Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Alumina Ceramic
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for alumina ceramic
Alumina ceramic has become a cornerstone material in various industries due to its exceptional properties, including high hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. These characteristics make it indispensable in applications ranging from electronics and aerospace to healthcare and automotive sectors. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the dynamics of the alumina ceramic market is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of alumina ceramic, providing insights into various types, materials, and manufacturing processes. We will explore quality control measures that ensure product reliability, identify leading suppliers across different regions, and discuss cost factors that influence procurement strategies. Additionally, the guide will analyze market trends and forecasts, helping buyers anticipate shifts that could impact their sourcing decisions.
By leveraging the information presented here, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the global alumina ceramic market with confidence. Whether you are sourcing for production needs or seeking innovative solutions to enhance your product offerings, this guide empowers you to make strategic choices that align with your business goals. Understanding these elements will not only streamline your procurement process but also enhance your competitive edge in an increasingly dynamic marketplace.
Understanding alumina ceramic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Alumina | Contains over 99.5% alumina; excellent chemical resistance | Electronics, Aerospace, Biomedical | Pros: High performance; Cons: Higher cost |
| Spherical Alumina | Uniform spherical shape; ideal for advanced applications | Additives in ceramics, Catalysts, Coatings | Pros: Enhanced flowability; Cons: Limited supply |
| Alumina Ceramics | Good hardness and wear resistance; versatile | Industrial machinery, Automotive, Electrical Insulation | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited thermal resistance |
| Porous Alumina | Features interconnected porosity; lightweight | Filtration, Catalysis, Insulation | Pros: Lightweight and customizable; Cons: Lower mechanical strength |
| Dense Alumina | High density and strength; excellent thermal stability | Cutting tools, Wear parts, High-temperature applications | Pros: Superior durability; Cons: Heavier and more expensive |
High-Purity Alumina
High-purity alumina typically contains over 99.5% alumina, making it an ideal choice for applications that require superior chemical resistance and mechanical properties. This type is particularly suited for sectors like electronics and aerospace, where precision and reliability are critical. B2B buyers should consider the higher cost associated with high-purity alumina, which is justified by its exceptional performance and durability in demanding environments.
Spherical Alumina
Spherical alumina features a uniform spherical shape, which enhances its flowability and packing density. This type is commonly used as an additive in ceramics, catalysts, and coatings, making it essential in advanced manufacturing processes. When purchasing spherical alumina, buyers should evaluate supplier capabilities, as the production process can limit availability. The enhanced flowability can lead to improved efficiency in production, offsetting potential sourcing challenges.
Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics are known for their good hardness and wear resistance, making them versatile across various industries, including automotive and electrical insulation. Buyers often appreciate the cost-effectiveness of alumina ceramics, as they provide a balance between performance and price. However, they may have limited thermal resistance, which is an essential consideration for applications involving high temperatures.
Porous Alumina
Porous alumina is characterized by its interconnected porosity, making it lightweight and suitable for applications like filtration and catalysis. Its customizable nature allows B2B buyers to specify pore size and distribution to meet particular application needs. While the lightweight design is a significant advantage, buyers should be aware of its lower mechanical strength, which may limit its use in high-stress environments.
Dense Alumina
Dense alumina is known for its high density and strength, making it an excellent choice for cutting tools and wear parts in high-temperature applications. Its thermal stability is a key feature that appeals to industries such as aerospace and manufacturing. While dense alumina offers superior durability, B2B buyers should consider the increased weight and cost, which may impact overall project budgets and logistics.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of alumina ceramic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alumina ceramic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Engine components and thermal barriers | High strength and thermal stability, essential for high-performance applications | Certification standards, sourcing from reliable suppliers, and quality assurance processes |
| Healthcare | Dental implants and prosthetics | Biocompatibility and durability, leading to better patient outcomes | Compliance with medical regulations, consistent supply chains, and traceability of materials |
| Electronics | Substrates for electronic circuits | Excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity, enhancing device performance | Precision manufacturing capabilities and adherence to international quality standards |
| Automotive | Wear-resistant components (e.g., brake pads) | Improved durability and safety, reducing maintenance costs | Supplier reliability, material specifications, and performance testing data |
| Industrial Equipment | Cutting tools and wear parts | Increased lifespan and efficiency, resulting in lower operational costs | Material sourcing quality, customization options, and delivery timelines |
Aerospace & Defense
In the aerospace and defense sectors, alumina ceramic is used in engine components and thermal barriers due to its exceptional strength and thermal stability. These characteristics are critical for components that operate under extreme conditions. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, should ensure that their suppliers meet stringent certification standards and maintain robust quality assurance processes to guarantee the reliability of these critical components.
Healthcare
Alumina ceramic plays a vital role in the healthcare industry, particularly in dental implants and prosthetics. Its biocompatibility and durability not only enhance the performance of these medical devices but also contribute to better patient outcomes. Buyers in this sector must prioritize compliance with medical regulations and ensure that their suppliers can provide consistent supply chains and traceability for materials, particularly when sourcing from different regions such as South America and Europe.
Electronics
In electronics, alumina ceramic is predominantly used as substrates for electronic circuits, leveraging its excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. This application significantly enhances device performance and reliability. International B2B buyers should focus on suppliers with precision manufacturing capabilities and adherence to international quality standards to ensure that the components meet their technical specifications.
Automotive
The automotive industry utilizes alumina ceramic in wear-resistant components such as brake pads. The material’s durability and performance improvements lead to reduced maintenance costs and enhanced safety. Buyers should consider supplier reliability and material specifications, as well as request performance testing data to verify the effectiveness of these components in real-world applications.
Industrial Equipment
Alumina ceramic is essential in industrial equipment for manufacturing cutting tools and wear parts. Its ability to withstand harsh conditions increases the lifespan and efficiency of these tools, ultimately lowering operational costs. When sourcing, businesses should evaluate the quality of material sourcing, customization options, and delivery timelines to ensure they meet their production needs effectively.
Related Video: How to Make Alumina Ceramic Industrial Parts
Strategic Material Selection Guide for alumina ceramic
When selecting materials for alumina ceramic applications, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in alumina ceramics, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, impact on applications, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. High-Purity Alumina (99.5% Al2O3)
Key Properties:
High-purity alumina offers excellent thermal stability, high mechanical strength, and superior corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 1650°C and is highly resistant to chemical attack from acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of high-purity alumina makes it ideal for demanding applications, but it comes at a higher manufacturing cost. The complexity of processing this material can also lead to longer lead times for production.
Impact on Application:
This material is particularly suitable for applications requiring high thermal and chemical resistance, such as in electronics and aerospace components. However, it may not be the best choice for applications involving abrasive environments due to its brittleness.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. Additionally, sourcing from certified suppliers can mitigate risks associated with material quality.
2. Alumina-Titania Composite
Key Properties:
Alumina-titania composites combine the properties of both materials, resulting in improved toughness and thermal stability. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 1400°C and offer enhanced wear resistance.
Pros & Cons:
These composites are generally more cost-effective compared to high-purity alumina while providing better toughness. However, they may not achieve the same level of chemical resistance, which can limit their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for applications in the automotive and manufacturing sectors, alumina-titania composites are suitable for components exposed to wear and thermal cycling. Their moderate cost makes them attractive for mass production.
Considerations for Buyers:
International buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to local and international quality standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations such as Europe and North America.
3. Spherical Alumina
Key Properties:
Spherical alumina features a unique shape that enhances flowability and packing density, making it ideal for applications in advanced ceramics and composites. It maintains high thermal stability and can withstand temperatures up to 1600°C.
Pros & Cons:
The spherical shape allows for improved processing and performance in applications like 3D printing and advanced coatings. However, the production process can be more complex and costly compared to traditional alumina forms.
Impact on Application:
Spherical alumina is particularly beneficial in industries like electronics and automotive for applications requiring fine-tuned material properties. Its unique shape can improve the performance of composite materials.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers must consider logistics and sourcing strategies, especially when importing from regions with limited local suppliers. Compliance with international standards is also critical to ensure product quality.
4. Alumina-Zirconia Composite
Key Properties:
Alumina-zirconia composites exhibit exceptional toughness and wear resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1500°C. The addition of zirconia enhances the material’s fracture toughness significantly.
Pros & Cons:
These composites offer a balance between cost and performance, making them suitable for high-stress applications. However, they can be more expensive than standard alumina due to the complexity of manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for use in cutting tools, wear-resistant components, and dental applications, alumina-zirconia composites provide enhanced durability in harsh environments.
Considerations for Buyers:
International buyers should assess the availability of these composites in their regions, as well as the suppliers’ ability to meet specific quality certifications and standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for alumina ceramic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Alumina | Aerospace components | Excellent thermal and chemical resistance | Higher manufacturing cost | High |
| Alumina-Titania Composite | Automotive parts | Cost-effective with good toughness | Limited chemical resistance | Medium |
| Spherical Alumina | 3D printing and advanced coatings | Improved flowability and packing density | Complex production process | High |
| Alumina-Zirconia Composite | Cutting tools and wear-resistant parts | Exceptional toughness | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into alumina ceramics, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for alumina ceramic
Alumina ceramics are crucial in various applications due to their outstanding mechanical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This section delves into the main stages of alumina ceramic manufacturing, key techniques employed, relevant quality control (QC) standards, and actionable insights for verifying supplier QC.
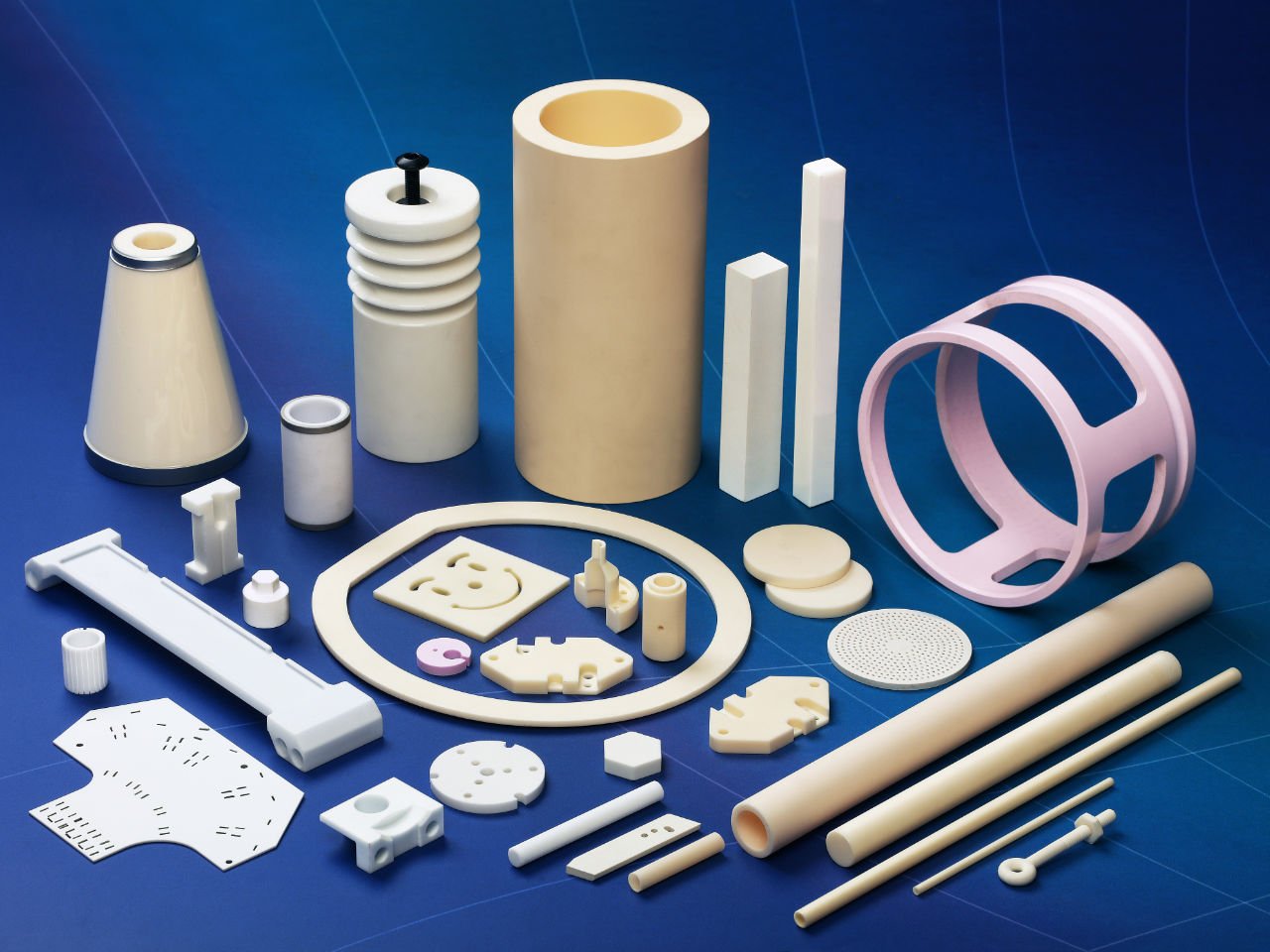

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Processes
Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing of alumina ceramics involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. Typically, high-purity alumina powder is used, which may be sourced from various suppliers. The preparation process includes:
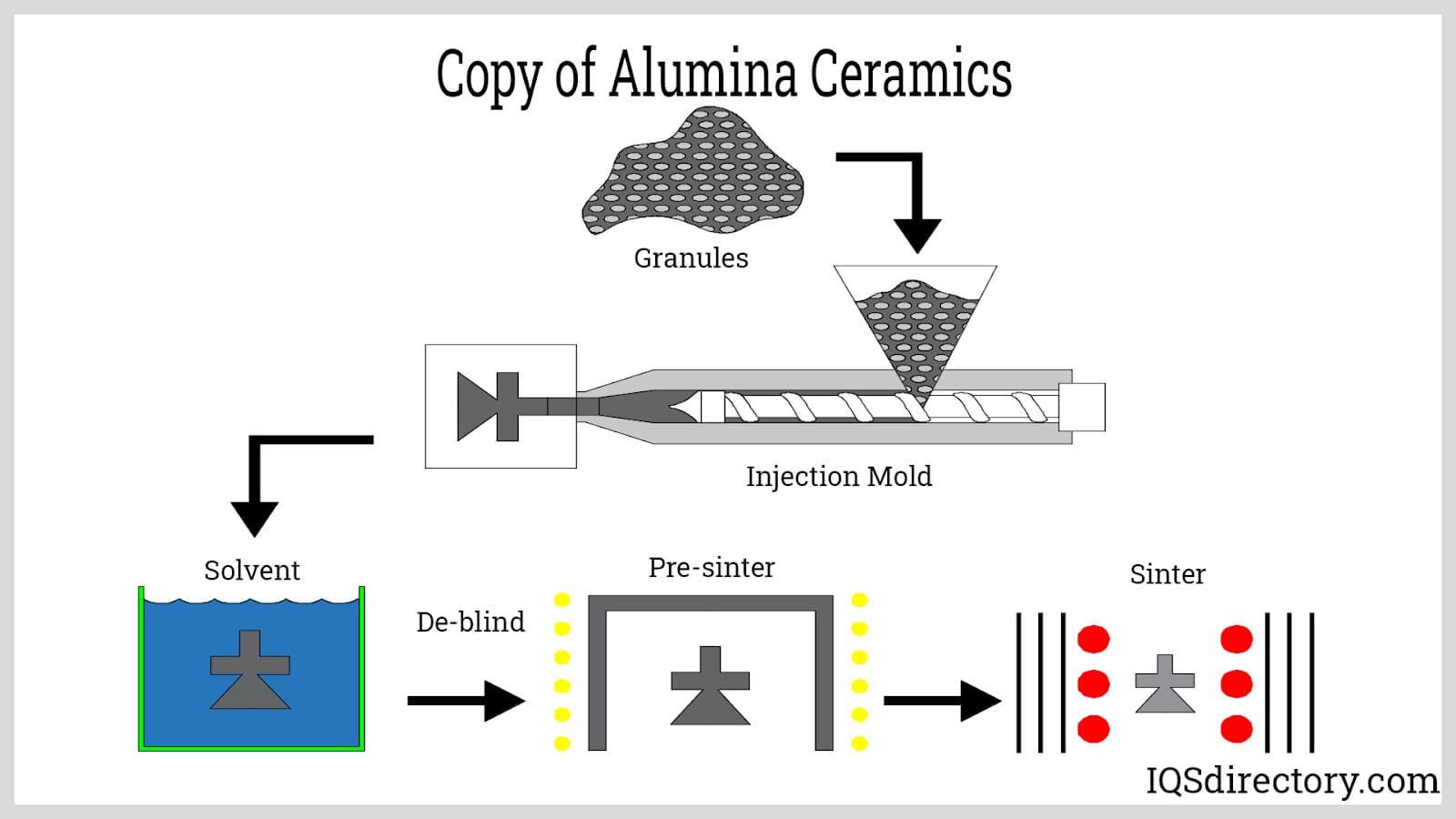
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Crushing and Milling: The alumina is crushed and milled to achieve the desired particle size. This step is critical as the particle size influences the final product’s density and mechanical strength.
- Additive Mixing: Depending on the application, various additives such as binders, plasticizers, and sintering aids are mixed with the alumina powder to enhance specific properties.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This can be accomplished through several techniques:
- Dry Pressing: In this traditional method, the mixed powder is placed in a mold and compressed under high pressure to form a green body. This process is commonly used for producing dense and uniform parts.
- Injection Molding: This technique involves injecting the powder mixture into a mold under high pressure. It is suitable for complex shapes and high-volume production.
- Slip Casting: A slurry of alumina is poured into porous molds, allowing water to be absorbed and leaving behind a solid ceramic shape. This method is often used for intricate designs.
Assembly
In some applications, multiple components are assembled before sintering. This stage might include:
- Joining Techniques: Various techniques, such as adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening, may be employed to assemble different parts, especially when producing multi-component systems.
- Pre-Sintering Adjustments: Adjustments may be made to ensure dimensional accuracy before the final firing process.
Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes to achieve the desired surface quality and dimensional tolerances. Techniques include:
- Sintering: The green body is heated in a kiln to a temperature below its melting point, causing the particles to bond and densify. The sintering temperature and time are critical for achieving optimal properties.
- Grinding and Polishing: After sintering, components may undergo grinding and polishing to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. This is especially important for components used in high-tech applications.
Quality Assurance
International Standards
For B2B buyers, understanding the quality assurance landscape is vital. Key international standards relevant to alumina ceramic manufacturing include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance indicates that a manufacturer consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements.
- ISO 14001: This standard focuses on effective environmental management systems, which is increasingly important for international buyers concerned about sustainability.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Depending on the application, additional certifications may be required. For example, the API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are crucial for ceramics used in the oil and gas industry, while CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have rigorous IQC protocols to prevent defects in the final product.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring during production helps identify issues early. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) can be beneficial.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo comprehensive testing before shipment. This includes dimensional checks, mechanical testing, and surface inspections.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are commonly employed to verify the quality of alumina ceramics:
- Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile, compressive, and flexural strength tests to ensure the material can withstand operational stresses.
- Thermal Analysis: Techniques like Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) assess thermal stability and phase transitions.
- Chemical Analysis: X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and other methods ensure the chemical composition meets specified standards.
Verifying Supplier QC
For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial to mitigate risks. Here are actionable strategies:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, QC systems, and compliance with international standards. Consider third-party audit services for an unbiased evaluation.
- Request QC Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports, including results from mechanical and chemical tests, to ensure transparency.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage third-party inspection agencies to verify the quality of products before shipment. This can help identify issues that may not be apparent in supplier reports.
QC and Certification Nuances
B2B buyers must be aware of certification nuances when sourcing from different regions:
- Local Regulations: Ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations, which may differ from international standards. For instance, specific certifications may be required for products used in critical applications in the EU or Middle East.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can provide insight into a supplier’s commitment to quality. Countries with strict regulatory environments often have more robust QC practices.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for alumina ceramics is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, and rigorous QC measures, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Manufacturing Process of Holed Alumina Ceramic Plates
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for alumina ceramic Sourcing
Alumina ceramics are pivotal in various industries, from aerospace to electronics, and understanding their cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis provides insights into the components affecting costs and pricing, as well as actionable tips for negotiating better deals.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the raw materials used to produce alumina ceramics. High-purity alumina is often required, which can fluctuate significantly based on market demand and sourcing regions. Buyers should be aware of the current market prices and consider sourcing from regions with lower raw material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the geographical location of the manufacturing facility. Countries with lower labor costs, such as some in Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing. However, the skill level required for producing high-quality ceramics can also affect these costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these overheads, impacting the final pricing of the products.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should factor in these costs when considering custom specifications, as they may lead to higher prices initially but can reduce per-unit costs in large orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount in ceramics production. Rigorous QC processes add to costs but are essential for meeting industry standards. Buyers should request information on QC procedures to assess the value they are getting.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer and the chosen shipping method. Incoterms also play a crucial role in determining who bears these costs. Buyers from Africa, for example, may face higher logistics costs compared to European buyers due to infrastructure challenges.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a margin into their pricing to cover risks and ensure profitability. Understanding the average margins in the industry can help buyers gauge if they are receiving a fair price.
Price Influencers
- Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can leverage better pricing.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications generally result in higher costs. Buyers should assess whether they need customized products or if standard offerings will suffice.
- Quality/Certifications: Products with higher quality ratings or certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices. However, they often provide better performance and longevity, which can justify the investment.
- Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and past performance can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record.
- Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect total costs. For instance, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) might result in higher prices compared to EXW (Ex Works), where the buyer assumes more responsibility.
Buyer Tips
- Negotiation: Engage in discussions about pricing and be prepared to negotiate based on volume, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing over time.
- Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Factor in logistics, installation, and maintenance costs to understand the true value of the products.
- Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and geopolitical factors that could impact pricing. Regularly review market conditions and adjust procurement strategies accordingly.
Disclaimer
Prices for alumina ceramics can vary widely based on the above factors and market conditions. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential alumina ceramic Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘alumina ceramic’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for alumina ceramic
Alumina ceramics are widely utilized in various industries due to their excellent mechanical properties and resistance to wear and corrosion. Understanding the essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing these materials for manufacturing or production processes.
Key Technical Properties of Alumina Ceramics
-
Material Grade
– Alumina ceramics are classified based on their purity levels, typically ranging from 90% to 99.9% Al2O3. Higher purity grades exhibit enhanced mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it directly impacts the performance and durability of the final product. -
Density
– The density of alumina ceramics typically varies between 3.5 to 4.0 g/cm³. Higher density materials generally provide better mechanical properties, including increased hardness and wear resistance. Buyers should consider density when evaluating the suitability of alumina ceramics for specific applications, especially in high-stress environments. -
Flexural Strength
– This property measures the ability of alumina ceramics to withstand bending forces without breaking. Typical values range from 200 to 400 MPa. Understanding flexural strength is essential for buyers in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where material failure can lead to significant safety concerns. -
Thermal Conductivity
– Alumina ceramics have thermal conductivities ranging from 20 to 30 W/mK. This property is crucial for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation, such as in electronic components. Buyers should assess thermal conductivity based on the operational environment of their products to ensure optimal performance.
-
Vickers Hardness
– This test measures the material’s hardness, with alumina ceramics typically scoring between 15 to 20 GPa. High hardness values make alumina ceramics suitable for abrasive applications. Buyers should prioritize hardness when sourcing materials for components exposed to wear and abrasion. -
Tolerance
– Tolerances in alumina ceramics refer to the permissible limits of variation in dimensions and properties during manufacturing. Common tolerances range from ±0.1 to ±0.5 mm. Understanding tolerance is critical for buyers to ensure that the manufactured parts fit correctly within their assembly processes, minimizing the risk of defects.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For B2B buyers, engaging with OEMs can streamline sourcing processes and ensure quality components tailored for specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory levels and cost-effectiveness in procurement. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping, risk, and insurance responsibilities, facilitating smoother international trade. -
Lead Time
– The lead time is the time between placing an order and receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight deadlines. -
Certification
– Refers to the process of validating that products meet specific standards and regulations. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers provide relevant certifications, as this impacts product reliability and compliance with industry standards.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing alumina ceramics, ensuring they select the right materials and manage procurement effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the alumina ceramic Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global alumina ceramic market is being driven by several key factors, including increased demand across various sectors such as electronics, aerospace, and healthcare. The rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and precision machining, is creating new opportunities for alumina ceramics in applications requiring high performance and durability. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for sourcing decisions.
Emerging sourcing trends include a shift towards local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in long-distance sourcing, prompting companies to seek closer partnerships. Additionally, the adoption of digital procurement platforms is transforming how businesses source materials, allowing for real-time price comparisons and supplier evaluations. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that leverage technology to enhance transparency and efficiency in their operations.
Market dynamics are further influenced by fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical tensions. For instance, alumina prices have been volatile, affecting production costs. Buyers should monitor market reports and forecasts to anticipate price changes and adjust their sourcing strategies accordingly. Collaboration with suppliers who can provide insights into market trends will also be beneficial.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the alumina ceramic sector. The environmental impact of production processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on greener practices. B2B buyers are encouraged to partner with manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as recycling and using renewable energy sources in production.
Ethical sourcing is equally significant, with an emphasis on supply chain transparency. Buyers should assess their suppliers’ adherence to ethical standards and certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or Fair Trade certifications. These certifications not only ensure compliance with environmental regulations but also enhance the brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the development of ‘green’ materials in alumina ceramics is gaining traction. Innovations in sustainable materials, such as bio-based or recycled alumina, present opportunities for buyers to reduce their carbon footprint. Engaging with suppliers who invest in research and development of sustainable products can lead to a competitive advantage in the market.
Brief Evolution/History
The alumina ceramic industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially utilized for traditional applications like electrical insulators and tableware, alumina ceramics have expanded into high-tech fields. The advent of advanced manufacturing techniques in the late 20th century catalyzed this evolution, allowing for the production of complex shapes and improved material properties.
Today, alumina ceramics are integral to sectors requiring high wear resistance, thermal stability, and electrical insulation, such as aerospace and electronics. As the industry progresses, continuous innovations in material science and production techniques will shape the future landscape, making it imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed about these advancements for effective sourcing strategies.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of alumina ceramic
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of alumina ceramic?
When vetting suppliers, evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, experience, and reputation in the industry. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 or other relevant quality standards. Request references from other clients, especially those in your region, to assess reliability and performance. Additionally, inquire about their capacity to meet your specific needs in terms of customization and volume. -
Can I customize alumina ceramic products to suit my specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for alumina ceramic products. Discuss your specific needs regarding dimensions, shapes, and applications with potential suppliers. Ensure they have the technical capability to produce custom designs and ask for samples before placing larger orders. This process will help ensure that the final product meets your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for alumina ceramic?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from 50 to several hundred units depending on the product and supplier capacity. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors such as customization, production schedules, and shipping logistics. Always confirm these details before placing an order to ensure alignment with your project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alumina ceramic?
Payment terms can differ by supplier but typically include options such as upfront payment, net 30, or net 60 days. Some suppliers may require a deposit before production, especially for custom orders. Discuss payment options early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings later. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods or letters of credit for larger transactions to protect your investment. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for alumina ceramic products?
Request detailed documentation of quality assurance processes from your supplier, including any relevant certifications such as ISO or ASTM standards. Many suppliers provide a certificate of compliance or test reports for their products. It’s also advisable to conduct periodic audits or quality checks, especially for high-volume orders, to ensure that the products meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing alumina ceramic?
Logistics can be complex when importing alumina ceramic, so it’s essential to consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide guidance on documentation needed for customs clearance. Additionally, factor in shipping timeframes and costs to ensure they fit within your budget and project timelines. -
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively resolved?
To mitigate disputes, ensure that all agreements are documented in a detailed contract that outlines responsibilities, quality expectations, and payment terms. If disputes arise, initiate a direct conversation with the supplier to seek resolution. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract, as these methods can be more efficient than legal action and help preserve business relationships. -
What are the current global risks affecting the supply of alumina ceramic?
Global risks include supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and trade restrictions. Buyers should stay informed about market trends and potential shortages by subscribing to industry reports and news. Diversifying your supplier base and sourcing from multiple regions can help mitigate risks associated with supply chain vulnerabilities, ensuring a more stable procurement process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for alumina ceramic
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of alumina ceramics presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways include the necessity of understanding regional supply chain dynamics and the potential impact of global disruptions on material availability. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers who can ensure consistent quality and timely delivery, mitigating risks associated with fluctuating market conditions.
Moreover, leveraging data analytics to assess supplier performance and market trends can greatly enhance procurement strategies. As the demand for high-performance materials like alumina ceramics continues to grow across various industries—including healthcare, aerospace, and energy—buyers must remain proactive in their sourcing efforts.
Looking ahead, it is vital for businesses to stay informed about evolving market trends and technological advancements in alumina ceramics. Embracing innovation and fostering collaborative relationships with suppliers will be essential for maintaining competitive advantage. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore new sourcing opportunities, and align your strategies with market needs to secure your position in the global alumina ceramic landscape.