Mastering Electrical Motor Sourcing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrical motor
Electric motors serve as the backbone of modern industry, powering a vast array of applications from manufacturing processes to agricultural innovations. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting the right electric motor is not merely a technical choice; it’s a strategic decision that directly influences productivity, efficiency, and operational reliability. In an increasingly interconnected global market, understanding the nuances of motor sourcing can be the difference between seamless operations and costly downtimes.
This comprehensive guide demystifies the complexities of electric motor procurement. It covers a wide range of topics, including various motor types and their applications, materials and manufacturing processes, and the essential quality control benchmarks that ensure long-lasting performance. Additionally, it provides a structured framework for selecting and qualifying suppliers, managing procurement costs, and mitigating risks associated with sourcing decisions.
With up-to-date market intelligence and answers to frequently asked questions, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the diverse regulatory landscapes and supply chain challenges they face. By equipping procurement leaders with actionable insights, this resource enhances the ability to make informed, value-driven decisions that build competitive advantage in both established and emerging markets.
Understanding electrical motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Induction Motor | Simple, robust design; operates on AC; squirrel cage or wound rotor types | Pumps, compressors, conveyors, fans | Reliable and widely available; less efficient at variable speeds |
| Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor | Electronic commutation; high efficiency; no brushes | Electric vehicles, HVAC, medical equipment | Long lifespan, compact; higher upfront cost, requires electronic control |
| Synchronous Motor | Rotor speed synchronized with supply frequency; precise speed regulation | Process plants, mills, power factor correction | High efficiency, precise speed; complex start-up, higher cost |
| Servo Motor | Precise position/speed control; closed-loop feedback | Robotics, CNC, high-precision automation | Exceptional accuracy; more expensive, complex commissioning |
| Gear Motor | Integrated gearbox with motor for torque and speed adaptation | Packaging, materials handling, agitators | Simplifies system design; gearbox wear, modest efficiency loss |
AC Induction Motor
AC induction motors are favored for their durability and versatility across various industrial applications. They operate on alternating current and are available in both squirrel cage and wound rotor designs. Ideal for environments with fluctuating voltage, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, buyers should ensure compatibility with local standards and assess the availability of spare parts. While they are cost-effective and straightforward to integrate, they may not perform efficiently in applications requiring variable speeds.
Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor
BLDC motors are increasingly popular due to their high efficiency and low maintenance requirements, as they utilize electronic commutation instead of brushes. This type of motor is compact and particularly well-suited for applications where space and energy savings are critical, such as in electric vehicles and HVAC systems. B2B buyers should consider the higher initial investment and ensure that local technicians are equipped to handle the electronic controls necessary for operation and maintenance.
Synchronous Motor
Synchronous motors excel in applications that require precise speed control and improved power factor, making them suitable for process plants and critical infrastructure in Europe and the Middle East. Their operation is synchronized with the supply frequency, ensuring a constant speed. However, the complexity of their start-up process and higher costs can be drawbacks. Buyers must evaluate the technical expertise required for installation and maintenance, alongside the potential long-term efficiency benefits.
Servo Motor
Servo motors are designed for applications that demand high precision in speed and position control, often utilized in robotics and CNC machinery. Their closed-loop feedback systems enable exceptional accuracy, making them indispensable in high-precision automation tasks. While they offer significant performance advantages, the complexity of commissioning and higher costs can deter some buyers. Organizations should weigh the benefits of precision against their budget and technical capabilities.
Gear Motor
Gear motors combine a motor with an integrated gearbox, providing a compact solution for applications requiring specific torque and speed adaptations. Commonly used in packaging and materials handling, these motors simplify system design and installation. However, potential buyers should consider the wear and tear on the gearbox, which can lead to efficiency losses over time. Evaluating the balance between design simplicity and long-term maintenance costs is crucial for effective procurement decisions.
Related Video: Electric Motor Types and Complete Overview
Key Industrial Applications of electrical motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electrical Motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhanced productivity and reduced labor costs | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and local voltage standards. |
| Agriculture | Water Pumping Systems | Improved irrigation efficiency and crop yield | Assess durability against environmental conditions; local service availability. |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling Equipment | Increased operational uptime and safety | Evaluate motor reliability under harsh conditions; consider maintenance support. |
| HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning) | Air Handling Units | Energy efficiency and improved climate control | Focus on energy ratings and compliance with local regulations. |
| Logistics | Automated Sorting Systems | Streamlined operations and reduced processing time | Confirm integration with existing technologies and after-sales support. |
Manufacturing: Conveyor Systems
In the manufacturing sector, electrical motors are crucial for powering conveyor systems that transport materials and products through production lines. These motors enhance productivity by automating the movement of goods, thereby reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. Buyers must ensure that the motors they source are compatible with existing systems and can operate efficiently under local voltage standards. Additionally, considering the availability of spare parts and technical support is vital to maintain operational continuity.
Agriculture: Water Pumping Systems
Electrical motors are widely used in agricultural water pumping systems, providing essential irrigation for crops. By optimizing water delivery, these motors can significantly improve irrigation efficiency and crop yield, which is critical for food security in regions like Africa and South America. Buyers should assess the motor’s durability against environmental conditions such as dust and moisture, as well as the local availability of service technicians to ensure reliable maintenance and support.
Oil & Gas: Drilling Equipment
In the oil and gas industry, electrical motors power drilling equipment, contributing to increased operational uptime and enhanced safety. These motors must perform reliably in extreme conditions, making sourcing decisions critical. Buyers should evaluate the motor’s specifications for reliability and efficiency under harsh operational environments. Furthermore, considering the availability of maintenance support and spare parts is essential to mitigate risks associated with downtime.
HVAC: Air Handling Units
Electrical motors are integral to air handling units in the HVAC sector, driving fans and compressors that maintain indoor climate control. The energy efficiency of these motors directly impacts operational costs and compliance with environmental regulations. Buyers should focus on sourcing motors with high energy ratings and ensure they meet local regulatory standards. Understanding the specific requirements for installation and maintenance in their region can prevent costly errors and enhance system longevity.
Logistics: Automated Sorting Systems
In logistics, electrical motors are essential for powering automated sorting systems that streamline operations in warehouses and distribution centers. These systems improve processing times and reduce labor costs by automating material handling. When sourcing motors for these applications, buyers should confirm compatibility with existing technologies and prioritize suppliers that offer robust after-sales support. Understanding the integration requirements is crucial to ensure seamless operation and minimal disruptions.
Related Video: How Electric Motors Work – 3 phase AC induction motors ac motor
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrical motor
When selecting materials for electrical motors, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that directly affect performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in electrical motors, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 200°C) without significant degradation, making it suitable for various motor applications.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s high conductivity results in lower energy losses, enhancing motor efficiency. However, it is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires careful handling to avoid oxidation during production.
Impact on Application:
Copper is ideal for motors that require high efficiency and reliability, such as those used in industrial machinery and electric vehicles. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for humid environments.
Specific Considerations:
International buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is high, the price of copper can be a significant factor in procurement decisions.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good electrical conductivity (around 60% that of copper), and excellent corrosion resistance. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low cost and lightweight nature, which can reduce overall motor weight and installation costs. However, its lower conductivity may lead to higher energy losses compared to copper. Manufacturing processes are generally simpler, allowing for mass production.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is commonly used in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in automotive and aerospace motors. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
Specific Considerations:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider compliance with EN 60204 for electrical equipment safety. In regions with less stringent regulations, the lower cost of aluminum may be appealing, but buyers should be cautious about potential performance trade-offs.
3. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel, particularly low-carbon steel, is often used for motor frames and components due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons:
Steel is cost-effective and provides excellent mechanical strength, which is crucial for structural integrity. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can corrode if not properly treated or coated. Manufacturing complexity can be high due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application:
Steel is ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as mining or heavy manufacturing, where durability is paramount. Its strength allows for the construction of robust motor housings.
Specific Considerations:
International buyers should be aware of compliance with standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel. In developing regions, the availability of quality steel can vary, impacting procurement timelines and costs.
4. Composites
Key Properties:
Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, offer excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. They can operate effectively in a range of temperatures, typically up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons:
Composites are highly resistant to environmental factors, making them suitable for outdoor applications. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Composites are often used in applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in marine or chemical processing environments. They also provide electrical insulation, which can enhance motor safety.
Specific Considerations:
B2B buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management. In regions like the Middle East, where humidity can be high, the benefits of composites may outweigh their costs.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electrical motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Industrial machinery, electric vehicles | High conductivity, low energy loss | Expensive compared to alternatives | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace motors | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower conductivity, higher energy losses | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications, mining | Excellent strength and durability | Heavier, potential for corrosion | Low |
| Composites | Marine, chemical processing | Corrosion resistant, lightweight | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a clear understanding of material options for electrical motors, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrical motor
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for electrical motors is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section provides an in-depth overview of typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, and quality control measures that ensure reliability and performance.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of electrical motors involves several critical stages, each requiring precision and adherence to specific standards. The primary stages include:
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials used in motor production include copper for windings, silicon steel for the stator and rotor laminations, and various alloys for the casing.
- Key Techniques:
- Material Selection: Ensure materials meet international standards such as ASTM or ISO.
- Cutting and Shaping: Metals are often cut using laser cutting or stamping processes to achieve the desired dimensions.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes to create essential components of the motor.
- Key Techniques:
- Lamination Stacking: Stator and rotor laminations are stacked to reduce eddy current losses. This is crucial for efficiency, particularly in regions with variable power supply qualities.
- Winding: Copper wire is wound around the stator and rotor. Automated winding machines are commonly used for precision.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves fitting together all the components to form a complete motor.
- Key Techniques:
- Fitting Components: Components like bearings, shafts, and end caps are assembled. Precision is vital to ensure proper alignment and minimize vibration.
- Electrical Connections: The windings are connected to the motor terminals, and insulation is checked to prevent short circuits.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing includes various finishing processes that enhance durability and performance.
- Key Techniques:
- Coating and Painting: Motors are often coated with protective finishes to prevent corrosion, especially in humid or harsh environments typical in regions like Africa and South America.
- Final Assembly Checks: Before packaging, motors undergo visual inspections and functional testing.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of electrical motors, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard emphasizes a quality management system that enhances customer satisfaction through effective process implementation.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, ensuring compliance with safety and environmental requirements.
- API Standards: Particularly important for motors used in oil and gas applications, focusing on performance and safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To maintain high-quality standards, several quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications upon arrival.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to detect defects early, minimizing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and inspection of finished motors, including performance tests and safety checks.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of common testing methods used to ensure product reliability:
- Electrical Testing: Checks for insulation resistance, winding continuity, and phase balance.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates motor efficiency, torque, speed, and thermal performance under various loads.
- Environmental Testing: Assesses the motor’s performance in extreme conditions, such as temperature and humidity, which is crucial for buyers in diverse climates.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to verify a supplier’s quality control measures:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess the manufacturing and quality control processes, ensuring compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC tests.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing processes and final products, providing an unbiased assessment of quality.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
- Local Regulations: Understand local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms, as this can impact the usability and acceptance of motors in local markets.
- Cultural Considerations: Be mindful of cultural differences that may influence communication and expectations regarding quality standards.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ensure that suppliers provide transparency in their sourcing and production processes, which is particularly important in regions where material sourcing may vary significantly.
Conclusion
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards of electrical motors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. Ensuring robust quality control measures and verifying supplier capabilities are essential steps in mitigating risks associated with motor procurement, particularly in diverse and challenging markets.
Related Video: How to Make Electric MOTOR in Factory | Amazing Electrical Motors Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrical motor Sourcing
When sourcing electric motors, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will equip you with insights necessary for making informed procurement decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in electric motor manufacturing is the raw materials used, which typically include copper, steel, and various alloys. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on global demand and supply chain issues. For instance, copper prices are particularly volatile and can significantly impact the final motor cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely by region. In high-wage countries in Europe, labor can represent a larger portion of the overall costs, while in regions like Africa or South America, labor may be less expensive but can come with varying skill levels. Investing in skilled labor often results in better-quality products and lower defect rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, ultimately impacting pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for producing electric motors involves substantial tooling costs. Custom designs or specifications may require specialized tooling, which can increase the upfront investment for buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is essential to ensure reliability and compliance with standards. While this may add to the cost, it is a critical investment to minimize future maintenance and operational disruptions.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary dramatically based on the motor’s size, weight, and destination. International buyers must account for potential tariffs and customs duties that could affect overall pricing.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary significantly based on market competition, brand reputation, and product differentiation. Understanding the typical margins in your target market can help you identify fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should evaluate their needs and consider bulk purchasing to lower costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom motors tailored to specific applications can significantly increase costs. Standardized products usually come at a lower price point, so assess whether customization is essential for your application.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used can affect pricing. Higher quality materials may result in higher upfront costs but can lead to lower maintenance and operational costs over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Motors that meet international standards and certifications may come at a premium. However, these certifications can assure reliability and compliance, reducing long-term risks.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and their production capacity can influence costs. Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs but may not always have the same quality assurance as established international brands.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can impact overall costs by determining who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to negotiate better pricing. Understanding your supplier’s cost structure can also empower you during negotiations.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, energy consumption, and disposal costs. A higher-quality motor might have a steeper initial cost but save money in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be mindful of currency fluctuations and economic conditions in your sourcing regions. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate some risks.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It’s important to note that prices can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above, and the information provided serves as a guideline. Always seek updated quotes that reflect current market conditions.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of electric motor sourcing more effectively, ensuring they make choices that align with their operational goals and financial constraints.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential electrical motor Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electrical motor’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrical motor
Key Technical Properties of Electrical Motors
When sourcing electrical motors, understanding key technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are several critical properties that international B2B buyers should consider:
-
Horsepower (HP)
– Definition: A measure of the motor’s output power, indicating how much work it can perform over time.
– Importance: Selecting the appropriate horsepower ensures that the motor can handle the required load without overheating or failing. Underestimating horsepower can lead to operational inefficiencies and equipment damage. -
Rated Voltage
– Definition: The voltage level at which the motor is designed to operate efficiently.
– Importance: Compatibility with local electrical supply is essential. Motors that operate at mismatched voltage levels can lead to performance issues and potential hazards, especially in regions with variable power supply conditions. -
Speed (RPM)
– Definition: The rotational speed of the motor, typically expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM).
– Importance: The required speed affects the motor’s application and its efficiency. For applications requiring variable speeds, it’s important to choose motors that can handle such variations without significant efficiency losses. -
Temperature Classifications
– Definition: Ratings that indicate the maximum temperature a motor can operate under, based on its insulation materials.
– Importance: Motors operating in extreme environments must be rated accordingly to prevent insulation failure and ensure longevity. This is especially relevant in hot climates or in industries with high ambient temperatures. -
Frame Size
– Definition: The physical dimensions of the motor, which determines its mounting compatibility with existing equipment.
– Importance: Correct frame size ensures that the motor can be installed without modifications. This can save time and costs associated with retrofitting or structural adjustments in facilities. -
Enclosure Type
– Definition: The design of the motor’s housing, which protects it from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and temperature variations.
– Importance: Choosing the right enclosure type (e.g., open, totally enclosed, explosion-proof) is critical based on the operating environment. An inappropriate enclosure can lead to motor failure and increased maintenance costs.
Common Trade Terminology in Electrical Motor Procurement
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication with suppliers and understanding procurement processes. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify reliable sources for motors that meet specific quality standards, ensuring compatibility with existing machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It’s essential to negotiate favorable terms to avoid overstocking or underordering. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to solicit pricing and terms from suppliers.
– Importance: Crafting a clear RFQ can streamline the procurement process, ensuring that all vendors provide comparable quotes, which simplifies decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that delineate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, particularly in international transactions where logistics can be complex. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Awareness of lead times helps businesses plan operations effectively, ensuring that equipment downtime is minimized and production schedules are maintained. -
After-Sales Support
– Definition: Services provided by the supplier post-purchase, including maintenance, repairs, and technical assistance.
– Importance: Strong after-sales support is vital for ensuring the longevity and reliability of motors, particularly in regions where access to repair services may be limited.
By understanding these specifications and terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of electric motor procurement more effectively, leading to better decision-making and enhanced operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electrical motor Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global electric motor market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology, increasing energy efficiency mandates, and rising demand for automation across various industries. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for informed sourcing decisions.
A notable trend is the shift towards smart motors equipped with IoT capabilities, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This integration enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, which is particularly valuable in sectors like manufacturing and logistics. Moreover, the push for energy-efficient motors is reshaping sourcing priorities; buyers are increasingly considering motors that meet or exceed efficiency standards, such as those outlined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).
Emerging supply chain trends also highlight the importance of local sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. For buyers in developing regions, establishing relationships with local suppliers can improve lead times and ensure compatibility with regional electrical standards. Additionally, the focus on sustainability is prompting companies to seek out suppliers that can provide transparency in their sourcing processes, emphasizing the need for ethical and environmentally responsible practices.
In summary, the interplay of technological innovation, energy efficiency demands, local sourcing strategies, and sustainability will shape the future of electric motor procurement, requiring B2B buyers to stay informed and adaptable.
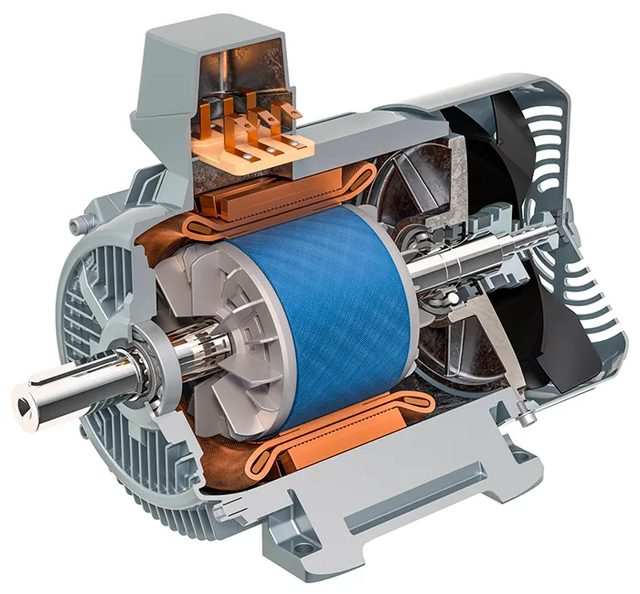
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As the world increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the electric motor sector is no exception. The environmental impact of motor production and usage cannot be overstated; motors contribute significantly to global electricity consumption. B2B buyers must therefore prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that implement sustainable practices throughout their production processes.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a critical consideration in procurement strategies. Buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to internationally recognized sustainability standards, such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. Additionally, certifications like the Energy Star label can help identify energy-efficient motors that reduce overall carbon footprints.
In terms of materials, sourcing motors made from recyclable components or those that utilize eco-friendly lubricants can further enhance sustainability efforts. It’s also essential to consider the lifecycle of motors; selecting products designed for easy disassembly can facilitate recycling and reduce waste at end-of-life.
By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also strengthen their brand reputation and foster loyalty among environmentally conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electric motors dates back to the early 19th century, when pioneers like Michael Faraday and Thomas Davenport first harnessed electrical energy for mechanical work. Over the decades, motor technology has advanced significantly, transitioning from simple DC motors to more complex AC induction and synchronous motors.
In recent years, technological innovations have led to the development of brushless DC motors and smart motors, integrating digital controls and IoT capabilities. This evolution reflects the growing need for efficiency, precision, and adaptability in industrial applications. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential, as it highlights the ongoing trends in performance, energy efficiency, and sustainability that are shaping today’s motor market.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrical motor
-
How can I effectively vet potential suppliers of electrical motors?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and compliance with international standards. Request references from past clients and check their financial stability through credit ratings or trade references. Evaluate their production capacity to ensure they can meet your demand and assess their quality assurance processes, including certifications like ISO 9001. Conduct site visits, if feasible, to inspect their manufacturing facilities and capabilities. Additionally, ensure they have a reliable supply chain for spare parts and after-sales service to minimize downtime. -
Can electrical motors be customized to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electrical motors. Customization can include alterations in size, power output, voltage specifications, and specific features like enclosure type for environmental protection. When seeking customized solutions, clearly communicate your operational requirements, including any unique application needs. Be aware that customization may impact lead times and costs, so factor these into your procurement strategy. Collaborate with suppliers who have experience in your industry to ensure they understand the nuances of your requirements. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for electrical motors?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the motor. Generally, standard motors may have lower MOQs, while customized or specialized motors may require larger orders. Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on production schedules and whether the motors are in stock. To mitigate risks, discuss your needs with suppliers early in the sourcing process and explore the possibility of staggered deliveries or inventory agreements to align with your operational timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electrical motors internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers and may include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It is common for international transactions to require partial upfront payment, especially for custom orders. Discuss payment terms early in negotiations and ensure they align with your cash flow management practices. Be cautious of any terms that appear overly favorable or unfavorable; conduct due diligence on the supplier’s reputation to avoid potential disputes. -
How important are quality assurance certifications for electrical motors?
Quality assurance certifications are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to manufacturing reliable and safe products. Look for certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management systems and compliance with international standards such as IEC or NEMA, which ensure the motors meet specific performance criteria. Certifications can also provide insight into the supplier’s testing and inspection processes. Ensure that any certifications are current and relevant to your region and industry to avoid compliance issues down the line. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electrical motors?
Logistics play a crucial role in the sourcing of electrical motors. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties that may affect overall costs and delivery times. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial equipment to navigate potential challenges. Confirm that the supplier can provide necessary shipping documentation and ensure that motors are adequately packaged to prevent damage during transit. Establish a clear communication channel for tracking shipments and addressing any unforeseen delays. -
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively managed?
Disputes can arise for various reasons, including delays, quality issues, or miscommunication. To manage disputes effectively, establish clear contracts that outline all terms, including specifications, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. Maintain open communication with your supplier throughout the sourcing process, addressing concerns promptly to prevent escalation. If disputes arise, consider mediation or arbitration as a first step before pursuing legal action. Building a collaborative relationship with your supplier can also help in resolving conflicts amicably. -
What factors should I consider regarding after-sales support for electrical motors?
After-sales support is vital for ensuring long-term operational reliability and minimizing downtime. Assess the supplier’s ability to provide technical support, warranty terms, and availability of spare parts. Inquire about their service response times and whether they offer on-site support or remote assistance. Evaluate the supplier’s track record in handling maintenance issues and their commitment to customer service. A reliable after-sales support system can significantly enhance your operational efficiency and reduce the total cost of ownership for your electrical motors.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrical motor
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of electrical motors is a critical process that directly influences operational efficiency and long-term success for businesses across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing comprehensive criteria—such as electrical specifications, mechanical compatibility, and after-sales support—buyers can avoid common pitfalls associated with motor procurement. Leveraging market intelligence and supplier evaluation frameworks enables organizations to make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs.
As the global landscape continues to evolve, staying ahead of trends and technological advancements will be essential. Buyers are encouraged to actively engage with suppliers, consider innovative motor solutions, and evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just upfront expenses.
The future of electric motor sourcing promises exciting opportunities for those willing to adapt and invest wisely. By prioritizing strategic sourcing practices, international B2B buyers can not only enhance their operational capabilities but also position themselves for sustainable growth in a competitive marketplace. Engage today and empower your organization to thrive in the dynamic world of electrical motors.