Master the Types of Bolts and Nuts: Your Essential B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of bolts and nuts
In today’s interconnected economy, the global market for bolts and nuts is a vital component of countless industries, from construction to automotive manufacturing. As international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate this complex landscape, understanding the various types of bolts and nuts becomes essential for making informed sourcing decisions. These fasteners are not merely functional; they are critical to ensuring the integrity and safety of structures and machinery.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the myriad types of bolts and nuts available in the market. We delve into the different materials used—ranging from stainless steel to plastic—and their respective applications, allowing buyers to select the right components for their specific needs. Furthermore, we address the manufacturing processes and quality control measures that ensure reliability and performance, which are crucial for maintaining operational standards.
Additionally, this guide provides insights into identifying reputable suppliers, understanding cost structures, and analyzing market trends. With a dedicated FAQ section, we aim to clarify common queries that can impact sourcing strategies. By equipping international B2B buyers with this knowledge, we empower them to make strategic decisions that can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and foster stronger supply chain relationships across diverse regions such as Mexico and Nigeria. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your procurement processes with our detailed insights into the world of bolts and nuts.
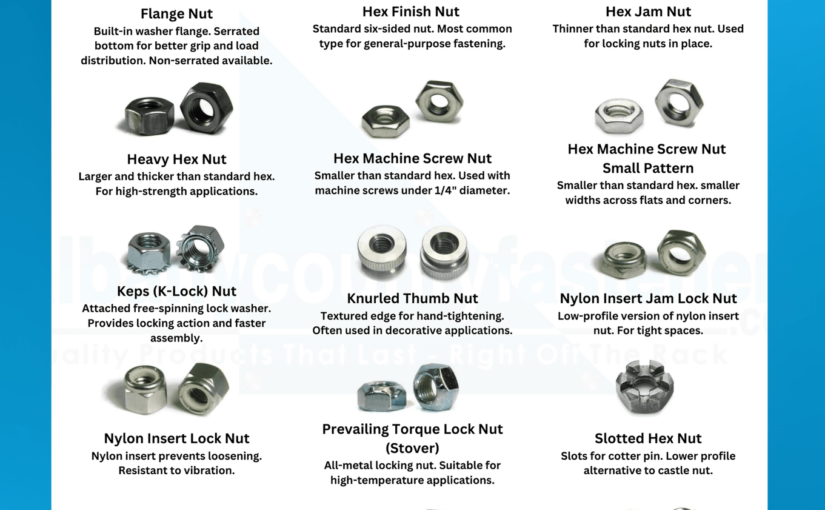
Understanding types of bolts and nuts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Bolts | Six-sided head, often used with a nut | Construction, machinery assembly | Pros: Versatile, high strength; Cons: Can be difficult to tighten in tight spaces. |
| Carriage Bolts | Rounded head, square neck prevents rotation | Wood-to-wood applications, furniture | Pros: Easy installation; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Lag Bolts | Large, heavy-duty screws with a hexagonal head | Timber construction, heavy fixtures | Pros: Excellent holding power; Cons: Requires pre-drilling. |
| Flange Nuts | Integrated washer for improved load distribution | Automotive, construction | Pros: Reduces risk of loosening; Cons: Higher cost compared to standard nuts. |
| Lock Nuts | Designed to resist loosening under vibration | Aerospace, automotive, machinery | Pros: Enhanced security; Cons: More expensive than standard nuts. |
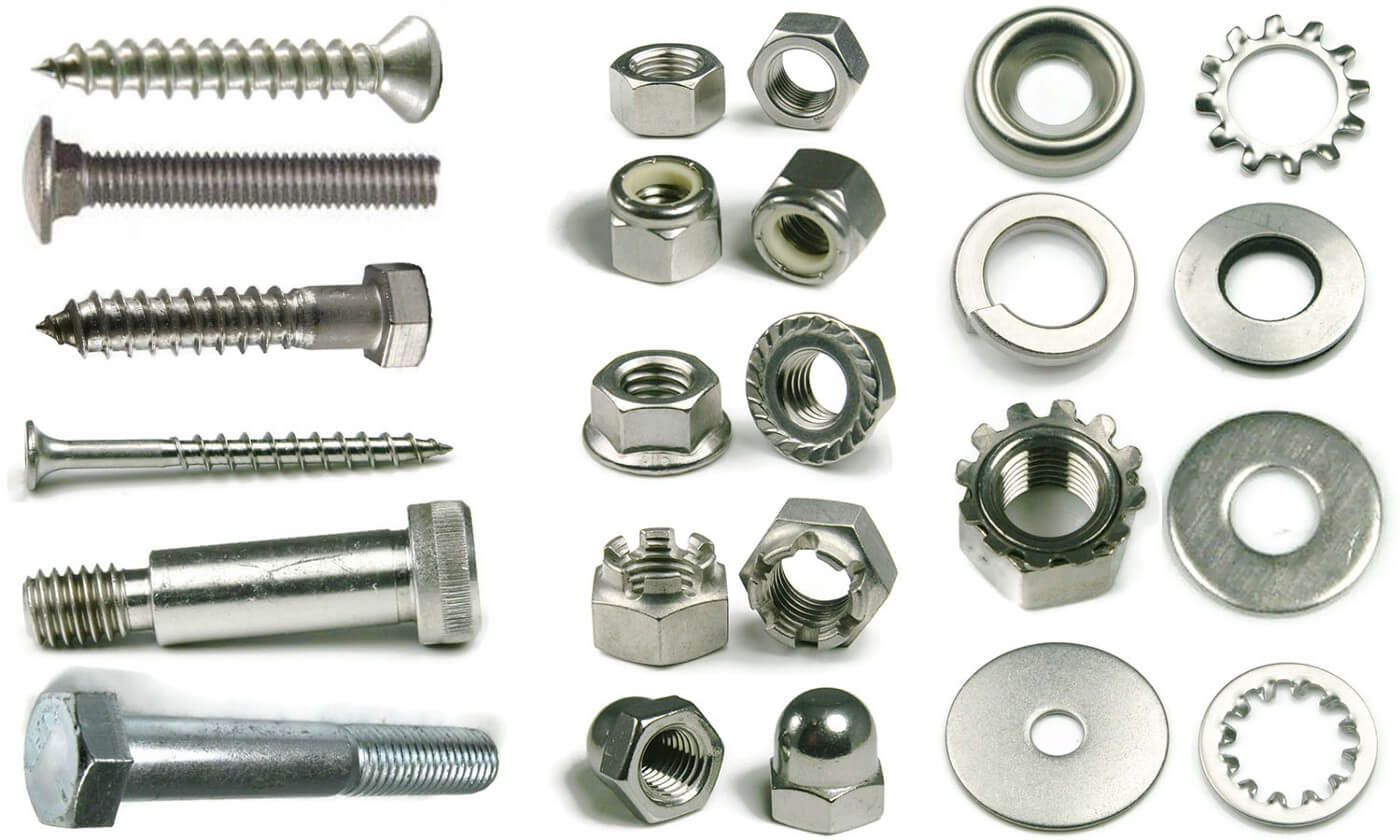
Hex Bolts
Hex bolts are characterized by their six-sided heads, which provide a robust grip for wrenches. They are widely used in construction and machinery assembly due to their strength and versatility. When considering hex bolts, buyers should focus on the material quality, as it affects durability and resistance to corrosion. Additionally, the size and grade of the bolt are crucial for ensuring compatibility with the intended application.
Carriage Bolts
Carriage bolts feature a rounded head and a square neck that prevents rotation when tightened. They are commonly used in applications where wood connects to wood, such as in furniture assembly. For B2B buyers, the ease of installation is a significant advantage, but it’s essential to ensure that the bolt length is suitable for the thickness of the materials being joined. They are less versatile than other bolt types, which can limit their use in certain projects.
Lag Bolts
Lag bolts are heavy-duty fasteners with a hexagonal head, designed for fastening large wooden structures or heavy fixtures. Their robust design allows for exceptional holding power, making them ideal for timber construction. B2B buyers must consider the need for pre-drilling, which can add time to the installation process. Additionally, selecting the right size and thread type is vital to ensure optimal performance in demanding applications.
Flange Nuts
Flange nuts come with an integrated washer, which enhances load distribution and minimizes the risk of loosening. These nuts are commonly used in automotive and construction applications where vibration is a concern. For international buyers, the added cost of flange nuts can be justified by their performance benefits. It’s important to evaluate the compatibility with the corresponding bolts and the specific load requirements of the application.
Lock Nuts
Lock nuts are specifically designed to resist loosening due to vibration, making them essential in high-stakes industries such as aerospace and automotive. They often feature a nylon insert or a serrated surface to enhance grip. For B2B buyers, the added security of lock nuts is a significant advantage, but they typically come at a higher price point. Buyers should assess the operational environment and choose the appropriate lock nut type to maximize effectiveness.
Related Video: Types of Nuts and Bolts | The Home Depot
Key Industrial Applications of types of bolts and nuts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of bolts and nuts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine assembly and chassis construction | Ensures structural integrity and performance | Compliance with international standards, corrosion resistance, and availability of specific grades. |
| Construction | Structural framing and fastening | Provides safety and durability in building structures | Sourcing certified materials to meet regional building codes and environmental conditions. |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline construction and maintenance | Enhances operational efficiency and leak prevention | Consideration of high-temperature and pressure ratings, along with certifications for hazardous environments. |
| Aerospace | Aircraft assembly and maintenance | Critical for safety and reliability in flight | Need for high-strength, lightweight materials and compliance with strict aerospace regulations. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine assembly and solar panel installation | Supports sustainable energy initiatives and reduces downtime | Focus on sourcing materials that withstand environmental stressors and have a low carbon footprint. |
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, bolts and nuts are pivotal for engine assembly and chassis construction. These fasteners ensure the structural integrity of vehicles, which is crucial for performance and safety. International B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing bolts and nuts that comply with international quality standards, such as ISO or SAE, to guarantee reliability. Additionally, corrosion resistance is vital, especially in regions with harsh climates, making the choice of materials and coatings essential for long-lasting applications.
Construction Industry
In construction, bolts and nuts are essential for structural framing and fastening. They provide the necessary strength and durability to withstand various loads and environmental conditions. For buyers, sourcing certified materials that meet local building codes is crucial to ensure compliance and safety. Moreover, understanding the specific requirements for different construction environments, such as seismic zones or coastal areas, can guide the selection of appropriate fasteners that can endure environmental stressors.
Oil & Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on bolts and nuts for pipeline construction and maintenance. These fasteners enhance operational efficiency and are critical for preventing leaks, which can have severe environmental and financial repercussions. Buyers in this sector need to consider high-temperature and pressure ratings for their fasteners, ensuring they are suitable for the demanding conditions typical in oil and gas applications. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers that offer certifications for hazardous environments is essential for maintaining safety standards.
Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, the role of bolts and nuts is vital for aircraft assembly and maintenance, where safety and reliability are paramount. These fasteners must meet stringent aerospace regulations and often require high-strength, lightweight materials to minimize overall aircraft weight without compromising safety. International buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers who provide detailed documentation and compliance certifications, ensuring that all materials meet the rigorous standards of the aerospace industry.
Renewable Energy Industry
The renewable energy sector utilizes bolts and nuts extensively in wind turbine assembly and solar panel installation. These fasteners support sustainable energy initiatives by ensuring the structural integrity of installations, which can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs. Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that can withstand environmental stressors, such as high winds or extreme temperatures, and consider the carbon footprint of their sourcing practices to align with sustainability goals.
Related Video: Types of Bolts, Nuts, and Washers | A Complete Guide of Fasteners
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of bolts and nuts
When selecting materials for bolts and nuts, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of bolts and nuts, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel bolts and nuts are known for their high tensile strength and ability to withstand high temperatures. They typically have a temperature rating up to 300°C and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its durability and strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can limit its use in harsh environments. Manufacturing carbon steel fasteners is relatively straightforward and cost-effective, but the need for protective coatings can add to overall costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with various media, but its susceptibility to rust makes it less ideal for applications involving moisture or corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM A307 and DIN 933. In regions like Africa and South America, where humidity levels can be high, it is advisable to consider galvanized or coated options to enhance corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel bolts and nuts exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 800°C. They are often used in environments that require sanitation, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its ability to resist oxidation and corrosion, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel, and its manufacturing process can be more complex due to the need for precise alloy compositions.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is highly compatible with aggressive media, including saltwater and acids, making it ideal for maritime and chemical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A193 and JIS B1180 is essential. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the varying grades of stainless steel (like 304 and 316) and select the appropriate grade based on their specific environmental conditions.
Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steel bolts and nuts are engineered to provide enhanced mechanical properties, including increased hardness and tensile strength. They can typically withstand higher temperatures and pressures than standard carbon steel.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of alloy steel is its superior performance in high-stress applications, such as automotive and aerospace industries. However, it can be more expensive due to its complex manufacturing process and may require additional heat treatment.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is suitable for high-pressure applications and environments where mechanical strength is critical. However, its corrosion resistance is lower than that of stainless steel, which may limit its use in certain applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM A574 and DIN 6912. In regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure may be less developed, the availability of alloy steel products may vary, necessitating careful supply chain management.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass bolts and nuts are composed of copper and zinc, providing good corrosion resistance and excellent machinability. They can typically handle temperatures up to 200°C and are not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of brass is its aesthetic appeal and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for decorative applications. However, brass is softer than steel, which limits its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is highly compatible with non-corrosive media and is often used in plumbing and electrical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 and DIN 17660. In regions with varying economic conditions, brass may be more expensive, and buyers should assess the cost-benefit ratio for their specific applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of bolts and nuts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Heavy machinery, construction | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Alloy Steel | Automotive, aerospace | Superior performance under stress | More expensive and requires heat treatment | High |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical applications | Aesthetic appeal and machinability | Limited strength for heavy-duty use | Medium |
This guide provides a strategic overview for B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding the selection of bolts and nuts based on material properties, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of bolts and nuts
Manufacturing Processes for Bolts and Nuts
Understanding the manufacturing processes for bolts and nuts is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking quality components. The production of these fasteners involves several stages, each with specific techniques and practices that can significantly influence the final product’s quality.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing bolts and nuts is material preparation. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, selected based on application requirements.
- Material Selection: Buyers should ensure that the material meets industry standards, as this affects strength and corrosion resistance.
- Heat Treatment: Processes such as annealing, hardening, and tempering may be employed to enhance the material properties before forming.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the metal into the desired bolt or nut configuration.
- Cold Heading: This method is prevalent for producing bolts, where metal wire is compressed into shape at room temperature. It helps achieve high precision and reduces waste.
- Forging: Used for high-strength applications, forging involves shaping the metal by applying compressive forces, often at elevated temperatures.
- Machining: For nuts, machining processes like turning and milling are often used to achieve precise dimensions and threads.
3. Assembly
In some cases, the assembly of multiple components may be necessary. For example, bolts might require washers or nuts to be fitted together.
- Threading: The threading process is critical, as it ensures compatibility with corresponding nuts and sockets. This can be accomplished through cutting, rolling, or grinding techniques.
- Integration: For assemblies that require multiple fasteners, ensuring proper alignment and torque specifications is essential.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of bolts and nuts.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as plating (zinc, nickel), galvanization, or powder coating improve corrosion resistance and appearance. Buyers should confirm the suitability of these finishes for their specific environments.
- Passivation: For stainless steel fasteners, passivation removes free iron from the surface, enhancing corrosion resistance.
Quality Assurance (QA) in Fastener Manufacturing
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of bolts and nuts, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications.
International Standards
Several international standards govern the manufacturing and quality of fasteners:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for fasteners used in the oil and gas industry, focusing on safety and reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet specified requirements before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify issues early. This includes dimensional checks and process parameter validations.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, final inspections are conducted, including testing for strength, hardness, and surface defects.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of bolts and nuts:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the material.
- Hardness Testing: Determines the hardness level, which can indicate the material’s suitability for its intended application.
- Surface Roughness Measurement: Assesses the finish quality, which can impact performance and aesthetic appeal.
- Non-destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing can identify internal defects without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control standards. Here are actionable insights for verification:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. Look for adherence to ISO standards and other relevant certifications.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of quality. This is particularly important for buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local standards may vary.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, API) and that they are up-to-date.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential:
- Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with local standards and how they compare to international ones. For example, South American countries might have specific regulations that differ from European standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying attitudes towards quality and compliance. Building relationships with suppliers can enhance communication and ensure adherence to quality expectations.
- Logistics and Transportation: Consider how quality may be affected during transportation. Suppliers should demonstrate that they have measures in place to protect products during shipping, especially for long-distance trade.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for bolts and nuts, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they procure high-quality components that meet their specifications and industry standards.
Related Video: The manufacturing process of hex nuts. mass production factory in korea.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of bolts and nuts Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for bolts and nuts is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the intricate details of cost components and pricing influencers can lead to better sourcing decisions and improved negotiation strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials
The primary cost driver in the production of bolts and nuts is the raw materials used, typically steel, stainless steel, or other alloys. Prices fluctuate based on global commodity markets, so buyers should monitor these trends to anticipate cost changes. Additionally, sourcing from local suppliers can mitigate import tariffs and reduce transportation costs. -
Labor
Labor costs vary significantly across regions. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, manufacturers might incorporate automation to maintain competitiveness. Conversely, countries in Africa and South America may have lower labor costs, but quality assurance becomes crucial to ensure compliance with international standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes expenses related to the facilities, utilities, and equipment necessary for production. Buyers should evaluate manufacturers’ overhead structures to understand how these costs impact the final price. Suppliers with efficient operations may pass savings on to buyers. -
Tooling
Tooling costs are essential for custom or specialized bolts and nuts. Investing in tooling can significantly affect the unit price, particularly for low-volume orders. Buyers should assess whether the tooling costs can be amortized over larger orders to achieve better pricing. -
Quality Control (QC)
Implementing rigorous QC processes adds to the manufacturing cost but ensures product reliability. Buyers should inquire about a supplier’s QC practices and certifications, as this can justify a higher price point while ensuring long-term performance. -
Logistics
Transportation costs, which include shipping, handling, and customs duties, can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and the destination market. Understanding Incoterms is crucial, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs and risks. -
Margin
Manufacturers typically apply a margin to cover risks and profit. This margin can differ based on market demand, competition, and supplier reputation. Buyers should research market rates to gauge whether a supplier’s pricing is reasonable.
Price Influencers
- Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases usually lead to discounts. Establishing long-term contracts can also secure better pricing.
- Specifications/Customization: Customized products often incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential price increase.
- Materials: Higher-quality materials generally command higher prices. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in quality.
- Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international standards or possess certifications may have a higher initial cost but can reduce long-term risks and liabilities.
- Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and historical performance of suppliers can influence pricing. Conducting due diligence is essential.
- Incoterms: Understanding these terms is crucial for cost management, as they determine who bears the shipping costs and risks.
Buyer Tips
- Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially when dealing with large orders. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your position.
- Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential replacement costs. Sometimes paying more upfront can lead to savings in the long run.
- Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing strategies. In emerging markets, prices may be more negotiable, while established markets might have fixed pricing due to higher competition.
- Market Research: Regularly conduct market research to stay informed about price trends and supplier performance. This knowledge can significantly enhance negotiation tactics and sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices indicated in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers for the most accurate pricing information.
Spotlight on Potential types of bolts and nuts Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘types of bolts and nuts’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of bolts and nuts
Key Technical Properties of Bolts and Nuts
Understanding the essential technical properties of bolts and nuts is critical for international B2B buyers. These specifications not only determine the performance and durability of the fasteners but also influence the overall quality of the finished product. Here are some of the most important properties to consider:
-
Material Grade: The material grade of bolts and nuts indicates their strength and corrosion resistance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. For instance, stainless steel grades such as A2 and A4 offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for marine or humid environments. Buyers must select the appropriate grade based on application requirements to avoid premature failure.
-
Tensile Strength: This property measures the maximum stress a bolt or nut can withstand while being stretched before breaking. It is typically expressed in megapascals (MPa) or pounds per square inch (PSI). Higher tensile strength is crucial for applications involving heavy loads, such as construction or automotive industries. Ensuring the correct tensile strength helps prevent mechanical failures that could lead to costly downtime.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in dimensions. It is vital for ensuring that bolts and nuts fit together properly during assembly. Tight tolerances can improve the precision of mechanical assemblies, enhancing overall performance. International buyers should verify tolerance specifications to guarantee compatibility with existing components.
-
Finish: The finish of bolts and nuts affects their corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Common finishes include zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, and black oxide. A suitable finish not only extends the lifespan of the fasteners but also aligns with industry standards, particularly in markets that prioritize sustainability and environmental impact.
-
Thread Type: The thread type (e.g., coarse, fine, or metric) determines how bolts and nuts engage with each other. Different applications may require specific thread types to ensure optimal performance. Understanding thread standards is essential for international buyers to ensure compatibility with local or imported components.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several key terms that international buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source high-quality components or negotiate better pricing based on bulk orders.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for international buyers to consider when assessing pricing structures and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help in planning procurement strategies effectively.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. Crafting a clear RFQ can lead to more accurate responses and better supplier relationships.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify responsibilities between buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for mitigating risks associated with international logistics and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the total time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is critical for supply chain management and project planning. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers about expected lead times to avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs in their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the types of bolts and nuts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for bolts and nuts is witnessing dynamic shifts driven by several factors that B2B buyers must navigate. The demand for high-strength fasteners, particularly in sectors like automotive, construction, and energy, is on the rise. This trend is propelled by the increasing emphasis on safety and reliability in manufacturing. Additionally, the rapid adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming sourcing practices. Digital platforms and e-commerce are enabling buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to access suppliers more efficiently, facilitating real-time pricing and inventory management.
Emerging trends also include the customization of fasteners to meet specific industry needs. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that can provide tailored solutions, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime. Moreover, the shift towards automation in manufacturing processes is influencing the type of fasteners being sourced, with a growing preference for automated assembly systems that require specialized fasteners.
In terms of market dynamics, fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical factors are significant considerations. B2B buyers need to stay informed about trade policies and tariffs, particularly when sourcing from different regions. Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers who can mitigate these risks is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the bolts and nuts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices. For instance, using recycled materials in the production of fasteners not only reduces waste but also appeals to an increasingly conscious consumer base.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to labor standards and environmental regulations, particularly in regions where these practices may be lax. This can be achieved by looking for certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety.
Furthermore, buyers can enhance their sustainability profiles by opting for “green” materials, such as low-carbon steel or coatings that minimize environmental impact. Engaging with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices can lead to improved brand reputation and customer loyalty, while also aligning with global sustainability goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The bolts and nuts industry has evolved significantly over the centuries, transitioning from basic hand-forged products to highly engineered components essential for modern manufacturing. The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal moment, as mass production techniques emerged, leading to standardized sizes and improved strength characteristics. In recent decades, advancements in materials science and manufacturing technology have driven innovations in fastener design, including the use of high-performance alloys and coatings that enhance durability and resistance to corrosion. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of selecting suppliers who are at the forefront of these advancements to ensure product reliability and performance in their applications.
Related Video: Understanding the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of bolts and nuts
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers for bolts and nuts?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their certifications, production capacity, and reputation in the market. Check for ISO certifications or industry-specific standards that demonstrate quality assurance. Additionally, consider their experience with international trade, particularly with your region. Request references from previous clients and assess their ability to meet your specific requirements, including technical specifications and customization capabilities. -
Can I customize bolts and nuts to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for bolts and nuts. This can include variations in size, material, and coatings. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and consider the implications on lead times and costs. Confirm the supplier’s ability to produce samples before finalizing large orders, as this ensures that the final product meets your expectations. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for bolts and nuts?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and can depend on the type of bolts and nuts required. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times also vary based on the complexity of your order and the supplier’s production capacity, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. Discuss these factors upfront to avoid delays in your procurement process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bolts and nuts internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or letters of credit. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as PayPal or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify the payment terms in the contract, including currency exchange rates and any potential additional fees for international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for my orders?
Request detailed quality assurance protocols from your suppliers, including inspection processes and testing methods. Ask for copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, to ensure they adhere to international quality standards. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or audits, especially for larger orders, to verify compliance with your specifications and ensure product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing bolts and nuts?
Logistics can be complex, especially for international shipments. Assess shipping options, including air freight for urgency or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Understand import duties and taxes applicable to your region, as these can significantly affect overall costs. Work closely with your supplier and logistics provider to ensure timely delivery and compliance with local regulations. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding product quality or delivery issues?
Establish clear communication channels and maintain a written record of all agreements and transactions. In case of disputes, first approach the supplier to discuss the issue amicably. If resolution is not achieved, refer to the contract’s dispute resolution clause, which may include mediation or arbitration. Engaging a legal professional familiar with international trade can also provide guidance on the best course of action. -
What are the best practices for maintaining ongoing supplier relationships?
Maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is crucial for long-term success. Regularly communicate your needs and feedback, and ensure timely payments to build trust. Consider scheduling periodic visits to their facilities to strengthen ties and gain insights into their operations. Collaborate on improvements or new product developments, which can foster loyalty and enhance your supply chain efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of bolts and nuts
In summary, the strategic sourcing of bolts and nuts plays a crucial role in optimizing supply chains and ensuring quality in various industries. Buyers should prioritize understanding the specifications and applications of different types of fasteners, as well as the regional suppliers who can meet their needs effectively. Key takeaways include the importance of building strong relationships with manufacturers, leveraging technology for better procurement processes, and considering local sourcing to reduce lead times and costs.
Strategic sourcing is not just about price; it encompasses quality, reliability, and sustainability. By adopting a comprehensive sourcing strategy, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with fluctuating markets and supply chain disruptions, particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America where local sourcing can enhance resilience.
Looking ahead, international buyers should remain proactive in exploring emerging trends in materials and manufacturing technologies, such as sustainable fasteners and smart manufacturing practices. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize innovation will position businesses favorably in a competitive landscape.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing bolts and nuts, consider this an opportunity to enhance your procurement strategies and drive growth. Embrace the future of fastener sourcing with confidence, and foster partnerships that will support your business objectives.