Master the Types of Electrical Connectors for Optimal
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of electrical connectors
In today’s interconnected world, the reliability and efficiency of electronic devices hinge significantly on the unseen yet vital components known as electrical connectors. These connectors are not merely functional; they are the backbone of communication and power transmission across diverse sectors, from automotive to telecommunications. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the various types of electrical connectors is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that can impact the performance and longevity of your products.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted realm of electrical connectors, covering an extensive range of topics including different types, materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards. We will explore the nuances of connectors such as pogo pins, crown spring connectors, and screw terminations, highlighting their specific applications and advantages. Additionally, the guide will provide insights into supplier options, cost considerations, and market trends, empowering you to navigate the complexities of global sourcing effectively.
By equipping yourself with the knowledge contained within this guide, you will be better positioned to select the right electrical connectors for your specific needs, ultimately enhancing product reliability and performance. This resource aims to demystify the connector landscape, enabling you to make decisions that drive efficiency and innovation in your business operations.
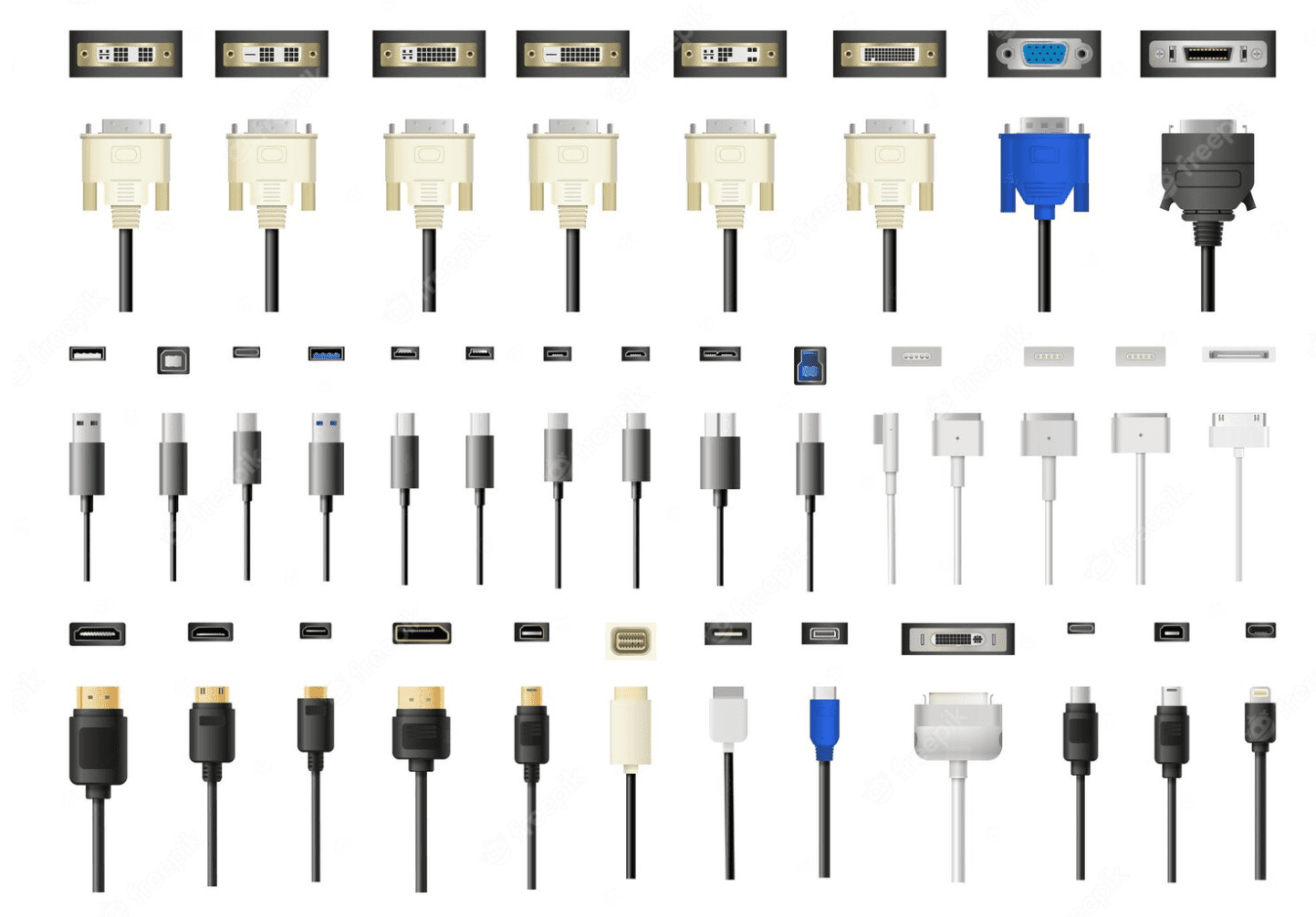
Understanding types of electrical connectors Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pogo Pins | Spring-loaded, adaptable to misalignments, compact design | Consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices | Pros: Reliable, easy to connect; Cons: Limited to low-power applications. |
| Crown Spring Connectors | Multiple contact points, high current capacity, low insertion force | Electric vehicles, industrial machinery, aerospace | Pros: Excellent for high power; Cons: Higher production costs, bulkier design. |
| Screw Terminations | Direct metal-to-metal contact, robust construction | Industrial equipment, automotive, telecommunications | Pros: Highly reliable; Cons: Slower installation process. |
| Circular Connectors | Multi-pin, versatile for power and signal, rugged design | Military, aerospace, industrial automation | Pros: Durable, suitable for harsh environments; Cons: Can be expensive. |
| D-sub Connectors | Polarized design, sturdy construction, standardized pin configurations | Computers, telecommunications, industrial systems | Pros: Widely used, reliable; Cons: Limited current capacity. |
Pogo Pins
Pogo pins are spring-loaded connectors that offer flexibility and reliable electrical connections, particularly in applications requiring frequent engagement and disengagement. Their compact design makes them suitable for consumer electronics, automotive diagnostics, and portable medical devices. When considering B2B purchasing, buyers should evaluate the application’s power requirements and the need for temporary connections, as pogo pins are typically limited to lower power uses.
Crown Spring Connectors
Crown spring connectors are engineered for high-current applications, featuring multiple contact points that enhance electrical connectivity. They are ideal for electric vehicles and industrial machinery where efficient power delivery is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the complexity and cost of manufacturing these connectors, along with their space requirements in design layouts. Their advantages in high-power scenarios must be weighed against potential higher production costs.
Screw Terminations
Screw terminations provide a robust method for securing electrical connections through direct metal-to-metal contact. This design ensures high reliability, making them suitable for industrial equipment and automotive applications. Buyers should note that while screw terminations enhance connection stability, they may slow down the installation process. Evaluating the balance between installation speed and connection reliability is essential for B2B purchasing decisions.
Circular Connectors
Circular connectors are versatile, multi-pin connectors designed for robust signal and power transmission, often used in military and aerospace applications. Their rugged design allows them to withstand harsh environmental conditions. B2B buyers should consider the durability and reliability of circular connectors in demanding settings, although their cost may be higher than standard connectors. Understanding the specific application requirements can help buyers choose the right connector type.
D-sub Connectors
D-sub connectors are characterized by their polarized design and sturdy construction, making them a popular choice in telecommunications and industrial systems. Their standardization simplifies integration into various devices. B2B buyers should assess the current capacity and specific application needs, as D-sub connectors may not support high-power applications effectively. Their widespread use can be an advantage for compatibility across different systems, but buyers should remain aware of their limitations.
Related Video: Types of Wire Connectors and Wire Terminals | The Home Depot
Key Industrial Applications of types of electrical connectors
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of electrical connectors | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Use in vehicle diagnostic systems and infotainment units | Enhances reliability in high-vibration environments | Ensure connectors meet automotive standards and environmental ratings |
| Industrial Machinery | Heavy-duty power connections in manufacturing equipment | Supports high current capacity, reducing downtime | Look for durability and resistance to harsh conditions |
| Consumer Electronics | Connections in smartphones and wearables | Facilitates compact designs while ensuring reliability | Prioritize miniaturization and ease of assembly |
| Renewable Energy | Connectors in solar panel systems | Increases efficiency and safety in energy transfer | Verify compatibility with specific energy systems and standards |
| Medical Devices | Pogo pins in diagnostic and wearable health monitors | Ensures reliable data transmission and ease of connection | Focus on biocompatibility and regulatory compliance |
Automotive Applications
In the automotive sector, electrical connectors are vital for vehicle diagnostic systems and infotainment units. These connectors must withstand high levels of vibration and temperature fluctuations common in vehicles. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like the UAE and Egypt, sourcing connectors that meet stringent automotive standards (such as ISO and SAE) is crucial. Ensuring that these connectors provide robust performance can significantly enhance vehicle reliability and reduce maintenance costs.
Industrial Machinery Applications
Heavy-duty electrical connectors are essential in industrial machinery for applications requiring high power delivery. These connectors facilitate the connection of motors, sensors, and control systems, ensuring seamless operation of manufacturing equipment. Buyers in Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing connectors that are designed for durability and can withstand harsh industrial environments. Factors such as resistance to moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures are critical for minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Consumer Electronics Applications
In consumer electronics, types of electrical connectors play a pivotal role in smartphones, wearables, and other compact devices. These connectors must be designed for miniaturization while maintaining reliability to support frequent connections and disconnections. B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East should seek connectors that not only fit compact design requirements but also comply with international safety and performance standards. This ensures that the final products are both functional and market-ready.
Renewable Energy Applications
Electrical connectors are increasingly used in renewable energy systems, particularly in solar panel installations. They are essential for connecting solar panels to inverters and batteries, where efficiency and safety are paramount. International buyers must consider sourcing connectors that are compatible with various solar technologies and meet relevant safety standards. Ensuring that connectors can handle high currents and are resistant to environmental factors will enhance the overall performance of renewable energy systems.
Medical Device Applications
Pogo pins are widely used in portable medical devices, such as diagnostic tools and wearable health monitors. They provide reliable connections that are crucial for accurate data transmission in critical health applications. Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should focus on sourcing connectors that are biocompatible and meet regulatory compliance for medical devices. This ensures not only the functionality of the devices but also the safety of the end-users.
Related Video: Types of electrical wire connectors. Explained
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of electrical connectors
When selecting materials for electrical connectors, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in electrical connectors: copper, aluminum, plastic, and stainless steel. Each material has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and ductility. It typically operates well in a temperature range from -200°C to 200°C and has a high resistance to corrosion, especially when coated.
Pros & Cons: Copper connectors are highly durable and provide reliable connections, making them ideal for high-performance applications. However, they can be more expensive than alternatives and may require additional coatings to prevent oxidation, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Copper is particularly suitable for applications involving high-frequency signals and power transmission, such as in telecommunications and automotive industries. Its compatibility with various media types, including water and oils, enhances its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B187 for copper products. Additionally, the availability of copper may vary based on local sourcing capabilities, impacting cost and logistics.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good electrical conductivity (though not as high as copper), and offers excellent corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. It operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -50°C to 150°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum connectors is their low weight, making them suitable for portable applications. However, they are less conductive than copper, which may necessitate larger connector sizes to achieve the same performance, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum connectors are commonly used in aerospace and automotive applications where weight is a critical factor. They are also effective in outdoor applications due to their resistance to environmental factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as DIN 17615 for aluminum products, particularly in Europe. The cost-effectiveness of aluminum can be appealing in regions with high copper prices, but sourcing quality aluminum may be a challenge in some markets.
Plastic
Key Properties: Plastics used in connectors, such as polyamide (nylon) and polycarbonate, offer good insulation properties, are lightweight, and can withstand temperatures between -40°C and 120°C. They are also resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: Plastic connectors are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for complex designs. However, they are less durable than metal connectors and may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic connectors are widely used in consumer electronics and low-power applications, where insulation is more critical than conductivity. They are ideal for environments that require lightweight and corrosion-resistant solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as UL 94 for flammability is crucial. In regions like South America and Africa, where environmental conditions can be harsh, selecting high-quality plastics that meet local regulations is essential.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel connectors offer excellent mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and can operate in extreme temperatures ranging from -200°C to 800°C. They are often used in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The durability and strength of stainless steel make it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, the higher cost and weight compared to other materials can be a limiting factor, especially in applications where weight is a concern.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel connectors are commonly found in industrial machinery, oil and gas, and aerospace applications, where reliability in extreme conditions is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM A276 for stainless steel products. In regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe, ensuring sustainability in sourcing and manufacturing is increasingly important.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of electrical connectors | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Telecommunications, automotive | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost, oxidation risk | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight | Lower conductivity | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics, low-power applications | Cost-effective, lightweight | Less durable | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial machinery, oil and gas | High strength, corrosion resistant | Higher cost, heavier | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of electrical connectors
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for electrical connectors is vital for international B2B buyers. The intricacies of these processes not only affect the performance and reliability of connectors but also impact the overall supply chain and cost-effectiveness. This section will provide a detailed overview of the manufacturing stages, quality control measures, and the standards that ensure the integrity of these critical components.
Manufacturing Processes for Electrical Connectors
The manufacturing of electrical connectors involves several key stages, each critical to the final product’s quality and performance. The main stages include:
1. Material Preparation
The choice of materials is foundational in connector manufacturing. Common materials include copper alloys for electrical conductivity, various plastics for insulation, and metals like stainless steel for mechanical strength. During this stage, raw materials are sourced, inspected for quality, and prepared for further processing.
Key Techniques:
– Material Selection: Selecting the right materials based on application requirements (e.g., high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance).
– Material Testing: Conducting tests for mechanical properties and electrical conductivity to ensure suitability.
2. Forming
The forming process shapes the prepared materials into the desired connector components. This may involve various techniques, including:
- Stamping: Used for creating terminals and contact points from metal sheets.
- Injection Molding: Essential for producing housing and insulators from plastic.
- Machining: Employed for precision parts requiring tight tolerances.
Key Techniques:
– Progressive Die Stamping: Allows for high-volume production of complex shapes.
– CNC Machining: Ensures precision in the fabrication of connectors.
3. Assembly
In the assembly phase, individual components are put together to form the complete connector. This stage may involve:
- Soldering or Crimping: Connecting wires to terminals.
- Mechanical Assembly: Fastening components together, often using screws or clips.
Key Techniques:
– Automated Assembly: Utilizing robotics for consistent and efficient assembly processes.
– Manual Assembly: Employed for complex connectors that require a high degree of skill.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the connector’s performance and aesthetics. This includes surface treatments such as plating (e.g., gold or tin) to improve conductivity and prevent corrosion.
Key Techniques:
– Electroplating: Provides a conductive layer for enhanced electrical performance.
– Coating: Adding protective layers to improve durability against environmental factors.
Quality Assurance (QA) in Connector Manufacturing
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that connectors meet industry standards and customer expectations. Key elements of the QA process include:
International Standards
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. For electrical connectors, specific industry standards may also apply, including:
- CE Marking: Ensures compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Applicable in industries such as oil and gas, focusing on safety and reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials for compliance with specifications before processing.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors production processes to ensure ongoing compliance with quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts thorough testing of finished products before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods vary based on the connector type and application but typically include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying conductivity, insulation resistance, and dielectric strength.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing durability through vibration, thermal cycling, and pull-out tests.
- Environmental Testing: Simulating conditions such as humidity, temperature extremes, and corrosion.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
- Audits: Conduct on-site audits of supplier facilities to review their manufacturing processes and quality systems.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports, including testing results and compliance certificates, to assess the supplier’s adherence to standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the quality of the products before shipment.
Considerations for International Buyers
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital:
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of varying standards and practices in different regions. For example, some suppliers may prioritize cost over quality, impacting reliability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with local and international regulations, particularly regarding environmental and safety standards.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Seek suppliers that provide clear visibility into their manufacturing processes, as this can help mitigate risks associated with quality issues.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electrical connectors. This knowledge not only helps in selecting reliable suppliers but also ensures that the connectors meet the specific requirements of their applications, ultimately leading to better performance and customer satisfaction.
Related Video: How Electric Wires are Made in Factory with Amazing Process | Electric Cables Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of electrical connectors Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of electrical connectors is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis outlines the key cost components, price influencers, and essential tips for buyers navigating this market.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost of electrical connectors. Common materials include metals for terminals (like copper and aluminum) and plastics for housings. High-quality materials can enhance durability but come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can sometimes compromise quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and general operational expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overhead, positively affecting pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom connectors require specialized tooling, which can be a significant upfront cost. This is especially relevant for buyers needing unique specifications or designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent QC processes ensure product reliability and adherence to international standards (such as DIN EN 61076). While this adds to the manufacturing cost, it ultimately safeguards against failures that could lead to higher costs in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are crucial, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and import duties can vary widely, impacting the final cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and risks. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating MOQs can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized connectors tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects durability but also the price. Advanced materials that enhance performance can lead to increased costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Connectors that meet higher quality standards or possess specific certifications (e.g., RoHS, ISO) may command higher prices. However, these certifications often justify the cost through enhanced reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation and experience can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly impact the final cost. Understanding terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for budgeting and cost management.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to discuss pricing, especially for larger orders. Leverage your purchasing power to obtain better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential failure costs. A slightly more expensive connector that offers higher reliability may save money over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and local market conditions that may affect pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers can also provide insights into cost-saving opportunities.
-
Quality vs. Cost: Prioritize quality, especially in critical applications. A lower-priced connector might not provide the necessary reliability, leading to higher long-term costs.
Disclaimer
Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, materials availability, and supplier policies. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential types of electrical connectors Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘types of electrical connectors’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of electrical connectors
Key Technical Properties of Electrical Connectors
When selecting electrical connectors, understanding their technical properties is essential for ensuring reliability and performance in various applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used for connectors significantly impacts their conductivity, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Common materials include copper, which offers excellent conductivity, and various grades of plastics, which provide insulation. Selecting the right material is vital for achieving optimal performance and longevity, especially in harsh environments like industrial or outdoor settings. -
Current Rating
This specification indicates the maximum current a connector can handle without overheating or failing. It’s crucial for B2B buyers to match the current rating with their application’s requirements to prevent electrical failures. For instance, connectors used in electric vehicle charging must support high current ratings to facilitate quick charging without compromising safety. -
Temperature Range
Connectors are rated for specific operating temperature ranges. Understanding this property is critical, especially in regions with extreme climates. If a connector is exposed to temperatures outside its specified range, it can lead to material degradation, poor performance, or even failure. Selecting a connector with an appropriate temperature range for the intended environment ensures reliability. -
Mechanical Tolerance
This refers to the acceptable limits of variation in the dimensions of the connector components. High tolerance levels ensure a snug fit, reducing the risk of intermittent connections. For applications requiring frequent connections and disconnections, such as in automotive and consumer electronics, precise mechanical tolerances enhance durability and functionality. -
IP Rating (Ingress Protection)
The IP rating indicates the level of protection a connector has against dust and moisture. A higher IP rating means better resistance to environmental conditions. B2B buyers in industries like telecommunications or outdoor equipment should prioritize connectors with suitable IP ratings to ensure longevity and reliability in challenging conditions. -
Termination Type
This specification defines how wires are connected to the connector. Common types include solder, crimp, and screw terminations. Each method has its advantages and drawbacks regarding installation ease, reliability, and cost. Understanding the best termination type for your application can lead to improved assembly efficiency and reduced maintenance issues.
Common Trade Terminology
Navigating the landscape of electrical connectors also involves understanding industry-specific terminology. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electrical connectors, working with an OEM ensures that you receive components that meet industry standards and specifications tailored for specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for businesses in Africa and South America where capital investment can be a concern. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing information and terms for specific products. This is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing B2B buyers to compare options and negotiate pricing effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, as it helps mitigate risks and ensures compliance with trade regulations. -
Lead Time
This term indicates the amount of time between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is vital for supply chain management and inventory planning, especially in regions with varying logistical challenges. -
Certification Standards
These are industry standards that connectors must meet to ensure safety and performance, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. Knowing about certification standards helps buyers ensure compliance with regulations and enhances product reliability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electrical connectors, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and product performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the types of electrical connectors Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electrical connectors market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for advanced connectivity solutions in sectors such as telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics is a primary market driver. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of the ongoing digital transformation, which necessitates reliable and efficient electrical connectors. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy solutions is also pushing the demand for high-performance connectors, particularly in charging systems and energy distribution networks.
Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0, are shaping sourcing trends in this sector. B2B buyers should look for connectors that support enhanced data transfer and connectivity, such as circular and D-sub connectors, which are increasingly being utilized in smart devices and industrial automation. Furthermore, the shift towards miniaturization is compelling manufacturers to innovate with smaller, more efficient connector designs, such as pogo pins, which can accommodate the need for compactness in electronic applications.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions. Buyers must be prepared to navigate these challenges by diversifying their supplier base and considering local manufacturing options. In regions like the Middle East and Africa, where infrastructure development is booming, sourcing connectors that meet international standards can provide a competitive edge in terms of quality and reliability.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming increasingly crucial in the electrical connectors sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in connectors is under scrutiny, with a growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and waste. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled materials and reducing energy consumption during production.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers must ensure their suppliers adhere to labor standards and environmental regulations, particularly in regions where oversight may be lax. This not only enhances brand reputation but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliance are vital indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In addition to ethical sourcing, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of electrical connectors is gaining traction. Materials that are recyclable or biodegradable can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of connectors. Buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers who invest in research and development to create innovative, sustainable products that meet the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electrical connectors can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the development of basic pin connectors for telecommunication applications. As technology advanced, so did the complexity and functionality of connectors, leading to the introduction of various types tailored for specific applications, such as audio, automotive, and industrial uses. The 1970s and 1980s marked a significant turning point with the rise of printed circuit boards (PCBs), necessitating more sophisticated connector designs like card edge and D-sub connectors. Today, the focus is on miniaturization, high-speed data transfer, and sustainability, reflecting the dynamic needs of modern industries. B2B buyers must remain cognizant of these historical trends to make informed sourcing decisions that align with current technological advancements.
Related Video: Chapter 9: International Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of electrical connectors
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of electrical connectors?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 or specific industry certifications like UL or CE. Request references or case studies to evaluate their previous work, particularly with clients in your region. Conduct background checks on their financial stability and production capacity. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible, or using third-party services for supplier audits to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing connectors?
Customization options can include specific pin configurations, housing materials, and connector sizes tailored to your application needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Ensure they can accommodate design changes without significant delays. Also, inquire about their experience with similar custom projects to gauge their expertise. Understanding the extent of customization they offer can help you find a supplier that aligns with your unique needs. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electrical connectors?
MOQs for electrical connectors can vary widely depending on the type and customization level. Standard connectors might have MOQs as low as 100 units, while specialized or custom connectors could require orders of 1,000 or more. Lead times also depend on factors such as customization and supplier location, ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. Always clarify these details upfront to align your procurement strategy with your project timelines and budget constraints. -
How should I approach payment terms when sourcing connectors internationally?
When dealing with international suppliers, negotiate payment terms that minimize risk. Common practices include a 30% deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after quality inspection. Consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit (LC) or escrow services to protect both parties. Be aware of any currency exchange risks and consider including clauses that address potential price fluctuations in your contracts to safeguard your interests. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for?
Ensure that your suppliers adhere to rigorous quality assurance protocols. Ask for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. Additionally, inquire about specific testing standards relevant to electrical connectors, such as IPC-A-610 for electronic assemblies. Request documentation of quality control processes and any third-party testing results to confirm that the connectors meet industry specifications and your quality expectations. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping effectively when sourcing connectors?
To manage logistics effectively, choose suppliers with experience in international shipping and a solid understanding of import/export regulations in your country. Discuss shipping options, including air versus sea freight, to balance cost and delivery speed. Utilize freight forwarders who can handle customs clearance and documentation. Ensure you have clarity on shipping costs, delivery timelines, and any potential tariffs or duties that may apply to your order to avoid unexpected expenses. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers?
To resolve disputes with suppliers, start by documenting all communications and agreements in writing. Open a dialogue to address the issue directly and seek an amicable resolution. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration. Having a clear understanding of legal recourse options in both your jurisdiction and that of the supplier can also aid in resolving conflicts effectively and efficiently.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What are the best practices for ongoing supplier relationship management?
Maintain strong supplier relationships by establishing regular communication and feedback mechanisms. Schedule periodic reviews to assess performance, address issues, and discuss future needs. Sharing your strategic goals can help suppliers align their offerings with your business objectives. Additionally, consider fostering collaboration on product development or innovation projects to strengthen the partnership. Recognizing and rewarding good performance can also enhance loyalty and commitment from your suppliers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of electrical connectors
Understanding the diverse landscape of electrical connectors is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Strategic sourcing not only enhances procurement efficiency but also ensures that businesses leverage the most suitable connector types for their specific applications. Key takeaways include recognizing the importance of connector design—such as the adaptability of pogo pins and the robustness of crown spring connectors—to meet the demands of various industries, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery.
Buyers should prioritize connectors that align with their operational needs, considering factors such as current capacity, environmental resilience, and ease of integration. Engaging with reputable suppliers who adhere to international manufacturing standards will guarantee quality and reliability in the connections that power your devices and systems.
As the market evolves, staying abreast of innovations in connector technology will be vital for maintaining a competitive edge. Investing in strategic sourcing now will prepare your business to capitalize on future trends, ensuring you remain at the forefront of connectivity solutions. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your supply chain and drive success in your projects by making informed connector choices today.