Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Ball Screw Actuator
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ball screw actuator
The ball screw actuator is a pivotal component in modern automation and motion control systems, offering precision, efficiency, and reliability across various industries. As international B2B buyers increasingly seek to enhance their operational capabilities, understanding the nuances of ball screw actuators becomes essential. These devices convert rotary motion into linear motion, making them integral in applications ranging from robotics to aerospace.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of ball screw actuators, covering critical aspects such as types, materials, manufacturing processes, quality control standards, and supplier evaluations. We will also explore cost considerations, market trends, and address frequently asked questions to equip buyers with the knowledge needed for informed sourcing decisions.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets in Italy and France—this guide serves as a crucial resource. By empowering stakeholders with actionable insights and a deep understanding of the global ball screw actuator market, businesses can optimize their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the right products that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. Whether you are a seasoned industry professional or new to the field, navigating this guide will enhance your ability to make strategic purchasing decisions that drive success.
Understanding ball screw actuator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Ball Screw Actuators | High efficiency, low friction, various lead options | CNC machines, robotics | Pros: Versatile, high precision. Cons: May require regular maintenance. |
| Miniature Ball Screw Actuators | Compact design, lightweight, precision-engineered | Medical devices, small machinery | Pros: Space-saving, high accuracy. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| High-Load Ball Screw Actuators | Robust design, capable of handling heavy loads | Industrial automation, heavy machinery | Pros: Durable, suitable for high-stress applications. Cons: Bulkier, potentially higher cost. |
| Ball Screw Actuators with Integrated Motors | Combines actuator and motor for compact design | Automated assembly lines, packaging | Pros: Space-efficient, reduced assembly time. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Ball Screw Actuators with Anti-Backlash Features | Designed to minimize backlash, enhancing precision | Aerospace, high-precision machining | Pros: Superior accuracy, improved performance. Cons: More complex, higher maintenance. |
Standard Ball Screw Actuators
Standard ball screw actuators are widely used due to their high efficiency and low friction characteristics. They come in various lead options, making them suitable for diverse applications such as CNC machines and robotics. When considering this type, buyers should evaluate the required precision and load capacity, as well as the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Miniature Ball Screw Actuators
Miniature ball screw actuators are designed for applications where space is at a premium, such as in medical devices and small machinery. Their lightweight and precision-engineered design allows for high accuracy in tight spaces. Buyers should consider the load capacity and the specific dimensions of their application, as these actuators, while precise, may not handle heavy loads effectively.
High-Load Ball Screw Actuators
These actuators are built to endure heavy loads, making them ideal for industrial automation and heavy machinery applications. Their robust design ensures durability and reliability under stress. Buyers should assess the actuator’s size and weight, as well as the potential trade-offs in terms of bulkiness and cost compared to standard models.
Ball Screw Actuators with Integrated Motors
This type combines the actuator with an integrated motor, offering a compact solution for applications such as automated assembly lines and packaging. This design can significantly reduce assembly time and space requirements. However, buyers need to weigh the higher initial investment against the benefits of increased efficiency and reduced installation complexity.
Ball Screw Actuators with Anti-Backlash Features
Designed to minimize backlash, these actuators are essential in high-precision applications such as aerospace and machining. The enhanced accuracy and performance are significant advantages, but the complexity of the design may lead to higher maintenance needs. Buyers should consider the precision requirements of their applications and the potential need for more frequent servicing.
Related Video: Factory Vlog – Aluminum Profile Ball Screw Linear Actuator
Key Industrial Applications of ball screw actuator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ball screw actuator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision CNC Machines | Enhances accuracy and repeatability in machining. | Consider load capacity and speed specifications. |
| Automation | Robotic Systems | Increases efficiency and reduces manual labor. | Evaluate compatibility with existing systems. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical Equipment | Provides precise movement and control. | Ensure compliance with medical regulations. |
| Textile Industry | Automated Looms | Improves production speed and product quality. | Focus on durability and maintenance requirements. |
| Aerospace | Flight Simulation Systems | Enhances realism and accuracy in training. | Prioritize high precision and reliability standards. |
Manufacturing: Precision CNC Machines
In the manufacturing sector, ball screw actuators are integral to precision CNC machines. They enable high-speed, accurate positioning of cutting tools, ensuring that parts are manufactured to exact specifications. This precision reduces material waste and improves overall production efficiency. For international buyers, particularly those in Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality actuators that can withstand local environmental conditions is crucial. Buyers should also consider the actuator’s load capacity and speed specifications to match their specific machining needs.
Automation: Robotic Systems
Ball screw actuators play a vital role in robotic systems used for automation across various industries. They provide precise linear motion, allowing robots to perform tasks such as assembly, welding, and packaging with high efficiency. This results in reduced labor costs and increased productivity. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, compatibility with existing automation systems is a key consideration. It’s essential to assess the actuator’s integration capabilities and performance under varying load conditions to optimize operational efficiency.
Medical Devices: Surgical Equipment
In the medical field, ball screw actuators are used in surgical equipment to ensure precise movement and control during procedures. This capability is critical for minimizing patient risk and enhancing surgical outcomes. International buyers, especially in Europe, must ensure that the actuators comply with stringent medical regulations and standards. Additionally, sourcing actuators that offer reliability and longevity is vital for maintaining operational efficiency in medical facilities.
Textile Industry: Automated Looms
Ball screw actuators are utilized in automated looms within the textile industry to enhance production speed and improve product quality. By providing consistent and accurate motion, these actuators help in achieving finer fabric textures and reducing defects. Buyers in Africa and South America should focus on the durability and maintenance requirements of the actuators, as these factors can significantly impact production downtime and costs. Selecting actuators designed for high-volume textile applications can lead to substantial efficiency gains.
Aerospace: Flight Simulation Systems
In the aerospace sector, ball screw actuators are essential components of flight simulation systems, providing realistic and precise control movements that mimic actual flight dynamics. This technology is crucial for pilot training programs, enhancing the effectiveness and safety of training. Buyers in Europe must prioritize high precision and reliability standards when sourcing these actuators, as the aerospace industry is subject to rigorous safety regulations. Ensuring that the actuators can operate effectively in varying conditions is also critical for maintaining simulation accuracy.
Related Video: NEMA 23 Ball Screw Linear Actuator | linear actuator | Stepper Motor | Bholanath | English Version
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ball screw actuator
When selecting materials for ball screw actuators, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Below are detailed analyses of four common materials used in the construction of ball screw actuators, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, application impacts, and specific considerations for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It typically has excellent temperature and pressure ratings, making it suitable for high-load applications. Corrosion resistance can be enhanced through surface treatments like galvanization.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of steel include its robustness and long service life, which can lead to lower replacement costs. However, steel can be heavy, which may affect the overall weight of the actuator. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and lubricants, making it versatile for various industrial applications. However, it may not be suitable for environments with high humidity or corrosive substances unless properly treated.
Specific Considerations:
Buyers in Europe, particularly in Italy and France, must ensure compliance with EU regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Common standards like DIN and ASTM are relevant for quality assurance.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance. It has a lower tensile strength compared to steel but can be alloyed to improve its mechanical properties. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can reduce energy consumption in applications requiring movement. However, its lower strength limits its use in high-load scenarios, and it may be more expensive than steel in some markets.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for environments exposed to moisture.
Specific Considerations:
International buyers should be aware of the availability of aluminum alloys that meet specific mechanical and corrosion resistance requirements. Compliance with standards such as JIS and ASTM is essential for quality assurance.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for harsh environments. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is advantageous in demanding applications.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel provides superior durability and resistance to corrosion, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel. The manufacturing process can also be more complex, leading to higher production costs.
Impact on Application:
This material is particularly useful in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount. Its compatibility with various lubricants and coolants enhances its applicability.
Specific Considerations:
Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should consider the local availability of stainless steel grades that comply with international standards. Understanding the specific grades (e.g., 304, 316) is crucial for ensuring optimal performance.
4. Plastic Composites
Key Properties:
Plastic composites are lightweight and can be engineered for specific properties, including chemical resistance and low friction. They typically have lower strength compared to metals but can be designed to meet specific application needs.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of plastic composites is their resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for specialized applications. However, they may not withstand high loads as effectively as metals, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application:
These materials are ideal for applications in chemical processing and environments where metal corrosion is a concern. Their low weight can also contribute to energy savings in motion systems.
Specific Considerations:
B2B buyers should ensure that the selected plastic composite meets relevant industry standards and regulations, particularly in Europe. Understanding the specific chemical compatibility of the composite is also essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for ball screw actuator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-load industrial applications | High strength and durability | Heavy and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex processing | High |
| Plastic Composites | Chemical processing and low-load systems | Corrosion resistant and lightweight | Lower strength for heavy-duty use | Medium |
This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed material selections for ball screw actuators, enhancing their operational efficiency and compliance with industry standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ball screw actuator
The manufacturing of ball screw actuators is a meticulous process that requires precision and adherence to quality standards. For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Process of Ball Screw Actuators
-
Material Preparation
– Raw Material Selection: The primary materials for ball screw actuators include high-quality steel alloys, which provide the necessary strength and durability. Some manufacturers may also use stainless steel or specialized alloys for specific applications.
– Heat Treatment: Materials often undergo heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering to enhance hardness and wear resistance. This is critical for ensuring the longevity of the actuator under load. -
Forming
– Machining: The manufacturing process begins with precision machining of the screw and nut components. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are typically employed to achieve the required tolerances and surface finishes.
– Ball Groove Formation: The screw threads are formed into a ball groove profile, which is essential for the rolling motion of the balls. This is achieved through specialized grinding techniques, ensuring minimal friction and maximum efficiency. -
Assembly
– Ball Insertion: After the screw and nut are machined, balls are inserted into the ball groove. This can be done using automated systems to ensure uniformity and reduce the risk of contamination.
– Preloading: The assembly may include preloading the nut and screw to eliminate backlash. This process ensures that the actuator operates smoothly and with high precision.
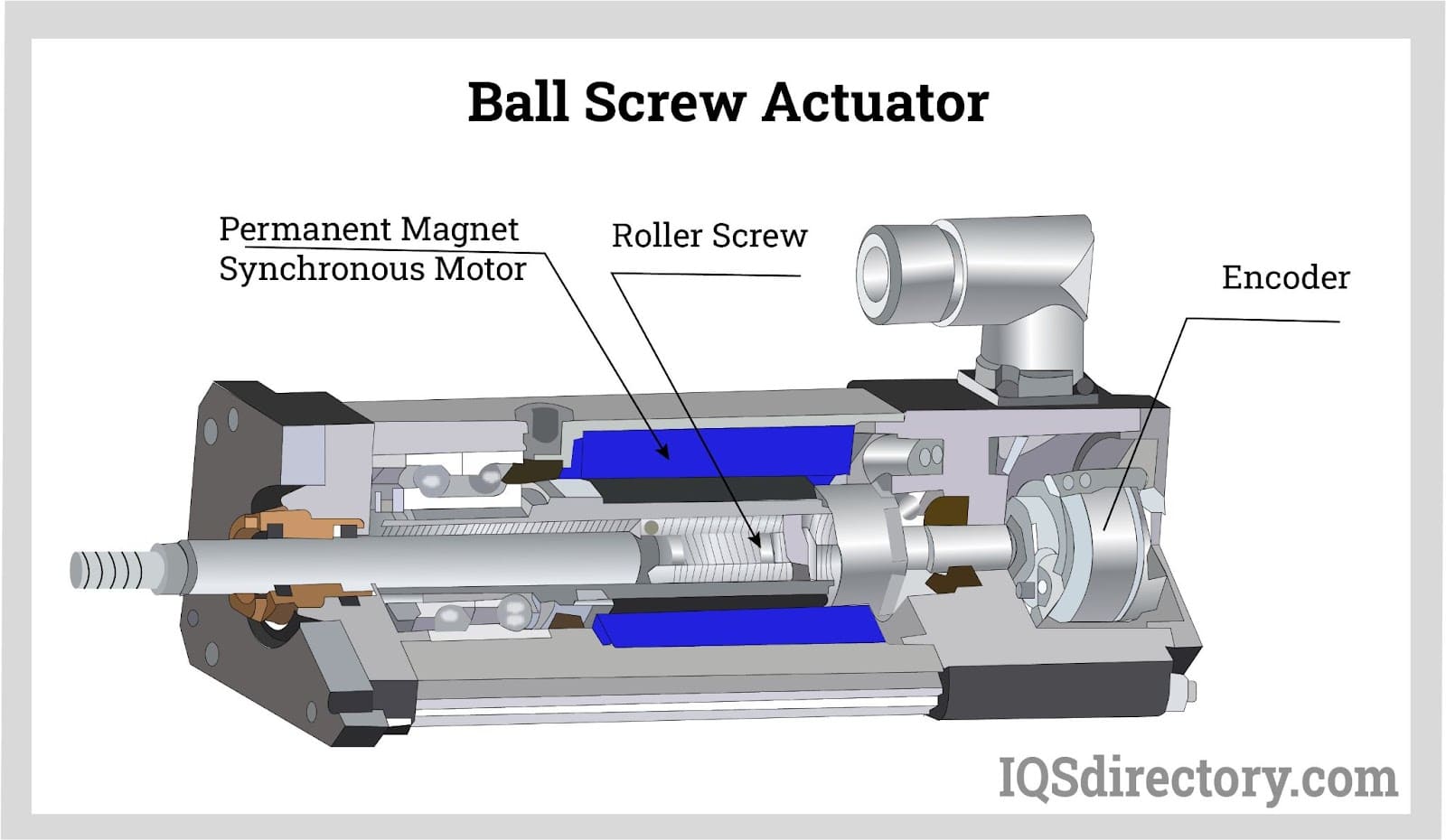
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Finishing
– Surface Treatment: The final components often undergo surface treatments such as coating or plating (e.g., zinc plating, anodizing) to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
– Final Assembly: The actuator is assembled with other components such as motors or brackets as required. This step may involve additional quality checks to ensure that all parts fit and function correctly.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Ensuring the quality of ball screw actuators involves strict adherence to international and industry-specific standards. This is vital for B2B buyers who need reliable and durable products.
-
International Standards
– ISO 9001: This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems. Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance through continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
– CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is crucial for European buyers to verify this certification. -
Industry-Specific Standards
– API Standards: For actuators used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with API (American Petroleum Institute) standards is necessary. These standards ensure that the products can withstand harsh operational environments.
– ASTM Standards: These standards cover material specifications and testing methods, ensuring that the materials used are of the highest quality. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to monitor critical parameters such as dimensions, surface finish, and assembly integrity.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the finished products undergo comprehensive testing. This includes load testing, operational testing, and dimensional verification. -
Common Testing Methods
– Functional Testing: Ensures that the actuator operates as expected under specified loads and conditions.
– Durability Testing: Assess the actuator’s performance over an extended period to simulate real-world usage.
– Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are employed to detect internal defects without damaging the components.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality assurance processes of potential suppliers. Here are some practical strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with relevant standards. This firsthand observation is invaluable for assessing supplier capabilities.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers can ask suppliers for quality assurance documentation, including test results, certifications, and inspection reports. This information helps validate the supplier’s claims regarding their quality control measures.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s operations and product quality. This is particularly beneficial for buyers in regions where they cannot easily access suppliers.
-
Understanding Regional Compliance Nuances: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must ensure that suppliers can meet the specific compliance requirements of their respective markets.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for ball screw actuators is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on material quality, precise manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select suppliers that deliver reliable, high-performance products tailored to their specific needs.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Pull Systems
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ball screw actuator Sourcing
When sourcing ball screw actuators, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. The following analysis breaks down the cost components and price influencers, providing actionable insights for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Ball Screw Actuators
-
Materials: The primary materials used in ball screw actuators include high-quality steel and other alloys, which can significantly affect costs. Sourcing materials from reputable suppliers ensures durability and performance but may increase the upfront costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, the overall manufacturing cost of ball screw actuators may be elevated compared to regions in Africa or South America. Understanding local labor markets can aid in assessing total costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s overhead rates to better understand how these affect pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific actuator designs can incur significant costs. For standard designs, tooling costs are generally lower, making it crucial to evaluate the need for customization early in the procurement process.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Manufacturers with robust QC protocols may charge higher prices, but this investment often leads to long-term savings by reducing failure rates.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary widely based on shipping distances and modes. Buyers should consider logistics as part of the total cost, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and business expenses. Understanding the market standard margins can help buyers negotiate better prices.
Price Influencers for Ball Screw Actuators
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit prices. Buyers should assess their needs to determine the most cost-effective order size.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized actuators tailored to specific applications may carry premium prices. Buyers should balance the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or CE) can increase costs but are crucial for applications requiring high reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more, but they often provide better service and product quality.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can significantly affect the final price, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties. Buyers should negotiate favorable terms to minimize their total expenditure.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially regarding bulk orders or long-term contracts. Suppliers may offer discounts for committed relationships.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost of the actuator, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of fluctuations in currency exchange rates, tariffs, and import duties that may affect pricing. This understanding can help mitigate unexpected costs.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices from different suppliers. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help identify the best value options.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of cost components and price influencers is vital for B2B buyers sourcing ball screw actuators. By considering the factors outlined above, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their budget and operational requirements. Always remember that prices can vary significantly based on specifications and market conditions, so seeking multiple quotes and conducting due diligence is essential for achieving the best deal.
Spotlight on Potential ball screw actuator Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘ball screw actuator’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ball screw actuator
Ball screw actuators are pivotal components in various automation and motion control systems. Understanding their essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here’s a breakdown of the key specifications and terms that you need to be familiar with.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in the ball screw actuator, often categorized as stainless steel, carbon steel, or specialized alloys.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade materials typically offer better corrosion resistance and durability, which can significantly extend the lifespan of the actuator, making it a more cost-effective choice in the long run. -
Load Capacity
– Definition: The maximum load that the ball screw actuator can handle while maintaining performance.
– B2B Importance: Accurately assessing load capacity ensures that the actuator can meet specific application requirements without risk of failure, which is critical for operational safety and efficiency. -
Precision and Tolerance
– Definition: The degree of accuracy in the actuator’s movement, often expressed in microns.
– B2B Importance: High precision is essential in applications requiring exact positioning, such as CNC machines or robotics. Tighter tolerances can lead to higher costs, so balancing precision with budget is vital. -
Lead Screw Pitch
– Definition: The distance the actuator moves with one complete rotation of the screw.
– B2B Importance: The pitch affects the speed and resolution of movement. A finer pitch provides more precise control, which is crucial in applications where exact positioning is necessary. -
Efficiency Rating
– Definition: A measure of how effectively the actuator converts input power into mechanical output.
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency ratings lead to reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs, making the actuator more sustainable and cost-effective over time. -
Backlash
– Definition: The degree of play or lost motion in the actuator when reversing direction.
– B2B Importance: Minimizing backlash is essential for applications requiring high precision and repeatability. Understanding this property helps in selecting the right actuator for specific applications.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller companies that may not require large quantities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and freight.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, facilitating smoother international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for planning and inventory management, especially in just-in-time manufacturing environments. -
Customization
– Definition: The ability to tailor a product to meet specific requirements.
– Importance: Customization can provide competitive advantages by enabling the development of specialized solutions that address unique operational challenges.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make more informed decisions when sourcing ball screw actuators, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the ball screw actuator Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The ball screw actuator market is experiencing significant growth driven by advancements in automation, increased demand for precision machinery, and the push for efficient energy usage across various industries. Key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing are increasingly adopting ball screw actuators due to their high efficiency and reliability. In particular, the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping how manufacturers approach sourcing, emphasizing connectivity and integration of intelligent systems.
International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take note of several emerging trends. First, there is a growing preference for modular designs that allow for easy customization and scalability. This trend is particularly relevant for companies seeking to optimize production processes without extensive downtime. Second, the integration of smart technology is becoming more prevalent, with actuators now equipped with sensors that provide real-time data on performance and maintenance needs. This data-driven approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces overall costs.
Furthermore, international trade dynamics are influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking to diversify their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions. Countries in Europe, such as Italy and France, are seeing a resurgence in local manufacturing, which offers benefits such as reduced lead times and improved communication with suppliers.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As sustainability becomes a core focus for businesses globally, the ball screw actuator sector is no exception. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. International buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it reflects a company’s commitment to social responsibility. Buyers should seek out suppliers who maintain transparent supply chains and adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Additionally, the market is seeing a rise in the use of ‘green’ materials in ball screw actuator manufacturing. Buyers should inquire about the materials used in production, looking for alternatives that are both environmentally friendly and durable. This not only contributes to a company’s sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation in a competitive marketplace.
Brief Evolution/History
The ball screw actuator has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally developed for mechanical applications, advancements in materials science and precision engineering have transformed these devices into essential components in modern automation. By the late 20th century, with the advent of computer-controlled machinery, ball screw actuators became integral to various industries, offering enhanced precision and efficiency. Today, they are synonymous with high-performance applications, reflecting the ongoing innovation in engineering and technology that continues to shape their design and functionality.
As international B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding these trends and principles will be crucial for making informed sourcing decisions and fostering sustainable partnerships in the ball screw actuator sector.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ball screw actuator
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for ball screw actuators?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience and reputation. Check for certifications relevant to your region, such as ISO or CE marks, to ensure compliance with international standards. Request references from previous clients to gauge reliability and service quality. Additionally, assess their technical support capabilities and response times, as effective communication can significantly impact your project’s success. Finally, consider their production capacity and whether they can meet your demands consistently. -
Can ball screw actuators be customized to fit specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for ball screw actuators. You can specify dimensions, load capacities, and speed requirements based on your application needs. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly during the design phase to avoid costly modifications later. Ask potential suppliers about their design capabilities and experience with similar custom projects. Additionally, inquire about the engineering support they provide throughout the customization process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for ball screw actuators?
MOQs for ball screw actuators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the actuator. Generally, MOQs range from 5 to 50 units. Lead times are also dependent on customization and supplier location, typically spanning from 2 to 12 weeks. When negotiating, confirm these details upfront and consider the implications for your inventory management and project timelines. Suppliers may offer expedited options at an additional cost, which can be useful in urgent scenarios. -
What payment options are available for international purchases of ball screw actuators?
Payment options for international purchases often include bank transfers, letters of credit, and online payment platforms. It’s crucial to discuss and agree upon payment terms before placing an order. In many cases, suppliers may require a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Ensure you understand the implications of currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees. Additionally, consider using escrow services for larger transactions to safeguard your investment.
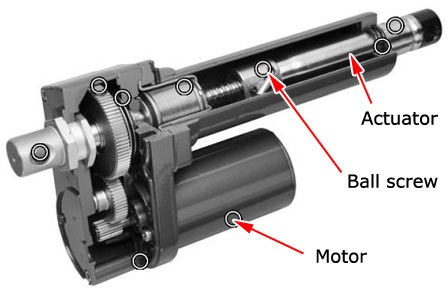
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for ball screw actuators?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications and quality control processes from your supplier. Common certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Inquire about their testing protocols, including load testing and durability assessments. Additionally, consider conducting on-site inspections or third-party audits if feasible, especially for large orders. Establishing clear quality expectations in your contract can also help mitigate risks. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing ball screw actuators?
Logistical considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Determine the most cost-effective shipping method based on your timeline and budget—options typically include air freight for speed or sea freight for cost savings. Familiarize yourself with customs documentation requirements to avoid delays. Additionally, consider engaging a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial equipment to streamline the process and ensure compliance with local laws. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers effectively?
To handle disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and protocols before any issues arise. Include dispute resolution procedures in your contract, such as mediation or arbitration clauses, to provide a framework for resolving conflicts amicably. Maintain thorough documentation of all transactions and communications, as this can support your position if disputes escalate. If necessary, seek legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to navigate complex situations. -
What should I know about after-sales support for ball screw actuators?
After-sales support is crucial for the long-term performance of your ball screw actuators. Inquire about warranty terms, including coverage duration and conditions for claims. Assess the availability of technical support and spare parts, as this can significantly impact maintenance and repairs. Additionally, determine whether the supplier offers training for your staff on installation and operation, which can enhance efficiency and reduce downtime. A strong after-sales support system can lead to better equipment longevity and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ball screw actuator
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of ball screw actuators is pivotal for international B2B buyers seeking efficiency and precision in their operations. By prioritizing quality, compatibility, and supplier reliability, businesses can significantly enhance their production capabilities. Key takeaways include the importance of understanding local regulations, selecting suppliers with robust after-sales support, and leveraging technological advancements in actuator design.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, forging strong partnerships with reputable manufacturers can lead to cost-effective solutions and improved supply chain resilience. As industries continue to evolve, staying abreast of market trends and innovations will be essential.
The future of ball screw actuators looks promising, with advancements in automation and smart technologies driving demand. Now is the time to act—assess your sourcing strategies, engage with leading suppliers, and position your business at the forefront of this dynamic market. Embrace the potential of strategic sourcing to secure a competitive edge and foster sustainable growth.