are now essential, as buyers are increasingly inclined to partner with suppliers that prioritize sustainable materials and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
When evaluating solenoid valves, buyers should consider options that incorporate recyclable materials and comply with international environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the use of “green” materials, such as biodegradable plastics or non-toxic coatings, is gaining traction as businesses seek to minimize their environmental impact.
By focusing on ethical sourcing, companies can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for responsible business practices. This shift towards sustainability is particularly relevant in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe, where compliance can significantly affect market access and competitiveness.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of solenoid control valves can be traced back to the early 19th century when electromagnetic technology began to gain traction. Initially used in telegraph systems, the application of solenoids in fluid control emerged as industries sought more efficient ways to manage the flow of liquids and gases. Over the decades, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have led to the development of more reliable and versatile solenoid valves.
Today, these devices are integral to a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to consumer appliances. The shift towards automation and smart technologies marks a significant milestone in their history, positioning solenoid control valves as essential components in modern fluid management systems. This evolution underscores the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements to ensure optimal performance and competitiveness in the global market.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solenoid control valve
-
What factors should I consider when vetting solenoid valve suppliers?
When vetting suppliers for solenoid valves, prioritize their industry experience, certifications, and quality control processes. Look for suppliers with ISO 9001 or similar certifications, indicating adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, assess their manufacturing capabilities, including the materials they use and their ability to meet specific industry standards. Reading customer reviews and requesting references can also provide insights into their reliability and service quality. -
Can solenoid control valves be customized to fit my specific application?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for solenoid control valves. Customizations may include size, material, port configurations, and specific features tailored to your operational needs. When discussing customization, clearly communicate your requirements and any industry-specific regulations that must be met. Ensure that the supplier has a robust design and prototyping process to facilitate these custom solutions. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for solenoid valves?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly by supplier and product specifications. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units, depending on the complexity and customization of the valves. Standard lead times are typically between 4 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and request a clear timeline and pricing structure to avoid unexpected delays. -
What payment options are available for international purchases of solenoid valves?
Payment options for international purchases may include bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment through escrow services. Discuss these options with your supplier to find a mutually agreeable method that ensures security and compliance with your local banking regulations. Consider negotiating payment terms that align with your cash flow requirements, such as partial payments upon order and the balance upon delivery. -
How can I ensure the quality and compliance of solenoid valves?
To ensure quality and compliance, request detailed quality assurance documentation from your supplier, including certificates of compliance with industry standards (e.g., CE, UL). Conducting factory audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality control. Additionally, consider third-party inspection services that can verify product quality before shipment.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing solenoid valves?
When importing solenoid valves, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Partnering with a freight forwarder can also help navigate logistics complexities and provide guidance on the best shipping options. -
How should disputes with suppliers be managed?
Disputes with suppliers can arise over quality issues, delivery delays, or contract misunderstandings. Establish clear communication channels and document all agreements to mitigate risks. In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct dialogue. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract, which can provide a structured approach to resolving conflicts without resorting to litigation. -
What are the best practices for maintaining solenoid valves after purchase?
To maintain solenoid valves effectively, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation and operation. Regularly inspect the valves for signs of wear or damage, and ensure they are cleaned to prevent buildup that could impair functionality. Implement a preventive maintenance schedule that includes testing the valves periodically to ensure they are operating correctly. Keeping detailed maintenance records can also help track performance and inform future purchasing decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solenoid control valve
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation, strategic sourcing of solenoid control valves is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring reliable fluid management. International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize understanding the diverse types and applications of solenoid valves to select the most suitable options for their specific needs. Key considerations include the valve’s material compatibility, actuation method, and installation requirements, which directly impact performance and longevity.
Investing in high-quality solenoid control valves can yield significant benefits, such as reduced maintenance costs, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced process control. As industries increasingly move towards automation, the demand for these versatile devices will continue to grow.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should engage with reputable manufacturers and suppliers to explore innovative solutions that align with their operational goals. By fostering relationships with key industry players, businesses can secure a competitive edge and navigate the complexities of global supply chains effectively. Take action today: assess your current valve solutions and consider how strategic sourcing can elevate your operational capabilities.