Unlock the Best Metal Stamping Die Solutions for Your
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal stamping die
In today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape, metal stamping dies play a pivotal role in shaping not only metal components but also the future of various industries. These essential tools are critical for producing high-quality parts used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods sectors. As global competition escalates, understanding the nuances of sourcing and utilizing metal stamping dies becomes increasingly vital for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the world of metal stamping dies, covering the diverse types and materials best suited for different applications. Buyers will gain insights into the latest manufacturing and quality control practices, ensuring they are equipped to select the right die for their production needs. Furthermore, a thorough analysis of suppliers will identify reputable manufacturers and distributors, helping buyers make informed sourcing decisions aligned with their budget constraints.
Additionally, the guide delves into cost factors and market trends, providing essential data that empowers buyers to negotiate effectively and optimize their procurement strategies. With a dedicated section addressing common FAQs, this resource is tailored to enhance operational efficiency and reduce production costs. By leveraging the insights within this guide, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of the global market for metal stamping dies, driving their businesses toward greater success.
Understanding metal stamping die Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progressive Dies | Multi-station design for sequential operations | Automotive, Appliances | Pros: High efficiency, reduced handling. Cons: Higher initial cost, complex setup. |
| Compound Dies | Single-station die performing multiple operations | Electronics, Aerospace | Pros: Simplifies production, reduces cycle time. Cons: Limited to specific tasks. |
| Transfer Dies | Transfers material between stations for complex shapes | Heavy Machinery, Automotive | Pros: Versatile for complex parts, high precision. Cons: Requires more space and maintenance. |
| Deep Draw Dies | Forms deep shapes by pulling metal into a die | Cookware, Automotive Components | Pros: Efficient for complex geometries, reduces waste. Cons: Higher tooling costs, longer lead times. |
| Blanking Dies | Cuts flat shapes from sheet material | Metal Fabrication, Construction | Pros: Cost-effective for high volumes. Cons: Limited to flat shapes, less flexibility. |
Progressive Dies
Progressive dies are designed with multiple stations, allowing for various operations such as cutting, punching, and bending to occur in one continuous process. This design is particularly beneficial for industries like automotive and appliances, where production efficiency is paramount. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the upfront investment against the long-term savings in labor and production costs, as well as the complexity of setup and maintenance.
Compound Dies
Compound dies operate within a single station but can perform multiple functions simultaneously, such as cutting and bending. This versatility makes them ideal for applications in electronics and aerospace, where precision and speed are critical. Buyers should consider the specific tasks their operations require, as these dies are optimized for particular processes, which may limit their applicability for broader manufacturing needs.
Transfer Dies
Transfer dies are engineered to move material through various stations, enabling the production of intricate parts. Commonly used in heavy machinery and automotive sectors, they offer high precision and versatility. Buyers should weigh the benefits of producing complex components against the need for additional space and maintenance, making these dies suitable for manufacturers focused on high-quality, detailed work.
Deep Draw Dies
Deep draw dies are specialized tools that pull a blank metal sheet into a die to create deep, complex shapes. This method is especially effective for producing items like cookware and automotive parts. While deep draw stamping can be more efficient than traditional methods, buyers should be mindful of the higher tooling costs and longer lead times associated with these dies, which may affect project timelines and budgets.
Blanking Dies
Blanking dies focus on cutting flat shapes from sheet material, making them ideal for high-volume applications in metal fabrication and construction. They are cost-effective for producing large quantities of flat components but are limited in their versatility. Buyers should assess their production requirements and consider whether the simplicity and efficiency of blanking dies align with their operational goals, especially if they need to produce more complex shapes.
Related Video: Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
Key Industrial Applications of metal stamping die
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal stamping die | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of chassis components | High precision and efficiency in mass production | Need for reliable suppliers with advanced technology and certifications. |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of structural components | Critical for safety and compliance with strict regulations | Suppliers must adhere to aerospace standards and provide traceability. |
| Electronics | Fabrication of connectors and housings | Cost-effective production with high repeatability | Focus on suppliers with experience in high-volume production and quality assurance. |
| Construction | Creation of metal brackets and supports | Durability and strength for structural integrity | Consider local suppliers to reduce shipping costs and lead times. |
| Consumer Goods | Production of household appliances and tools | Versatility in design and cost savings on high volumes | Evaluate suppliers for design capabilities and customization options. |
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, metal stamping dies are essential for producing chassis components, which require high precision and durability. This process enables manufacturers to achieve economies of scale by producing large quantities of identical parts efficiently. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who utilize advanced technologies and possess necessary certifications, ensuring quality and reliability. Additionally, understanding local regulations and standards in different regions, such as those in Europe or the Middle East, can enhance compliance and operational success.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies heavily on metal stamping dies for the production of structural components, including brackets and frames. These components must meet stringent safety and quality standards due to the critical nature of their application. Buyers in this sector should focus on suppliers that adhere to aerospace regulations and can provide documentation for traceability and quality assurance. The complexity of designs and the need for lightweight materials also necessitate collaboration with manufacturers experienced in aerospace applications.
Electronics Industry
In electronics, metal stamping dies are used to fabricate connectors, housings, and other intricate parts. This application requires high repeatability and precision, as even minor defects can lead to significant failures in electronic devices. International buyers must seek suppliers who specialize in high-volume production and have robust quality control measures in place. Additionally, understanding regional market demands and technological trends can help buyers identify the best sourcing strategies to optimize production costs.
Construction Industry
Metal stamping dies play a critical role in the construction sector by creating metal brackets and supports that provide structural integrity. These components must be durable and capable of withstanding various environmental conditions. Buyers should consider sourcing from local suppliers to minimize shipping costs and lead times, enhancing overall project efficiency. It’s also important to evaluate the supplier’s capacity to meet project timelines and specifications, particularly in regions with rapid construction growth.
Consumer Goods Industry
In the consumer goods sector, metal stamping dies are utilized to produce a variety of household appliances and tools. The versatility of metal stamping allows for the creation of complex designs while maintaining cost-effectiveness, especially in high-volume production scenarios. Buyers should assess suppliers for their design capabilities and willingness to customize products according to specific needs. Understanding market trends and consumer preferences in different regions can further guide buyers in making informed sourcing decisions.
Related Video: Progressive Metal Stamping Die with in line Deburring and Packaging
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal stamping die
When selecting materials for metal stamping dies, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that affect performance, durability, and cost. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in metal stamping dies, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Tool Steel
Key Properties: Tool steel is known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°F (315°C) and can handle significant pressure without deforming.
Pros & Cons: Tool steel is highly durable and can produce high-quality stamped parts. However, it can be expensive and requires complex manufacturing processes, including heat treatment. Its suitability for high-volume production makes it a preferred choice for automotive and aerospace applications.
Impact on Application: Tool steel is compatible with various media, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and durability. However, it may not be the best choice for corrosive environments without proper coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A681 or DIN 17350. It’s also essential to consider the availability of tool steel in local markets, as import costs can be significant.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It can withstand temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and is often used for low-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, making it easier to handle and reducing shipping costs. However, it has lower wear resistance compared to tool steel, which may limit its lifespan in high-volume applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for stamping parts that do not require extreme durability, such as consumer goods and some automotive components. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying grades of aluminum and their corresponding properties. Compliance with standards like JIS H4000 is crucial, especially in regions with strict material regulations.
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
Key Properties: HSS is designed to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness, making it suitable for high-speed applications. It can operate effectively at temperatures exceeding 1000°F (538°C).
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of HSS is its ability to maintain sharpness and precision over extended periods. However, it is more expensive than standard tool steel and requires careful handling to avoid chipping.
Impact on Application: HSS is particularly effective for high-speed stamping operations, such as those found in the automotive and electronics industries. Its high-temperature resistance makes it suitable for applications involving rapid production cycles.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with international standards like ASTM A600. Additionally, sourcing HSS may be more challenging in regions with limited access to specialized suppliers.
Carbide
Key Properties: Carbide is extremely hard and wear-resistant, capable of withstanding high pressures and temperatures. It can handle temperatures up to 2000°F (1093°C) and is ideal for high-stress applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of carbide is its exceptional durability and longevity, which can lead to lower replacement costs over time. However, it is brittle and can be prone to chipping, making it less suitable for certain applications.
Impact on Application: Carbide is particularly useful in industries requiring high precision and durability, such as aerospace and heavy machinery. Its resistance to wear makes it ideal for high-volume production environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that carbide dies comply with standards like ASTM B311. The cost of carbide can be high, so buyers should evaluate their production needs carefully to justify the investment.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal stamping die | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool Steel | Automotive, Aerospace | High durability and wear resistance | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer goods, Low-pressure applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower wear resistance | Medium |
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | High-speed stamping operations | Maintains sharpness over time | More expensive and requires careful handling | High |
| Carbide | Aerospace, Heavy machinery | Exceptional durability and longevity | Brittle and prone to chipping | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for metal stamping dies, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal stamping die
Manufacturing Processes for Metal Stamping Dies
The manufacturing of metal stamping dies is a multi-stage process that requires precision and expertise. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages is crucial to ensure they select the right suppliers capable of meeting their needs. Here’s an overview of the typical manufacturing process:
1. Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting the right materials, which are often high-carbon steels or tool steels, depending on the required durability and application. Material preparation includes:
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on their mechanical properties, such as hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. This decision impacts the die’s longevity and performance.
- Cutting and Shaping: Large sheets of metal are cut into manageable sizes through processes like shearing or laser cutting. This ensures that the material is prepared for further shaping.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the actual shaping of the die occurs. This can involve several key techniques:
- Machining: Processes like milling, turning, and grinding are used to create the precise shapes required for the die components. CNC machines are commonly employed for their accuracy and repeatability.
- Heat Treatment: Post-machining, the die components often undergo heat treatment to enhance hardness and wear resistance. This step is critical for ensuring the die can withstand the pressures of stamping operations.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, the next step is assembly. This involves:
- Fitting Components: Precision is essential when assembling the die. Components must fit together perfectly to ensure smooth operation during stamping.
- Alignment Checks: Proper alignment is critical for the die’s performance. Misalignment can lead to defects in stamped parts, so thorough checks are necessary.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the die’s surface quality and prepares it for use. Key activities include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as polishing, coating, or nitriding are applied to improve the die’s surface properties, reducing friction and enhancing durability.
- Final Inspection: A detailed inspection is performed to ensure that all specifications have been met, and the die is ready for production.
Quality Assurance Practices
For international B2B buyers, quality assurance (QA) is paramount. It ensures that the dies produced meet industry standards and customer expectations. Here are key aspects of QA in metal stamping die manufacturing:
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard focuses on quality management systems. Suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high-quality processes and continuous improvement.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application, additional certifications like CE (for products sold in the European Economic Area) or API (for the petroleum industry) may be necessary.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control checkpoints are essential at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to monitor the quality and ensure adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a final inspection is conducted to verify that the finished dies meet all required standards and specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods play a crucial role in quality assurance:
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools such as calipers and gauges to ensure that the die dimensions are within specified tolerances.
- Material Testing: Conducting hardness tests, tensile tests, and metallurgical examinations to confirm that the material properties meet requirements.
- Functional Testing: Running trial stamps to ensure the die performs correctly under production conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control measures:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers helps assess their quality management systems and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can provide insight into the supplier’s processes and performance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
Navigating QC Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is essential. Factors to consider include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that must be met. Familiarize yourself with local regulations to ensure compliance.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes toward quality and manufacturing practices can help in establishing effective communication and expectations with suppliers.
- Logistical Considerations: Consider how international shipping and logistics may impact quality control, including handling and transportation risks.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for metal stamping dies is crucial for international B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who uphold the highest standards of quality and reliability. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to the overall success of their manufacturing endeavors.
Related Video: Manufacturing Video – Progressive Die Stamping Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal stamping die Sourcing
In the competitive landscape of metal stamping die sourcing, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the primary cost components, price influencers, and actionable insights for negotiating better deals, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost of metal stamping dies. High-quality steel and specialized alloys may incur higher upfront costs but can enhance durability and performance. Buyers should assess material specifications based on their specific applications to avoid overpaying for unnecessary features.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and supplier. For instance, manufacturers in regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing. However, it’s essential to consider the skill level of the workforce, as experienced labor can lead to better quality and efficiency in die production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production facility, equipment maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturers often have streamlined operations that minimize overhead, allowing them to pass savings onto buyers.
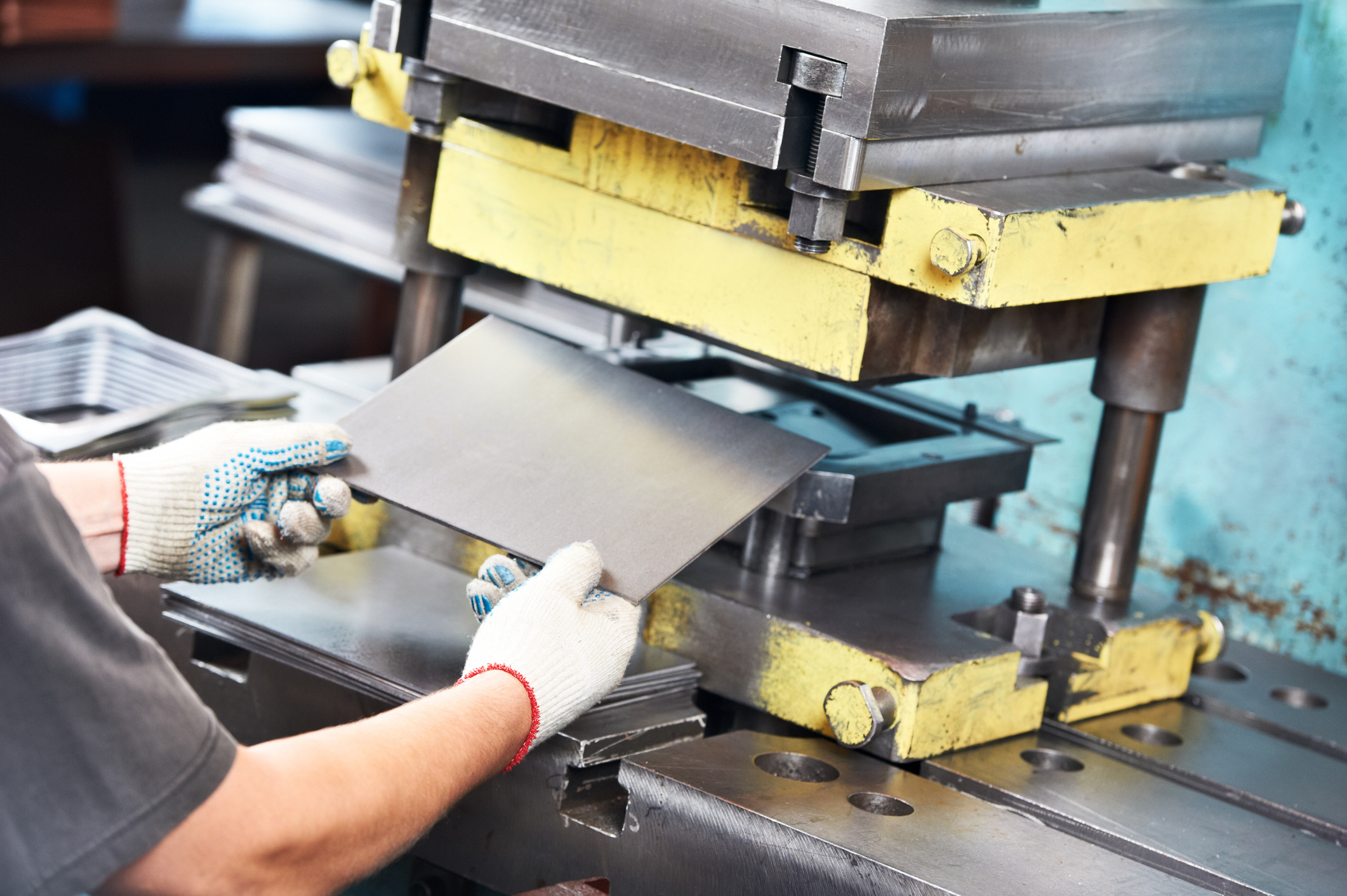

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tooling: Tooling costs encompass the initial investment in die design and production. Custom dies require more extensive tooling, which can elevate costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard dies.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures the dies meet required specifications and standards. While this may add to the cost, it mitigates risks associated with defective products, ultimately saving money in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the distance from the supplier, mode of transport, and Incoterms. Buyers should factor in these costs when comparing suppliers, particularly when sourcing from international markets.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the average margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better terms and identify suppliers who offer competitive pricing without compromising quality.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to discounts. Buyers should consider their production needs and explore the potential for bulk purchasing to reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom dies tailored to specific applications can significantly increase costs. Buyers must balance the need for customization with the potential for standard solutions that meet their requirements.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects initial costs but also long-term performance. Buyers should opt for materials that align with their production goals and environmental considerations.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers that comply with international quality standards may charge higher prices. However, investing in certified suppliers can lead to better quality assurance and lower failure rates.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but often offer better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should negotiate terms that align with their logistics capabilities and cost expectations.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your needs and the market landscape. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just initial costs. Consider factors such as maintenance, lifespan, and potential downtime when evaluating suppliers.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect overall costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these risks.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including reviews, certifications, and case studies. This due diligence can prevent costly mistakes and ensure high-quality sourcing.
Disclaimer
Prices for metal stamping dies can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The information provided serves as a general guideline, and buyers should conduct their own research and obtain specific quotes to ensure accurate pricing for their unique requirements.
Spotlight on Potential metal stamping die Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘metal stamping die’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal stamping die
When sourcing metal stamping dies, understanding critical technical properties and common trade terminology is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only facilitates informed purchasing decisions but also ensures that the dies meet the specific needs of various applications.
Essential Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of a stamping die, typically steel, dictates its strength, durability, and suitability for different stamping processes. Common grades include D2, A2, and S7, each offering varying hardness and wear resistance. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for achieving optimal performance and longevity, especially in high-volume production environments. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the die. In metal stamping, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring that the stamped parts fit together correctly and function as intended. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications can prevent costly errors and rework in manufacturing processes. -
Die Life
– Die life indicates the expected number of cycles a die can perform before it requires maintenance or replacement. A longer die life reduces downtime and maintenance costs, making it an important consideration for buyers looking to maximize productivity. Evaluating die life helps in calculating long-term operational costs. -
Die Design
– The design of a stamping die can significantly impact its efficiency and the quality of the stamped parts. Key design aspects include the complexity of the part being produced and the type of operations the die must perform (e.g., blanking, bending). Buyers should assess whether the die design aligns with their production capabilities and product specifications. -
Surface Finish
– The surface finish of a die affects the quality of the stamped part’s surface. Different finishes may be required based on the application, such as a smooth finish for aesthetic components or a rougher finish for parts requiring further processing. Understanding surface finish requirements is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets industry standards.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of metal stamping dies, buyers often work with OEMs to ensure that the dies meet specific requirements for their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ is important for budgeting and inventory management. Negotiating MOQs can lead to cost savings, especially for larger orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. When sourcing metal stamping dies, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, ultimately aiding in smoother logistics and procurement processes. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the buyer receives the product. For metal stamping dies, shorter lead times can significantly impact production schedules. Buyers should discuss lead times with suppliers to ensure timely delivery aligns with their operational needs.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing metal stamping dies more effectively, ensuring that their manufacturing processes are efficient and cost-effective.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the metal stamping die Sector
In the ever-evolving landscape of the metal stamping die sector, international B2B buyers must stay informed about market dynamics and sourcing trends to make strategic decisions. The global demand for metal stamping dies is driven by several factors, including the growth of the automotive and aerospace industries, where precision and efficiency are paramount. Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0, automation, and advanced manufacturing processes are reshaping sourcing practices. Buyers should be particularly aware of the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, which enhance predictive maintenance and quality control, ultimately reducing downtime and waste.
As competition intensifies, buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must also consider local market conditions, such as tariffs and trade agreements, which can impact sourcing costs. The rise of digital platforms for supplier discovery and procurement has simplified the sourcing process, allowing buyers to connect with a diverse range of manufacturers. Additionally, the trend toward just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing is leading companies to seek suppliers who can provide rapid turnaround times and flexibility in production volumes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of metal stamping die manufacturing is a crucial consideration for modern B2B buyers. As industries face increasing scrutiny over their carbon footprints, the demand for sustainable practices has surged. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to stringent environmental standards and offer transparency in their sourcing processes. This includes the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques that reduce waste and emissions.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with businesses seeking partners committed to fair labor practices and responsible supply chain management. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as benchmarks for evaluating potential suppliers. By aligning with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability, buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The metal stamping die industry has evolved significantly over the past century. Initially, stamping processes were labor-intensive and reliant on manual skills. However, technological advancements, including the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), revolutionized the industry. These tools enabled higher precision and efficiency in die production, paving the way for the complex geometrical components required in today’s manufacturing. As global supply chains expanded, the focus shifted toward optimizing production processes and ensuring quality control, leading to the sophisticated metal stamping die solutions available today. Understanding this evolution can provide B2B buyers with insights into the capabilities and innovations that modern suppliers can offer.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal stamping die
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for metal stamping dies?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and production capabilities. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific sector, such as automotive or aerospace. Verify certifications like ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management. Additionally, request references or case studies to understand their past projects and customer satisfaction levels. A thorough assessment of their manufacturing processes, technology, and workforce qualifications will ensure they meet your quality and delivery expectations. -
Can metal stamping dies be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for metal stamping dies to cater to unique specifications. Discuss your design requirements, including dimensions, material type, and production volume, during the initial consultations. Effective communication with your supplier is crucial, as it allows them to adapt their processes and tooling to meet your needs. Be prepared to share CAD files or prototypes to facilitate the design process, ensuring that the final product aligns perfectly with your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for metal stamping dies?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the die. Generally, you may encounter MOQs ranging from a few units for prototypes to hundreds for standard dies. Lead times also depend on the complexity of the design and the supplier’s workload; expect anywhere from a few weeks to several months. It’s essential to discuss these factors upfront to align your production schedules and avoid potential delays in your supply chain. -
What payment options are available for international B2B transactions involving metal stamping dies?
Payment methods for international transactions typically include wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect both parties, such as partial payments upfront and the balance upon delivery. Ensure that you understand the currency exchange implications and transaction fees associated with each method. Establishing clear payment terms in your contract can prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smoother transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for metal stamping dies?
To ensure quality, request detailed documentation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and certifications. Confirm that they adhere to international standards, such as ISO 9001 or specific industry-related certifications. Ask for samples or prototypes before placing a large order, and consider conducting an on-site audit if feasible. Additionally, establish a clear quality control agreement that outlines testing procedures, acceptance criteria, and recourse in case of defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing metal stamping dies internationally?
Logistics play a critical role in international sourcing. Assess the supplier’s ability to handle shipping, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Factor in transportation costs and potential duties or tariffs when evaluating overall expenses. Utilize reliable freight forwarders experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities. Additionally, consider the implications of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) on your responsibilities for shipping and insurance. -
How should I handle disputes or issues that arise with my metal stamping die supplier?
Establishing clear communication channels is essential for resolving disputes. Document all agreements and communications to provide a reference point in case of issues. If a dispute arises, first attempt to resolve it amicably through direct communication. If necessary, escalate the matter to a formal mediation or arbitration process as outlined in your contract. Including specific terms regarding dispute resolution in your agreement can streamline this process and minimize disruptions. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with metal stamping die suppliers?
Building a strong relationship with your suppliers involves consistent communication, transparency, and mutual respect. Regularly engage with them to discuss performance, feedback, and future needs. Consider conducting periodic reviews to assess their capabilities and address any concerns proactively. Additionally, fostering collaboration on design improvements or cost-saving measures can strengthen the partnership. A reliable supplier relationship can lead to better pricing, priority service, and enhanced innovation over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal stamping die
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing of metal stamping dies is essential for optimizing production efficiency and quality. By understanding the various types of dies—such as progressive, compound, transfer, single-operation, and blanking—international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Key takeaways include recognizing the importance of die selection based on specific applications, evaluating supplier capabilities, and considering long-term cost implications.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate this intricate sourcing process, prioritizing relationships with reputable manufacturers and understanding market trends will enhance their competitive edge. The emphasis on quality control, technological advancements, and cost management will further drive operational success.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative metal stamping solutions will continue to grow, propelled by advancements in automation and manufacturing technologies. B2B buyers are encouraged to remain agile and proactive in their sourcing strategies, leveraging this guide to explore new opportunities and partnerships that will lead to sustainable growth and increased market share.