Unlock Efficient Mixing Solutions with Inline Static Mixers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for inline static mixer
In today’s competitive global marketplace, the demand for inline static mixers is surging, driven by their efficiency and versatility in a multitude of applications. From municipal water treatment to chemical processing, these innovative devices offer B2B buyers a reliable solution for achieving optimal mixing without the need for moving parts or significant energy consumption. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Brazil and Argentina) seek to enhance operational efficiencies and reduce costs, understanding the role of inline static mixers becomes paramount.
This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for international B2B buyers, detailing various types of inline static mixers, including helical, blade, wafer, and custom designs. It also delves into critical considerations such as material selection, manufacturing quality control, and supplier evaluation. By exploring cost factors and market trends, this guide empowers buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Furthermore, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, demystifying the technical aspects of inline static mixers and their applications. Whether you are looking to enhance your water treatment processes or streamline chemical mixing operations, this resource will equip you with the insights needed to navigate the global market confidently and effectively. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your sourcing strategy and drive your business forward with inline static mixers.
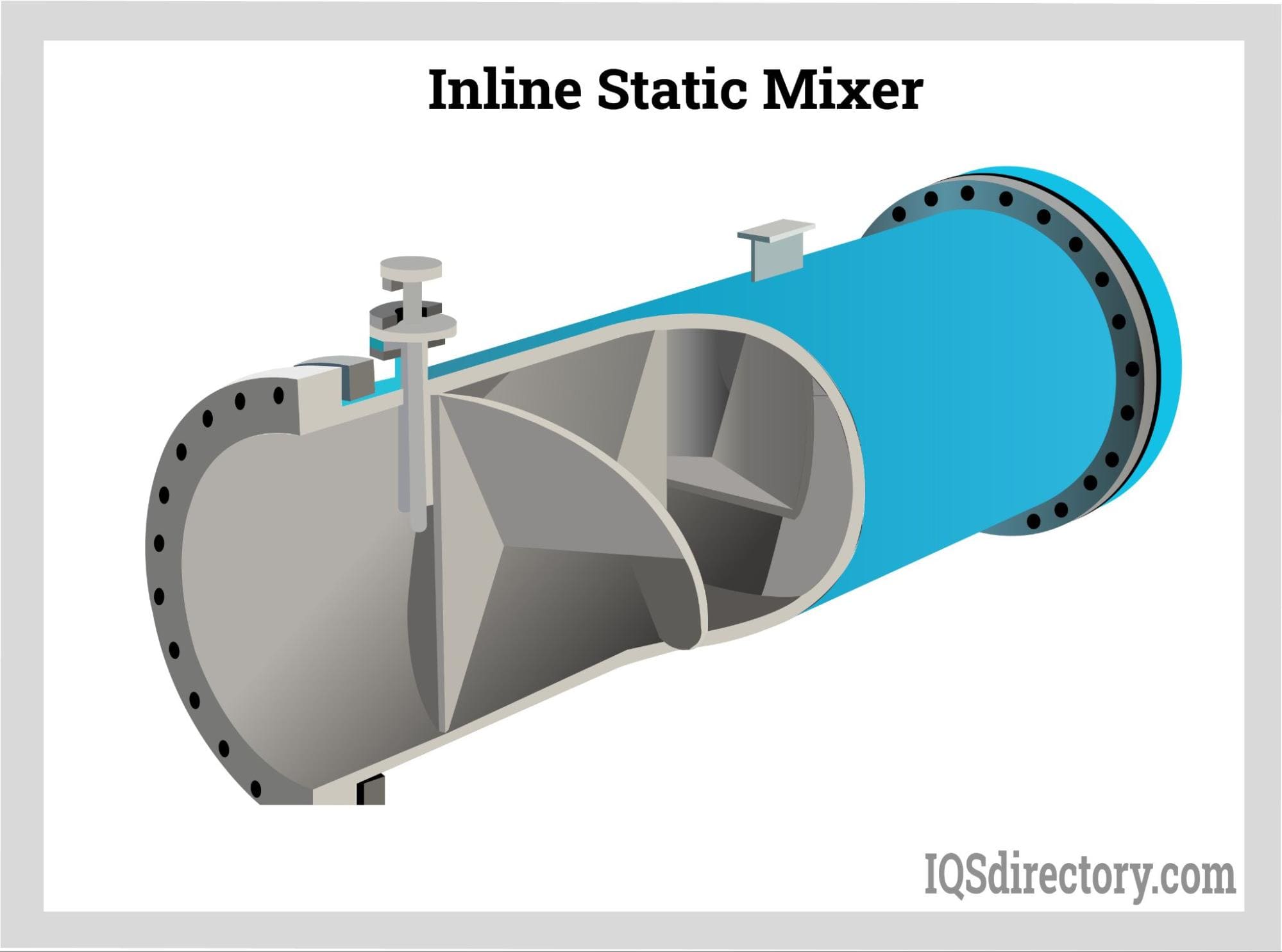
Understanding inline static mixer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helical Mixers | Spiral elements for swirling motion; ideal for laminar flow | Chemical processing, food and beverage | Pros: Effective for viscous fluids; compact design. Cons: May not perform as well in turbulent flow. |
| Blade Mixers | Alternating helical blades for radial mixing; high efficiency | Water treatment, chemical blending | Pros: High mixing efficiency; low-pressure drop. Cons: More complex design may increase cost. |
| Wafer Mixers | Flat, perforated plates for space efficiency | Pharmaceutical, food processing | Pros: Compact; easy installation. Cons: Limited to specific flow patterns. |
| Injection Mixers | Specialized ports for secondary fluid injection | Chemical dosing, wastewater treatment | Pros: Rapid dispersion; versatile applications. Cons: Requires precise design for optimal performance. |
| Custom Mixers | Tailored to specific application needs | Specialized chemical processes, R&D | Pros: Highly adaptable; meets unique requirements. Cons: Longer lead times and potentially higher costs. |
Helical Mixers
Helical mixers utilize a series of spiral elements that create a swirling motion, making them particularly effective for laminar flow conditions and viscous fluids. Their design promotes continuous division and recombination of flow streams, ensuring efficient mixing. Buyers should consider their application needs, as these mixers excel in environments where viscosity is a challenge. However, they may not be as effective in turbulent flow conditions, which could limit their use in certain industrial processes.
Blade Mixers
Blade mixers, often referred to as Kenics mixers, feature alternating helical blades that facilitate intricate flow patterns, promoting efficient radial mixing. They are particularly suited for turbulent flow regimes, making them ideal for applications such as water treatment and chemical blending. When purchasing, buyers should note their high mixing efficiency and low-pressure drop, which can lead to energy savings. However, the complexity of the design may result in higher initial costs compared to simpler mixer types.
Wafer Mixers
Wafer mixers consist of a series of flat, perforated plates that facilitate efficient mixing within a compact design. They are particularly advantageous in space-constrained applications, such as pharmaceutical and food processing industries. Buyers should appreciate their ease of installation and the minimal space they occupy. However, their mixing capabilities are somewhat limited to specific flow patterns, which may not suit all applications.
Injection Mixers
Injection mixers are designed to introduce a secondary fluid into the primary flow, ensuring rapid and uniform dispersion. They are commonly used in chemical dosing and wastewater treatment applications. B2B buyers should consider their versatility and ability to handle various fluids, but must also ensure that the design is optimized for their specific application to achieve the best performance. The need for precise engineering can be a drawback if not managed correctly.
Custom Mixers
Custom mixers are tailored to meet the unique requirements of specific applications, making them highly adaptable for specialized chemical processes and research and development projects. Buyers can benefit from a mixer designed to fit their exact needs, ensuring optimal performance. However, this customization often leads to longer lead times and potentially higher costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of inline static mixer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Inline Static Mixer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water and Wastewater Treatment | Chemical dosing for disinfection and flocculation | Ensures precise chemical mixing, improving treatment efficiency and compliance with regulations | Customization options for varying flow rates and chemical types |
| Chemical Processing | Blending of reactants and additives | Enhances product uniformity and reduces processing time | Material compatibility and resistance to corrosive substances |
| Food and Beverage | Homogenization of emulsions and ingredient blending | Improves product quality and consistency, enhancing consumer satisfaction | Sanitary design features and compliance with food safety standards |
| Oil and Gas | Mixing of additives in petroleum products | Optimizes product formulation and reduces waste | High-temperature and pressure ratings for specific applications |
| Pharmaceutical | Mixing of active ingredients and excipients | Ensures accurate dosing and consistent product quality | Regulatory compliance and customization for specific formulations |
Water and Wastewater Treatment
Inline static mixers are essential in the water and wastewater sector, particularly for applications involving chemical dosing for disinfection and flocculation. They enable precise mixing of chemicals, such as chlorine or coagulants, ensuring effective treatment while complying with stringent environmental regulations. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, considerations include the ability to customize mixers for varying flow rates and chemical types, as well as the durability of materials used to withstand harsh conditions.
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing, inline static mixers facilitate the blending of reactants and additives, which is critical for achieving homogeneity in products. The use of these mixers enhances product uniformity, reduces processing times, and minimizes the risk of reaction inconsistencies. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing mixers that offer material compatibility and resistance to corrosive substances, ensuring longevity and reliability in their processes.
Food and Beverage
The food and beverage industry utilizes inline static mixers for homogenizing emulsions and blending ingredients. This process significantly improves product quality and consistency, which is vital for maintaining consumer satisfaction and meeting market demands. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Brazil and Argentina, sourcing mixers with sanitary design features and compliance with food safety standards is crucial for ensuring product integrity and safety.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas sector, inline static mixers are employed for mixing additives into petroleum products. These mixers optimize product formulations and help reduce waste during the production process. Buyers in this industry should prioritize sourcing mixers with high-temperature and pressure ratings to ensure they meet the specific requirements of their applications, particularly in challenging operational environments.
Pharmaceutical
Inline static mixers play a pivotal role in the pharmaceutical industry by ensuring the accurate mixing of active ingredients and excipients. This capability is essential for maintaining consistent product quality and dosing accuracy, which are critical for regulatory compliance. International buyers must consider sourcing options that offer customization for specific formulations and ensure adherence to stringent regulatory standards, particularly in regions with robust pharmaceutical regulations.
Related Video: How Inline mixer work
Strategic Material Selection Guide for inline static mixer
When selecting materials for inline static mixers, it is crucial to consider the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards relevant to international markets. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of inline static mixers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand elevated temperatures (up to 800°F or 427°C). It also has good pressure ratings, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to rust and staining, which makes it ideal for food and pharmaceutical applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, such as welding and machining.
Impact on Application:
This material is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive chemicals and food products. Its sanitary design makes it a preferred choice in industries that require strict hygiene standards.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes. In regions like Europe, adherence to EN standards is also crucial. Buyers in Africa and South America should verify local regulations regarding food safety and chemical handling.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties:
PVC has a lower temperature rating (up to 140°F or 60°C) and is less pressure-resistant compared to metals. However, it is highly resistant to a variety of chemicals, making it suitable for many industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
PVC is lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to install, which reduces overall project costs. On the downside, its lower temperature and pressure ratings limit its use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application:
PVC is ideal for water treatment and chemical processing applications where temperatures and pressures are moderate. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for handling acids and bases.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check compliance with ASTM D1784 and local regulations regarding the use of PVC in water treatment. In regions like Brazil and Argentina, specific environmental regulations may impact the choice of PVC.
3. FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic)
Key Properties:
FRP offers excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight characteristics, and good thermal insulation properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) and moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons:
FRP is highly durable and resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for aggressive environments. However, it can be more expensive than PVC and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
FRP is particularly useful in wastewater treatment and chemical processing applications where corrosive substances are present. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation in challenging locations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM D3299 for FRP piping. In the Middle East, local standards may dictate specific resin formulations to withstand extreme environmental conditions.
4. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
Key Properties:
HDPE is known for its high strength-to-density ratio, excellent chemical resistance, and flexibility. It can handle temperatures up to 120°F (49°C) and is suitable for moderate pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
HDPE is cost-effective, lightweight, and easy to install. However, its lower temperature and pressure ratings limit its use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application:
HDPE is commonly used in water distribution and wastewater treatment applications due to its resistance to corrosion and chemicals. It is also suitable for applications involving abrasive media.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM D3350 for HDPE materials. In regions like South America, it is essential to consider local regulations regarding plastic materials in contact with drinking water.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for inline static mixer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceutical applications | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| PVC | Water treatment, chemical processing | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
| FRP | Wastewater treatment, aggressive chemical environments | High corrosion resistance and lightweight | More expensive and specialized manufacturing | Medium |
| HDPE | Water distribution, wastewater treatment | Cost-effective and flexible | Lower temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for inline static mixer
Manufacturing Processes for Inline Static Mixers
The manufacturing of inline static mixers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages will help B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Inline static mixers are typically made from various materials, including stainless steel, PVC, and other corrosion-resistant materials. The choice of material depends on the specific application, such as chemical compatibility and temperature resistance.
- Material Selection: It’s crucial to choose materials that can withstand the operational environment. For instance, stainless steel is preferred for water treatment applications due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Material Testing: Before production, materials undergo rigorous testing for properties like tensile strength and corrosion resistance to ensure they meet industry standards.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping the materials into the desired components of the inline static mixer.
- Techniques Used: Common forming techniques include extrusion for tubular components and machining for complex geometries. Advanced methods like laser cutting and CNC machining may also be employed for precision.
- Element Design: The design of mixing elements is crucial. Custom geometries are often created to optimize flow patterns, ensuring effective mixing and minimal pressure drop.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled into the final mixer product. This stage requires precision and attention to detail to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended.
- Assembly Techniques: Methods such as welding, adhesive bonding, and mechanical fastening are commonly used. The choice of technique depends on the materials and design requirements.
- Alignment and Calibration: During assembly, it’s vital to ensure that all components are aligned correctly to prevent operational issues. Calibration may also be necessary to ensure optimal performance.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which enhances both the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the inline static mixer.
- Surface Treatment: This may include polishing, coating, or passivation to improve corrosion resistance and hygiene, especially for mixers used in food and pharmaceutical applications.
- Quality Inspection: Each finished product undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets the required specifications and quality standards.
Quality Assurance for Inline Static Mixers
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of inline static mixers, ensuring reliability and performance across various applications. International B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant standards and QA processes.
International Standards
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that adhere to recognized international standards, which can significantly impact product quality.
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Suppliers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application, certifications like CE for European markets, API for the petroleum industry, and FDA for food-related applications may also be relevant.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure adherence to quality standards.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducts checks during the manufacturing process to identify any deviations from quality standards early on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive assessment of the finished product, including dimensional checks, functional testing, and visual inspections.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of inline static mixers:
- Hydraulic Testing: Assesses the mixer’s ability to withstand operational pressures without leaks or failures.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates mixing efficiency, including flow rates and residence time, to ensure optimal performance in real-world applications.
- Material Testing: Confirms that materials meet the required mechanical and chemical properties.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is essential to ensure product reliability.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facilities, QA processes, and adherence to standards firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide unbiased assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing inline static mixers, buyers from different regions should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. For example, European buyers must ensure compliance with CE marking, while Middle Eastern buyers may prioritize adherence to local regulatory standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices and communication styles can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who offer transparency in their supply chain, providing traceability of materials and manufacturing practices.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for inline static mixers is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, adherence to international standards, and effective quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable and efficient mixing solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for inline static mixer Sourcing
Cost Structure of Inline Static Mixers
When sourcing inline static mixers, understanding the cost components is essential for B2B buyers. The cost structure typically includes the following elements:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials include stainless steel, PVC, and various alloys. High-quality materials suitable for specific applications (e.g., food or chemical industries) tend to be more expensive.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the mixer design and the region of production. Skilled labor required for custom designs or specialized manufacturing processes can increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs or larger production runs can be a significant upfront cost. However, it is often amortized over high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that inline static mixers meet industry standards and certifications requires investment in quality control processes. These costs are often reflected in the final price.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the destination, weight, and dimensions of the mixer. International buyers should consider potential duties and tariffs when calculating total logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin based on their operational costs and desired profitability. This can vary widely among manufacturers.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of inline static mixers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often lead to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate terms that allow for scalable purchasing based on demand.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs and specific performance requirements can increase costs. It’s advisable to clearly outline needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: As mentioned, higher-grade materials for specialized applications will incur higher costs. Understanding the required specifications can help in selecting the right materials without overspending.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international standards (e.g., ISO, FDA) may come at a premium. Buyers must weigh the benefits of certifications against the additional costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their experience and guarantees, while newer players might offer lower prices to penetrate the market.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) impact shipping costs and responsibilities. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) on total costs.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable insights to optimize costs:
-
Negotiate: Engage in discussions with suppliers about pricing and terms. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can lead to favorable deals.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost might yield lower TCO if the mixer requires less maintenance.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and currency fluctuations. This can significantly impact the final cost for buyers in different markets.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to assess quality and compatibility with your processes. This helps avoid costly mistakes.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: Investigate local manufacturers or suppliers who might offer competitive pricing with reduced shipping costs. This can also mitigate risks associated with international logistics.
Disclaimer
Prices for inline static mixers can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to specific needs and circumstances.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential inline static mixer Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘inline static mixer’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for inline static mixer
Inline static mixers are essential components in various industrial applications, particularly in sectors such as water treatment, chemical processing, and food production. Understanding their technical properties and industry-specific terminology is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Below is an overview of the critical specifications and common trade terms relevant to inline static mixers.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type of material used to manufacture the mixer, commonly stainless steel, PVC, or polypropylene.
– Importance: Material selection impacts durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. For instance, stainless steel is preferred in food and pharmaceutical applications due to its hygienic properties. -
Flow Rate Capacity
– Definition: The maximum volume of fluid that can pass through the mixer per unit of time, typically measured in liters per minute (L/min).
– Importance: Understanding flow rate is essential for ensuring the mixer meets the operational demands of your process. Selecting a mixer with the appropriate flow rate can prevent underperformance and inefficient mixing. -
Pressure Drop
– Definition: The reduction in pressure as fluid flows through the mixer, usually measured in psi or bar.
– Importance: A low-pressure drop indicates efficient mixing with minimal energy loss. This is critical for reducing operational costs, especially in large-scale applications where energy consumption is a significant factor. -
Mixing Efficiency
– Definition: A measure of how effectively the mixer blends different fluids, often represented as a percentage.
– Importance: High mixing efficiency ensures uniformity in the final product, which is vital in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing where consistency is paramount. -
Temperature and Pressure Ratings
– Definition: The maximum temperature and pressure the mixer can withstand during operation.
– Importance: Knowing the operational limits helps in selecting a mixer that can handle specific process conditions, thereby enhancing safety and performance. -
Element Geometry
– Definition: The design and arrangement of the mixing elements inside the mixer, which can vary to accommodate different flow types (laminar or turbulent).
– Importance: Customizing the geometry allows for optimizing the mixing process according to specific application needs, which is crucial for achieving desired mixing results.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEMs is crucial when sourcing inline static mixers, as it helps identify reputable manufacturers known for quality and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and inventory levels effectively, ensuring they meet production requirements without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal process where a buyer solicits bids from suppliers to obtain pricing information for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ is essential for buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making and cost management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, which is critical when importing inline static mixers from different regions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Relevance: Knowing lead times is important for project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries where timely delivery is crucial.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting inline static mixers that meet their operational needs and compliance standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the inline static mixer Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The inline static mixer market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand for efficient mixing solutions across various industries, including water treatment, chemical processing, and food and beverage. Key global drivers include the need for sustainable practices, regulatory compliance, and the quest for operational efficiency. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on sourcing technologies that reduce energy consumption and operational costs while enhancing process efficiency.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing for inline static mixers include the adoption of advanced materials that improve durability and performance. Buyers are increasingly looking for custom designs tailored to specific application needs, leading to a rise in collaborations between manufacturers and end-users. Additionally, the integration of digital technologies, such as IoT-enabled monitoring systems, is becoming prevalent. These innovations allow for real-time data collection and process optimization, enhancing overall productivity.
Market dynamics also reflect a shift towards local sourcing to mitigate supply chain risks and reduce lead times. This is especially relevant for international buyers in emerging markets, where establishing relationships with local suppliers can lead to competitive advantages. As global supply chains adapt, buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough assessments of potential suppliers, focusing on their technological capabilities and service offerings.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the inline static mixer sector. The environmental impact of production processes, material sourcing, and product lifecycle must be evaluated. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to minimizing their carbon footprint and waste generation.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining traction, with buyers seeking transparency in sourcing practices. This includes ensuring that materials used in inline static mixers are obtained from sustainable sources, such as recycled or biodegradable materials. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) guidelines are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract environmentally conscious buyers.
Furthermore, the use of “green” certifications can enhance product appeal and marketability. Buyers should consider suppliers who can provide documentation of their sustainability practices and product certifications, as this will not only align with corporate social responsibility goals but also improve brand reputation in increasingly eco-aware markets.
Brief Evolution/History
The development of inline static mixers has evolved significantly since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially designed for simple blending applications, advancements in engineering and materials have transformed these devices into highly efficient mixing solutions suitable for complex industrial processes. The introduction of specialized mixing elements and custom designs has allowed for greater adaptability across various sectors, catering to diverse fluid types and flow conditions.
As industries increasingly emphasize efficiency and sustainability, inline static mixers have become integral components in modern manufacturing and treatment processes. Their ability to deliver consistent results with minimal energy consumption positions them as a preferred choice for B2B buyers focused on operational excellence and environmental stewardship.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of inline static mixer
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers of inline static mixers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, customer reviews, and certifications. Check if they have a proven track record in manufacturing inline static mixers specific to your industry, such as water treatment or chemical processing. Evaluate their production capacity and quality assurance processes, including ISO certifications. Communication responsiveness and after-sales support are also crucial, especially when dealing with international trade, to ensure smooth transactions and support throughout the product lifecycle. -
Can inline static mixers be customized to suit specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for inline static mixers. Customization can include altering the design, materials, and dimensions to meet specific operational requirements. For instance, you can request modifications for different fluid viscosities, flow rates, or installation constraints. Engage with your supplier early in the process to discuss your needs, as this can affect lead times and pricing. Ensure that they provide design validation and testing for any customized solutions. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for purchasing inline static mixers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly by supplier and application, ranging from a single unit for custom orders to larger batches for standardized products. Lead times also depend on the complexity of the order, customization, and the supplier’s production schedule. Generally, expect lead times of 4-12 weeks. For urgent needs, discuss expedited options with your supplier. Always confirm MOQs and lead times before finalizing your order to avoid potential delays in your project timeline. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of inline static mixers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, especially in international trade. Common practices include upfront payments, partial payments (e.g., 30% upfront, 70% upon delivery), and letters of credit for larger transactions. Consider using secure payment methods that provide buyer protection. Negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Always clarify the payment terms in the contract to prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How do I ensure the quality and certification of inline static mixers?
To ensure quality, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and relevant industry-specific certifications. Ask for test reports or quality assurance documentation that confirms the mixer’s performance under operational conditions. It’s also beneficial to visit the supplier’s facility or request samples for testing. Establishing a quality assurance protocol in the purchase agreement can further safeguard against receiving subpar products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing inline static mixers internationally?
Logistics are critical in international sourcing. Confirm shipping methods, costs, and estimated delivery times with your supplier. Understand the customs regulations and import duties applicable in your country, as these can significantly affect overall costs. Collaborate with a reliable freight forwarder who can manage documentation and ensure compliance with international shipping standards. Discuss the packaging to prevent damage during transit and specify whether you require insurance for high-value shipments. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers of inline static mixers?
Effective communication is key to preventing and resolving disputes. Always document all agreements, communications, and transactions to provide a clear record. If issues arise, address them directly with the supplier, seeking an amicable resolution. If necessary, refer to the dispute resolution clause in your contract, which may include mediation or arbitration. Consider involving legal counsel if the dispute escalates. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations in case of disagreements. -
What are the best practices for installation and maintenance of inline static mixers?
Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance of inline static mixers. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, ensuring correct orientation and alignment within the piping system. Regular maintenance is minimal due to the absence of moving parts, but periodic inspections are advisable to check for any buildup or blockages. Document maintenance activities and keep records of any operational issues. Training your staff on proper usage and troubleshooting can further enhance the longevity and efficiency of your mixers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for inline static mixer
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of inline static mixers presents significant advantages for international B2B buyers across diverse industries. By investing in high-quality static mixers, organizations can enhance operational efficiency through reduced chemical costs, lower energy consumption, and minimized maintenance needs. The versatility of these mixers allows them to adapt to various applications, including water treatment, chemical processing, and food production, making them essential for meeting industry-specific requirements.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of establishing strong supplier relationships cannot be overstated. Collaborating with experienced manufacturers ensures access to customized solutions tailored to unique operational challenges, while also benefiting from local support networks.
As the global market continues to evolve, the demand for efficient and sustainable mixing solutions will only grow. Now is the time to evaluate your current mixing technologies and consider the transition to inline static mixers. By doing so, you position your business to thrive in a competitive landscape, ensuring compliance with environmental standards and enhancing product quality. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and lead within your industry by prioritizing strategic sourcing today.