Master the Types of Power Cords for Computers to Optimize
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of power cords for computers
In today’s interconnected world, the choice of power cords for computers is not merely a technical detail; it is a critical factor that can significantly impact operational efficiency and safety in various business environments. As international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the diverse types of power cords available is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. This guide serves as your comprehensive resource, covering everything from the different types and materials used in power cords to manufacturing standards, quality control measures, and supplier options.
The global market for power cords is characterized by a myriad of standards, plug types, and voltage requirements, making it imperative for businesses to stay informed. This guide will delve into key topics, including the various power cord types—such as polarized, non-polarized, and grounded options—along with insights into the latest trends in materials and technology. You’ll also find valuable information on pricing structures, market dynamics, and frequently asked questions that can help clarify common concerns.
By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing power cords that meet both your operational needs and compliance standards. This guide empowers you to select reliable products that enhance safety, efficiency, and compatibility, ultimately driving your business success in a global marketplace.
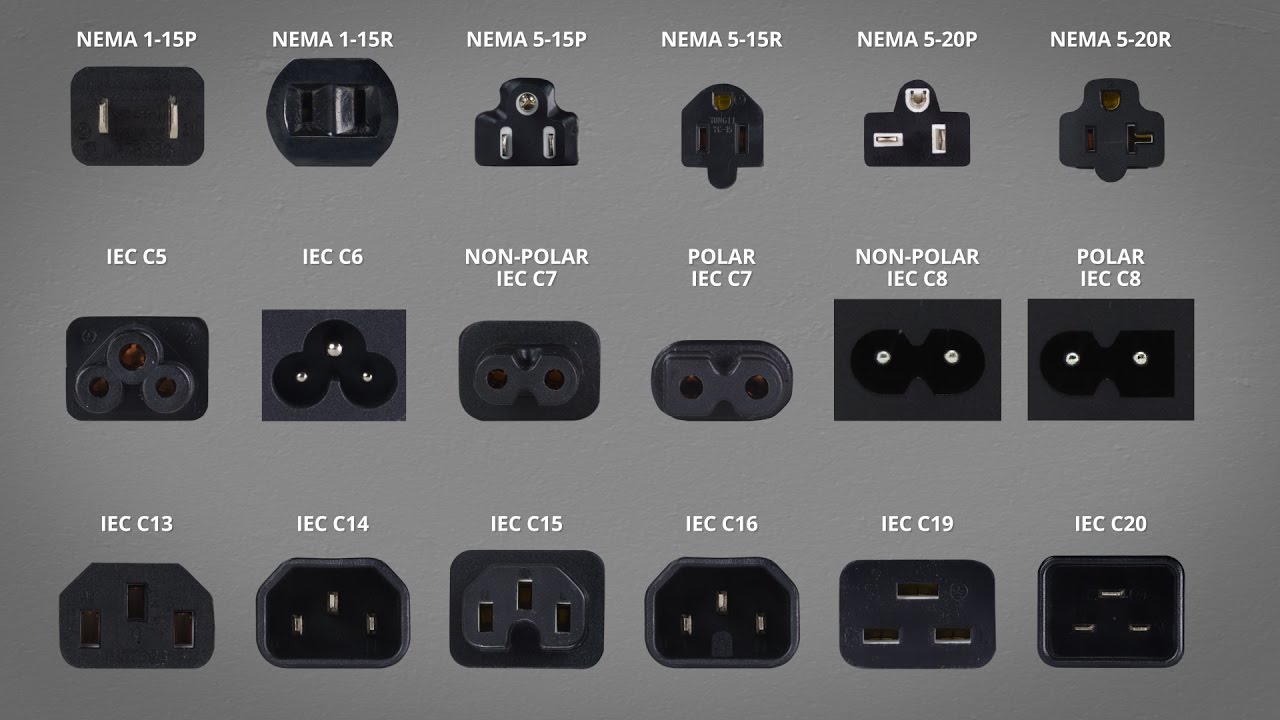
Understanding types of power cords for computers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 5-15 | Three-prong grounded design; supports 15 Amps | PCs, monitors, printers | Pros: Widely used in North America; safe. Cons: Limited to 120V systems. |
| IEC C13 | Standardized for computers; fits into IEC C14 socket | Laptops, servers, desktop computers | Pros: Universally accepted; flexible length options. Cons: Not suitable for high-power devices. |
| Type G | Square-shaped, three rectangular prongs | UK-based devices, IT equipment | Pros: Excellent grounding; robust. Cons: Bulkier design may not fit all sockets. |
| Type C | Two round prongs; often used in Europe and South America | Charging laptops, smaller electronics | Pros: Lightweight; versatile. Cons: Not grounded, less safe for high-power devices. |
| USB-C Power Delivery | Reversible connector; supports high power delivery | Modern laptops, smartphones, and tablets | Pros: Fast charging; universal compatibility. Cons: Requires compatible devices. |
NEMA 5-15
The NEMA 5-15 power cord is a staple in North America, featuring a three-prong grounded design capable of supporting devices up to 15 Amps. This cord is commonly used for desktop computers, monitors, and printers. When considering procurement, buyers should note its wide availability and compatibility with most North American outlets, making it a reliable choice. However, it is limited to 120V systems, which may not be suitable for high-power applications.
IEC C13
The IEC C13 power cable is widely recognized for its use in computers and server applications. It connects to an IEC C14 socket, making it a standard choice for laptops and desktop computers. Buyers appreciate its universal acceptance and the variety of lengths available, allowing for flexibility in workspace setups. However, it is important to ensure that this cable is not used for high-power devices, as it is rated for lower amperages.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Type G
Type G power cords are characterized by their square shape and three rectangular prongs, providing excellent grounding. This type is predominantly used in the UK and is common for IT equipment and other electronic devices. Buyers benefit from its robust design, which enhances safety, especially in high-power applications. However, its bulkier form may pose compatibility issues with certain sockets.
Type C
Type C power cords feature two round prongs and are prevalent in Europe and South America. They are often utilized for charging laptops and smaller electronics. The lightweight design makes it a versatile option for various devices. However, its lack of grounding may present safety concerns for high-power applications, which buyers should consider when making purchasing decisions.
USB-C Power Delivery
USB-C power delivery is an innovative and increasingly popular option for modern electronics, including laptops and smartphones. This reversible connector supports high power delivery, enabling faster charging and universal compatibility across devices. For B2B buyers, this presents an opportunity to streamline charging solutions. However, it is essential to ensure that devices are compatible with USB-C power delivery standards to avoid functionality issues.
Related Video: PC Power Supply Cables Explained
Key Industrial Applications of types of power cords for computers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of power cords for computers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information Technology | Data Centers and Server Farms | Ensures reliable power supply for continuous operation of servers | Compliance with local and international safety standards; cable length and gauge must match equipment needs. |
| Manufacturing | Computer-Controlled Machinery | Powers CNC machines and automation systems | Durability under industrial conditions; resistance to heat and abrasion. |
| Education | Computer Labs and Classrooms | Supports a variety of devices for teaching and learning | Compatibility with various plug types; adherence to safety regulations for student environments. |
| Healthcare | Medical Equipment and Diagnostic Machines | Provides stable power for sensitive medical devices | Must meet stringent health and safety certifications; ensure compatibility with hospital infrastructure. |
| Retail | Point of Sale (POS) Systems | Powers cash registers, card readers, and digital displays | Flexibility for various power configurations; robust design for high usage environments. |
Industry Applications of Power Cords for Computers
Information Technology: In data centers and server farms, types of power cords for computers play a critical role in ensuring that servers receive a consistent and reliable power supply. This reliability is vital for continuous operation, minimizing downtime, and protecting sensitive data. International buyers must consider local electrical standards and ensure that the cords used are compliant with both local and international safety standards, while also matching the specific voltage and current requirements of their equipment.
Manufacturing: In the manufacturing sector, power cords are essential for powering computer-controlled machinery, such as CNC machines and automated assembly lines. These environments often expose cables to harsh conditions, requiring cords that are not only reliable but also resistant to heat, abrasion, and other industrial hazards. Buyers should prioritize sourcing durable power cords that can withstand the rigors of industrial use while ensuring compatibility with the machinery in their specific operational context.
Education: Computer labs and classrooms rely heavily on various devices, from desktop computers to projectors. Power cords must be versatile enough to accommodate different plug types and voltages while adhering to safety regulations to protect students and faculty. International buyers in the education sector should focus on sourcing power cords that meet local electrical standards and provide adequate length and flexibility for classroom setups.
Healthcare: In healthcare settings, power cords are vital for powering medical equipment, including diagnostic machines and life-support systems. The reliability of these cords directly impacts patient safety and care quality. Buyers must ensure that the power cords meet stringent health and safety certifications, are compatible with hospital infrastructure, and can support the specific power requirements of sensitive medical devices.
Retail: In retail environments, point of sale (POS) systems require reliable power supply for cash registers, card readers, and digital displays. The types of power cords used must be flexible enough to accommodate various power configurations and robust enough to endure high-usage conditions. Sourcing considerations should include compatibility with existing retail setups and the ability to handle the electrical load of multiple devices operating simultaneously.
Related Video: Industrial Power Cables, LV cables, LT cables, Power cable Types and Markings, Cable classification
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of power cords for computers
When selecting power cords for computers, the choice of materials significantly influences performance, safety, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in power cords, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties:
PVC is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals. It can typically handle temperatures up to 70°C (158°F) and offers good flexibility, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
PVC is cost-effective and widely available, which makes it a popular choice for manufacturers. However, it has limitations in terms of temperature resistance and can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light. Additionally, PVC is less environmentally friendly compared to other materials.
Impact on Application:
PVC is commonly used in standard power cords for desktop computers and peripherals. Its compatibility with various devices makes it a versatile option, though it may not be suitable for high-performance or outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM in the U.S. and DIN in Europe. There is a growing preference for environmentally friendly alternatives, which may influence purchasing decisions.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
Key Properties:
TPE offers excellent flexibility and elasticity, with a temperature range of -40°C to 90°C (-40°F to 194°F). It also has good resistance to abrasion, UV light, and chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of TPE is its durability and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent movement. However, TPE can be more expensive than PVC, which may impact budget considerations for large orders.
Impact on Application:
TPE is suitable for power cords that require high flexibility, such as those used in mobile devices and outdoor applications. Its superior performance in adverse conditions makes it a preferred choice for high-end electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
TPE’s compliance with international safety standards is crucial, especially in markets with strict regulations like Europe. Buyers should verify certifications such as UL or CE to ensure product safety and performance.
Silicone
Key Properties:
Silicone is known for its exceptional temperature resistance, withstanding temperatures from -60°C to 200°C (-76°F to 392°F). It is also highly resistant to UV light, ozone, and various chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of silicone is its high-temperature tolerance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications in extreme conditions. However, it is generally more expensive than PVC and TPE, which could affect overall project budgets.
Impact on Application:
Silicone is often used in power cords for high-performance computing equipment and industrial applications where durability and heat resistance are critical. Its properties make it suitable for environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the higher cost of silicone when planning budgets. Compliance with international standards like IEC is essential to ensure the safety and reliability of silicone-based power cords.
Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber is highly flexible and offers excellent electrical insulation. It can endure a wide temperature range from -40°C to 90°C (-40°F to 194°F) and provides good resistance to wear and tear.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber power cords are durable and can withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for industrial applications. However, they can be heavier and bulkier compared to other materials, which may impact portability.
Impact on Application:
Rubber is commonly used in power cords for heavy-duty applications, such as in construction sites or industrial machinery. Its durability makes it ideal for environments where cords are subject to physical stress.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that rubber cords meet local safety standards. The weight and bulkiness may also be a consideration for shipping and handling in international transactions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of power cords for computers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Standard desktop power cords | Cost-effective and widely available | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| TPE | Mobile devices and outdoor applications | Excellent flexibility and durability | Higher cost than PVC | Medium |
| Silicone | High-performance computing and industrial applications | Exceptional temperature resistance | Generally more expensive | High |
| Rubber | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Durable and wear-resistant | Heavier and bulkier | Medium |
This guide provides a strategic overview for international B2B buyers, aiding in informed decision-making regarding the selection of power cord materials based on specific application needs and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of power cords for computers
The manufacturing of power cords for computers involves a series of well-defined processes and stringent quality assurance measures to ensure that the final product meets safety standards and performs reliably in various environments. For B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Power cords typically consist of:
- Conductors: Usually copper or aluminum, these materials must meet specific conductivity standards.
- Insulation: PVC, TPE, or rubber are commonly used for insulation, chosen for their durability and thermal resistance.
- Connectors and Plugs: Various types are manufactured according to regional standards (e.g., NEMA in the U.S., Type G in the UK).
The quality of these materials is critical, as they directly affect the performance and safety of the power cords. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers source materials from reputable manufacturers who comply with international standards.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into usable components. Key techniques include:
- Wire Drawing: Conductors are drawn to the required diameter.
- Extrusion: Insulation materials are extruded over the conductors to form a protective layer.
- Molding: Connectors and plugs are molded from thermoplastics, ensuring they fit securely and are durable.
Each process must be closely monitored to ensure that dimensions and properties meet specified standards. Advanced machinery is often employed to maintain precision.
3. Assembly
Once the components are ready, they undergo assembly. This involves:
- Connecting Conductors to Plugs: Skilled technicians or automated machines securely attach the wires to the connectors.
- Strain Relief Application: This step helps prevent the cable from breaking at the point of connection, enhancing durability.
Quality during assembly is paramount, as improper connections can lead to electrical failures. Buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques used by suppliers, as these can vary widely.
4. Finishing
The final stage includes several processes to ensure the power cords are ready for market:
- Testing for Electrical Integrity: Each cord is tested for continuity and insulation resistance.
- Labeling and Packaging: Proper labeling is crucial for compliance with regional standards, and packaging should protect the cords during shipping.
Quality Assurance
International Standards
Quality assurance in power cord manufacturing is guided by several international and industry-specific standards. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures a quality management system is in place.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- UL and CSA Standards: Commonly used in North America to certify safety.
B2B buyers should verify that suppliers have certifications for the relevant standards in their target markets.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is integrated into every stage of the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival at the manufacturing facility.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections occur throughout the production process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Completed products are rigorously tested before shipment to ensure they meet all specifications.
Buyers should request information about the QC process from suppliers, including details on how often inspections occur and what criteria are used.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are commonly employed to ensure the quality and safety of power cords:
- Voltage and Current Testing: Ensures the cord can handle its rated load.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the strength and flexibility of the cord.
- Thermal Testing: Checks the cord’s performance under high-temperature conditions.
These tests are essential for ensuring that power cords perform safely and effectively in various environments.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits can help assess compliance with quality standards. Buyers may consider engaging third-party auditors for impartial evaluations.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results and certifications.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide additional assurance regarding product quality before shipment.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is essential. Here are some considerations:
- Regulatory Compliance: Each region has specific regulations regarding electrical products. Ensure that suppliers are compliant with local laws and standards.
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality management. Establish clear communication with suppliers to understand their processes and expectations.
- Logistics and Shipping: Quality assurance doesn’t end at manufacturing; consider the conditions under which products are shipped. Poor handling during transport can compromise product quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for power cords, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish partnerships with reliable suppliers. This knowledge is essential for ensuring that the products meet safety standards and perform as expected in diverse applications.
Related Video: Power cord manufacturing machine 8882378542(8)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of power cords for computers Sourcing
When considering the sourcing of power cords for computers, it’s essential to understand the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics that influence procurement decisions. This analysis will help international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components of Power Cords
-
Materials: The primary materials used in power cords include copper for conductors, plastic for insulation, and metal for connectors. The quality and sourcing of these materials significantly impact the overall cost. Buyers should assess whether suppliers are using high-grade materials that comply with international safety standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the total cost. Regions with higher labor costs may produce higher-quality products but at a greater expense. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can reduce expenses but may compromise quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the operational costs associated with running a manufacturing facility, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. A more efficient manufacturing process can lead to lower overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and dies for production can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized power cords. This cost is often amortized over the production volume, making it crucial for buyers to consider their order quantities.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict quality control measures ensures that the products meet safety and performance standards. While this adds to the cost, it is essential for preventing failures that could lead to liability issues.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs play a significant role, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can greatly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the margin expectations in different regions can aid in negotiation.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders. Understanding Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom power cords designed to meet specific requirements can attract higher costs due to additional engineering and production time. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary.
-
Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials will affect pricing. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between cost and performance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products with recognized safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL) may command higher prices. However, these certifications can also mitigate risks and enhance product reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but provide better assurance of product performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs. This can significantly impact the overall cost of procurement.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. Leverage volume purchases and long-term relationships to secure better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential replacement costs over the product’s lifespan.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, local taxes, and tariffs that can affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local distributors may also provide cost advantages.
Disclaimer
Prices for power cords can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. This analysis serves as a guide; actual costs may differ based on specific requirements, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to determine the most accurate pricing for your needs.
Spotlight on Potential types of power cords for computers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘types of power cords for computers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of power cords for computers
Power cords for computers are critical components that require a comprehensive understanding of their technical properties and industry terminology. This knowledge is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Essential Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– The quality of materials used in power cords significantly impacts durability and safety. Common materials include copper for conductors, which offers excellent conductivity, and PVC or rubber for insulation, providing flexibility and protection against heat and abrasion. Selecting high-grade materials ensures longevity and compliance with safety standards. -
Voltage Rating
– This specification indicates the maximum voltage a power cord can handle without risk of failure. It’s crucial for buyers to match the voltage rating with their devices to avoid electrical hazards. For example, cords rated for 250V are common in Europe, while North American devices often use cords rated for 120V. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
– The current rating specifies the maximum amount of electric current a power cord can safely carry. Higher amperage ratings are necessary for devices with greater power demands, such as workstations or servers. Choosing the correct amperage rating is vital to prevent overheating and ensure operational efficiency. -
Length and Gauge
– The length of a power cord can affect performance, especially in terms of voltage drop over long distances. Additionally, the wire gauge determines the amount of current it can handle—lower gauge numbers indicate thicker wires capable of carrying more current. Buyers should consider both length and gauge based on their specific installation needs. -
Certification Standards
– Compliance with local and international safety standards, such as IEC or NEMA certifications, is essential. These certifications ensure that the power cords meet safety, performance, and environmental standards. B2B buyers should prioritize certified products to mitigate risks associated with electrical failures.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source reliable power cords that are compatible with specific devices, ensuring quality and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially when sourcing power cords from international suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific product or service. When looking for power cords, submitting an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive pricing and negotiate better terms with suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities when importing power cords.
-
ETL Certification
– This certification indicates that a product has been tested for safety and meets the standards set by the Electrical Testing Laboratories. For power cords, ETL certification is critical to ensure compliance with safety regulations, particularly in North America. -
Plug Type Standards
– Different regions utilize various plug types (e.g., Type A, Type B, Type C). Understanding these standards is vital for international buyers to ensure compatibility with local outlets and prevent operational disruptions.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power cords for computers, ensuring safety, compatibility, and efficiency in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the types of power cords for computers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The power cords market for computers is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for electronic devices, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is a significant driver. As businesses in these regions adopt digital technologies, the need for reliable and compliant power solutions has surged. Moreover, the ongoing transition to USB-C standards is influencing the types of power cords being produced and sourced, as manufacturers strive to meet the evolving needs of modern electronics.
In Europe, heightened regulatory standards regarding energy efficiency and safety are reshaping sourcing trends. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing power cords that comply with IEC and NEMA standards, ensuring compatibility and safety across diverse markets. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has facilitated a more extensive supply chain network, allowing buyers to source power cords from various global manufacturers. This trend is particularly beneficial for businesses seeking competitive pricing and diverse product options.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a core consideration for international buyers. There is a growing expectation for manufacturers to adopt environmentally friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing carbon footprints in production processes. As buyers become more conscientious about their supply chains, they are likely to favor suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability in the power cord sector is not merely a trend but a necessity for responsible B2B practices. The environmental impact of power cords is significant, given the materials used in production, such as plastics and metals, which can contribute to pollution and waste. Therefore, international buyers must prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled materials and implementing waste reduction strategies in their manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical. Buyers should consider the entire supply chain, ensuring that materials are sourced from suppliers who practice fair labor and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) are vital indicators of compliance with environmental standards. Additionally, seeking manufacturers with ISO certifications can provide assurance regarding their commitment to quality and sustainability.
By focusing on suppliers that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. This not only contributes to a healthier planet but also positions businesses favorably in a competitive marketplace.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brief Evolution/History
The history of power cords has evolved significantly from the early days of electrical engineering. Initially, power cords were simple two-pronged designs primarily used for basic appliances. With advancements in technology and a greater understanding of electrical safety, the introduction of grounded three-prong cords became standard, especially in regions like Europe and the United States.
As technology progressed, so did the designs of power cords, adapting to the needs of various devices. The advent of personal computers in the late 20th century necessitated specialized power cords, leading to the diversification of types, including IEC connectors and the now-emerging USB-C standard. This evolution reflects the broader trends in the electronics industry, where functionality, safety, and sustainability have become paramount in product design and sourcing strategies.
Related Video: Understanding the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of power cords for computers
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for power cords?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation, certifications, and experience in producing power cords compliant with international standards. Check for ISO certifications and adherence to safety standards like IEC or NEMA. Additionally, assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and previous client testimonials. Engaging with suppliers who have experience in your target market—be it Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—can also enhance reliability and communication. -
Can power cords be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for power cords. This can include variations in length, gauge, plug type, and additional features such as reinforced connectors or specific insulation materials. When seeking customization, clearly communicate your specifications and ensure the supplier can meet your technical requirements. Customization may affect pricing and lead times, so it’s essential to discuss these aspects upfront. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times?
MOQs for power cords can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of customization required. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times can also differ, typically ranging from 2 to 8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity. For urgent needs, inquire about expedited production options, but be prepared for potential cost increases. -
How can I ensure the quality and safety of the power cords I purchase?
To ensure quality, request documentation of compliance with relevant safety standards and certifications from the supplier. Third-party testing and inspection reports can provide additional assurance. Consider conducting your quality assurance checks upon receipt of goods. Establishing a clear quality agreement with the supplier, specifying acceptable tolerances and testing requirements, can help mitigate risks. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international orders?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include advance payments, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. For larger orders, negotiate terms that ensure mutual protection, such as partial payments tied to production milestones. Ensure that the payment method is secure and consider using an escrow service for high-value transactions to mitigate the risk of disputes. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing power cords?
When importing power cords, consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties in your country. It’s essential to work with a logistics partner experienced in handling electrical components to ensure compliance with local regulations. Additionally, factor in lead times for shipping and customs clearance, as these can impact your overall timeline and inventory management. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To manage disputes, maintain open lines of communication with your supplier to address issues promptly. Establish a clear contract outlining terms, conditions, and dispute resolution processes. If a dispute arises, try to resolve it amicably through negotiation first. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods before escalating to legal action, which can be costly and time-consuming. -
What certifications should I look for in power cords?
Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international safety standards, such as IEC, UL, or CE marks. These certifications indicate that the power cords have undergone rigorous testing for safety and performance. Additionally, inquire about any region-specific certifications that may apply, especially if you are sourcing from or selling to regions with strict regulatory requirements, such as Europe or the Middle East.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of power cords for computers
The global landscape of power cords for computers is diverse and complex, reflecting the varying standards and requirements across regions. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these differences is crucial. The key takeaways include the necessity of choosing cables that match local power specifications, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and recognizing the importance of sourcing reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality, certified products.
Strategic sourcing is vital not only for cost efficiency but also for ensuring the longevity and safety of electronic devices. By investing in the right power cords, businesses can minimize downtime and reduce risks associated with electrical failures. It is essential for buyers to stay informed about emerging trends, such as the gradual shift towards USB-C and other standardized connectors that promise greater compatibility and efficiency.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers and distributors who understand the local market dynamics and can offer tailored solutions. By taking proactive steps in their sourcing strategy, businesses can secure a competitive edge in their operations. Engage with trusted suppliers today to ensure your power needs are met with reliability and compliance, paving the way for future growth and innovation.