Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing 3 Phase Transformer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3 phase transformer
Navigating the global market for 3-phase transformers is essential for businesses that rely on efficient and reliable power distribution. As the backbone of the electrical industry, these transformers are crucial for managing the increasing demands of modern infrastructure, especially in regions experiencing rapid industrial growth such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The ongoing transformer supply chain crisis, marked by unprecedented lead times and rising costs, underscores the need for informed sourcing strategies.
This comprehensive guide offers B2B buyers a detailed exploration of 3-phase transformers, covering a variety of types and configurations, including their construction and materials. It delves into manufacturing processes and quality control measures that ensure product reliability and longevity. Buyers will also find insights into the current market landscape, including key suppliers, pricing trends, and the factors influencing costs.
Furthermore, the guide addresses common questions and challenges faced by international buyers, providing actionable insights to navigate the complexities of procurement in a volatile market. By empowering decision-makers with this knowledge, we aim to facilitate strategic sourcing decisions that not only meet operational needs but also align with broader energy goals, such as decarbonization and infrastructure modernization. Whether you’re in the energy sector or supporting industries like manufacturing and transportation, this guide is an invaluable resource for optimizing your transformer sourcing strategy.
Understanding 3 phase transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta-Wye Transformer | Combines Delta and Wye configurations; provides phase shift | Industrial power distribution | Pros: High efficiency, reduced harmonics; Cons: More complex installation |
| Wye-Wye Transformer | Both primary and secondary windings are in Wye; no phase shift | Renewable energy applications | Pros: Balanced load, good for neutral grounding; Cons: Less effective for unbalanced loads |
| Delta-Delta Transformer | Both primary and secondary windings are in Delta; no neutral connection | Heavy industrial machinery | Pros: High short-circuit current capability; Cons: Poor voltage regulation |
| Autotransformer | Single winding acts as both primary and secondary; compact design | Railways, electric traction systems | Pros: Smaller and lighter; Cons: Limited voltage transformation ratio |
| Isolation Transformer | Separates primary and secondary circuits; enhances safety | Medical equipment, sensitive electronics | Pros: Reduces noise and interference; Cons: Typically more expensive |
Delta-Wye Transformer
The Delta-Wye transformer configuration combines the advantages of both Delta and Wye setups. It provides a phase shift, which is beneficial for balancing loads in industrial power distribution. This type is particularly suitable for applications requiring efficient power transfer and reduced harmonic distortion. B2B buyers should consider installation complexity and the need for additional equipment, such as protective relays, which may increase overall costs.
Wye-Wye Transformer
In a Wye-Wye transformer, both the primary and secondary windings are connected in Wye configuration. This design is particularly effective for renewable energy applications, as it offers balanced loading and excellent neutral grounding. B2B buyers should evaluate the load conditions, as this type may struggle with unbalanced loads. However, its operational stability and reliability make it a favored choice in many sectors.
Delta-Delta Transformer
The Delta-Delta transformer is characterized by both primary and secondary windings being in a Delta configuration. This type is ideal for heavy industrial machinery where high short-circuit current capabilities are necessary. While it offers strong performance, B2B buyers should be mindful of its limitations in voltage regulation, which can affect sensitive equipment. The lack of a neutral connection may also necessitate additional considerations during installation.
Autotransformer
An autotransformer uses a single winding that serves as both the primary and secondary, making it a compact and cost-effective option. This design is commonly used in railways and electric traction systems where space and weight are critical factors. B2B buyers should assess the voltage transformation ratio, as it is limited compared to other transformer types. However, the reduced size and weight can lead to lower transportation and installation costs.
Isolation Transformer
Isolation transformers are designed to separate the primary and secondary circuits, enhancing safety and reducing electrical noise. They are particularly valuable in medical and sensitive electronic applications where interference can lead to operational issues. B2B buyers should be prepared for a higher upfront investment, as these transformers tend to be more expensive. However, their ability to provide cleaner power and increase safety makes them a worthwhile consideration for critical applications.
Related Video: 3-phase Transformer Connections | Star-to-Star, Delta-to-Delta, Star-to-Delta & Delta-to-Star
Key Industrial Applications of 3 phase transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3 Phase Transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Integration with solar and wind energy systems | Enhances grid stability and energy distribution efficiency | Ensure compatibility with renewable energy systems and regulatory compliance in local markets. |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Power supply for heavy machinery and production lines | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Focus on durability and capacity to handle peak loads; consider local service and maintenance options. |
| Transportation | Electrification of rail systems | Supports sustainable transport and reduces emissions | Evaluate transformer size and weight for installation; consider local infrastructure compatibility. |
| Data Centers | Power distribution for IT infrastructure | Ensures reliable power supply, crucial for uptime | Look for transformers with high efficiency ratings and cooling solutions to manage heat. |
| Mining and Metals | Power supply for extraction and processing equipment | Increases productivity and operational reliability | Assess ruggedness for harsh environments and compliance with safety standards. |
Renewable Energy
3-phase transformers play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid. They facilitate the transformation of voltage levels, enabling efficient energy distribution from generation sites to consumption points. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America where renewable projects are booming, it is essential to source transformers that comply with local regulations and are compatible with existing grid infrastructure. Additionally, buyers should consider the need for advanced monitoring and control systems to enhance operational efficiency.
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial manufacturing, 3-phase transformers provide power to heavy machinery and production lines, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. They help in managing large electrical loads and improving overall productivity. Buyers from Europe, particularly in manufacturing hubs like Germany and Italy, should prioritize transformers that can withstand high operational demands and offer robust after-sales support. Sourcing considerations include evaluating the manufacturer’s reputation for reliability and the availability of local technical support.
Transportation
The electrification of rail systems is increasingly reliant on 3-phase transformers to manage the power supply needed for trains. These transformers ensure that the electrical systems operate efficiently, thereby supporting sustainable transport initiatives. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is vital to assess the size and weight of transformers to ensure they fit within existing infrastructure. Furthermore, compliance with international safety and environmental standards is critical to avoid potential regulatory issues.
Data Centers
Data centers require a consistent and reliable power supply, where 3-phase transformers are instrumental in distributing electricity to critical IT infrastructure. These transformers help in maintaining uptime and preventing outages, which is essential for businesses that rely heavily on digital services. Buyers, particularly in Europe, should focus on sourcing high-efficiency transformers that can handle the increasing power demands of modern data centers while providing effective cooling solutions to manage heat generation.
Mining and Metals
In the mining and metals sector, 3-phase transformers are used to power extraction and processing equipment. They ensure a steady supply of electricity, which is crucial for maintaining high productivity levels in challenging environments. Buyers in Africa and South America should consider the ruggedness and durability of transformers, given the harsh conditions often found in mining operations. Additionally, compliance with safety and environmental regulations is paramount to ensure operational sustainability and avoid legal complications.
Related Video: How to install a 3-Phase Transformer | Maddox Industrial Transformer
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3 phase transformer
When selecting materials for 3-phase transformers, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of their products. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of 3-phase transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for different global markets.
1. Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel (GOES)
Key Properties: GOES is characterized by its high magnetic permeability and low core losses, making it ideal for transformer cores. It operates effectively at elevated temperatures and is designed to minimize energy losses during operation.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of GOES is its efficiency in reducing energy losses, which is crucial for transformer performance. However, it is relatively expensive compared to non-oriented steels, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring precise control over the grain orientation.
Impact on Application: GOES is particularly suited for applications where energy efficiency is paramount, such as in renewable energy integration and high-capacity transformers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe, particularly Germany and Italy, may prioritize GOES due to stringent energy efficiency regulations. Compliance with standards such as DIN EN 10106 is essential.
2. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and is highly durable under various operational stresses.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances transformer efficiency. However, the rising cost of copper can be a significant drawback, especially in regions where prices fluctuate due to market conditions.
Impact on Application: Copper is widely used in windings and connections within transformers, making it suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and reliability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and South America should be aware of local copper availability and pricing trends. Compliance with ASTM B170 standards for copper wire may also be relevant.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum has good electrical conductivity, is lightweight, and exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion. Its lower melting point compared to copper allows for easier manufacturing processes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness, as it is generally cheaper than copper. However, its lower conductivity means that larger cross-sectional areas are required to achieve the same performance, which can lead to increased size and weight of the transformer.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in lower-capacity transformers or in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in mobile or portable systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East may favor aluminum due to its cost benefits, but they should also consider the implications for transformer size and weight. Compliance with JIS standards for aluminum components is also important.
4. Insulating Materials (e.g., Polypropylene, Epoxy Resins)
Key Properties: Insulating materials are crucial for transformer performance, providing electrical insulation and thermal stability. They can withstand high temperatures and have excellent dielectric strength.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of modern insulating materials is their ability to enhance transformer safety and reliability. However, they can add to the overall cost and complexity of manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Insulating materials are essential in ensuring the safe operation of transformers, especially in high-voltage applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure that insulating materials comply with IEC standards for electrical insulation.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3 phase transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel | Transformer cores | High efficiency, low core losses | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | Windings and connections | Superior conductivity | Rising costs, market volatility | High |
| Aluminum | Lower-capacity transformers | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower conductivity, larger size | Medium |
| Insulating Materials | Electrical insulation | Enhanced safety and reliability | Increased cost and complexity | Medium to High |
This guide provides a foundational understanding of material selection for 3-phase transformers, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific market needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3 phase transformer
The manufacturing of 3-phase transformers is a complex process that requires precision, quality assurance, and adherence to international standards. B2B buyers need to understand these processes thoroughly to make informed purchasing decisions. Below, we delve into the key stages of manufacturing, quality control measures, and how buyers can verify supplier reliability.
Manufacturing Processes
Material Preparation
The manufacturing of 3-phase transformers begins with material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. The main components include:
- Electrical Steel: Grain-oriented electrical steel (GOES) is critical for transformer cores due to its magnetic properties. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers provide GOES that meets the required specifications to minimize losses.
- Copper or Aluminum Windings: The choice between copper and aluminum affects efficiency and cost. Copper is more conductive but costlier, while aluminum is lighter and cheaper.
- Insulation Materials: High-quality insulation is essential for safety and performance. Common materials include paper, resin, and various polymers.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This includes:
- Core Manufacturing: The core is constructed from laminated steel sheets to reduce eddy current losses. The laminating process typically involves stacking and bonding sheets to achieve the desired magnetic properties.
- Winding: The windings are created using automated machines that precisely layer copper or aluminum wire around the core. This step is critical for ensuring that the transformer can handle the required voltage and current.
Assembly
In the assembly stage, the core and windings are combined, and other components are added. This involves:
- Mounting the Core and Windings: The core is placed into a tank or housing, and the windings are securely attached.
- Adding Insulation and Cooling Systems: Insulation is applied to prevent electrical leakage, and cooling systems (like oil or air) are integrated to manage heat during operation.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves:
- Testing: Each transformer undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This includes electrical tests, insulation resistance testing, and thermal imaging.
- Painting and Coating: The exterior is painted or coated to protect against environmental factors and corrosion.
Quality Assurance
Ensuring quality in the manufacturing process is critical for the reliability and longevity of 3-phase transformers. International and industry-specific standards play a significant role in this.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems. Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 are more likely to maintain consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Essential for European markets, CE marking indicates that the product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For transformers used in oil and gas sectors, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically structured around several key checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive inspection ensures that the transformer meets all specifications and standards.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of transformers:
- Dielectric Testing: This checks the insulation quality to prevent electrical failures.
- Transformer Turns Ratio (TTR) Testing: This ensures the transformer is correctly configured and operates efficiently.
- Load Testing: Simulating operational conditions to ensure the transformer performs under expected loads.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can reveal their adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request audit reports and certifications.
- Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation outlining their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide unbiased verification of the supplier’s quality control measures.
- Review Certifications: Ensure that suppliers hold relevant certifications (ISO, CE, API) and check their validity.
QC/Cert Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with suppliers across different regions:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should be familiar with local laws and standards in their purchasing regions.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the business culture in regions such as Africa and the Middle East can help in negotiations and relationship-building with suppliers.
- Logistical Considerations: Lead times can vary significantly due to local supply chain issues. Buyers should account for these when planning orders, especially in light of the current transformer supply chain crisis.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures of 3-phase transformers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material quality, manufacturing stages, and robust quality control mechanisms, buyers can ensure they procure reliable transformers that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Transformer Testing | Transformer Testing and their Procedure
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3 phase transformer Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for sourcing 3-phase transformers is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various cost components and price influencers can significantly enhance sourcing strategies and decision-making processes.
Cost Components of 3-Phase Transformers
-
Materials: The primary materials required for 3-phase transformers include grain-oriented electrical steel (GOES), copper, and insulation materials. Fluctuations in raw material prices have seen costs increase by 60% to 80% since early 2020, primarily due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand for electrical components.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality. Skilled labor is essential for producing high-quality transformers, so it’s essential to balance cost with expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with facilities, equipment depreciation, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, leading to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for tooling can be substantial, particularly for customized transformers. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating quotes, as they can significantly impact the overall price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are vital for ensuring product reliability and compliance with industry standards. Investing in QC can lead to higher upfront costs but can save money in the long run by reducing failures and warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical factors, especially for international buyers. The choice of Incoterms can greatly influence these costs, and understanding the logistics involved in shipping large, heavy transformers is essential.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market conditions and competition. Buyers should be aware of typical margins in their region to negotiate effectively.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often qualify for bulk discounts, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized transformers may incur additional costs for design and manufacturing. Clear specifications can help avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Transformers that meet specific international quality standards or certifications may have higher prices. However, these standards often ensure better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact total landed costs. Understanding terms like FOB, CIF, and DDP can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate terms and pricing. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially if they are eager to secure a contract.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the purchase price. Consider installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the lifespan of the transformer to make informed decisions.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about global market trends affecting transformer pricing, such as commodity prices and supply chain dynamics. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. It may also provide better service and support.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs. This transparency allows for easier comparisons and better decision-making.
Disclaimer
Prices for 3-phase transformers can vary widely based on numerous factors and market conditions. The information provided here is for indicative purposes only and should not be considered a fixed price guide. Always request updated quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential 3 phase transformer Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘3 phase transformer’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3 phase transformer
When engaging in the international B2B market for 3-phase transformers, understanding essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below is a comprehensive overview tailored for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Technical Properties of 3-Phase Transformers
-
Material Grade
The quality of materials used in the construction of a transformer significantly influences its efficiency and lifespan. Common materials include grain-oriented electrical steel for the core and copper or aluminum for windings. Higher-grade materials can reduce energy losses and improve operational performance, which is critical for businesses aiming for sustainability and cost-effectiveness. -
Rated Power (kVA)
This specification indicates the transformer’s capacity to handle electrical load. It is essential for buyers to select a transformer with a rated power that meets or exceeds their operational requirements. Underestimating power needs can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and potential equipment failure. -
Voltage Rating
This refers to the voltage levels at which the transformer can operate safely and effectively. Understanding the input and output voltage ratings is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems. This knowledge helps prevent costly mistakes in installation and operation. -
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings, often expressed as a percentage, indicate how much of the input power is effectively converted to output power. High-efficiency transformers can lead to significant cost savings over time due to reduced energy consumption. Buyers should prioritize transformers with higher efficiency ratings, especially in regions where electricity costs are high. -
Cooling Method
Transformers can be air-cooled (natural or forced) or oil-cooled. The choice of cooling method affects the transformer’s performance and maintenance needs. For instance, oil-cooled transformers generally have a higher capacity and are more suitable for high-load applications, making them a preferred choice for industrial settings. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the acceptable range of deviation from the specified values, such as voltage and current. Understanding tolerance levels is crucial for ensuring the transformer operates within safe limits. Buyers should consider transformers with tighter tolerances to minimize the risk of equipment damage and operational inefficiencies.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or equipment that are then marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources of high-quality transformers and components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products. Submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and terms from multiple vendors, facilitating better negotiation and procurement decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined commercial terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics, costs, and risks associated with shipping and delivery. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Given the current supply chain challenges, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and operational continuity. Buyers should factor in potential delays when scheduling projects. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period specifies the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects. A longer warranty period can indicate higher confidence in product quality and provide buyers with peace of mind regarding their investment.
In summary, grasping these technical properties and trade terms is essential for international B2B buyers of 3-phase transformers. Knowledge in these areas not only facilitates informed decision-making but also enhances negotiation capabilities and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the 3 phase transformer Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for 3-phase transformers is currently experiencing significant shifts driven by various factors. Key among these is the accelerated transition to renewable energy sources, which has prompted a surge in demand for transformers capable of integrating with new grid technologies. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for energy independence and sustainability, the need for reliable and efficient power transmission systems has never been greater. The average lead times for transformers have ballooned to 115-210 weeks, creating pressure on manufacturers to innovate and expand capacity.
Emerging trends include the adoption of digital technologies and smart grid solutions, enhancing operational efficiency and providing real-time data for better decision-making. International buyers should be aware of the growing importance of advanced transformer designs that support higher voltage ratings and larger capacities, especially in urban development and industrial applications. Furthermore, with the rise of electric vehicles and increased electrification across sectors, the demand for robust transformer solutions is expected to remain strong.
Sourcing strategies are also evolving. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer not only competitive pricing but also shorter lead times and flexible manufacturing options. Partnerships with local manufacturers can mitigate supply chain disruptions, especially in regions where logistics can be challenging. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate resilience and adaptability in their operations.
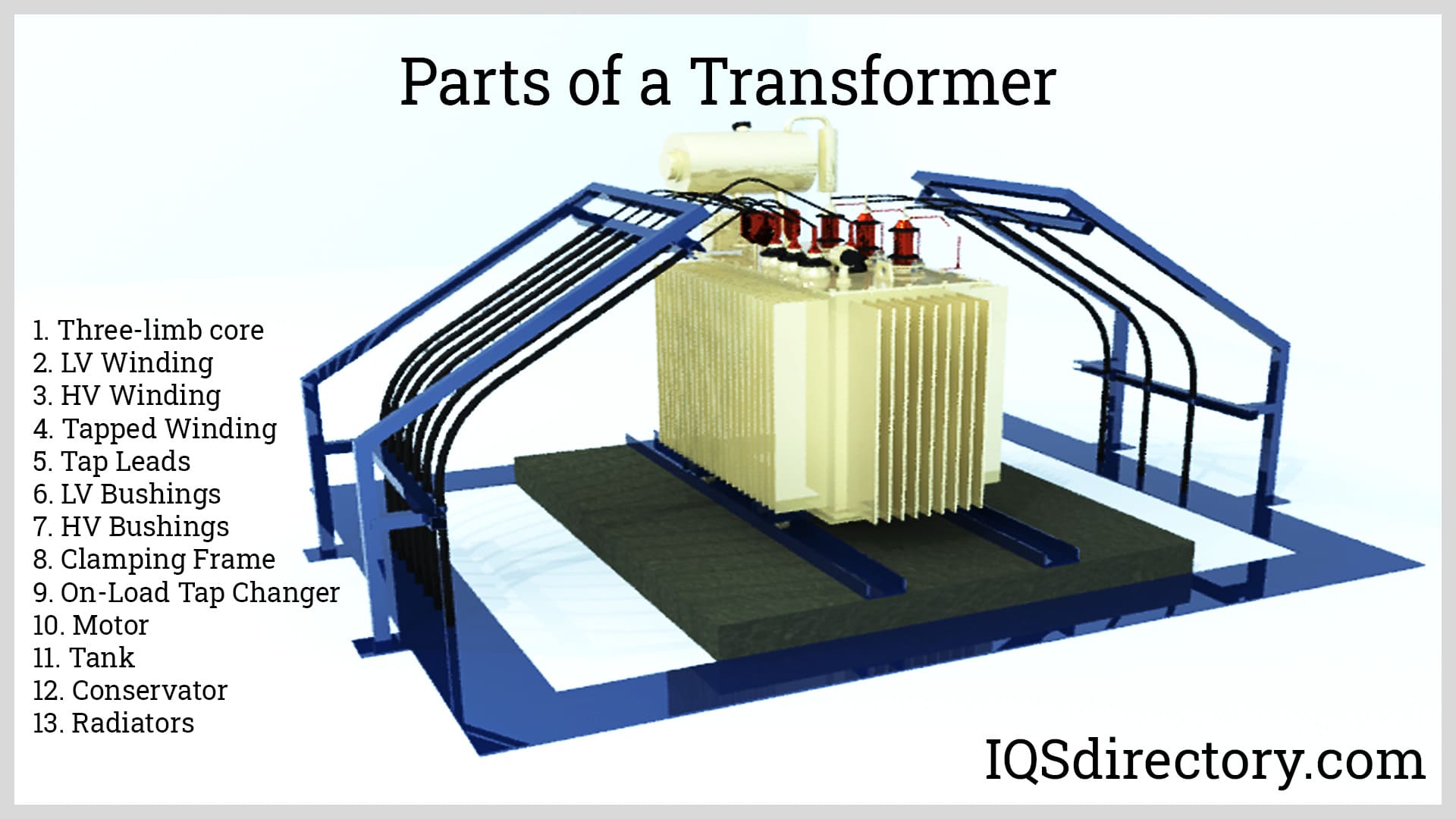
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has emerged as a crucial consideration in the procurement of 3-phase transformers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, from raw material extraction to waste management, must be evaluated. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, ensuring that their operations minimize carbon footprints and comply with local and international environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is also paramount. Buyers should seek out suppliers that implement responsible sourcing policies, particularly regarding materials such as copper and grain-oriented electrical steel. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to the Responsible Minerals Initiative can provide assurance that the supply chain is ethical and sustainable. Additionally, the integration of recycled materials in transformer production can further enhance sustainability efforts.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications into procurement processes not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust. For buyers in Europe, especially in countries like Germany and Italy, demonstrating commitment to sustainability can be a significant competitive advantage in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Brief Evolution/History
The 3-phase transformer has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century. Originally developed to facilitate efficient power transmission over long distances, its design has continually adapted to meet the demands of modern electrical systems. The introduction of advanced insulation materials and cooling technologies has enabled transformers to support higher capacities and voltages, essential for today’s energy-intensive applications.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards enhancing energy efficiency and integrating renewable energy sources. The transition from fossil fuels to sustainable energy has prompted innovations in transformer technology, such as the development of smart transformers equipped with digital monitoring capabilities. This evolution reflects the ongoing need for reliable, efficient, and sustainable power solutions in a rapidly changing energy landscape, making it essential for international buyers to stay informed about these advancements.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3 phase transformer
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of 3-phase transformers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and experience in producing 3-phase transformers. Request references from previous clients and verify their capacity to meet your specific needs, including customization options. Additionally, assess their financial stability and the robustness of their supply chain, especially in light of current global shortages. Conducting factory visits or audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. -
Can I customize a 3-phase transformer to suit my specific needs?
Yes, most manufacturers offer customization options for 3-phase transformers, including voltage ratings, power capacity, and specific insulation materials. Clearly outline your requirements during initial discussions to ensure the supplier can accommodate your needs. Customization may affect lead times and costs, so it’s crucial to have these details clarified early in the negotiation process. Always request a detailed proposal that includes specifications, timelines, and pricing for any custom features. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering 3-phase transformers?
Currently, lead times for 3-phase transformers can range from 120 to 210 weeks, significantly longer than pre-pandemic averages of 30 to 60 weeks. This increase is due to heightened demand, supply chain disruptions, and rising raw material costs. When planning your procurement, account for these extended lead times and discuss potential delivery schedules with your supplier. Consider placing orders well in advance to mitigate project delays. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 3-phase transformers?
The MOQ for 3-phase transformers varies by manufacturer and can depend on factors such as transformer specifications and customization needs. Typically, MOQs can range from a few units to several dozen. Always inquire about the MOQ during initial discussions and assess whether it aligns with your project requirements. Be aware that lower MOQs may result in higher unit costs, while larger orders could provide cost savings. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 3-phase transformers?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include a deposit upon order confirmation and the balance due prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit, especially for large orders. Negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s security. Always review the payment terms in the context of the total cost, including shipping and any potential tariffs for international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance certifications for 3-phase transformers?
Request documentation of quality assurance practices and compliance certifications from your supplier. Key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 and relevant industry standards such as IEC or ANSI. Additionally, inquire about their testing procedures and whether they conduct third-party inspections. Establishing clear quality expectations in your purchase agreement can help ensure that the transformers meet your operational requirements. -
What logistical considerations should I be aware of when importing 3-phase transformers?
Importing 3-phase transformers involves several logistical considerations, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Work with your supplier to understand the best shipping options that balance cost and delivery speed. Additionally, ensure you are aware of the import requirements in your country, including any necessary documentation. Engaging a logistics partner experienced in heavy equipment can facilitate smoother transportation and compliance. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding 3-phase transformers?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear communication channels and protocols in your contract. Include clauses that outline how disputes will be resolved, such as mediation or arbitration. If issues arise, document all communications and attempts at resolution. Engaging legal counsel familiar with international trade can provide guidance on your rights and obligations, ensuring you navigate disputes effectively while maintaining the supplier relationship.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3 phase transformer
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of 3-phase transformers is essential for international B2B buyers navigating a complex and evolving landscape. The ongoing transformer supply chain crisis, characterized by unprecedented lead times and rising costs, necessitates a proactive approach to procurement. By understanding market dynamics, buyers can leverage relationships with manufacturers and suppliers to secure competitive pricing and ensure timely delivery.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand Market Trends: Stay informed about supply chain challenges and market demands, particularly the impacts of increased renewable energy projects and aging infrastructure.
- Build Strong Supplier Relationships: Cultivate partnerships with reliable manufacturers to enhance flexibility in sourcing and potentially mitigate long lead times.
- Focus on Quality and Innovation: Prioritize suppliers that invest in advanced technologies and sustainable practices, ensuring long-term reliability and efficiency of transformers.
As we move forward, the need for robust and resilient power solutions will only intensify. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to act decisively, aligning their sourcing strategies with emerging trends. By doing so, they can position themselves advantageously in the global market and contribute to a sustainable energy future.