Mastering Stainless Steel Plate Grades: A Strategic Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stainless steel plate grades
Stainless steel plates are essential components across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and transportation. Their durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal make them a preferred choice for international B2B buyers seeking reliable materials for high-stakes applications. Understanding the different stainless steel plate grades is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific project requirements and environmental conditions.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of stainless steel plate grades, delving into key areas such as types of materials, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and supplier considerations. It also addresses cost factors and provides insights into current market trends, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing stainless steel plates globally.
Particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions experiencing rapid industrial growth—this guide empowers them to make strategic choices that enhance operational efficiency and product performance. With detailed FAQs and actionable insights, it serves as a vital resource for those looking to optimize their procurement processes and establish long-term supplier relationships. By leveraging the information in this guide, businesses can confidently select the right stainless steel plate grades to meet their unique needs, driving success in an increasingly competitive global market.
Understanding stainless steel plate grades Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | Non-magnetic, high corrosion resistance, excellent formability. | Food processing, chemical industries. | Pros: Excellent weldability; Cons: Lower strength at high temperatures. |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | Magnetic, high strength, and hardness; less corrosion resistant. | Aerospace, automotive, and tooling. | Pros: High wear resistance; Cons: Poor corrosion resistance compared to austenitic grades. |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | Magnetic, good resistance to stress corrosion; less ductile. | Automotive exhaust systems, kitchenware. | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited weldability and toughness. |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Combination of austenitic and ferritic properties; high strength. | Oil and gas, marine applications. | Pros: Excellent resistance to pitting; Cons: More expensive than standard grades. |
| Precipitation-Hardening Steel | High strength through heat treatment; good corrosion resistance. | Aerospace, medical devices. | Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: More complex processing. |
Austenitic Stainless Steel
Austenitic stainless steels, such as grades 304 and 316, are characterized by their non-magnetic properties and high levels of chromium and nickel. This grade is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and formability, making it ideal for applications in food processing, chemical industries, and construction. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific alloy content, as it significantly impacts performance in harsh environments.
Martensitic Stainless Steel
Martensitic stainless steels, like grade 410, are known for their high strength and hardness, achieved through heat treatment. They exhibit magnetic properties and are commonly used in applications requiring wear resistance, such as aerospace components and cutting tools. B2B buyers should weigh the trade-off between strength and corrosion resistance, as martensitic grades are typically less resistant than their austenitic counterparts.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ferritic Stainless Steel
Ferritic stainless steels, such as grade 430, are primarily characterized by their magnetic properties and good stress corrosion resistance. They are less ductile than austenitic grades but are cost-effective and suitable for applications like automotive exhaust systems and kitchenware. Buyers should be aware of their limitations in welding and toughness when considering ferritic options for critical applications.
Duplex Stainless Steel
Duplex stainless steels, including grades like 2205, combine the beneficial properties of austenitic and ferritic steels, offering high strength and excellent resistance to pitting and stress corrosion cracking. They are widely used in demanding environments, such as oil and gas and marine applications. Buyers should consider the higher cost but recognize the long-term savings associated with reduced maintenance and increased durability.
Precipitation-Hardening Steel
Precipitation-hardening stainless steels, such as 17-4 PH, achieve their high strength through heat treatment. They also offer good corrosion resistance, making them suitable for aerospace and medical device applications. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of processing and the specific heat treatment requirements, which can impact lead times and costs.
Related Video: Stainless Steel Grades Explained
Key Industrial Applications of stainless steel plate grades
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of stainless steel plate grades | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural components in buildings and bridges | High strength and durability ensure safety and longevity | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Manufacturing | Equipment for chemical processing and storage | Corrosion resistance enhances equipment lifespan | Verify material grade suitability for specific chemicals |
| Transportation | Shipbuilding and aircraft parts | Lightweight yet strong materials improve fuel efficiency | Assess weight-to-strength ratio and regulatory compliance |
| Food Processing | Kitchen equipment and processing machinery | Hygiene and easy cleaning minimize contamination risks | Consider surface finish and resistance to corrosion |
| Energy | Pressure vessels and heat exchangers | High-temperature stability is crucial for efficiency | Evaluate thermal conductivity and pressure ratings |
Construction
In the construction industry, stainless steel plate grades are essential for structural components in buildings and bridges. Their high strength and durability ensure that structures can withstand significant loads and environmental stresses, thereby enhancing safety and longevity. For international buyers, especially in regions with stringent building codes, it is crucial to ensure that the selected stainless steel plates comply with local regulations and standards, as well as international certifications.
Manufacturing
Stainless steel plates are widely used in manufacturing, particularly for equipment involved in chemical processing and storage. Their corrosion resistance is critical in preventing material degradation when exposed to harsh chemicals, which ultimately enhances the lifespan and reliability of the equipment. Buyers must verify the suitability of specific stainless steel grades for the chemicals they will encounter, ensuring that the material can withstand the operational conditions.
Transportation
In the transportation sector, stainless steel plate grades are utilized in shipbuilding and aircraft components due to their lightweight yet robust properties. These materials contribute to improved fuel efficiency by reducing overall weight while maintaining structural integrity. Buyers should assess the weight-to-strength ratio of the plates and ensure compliance with relevant aviation and maritime regulations to guarantee safety and performance.
Food Processing
The food processing industry relies on stainless steel plates for kitchen equipment and processing machinery. The material’s hygienic properties and ease of cleaning help minimize contamination risks, making it ideal for food handling applications. International buyers should consider the surface finish of the plates, as certain finishes can enhance corrosion resistance and facilitate cleaning, ensuring compliance with food safety standards.
Energy
Stainless steel plates are essential in the energy sector, particularly for pressure vessels and heat exchangers. Their ability to maintain stability at high temperatures is critical for operational efficiency in energy production processes. Buyers should evaluate the thermal conductivity and pressure ratings of the plates to ensure they meet specific performance requirements, particularly in regions with extreme operating conditions.
Related Video: [English] Stainless Steel (SS) – Basic concept, Classification, Grades and Applications
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stainless steel plate grades
When selecting stainless steel plate grades for various applications, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance characteristics of each material. Below are analyses of four common stainless steel grades, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Austenitic Stainless Steel (Grade 304)
Key Properties:
Austenitic stainless steel, particularly Grade 304, is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It maintains its strength at high temperatures and can withstand pressures up to 10,000 psi in appropriate applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of Grade 304 makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including food processing and chemical handling. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other grades, and its work-hardening properties can complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Grade 304 is compatible with a variety of media, including acidic and alkaline solutions, making it ideal for use in food and beverage industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from Africa, South America, and Europe should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088. The availability of Grade 304 in local markets can vary, so checking local suppliers is crucial.
2. Ferritic Stainless Steel (Grade 430)
Key Properties:
Ferritic stainless steel, particularly Grade 430, offers moderate corrosion resistance and good formability. It performs well in temperatures up to 800°C and is magnetic, which can be beneficial in certain applications.
Pros & Cons:
Grade 430 is generally less expensive than austenitic grades and provides good durability for applications like automotive components and kitchenware. However, its lower corrosion resistance compared to austenitic grades limits its use in harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
This grade is suitable for applications where exposure to corrosive environments is minimal, such as decorative trim and appliances.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in regions like Poland or Argentina, understanding local corrosion risks is essential. Compliance with standards such as DIN 1.4016 can help ensure quality.
3. Duplex Stainless Steel (Grade 2205)
Key Properties:
Duplex stainless steel, such as Grade 2205, combines the properties of both austenitic and ferritic grades, offering high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against pitting and stress corrosion cracking.
Pros & Cons:
The high strength-to-weight ratio of Grade 2205 makes it ideal for applications requiring durability without excessive weight, such as in oil and gas industries. However, its higher cost and complex welding requirements can be a drawback.
Impact on Application:
Grade 2205 is particularly well-suited for environments with high chloride exposure, such as seawater applications, making it a preferred choice in marine and chemical processing.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific welding techniques required for duplex stainless steel and ensure compliance with relevant standards like ASTM A240. Checking local suppliers for availability is also recommended.
4. Martensitic Stainless Steel (Grade 410)
Key Properties:
Martensitic stainless steel, such as Grade 410, is known for its high hardness and moderate corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications requiring wear resistance and can be heat-treated to enhance its strength.
Pros & Cons:
Grade 410 is relatively inexpensive and suitable for applications like cutlery and tooling. However, its corrosion resistance is lower than that of austenitic grades, limiting its use in corrosive environments.
Impact on Application:
This grade is ideal for applications where mechanical strength and wear resistance are critical, but exposure to corrosive elements is limited.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in the Middle East or South America, understanding the balance between cost and performance is vital. Compliance with standards like ASTM A276 can help in ensuring product quality.
| Material | Typical Use Case for stainless steel plate grades | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic (Grade 304) | Food processing, chemical handling | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Ferritic (Grade 430) | Automotive components, kitchenware | Cost-effective, good formability | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Duplex (Grade 2205) | Oil and gas, marine applications | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex welding | High |
| Martensitic (Grade 410) | Cutlery, tooling | High hardness, wear resistance | Lower corrosion resistance | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stainless steel plate grades
The manufacturing of stainless steel plates involves several critical processes that ensure the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. Understanding these processes is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section outlines the key manufacturing stages and quality assurance practices in detail.
Manufacturing Processes for Stainless Steel Plates
The production of stainless steel plates typically encompasses four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates specific techniques and technologies to achieve high-quality results.
1. Material Preparation
Before the actual manufacturing process begins, raw materials must be carefully selected and prepared. The primary materials used are various grades of stainless steel, such as 304, 316, and duplex stainless steels.
- Scrap Metal Recycling: Many manufacturers use recycled stainless steel scrap as a primary material source. This not only reduces costs but also promotes sustainability.
- Alloying: The alloying process involves combining different metals to achieve desired properties. For instance, adding nickel enhances corrosion resistance.
- Melting and Casting: The prepared materials are melted in electric arc furnaces (EAF) and then cast into slabs or blooms. Continuous casting techniques are often employed to produce uniform thickness and minimize waste.
2. Forming
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming the stainless steel into plates. This involves several techniques:
- Hot Rolling: The slabs are heated and passed through rollers to reduce thickness and improve mechanical properties. Hot rolling helps in achieving the desired plate dimensions (typically above 5mm).
- Cold Rolling: This technique may follow hot rolling to achieve finer tolerances and enhanced surface finishes. Cold-rolled plates exhibit improved surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
- Shearing and Blanking: After rolling, the plates are cut to size using shearing machines or blanking presses, ensuring they meet specific customer requirements.
3. Assembly
In certain applications, stainless steel plates may require additional assembly processes, especially when they are part of larger structures or systems.
- Welding: Plates may be welded together to form larger components. Techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding are commonly employed, depending on the required strength and application.
- Machining: Some applications may necessitate further machining, such as drilling or milling, to achieve precise dimensions or features.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functionality of stainless steel plates.
- Surface Treatments: Various surface finishes can be applied, including 2B, BA, No.4, and No.8. Each finish has specific applications, from industrial uses to decorative purposes.
- Passivation: This chemical treatment enhances corrosion resistance by removing free iron and other contaminants from the surface, thus increasing the longevity of the plates.
- Coating: Some manufacturers apply protective coatings to further enhance corrosion resistance and surface durability.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that stainless steel plates meet industry standards and customer expectations. International and industry-specific standards guide the QA process.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following standards that govern the quality of stainless steel plates:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- ASTM Standards: Various ASTM specifications detail the requirements for stainless steel plates, including mechanical properties, chemical composition, and dimensional tolerances.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must conform to specific safety and performance standards to receive CE marking, indicating compliance with EU legislation.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps detect any deviations from quality standards early, allowing for corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo thorough testing and inspection to verify compliance with specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are utilized to assess the quality of stainless steel plates:
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation tests determine the mechanical properties of the plates.
- Chemical Analysis: Spectrometry or chemical assays are used to confirm that the alloying elements meet the specified compositions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection help identify internal defects without damaging the plates.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control practices. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation, such as inspection reports and certificates of compliance, for the products being purchased.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to verify that the products meet the required specifications and quality standards before shipment.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing stainless steel plates from international suppliers, buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Quality expectations and regulatory requirements can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and practices in their respective markets.
- Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation, including mill test certificates (MTC) and certificates of origin, to verify the quality and traceability of materials.
- Warranty and Liability: Understand the warranty terms and conditions provided by suppliers, as this can vary between regions and impact the overall purchasing decision.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing stainless steel plates, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Top 5 Mass Production Techniques: Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stainless steel plate grades Sourcing
When sourcing stainless steel plates, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure influenced by various factors. Understanding these components and the dynamics of pricing can facilitate more informed purchasing decisions, especially for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the raw material itself, with stainless steel grades varying significantly in price based on alloy composition. For instance, austenitic grades like 304 and 316 are generally more expensive than ferritic grades due to their nickel and molybdenum content.
-
Labor: Labor costs are tied to the processing of stainless steel plates. This includes cutting, shaping, and finishing operations. Regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, may see an increase in overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and other operational costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead expenses, but these costs will vary by supplier.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling, necessary for machining and forming processes, can be substantial. Custom tooling for unique specifications adds to the initial investment but can lead to better long-term cost efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing and certification processes adds another layer of expense. Buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to international standards (like ISO or ASTM) for quality assurance.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the shipping method, distance, and Incoterms. Costs for handling heavy materials like stainless steel plates can add significant overhead, particularly for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add their markup to cover risks and profit margins. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can aid buyers in gauging fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate terms that optimize their purchasing volumes.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized plates or unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential price increases.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products certified to international standards may carry a premium. However, investing in certified materials can reduce long-term costs related to failures or compliance issues.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Suppliers from regions with lower production costs may offer competitive prices, but buyers should also consider lead times and service quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is essential. Different Incoterms can shift costs and responsibilities between buyer and seller, affecting the overall cost structure.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Always engage in negotiations. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing, especially with large orders or long-term contracts.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Assess total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just initial purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance, durability, and operational costs over the lifespan of the product.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices can fluctuate due to market conditions, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors. Regularly check market trends and adjust procurement strategies accordingly.
-
Regional Considerations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider regional suppliers who can provide better logistics and potentially lower shipping costs. Local suppliers may also offer insights into market-specific pricing nuances.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific requirements. Always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential stainless steel plate grades Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘stainless steel plate grades’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stainless steel plate grades
Key Technical Properties of Stainless Steel Plate Grades
When evaluating stainless steel plates for procurement, understanding the following technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions:
-
Material Grade
The grade of stainless steel is a fundamental specification that determines its composition, mechanical properties, and suitability for specific applications. Common grades include 304 and 316, where 304 is known for good corrosion resistance and 316 offers enhanced resistance to chlorides, making it ideal for marine environments. Buyers should select the grade based on the environmental conditions and performance requirements of their projects. -
Thickness
Stainless steel plates are classified based on their thickness, typically ranging from 5mm to over 100mm. The thickness impacts the strength and durability of the plate, influencing its application in heavy-duty environments. Buyers must specify the required thickness to ensure that the material can withstand operational stresses and loads in their applications. -
Tolerances
Tolerances define the allowable variation in dimensions of the plates, including length, width, and thickness. Precise tolerances are vital for applications requiring tight fits and high levels of accuracy. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can meet the necessary tolerances as outlined in international standards like ASTM or EN to avoid costly adjustments during fabrication. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of stainless steel plates affects both aesthetic and functional properties. Common finishes include 2B (matte), No. 4 (brushed), and No. 8 (mirror). The choice of finish can influence corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, and the overall appearance of the end product. Buyers should align the surface finish with the intended application, whether for industrial use or architectural design. -
Mechanical Properties
Key mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation are critical for assessing the performance of stainless steel plates under stress. For example, a tensile strength of 730MPa or higher indicates that the material can handle significant loads. Understanding these properties helps buyers select the right grade for their specific operational demands. -
Heat Resistance
Certain stainless steel grades exhibit excellent resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, making them suitable for applications in extreme environments. Buyers should consider the thermal properties of the material, especially for applications involving heat exchangers or high-temperature processing.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate better communication and negotiation with suppliers. Here are several essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the context of stainless steel plates, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the materials. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for buyers as it impacts inventory management and budget. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases and negotiating better terms with suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Preparing a detailed RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and avoid unexpected costs. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. It is a critical factor in supply chain management. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure they align with project schedules. -
Certification
Certification indicates that the stainless steel plates meet specific standards and regulations. Common certifications include ISO, ASTM, and EN standards. Buyers should prioritize certified materials to ensure quality and compliance with local regulations.
Understanding these properties and terms will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to successful procurement strategies for stainless steel plates.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the stainless steel plate grades Sector
Global stainless steel plate markets are currently influenced by several key drivers, including increased demand in construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. Emerging economies, particularly in Africa and South America, are witnessing rapid urbanization and industrialization, which are propelling the demand for durable and corrosion-resistant materials. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as automated welding and precision cutting, are enhancing production efficiency and reducing costs. B2B buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East are increasingly adopting digital platforms for sourcing, enabling them to compare prices and specifications efficiently. The rise of Industry 4.0 is also transforming supply chain dynamics, with a focus on real-time data analytics and IoT integration, which can lead to optimized inventory management and reduced lead times.
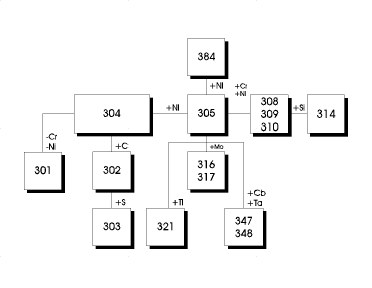
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, the stainless steel plate sector is experiencing a shift towards high-performance grades, such as duplex and high-nickel alloys, driven by stringent regulations concerning corrosion resistance and high-temperature applications. B2B buyers should be aware of the growing trend of customization, with suppliers increasingly offering tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements. Understanding the nuances of local regulations and standards is crucial for buyers operating in diverse markets, particularly in regions with varying compliance requirements like Europe and the Middle East.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The stainless steel industry is under increasing scrutiny regarding its environmental impact. B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainability through responsible sourcing practices. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste during manufacturing, and ensuring energy-efficient production processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, the move towards ethical supply chains is gaining traction, with companies increasingly focusing on transparency and accountability in their sourcing. Buyers should seek suppliers who can provide traceability of materials, ensuring that they are sourced from environmentally responsible and socially compliant operations. The adoption of “green” stainless steel grades—produced through low-carbon methods or from recycled sources—can significantly reduce the overall environmental footprint of projects. As consumer awareness grows, the demand for sustainable products is expected to influence purchasing decisions, making it imperative for B2B buyers to align with sustainability trends.
Brief Evolution/History
The stainless steel plate sector has evolved significantly since the early 20th century, when stainless steel was first developed as a corrosion-resistant alternative to traditional steel. Initially used in cutlery and kitchenware, its applications expanded to construction and industrial uses post-World War II, driven by advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing processes. Today, stainless steel plates are integral in various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and energy, reflecting a shift towards more durable and efficient materials. The continuous innovation in stainless steel grades, driven by the need for enhanced performance and sustainability, underscores the sector’s dynamic nature and its importance in global markets.
As B2B buyers navigate this landscape, understanding these historical trends and current dynamics will be essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both market demands and sustainability objectives.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stainless steel plate grades
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of stainless steel plate grades?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Check for ISO certifications, and compliance with international standards like ASTM or EN. Request references from previous clients, and assess their production capabilities, lead times, and quality control processes. Engaging in initial small orders can also help evaluate their reliability before committing to larger transactions. -
What customization options are available for stainless steel plates?
Many suppliers offer customization in terms of size, thickness, and surface finish. Be clear about your specifications, including any required mechanical properties or surface treatments. Discussing your needs upfront can help suppliers provide tailored solutions. Always confirm that customized products meet your industry standards, as this can significantly impact performance in specific applications. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for stainless steel plates?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific grade of stainless steel. Generally, larger orders can reduce per-unit costs. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s current workload. Always inquire about lead times during negotiations to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing stainless steel plates internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, or staggered payments based on shipment milestones. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing contracts. Also, consider using secure payment methods that protect both parties, especially for large transactions, to mitigate financial risk. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for from suppliers?
Ensure that your suppliers adhere to strict quality assurance protocols. Request certificates of analysis (COA) and mill test certificates (MTC) for verification of material specifications and properties. Additionally, inquire about their in-house testing capabilities, such as tensile tests and corrosion resistance evaluations, to ensure compliance with your required standards. -
How should I approach logistics and shipping for stainless steel plates?
Logistics can be complex due to the weight and size of stainless steel plates. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide guidance on freight options. Discuss packaging methods to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, understand customs regulations in your country to avoid delays and ensure compliance with import duties and taxes. -
What steps should I take if there is a dispute with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication with the supplier. Keep records of all correspondence and agreements. If unresolved, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, such as mediation or arbitration. Understanding local laws and regulations can also provide insights into your rights and options in the dispute. -
Are there specific certifications or standards I should look for in stainless steel plate grades?
Yes, look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and compliance with relevant ASTM, EN, or JIS standards. Additionally, specific grades may require further certifications, such as those for food-grade applications (e.g., 304 or 316 stainless steel). Ensure that any certificates provided are up to date and relevant to your intended application to guarantee performance and safety.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stainless steel plate grades
As the global demand for stainless steel plate grades continues to rise, strategic sourcing becomes increasingly vital for international B2B buyers. Understanding the unique characteristics of different stainless steel grades—such as austenitic, martensitic, ferritic, and duplex—enables companies to select materials that meet specific application needs while optimizing cost-efficiency.
Key takeaways include:
- Value of Quality: Prioritizing high-quality stainless steel plates ensures longevity and performance, particularly in challenging environments.
- Supplier Relationships: Establishing strong connections with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, consistent quality, and improved service.
- Market Awareness: Staying informed about global market trends and fluctuations in steel prices can help buyers make timely purchasing decisions.
Looking ahead, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively engage in the strategic sourcing of stainless steel plates to leverage emerging opportunities. By focusing on quality, supplier collaboration, and market intelligence, businesses can enhance their competitive edge and secure their supply chains. Take the next step—evaluate your sourcing strategies today to position your company for future success.