Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Broach Machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for broach machine
In the fast-paced global manufacturing landscape, broach machines stand out as vital tools for precision metalworking. These machines are essential for efficiently creating complex internal and external features, such as keyways and splines, which are crucial in various industries, from automotive to aerospace. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Turkey and Indonesia) seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, understanding the nuances of broach machines becomes imperative.
This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted world of broach machines, detailing types such as horizontal and vertical machines, and the broaching methods employed. We delve into the materials used in broach manufacturing, emphasizing the significance of high-speed steel and coatings that enhance durability. Additionally, we cover manufacturing processes and quality control measures that ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Buyers will also find insights into evaluating suppliers, analyzing cost factors, and understanding market trends to make informed sourcing decisions. The guide addresses common FAQs, providing clarity on operational concerns and maintenance practices. By equipping buyers with the necessary knowledge, this resource empowers them to navigate the global market effectively, ensuring they select the right broach machines that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Understanding broach machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Broaching Machine | Pull-type operation, larger floor space, handles heavy workpieces | Keyways, splines, and internal shapes | Pros: Efficient for heavy-duty jobs, good for long broaches. Cons: Requires more space. |
| Vertical Broaching Machine | Push or pull-type, compact design, versatile operations | Multiple operations, ideal for assembly lines | Pros: Space-efficient, easier material handling. Cons: May have limitations on heavy parts. |
| Surface Broaching Machine | Rigid ram movement, used for flat surfaces | Finishing flat surfaces and contours | Pros: High precision for surface finishing. Cons: Limited to surface applications. |
| Continuous Broaching Machine | Rotary or horizontal, designed for mass production | High-volume production of small parts | Pros: Maximizes efficiency for repetitive tasks. Cons: Higher initial investment and complexity. |
| Duplex Broaching Machine | Two rams for simultaneous operations | Large batch processing | Pros: Reduces cycle time, increases throughput. Cons: More complex setup and maintenance. |
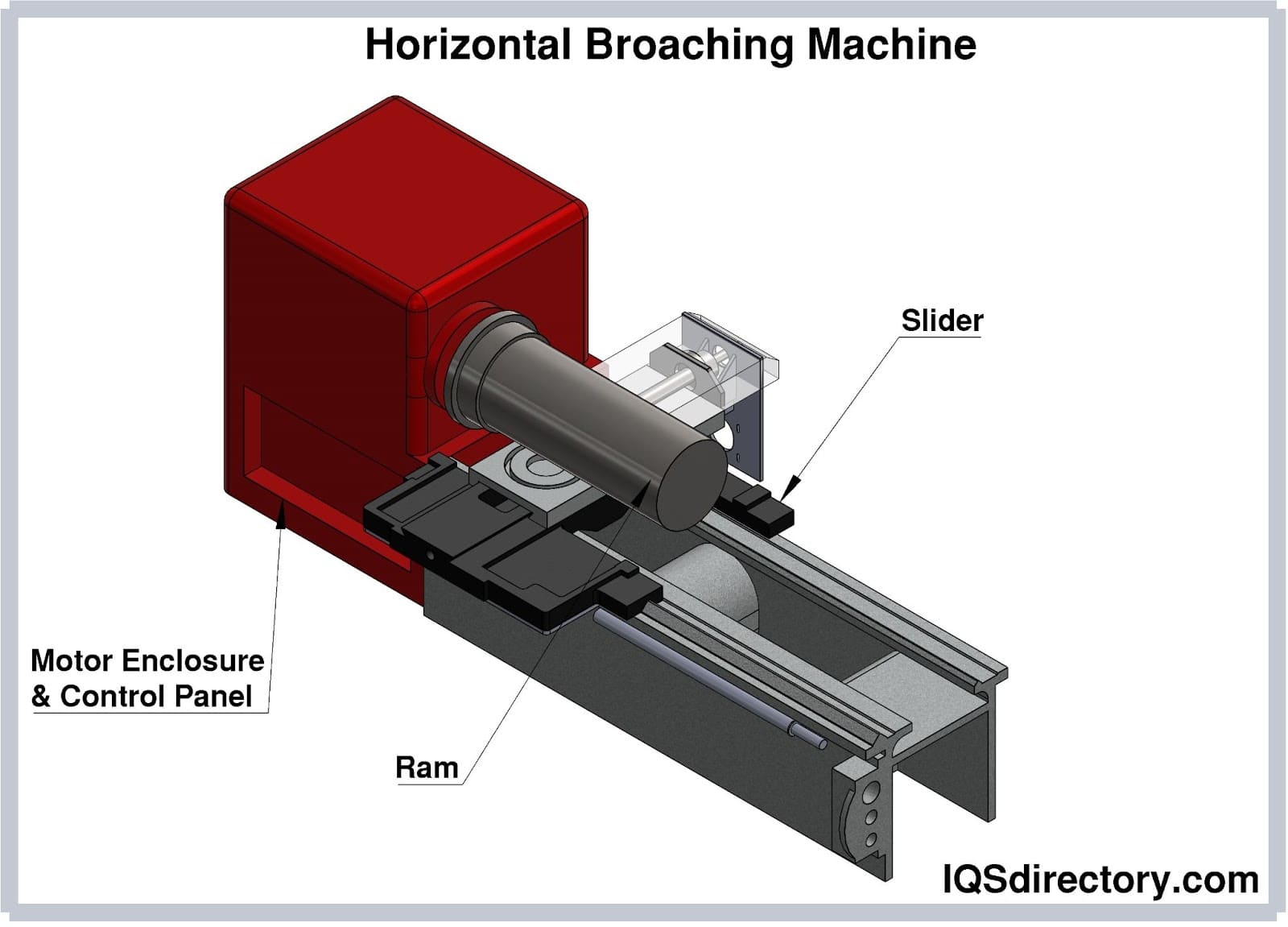
Horizontal Broaching Machine
Horizontal broaching machines are primarily pull-type systems, designed to handle heavy workpieces and long broaches. Their structure allows for efficient broaching of internal shapes such as keyways and splines. For B2B buyers, these machines are ideal for industries that require robust machinery capable of performing demanding tasks. However, their larger footprint may necessitate additional factory space, which should be considered when planning production layouts.
Vertical Broaching Machine
Vertical broaching machines can operate in both push and pull modes, making them versatile for various applications. Their compact design allows for efficient use of floor space, making them suitable for assembly lines where multiple operations occur in sequence. Buyers should consider their production needs; while these machines are economical in space, they may not be ideal for very heavy components due to their design limitations.
Surface Broaching Machine
Surface broaching machines are characterized by their ability to achieve high precision on flat surfaces. They employ a rigid ram that moves past the workpiece, making them ideal for finishing tasks where flatness and contour accuracy are critical. B2B buyers looking for machines focused on surface finishing will find these machines advantageous. However, their application is limited to surface work, which may not meet all manufacturing needs.
Continuous Broaching Machine
Continuous broaching machines are designed for high-volume production, utilizing rotary or horizontal mechanisms to streamline the manufacturing process. They are particularly effective for small parts, allowing for rapid throughput. For international B2B buyers, investing in continuous broaching can significantly enhance production efficiency, although the initial costs and complexity of setup may be higher than other types.
Duplex Broaching Machine
Duplex broaching machines feature two rams that operate simultaneously, allowing for faster processing of components. This design is particularly beneficial for large batch processing, where time efficiency is crucial. Buyers should assess their production volume needs, as the duplex design can significantly reduce cycle times. However, the complexity of setup and maintenance may require additional training and resources, making it essential to weigh the benefits against potential operational challenges.
Related Video: All Machine Learning Models Clearly Explained!
Key Industrial Applications of broach machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of broach machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Internal broaching for engine components | High precision and efficiency in part production | Supplier’s ability to provide custom broach designs and materials |
| Aerospace | Surface broaching for turbine blades | Enhanced performance and reliability of components | Certification standards and compliance with industry regulations |
| Oil & Gas | Broaching for valve and pump components | Reduced lead time and improved operational efficiency | Availability of heavy-duty machines capable of handling tough materials |
| Machinery & Equipment | Keyway and spline broaching for gear systems | Cost-effective mass production of complex parts | Machine versatility and support for various broaching techniques |
| Medical Devices | Broaching for surgical instruments | Precision manufacturing for critical applications | Supplier’s experience with biocompatible materials and finishes |
Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive sector, broach machines are primarily utilized for internal broaching of engine components such as keyways, splines, and other intricate features. This method ensures high precision and efficiency, essential for meeting the stringent performance standards of modern vehicles. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer custom broach designs tailored to specific engine specifications, as well as those who maintain strict quality control measures to ensure durability and reliability.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry employs broaching machines for surface broaching of turbine blades and other critical components. This application is vital for enhancing the performance and reliability of parts subjected to extreme conditions. Buyers in this sector must consider suppliers that adhere to rigorous certification standards and industry regulations, ensuring that the broaching process meets the exacting demands of aerospace applications.
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas sector, broaching is essential for manufacturing valve and pump components, where precision and reliability are paramount. Broach machines streamline production processes, significantly reducing lead times and improving operational efficiency. Buyers should look for suppliers that provide heavy-duty machines capable of handling the tough materials typical in this industry, as well as those that can support custom broaching solutions for specific applications.
Machinery & Equipment
Broaching machines are extensively used in the machinery and equipment sector for creating keyways and splines in gear systems. This method allows for cost-effective mass production of complex parts while maintaining a high level of accuracy. When sourcing broaching machines, international buyers should assess the versatility of the equipment and the supplier’s ability to support various broaching techniques, ensuring they can adapt to different production needs.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, broaching machines are employed to manufacture surgical instruments with high precision. The ability to produce intricate features and maintain tight tolerances is critical for ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices. Buyers should focus on suppliers with experience in working with biocompatible materials and finishes, as well as those who understand the regulatory requirements specific to medical manufacturing.
Related Video: Nachi Helical Broaching Machine, Hx T50 23DHAL 2 Axis
Strategic Material Selection Guide for broach machine
When selecting materials for broaching machines, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, cost, and application suitability. The following analysis covers four common materials used in broaching machine components, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
Key Properties:
High-speed steel is known for its excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for high-speed cutting applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C without losing its hardness, which is critical during broaching operations.
Pros & Cons:
HSS offers high durability and is relatively easy to manufacture into complex shapes. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its brittleness can lead to chipping under excessive stress.
Impact on Application:
HSS is compatible with various materials, including steel and aluminum, making it versatile for different broaching tasks. However, it may not perform well with softer materials, which can lead to rapid wear.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A681. The availability of HSS varies by region, so sourcing from local suppliers may reduce lead times and shipping costs.
Carbide
Key Properties:
Carbide is renowned for its extreme hardness and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-volume production. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, often exceeding 800°C, without degrading.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of carbide is its longevity, which reduces the frequency of tool changes. However, carbide tools are more expensive and can be brittle, leading to breakage if not handled properly.
Impact on Application:
Carbide is particularly effective for broaching hard materials like stainless steel or titanium. However, it may not be suitable for softer materials due to its tendency to chip.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of carbide that meet their operational needs. Compliance with standards like DIN 4972 is crucial, especially in Europe, to ensure quality and performance.
Alloy Steel
Key Properties:
Alloy steels combine various elements to enhance specific properties like toughness, strength, and wear resistance. They typically have good corrosion resistance and can be heat-treated to improve hardness.
Pros & Cons:
Alloy steel is more cost-effective than HSS and carbide, providing a good balance between performance and price. However, its performance can vary significantly depending on the alloying elements used, which may complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
Alloy steel is versatile and can be used for a range of broaching applications, particularly in automotive and machinery industries. Its compatibility with different media makes it a popular choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify the specific alloy composition to ensure it meets their operational requirements. Compliance with ASTM standards is essential for quality assurance, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments where moisture or chemicals are present. It maintains structural integrity at elevated temperatures.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, extending the lifespan of broaching tools. However, it is generally less hard than HSS or carbide, which can lead to quicker wear in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is ideal for broaching applications in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments due to its hygienic properties. However, it may not perform as well in heavy-duty applications compared to harder materials.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel grade complies with standards such as ASTM A276. Understanding regional preferences for specific grades can aid in sourcing the right materials.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for broach machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | General broaching applications | Excellent hardness and wear resistance | Brittle, can chip under stress | Medium |
| Carbide | High-volume production broaching | Extreme hardness and longevity | Expensive, brittle | High |
| Alloy Steel | Versatile applications in machinery | Cost-effective, good balance of properties | Variable performance based on composition | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments | Corrosion resistance | Less hard, quicker wear | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions when sourcing materials for broaching machines, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for broach machine
Manufacturing Processes for Broach Machines
Understanding the manufacturing processes of broach machines is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in this specialized equipment. The production of broach machines typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is vital in ensuring the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing a broach machine is selecting high-quality raw materials, primarily high-speed steel (HSS) or alloy steel. These materials are chosen for their hardness and durability, essential for the cutting tools of the broach. Material preparation involves:
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut to size using precision cutting machines. The shapes must conform to the designs specified in engineering drawings.
- Heat Treatment: To enhance the material’s hardness and wear resistance, heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering are applied. This step is critical for ensuring longevity and performance under operational stresses.
Forming
The forming stage involves shaping the various components of the broach machine, including the broach itself, using different manufacturing techniques:
- Machining: This includes processes such as milling, turning, and grinding to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for their accuracy and repeatability.
- Broach Manufacturing: Broaches are crafted with a specific tooth geometry to ensure optimal cutting performance. This involves multiple stages, including roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing, where each stage progressively refines the broach’s cutting edges.
Assembly
Once all components are formed, the next phase is assembly. This involves:
- Component Assembly: Individual parts, such as the broach tool, work-holding fixtures, and drive mechanisms, are assembled into the broach machine. The assembly must be done with precision to ensure proper alignment and functionality.
- Integration of Control Systems: Modern broach machines often feature hydraulic or electro-mechanical drives. During assembly, these control systems are integrated, requiring careful calibration to ensure smooth operation.
Finishing
The finishing stage is crucial for both aesthetic and functional purposes. It typically includes:
- Surface Treatments: Components may undergo surface treatments such as coating with titanium nitride (TiN) to enhance wear resistance and extend tool life.
- Quality Checks: Before final assembly, each component is subjected to rigorous quality checks to ensure compliance with design specifications.
Quality Assurance in Broach Machine Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of broach machines. It ensures that the machines produced meet international standards and customer expectations. Key aspects of QA include adherence to relevant international standards, establishing quality control checkpoints, and implementing common testing methods.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following international standards that govern the quality of manufacturing processes:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system and is applicable to any organization. It emphasizes a process-based approach and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For machines sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For broach machines used in the oil and gas sector, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducting checks during the manufacturing process to detect defects early. This may include monitoring machining tolerances and conducting dimensional checks.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection of the assembled broach machine before it is shipped. This includes functional testing and a thorough review of all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods used to verify the quality of broach machines include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure components meet precise specifications.
- Functional Testing: Operating the machine under load conditions to verify performance and operational efficiency.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection to identify internal flaws without damaging the components.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring the quality of broach machines from suppliers is vital. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing processes can provide insights into their quality management practices. This includes reviewing their adherence to ISO standards and internal quality protocols.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of quality checks, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. This transparency fosters trust and accountability.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality processes and final products. This is particularly beneficial for international transactions where buyers may not be able to visit the manufacturing site.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must be aware of specific nuances regarding quality control and certification that may vary by region:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the local manufacturing culture can help buyers assess the reliability of suppliers. For example, some regions may prioritize cost over quality, leading to potential compromises.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations in addition to international standards. This may include specific certifications required for machinery in their respective countries.
- Documentation and Traceability: Maintaining thorough documentation of all quality checks, certifications, and compliance is essential for international transactions. This ensures that any disputes regarding quality can be resolved effectively.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for broach machines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they invest in high-quality machinery that meets their operational needs.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for broach machine Sourcing
Broach machines are essential for a variety of manufacturing processes, and understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section provides a comprehensive analysis of the cost components, price influencers, and practical buyer tips tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in broach machine manufacturing include high-speed steel (HSS) or alloy steels. The choice of materials significantly affects the overall cost, with HSS being more affordable but potentially less durable than carbide options. Additionally, coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) can enhance tool life but add to material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary dramatically based on the region. In developing regions, labor may be less expensive, impacting the overall pricing structure favorably for buyers. However, skilled labor is necessary for the assembly and quality control of broach machines, which can lead to higher costs in areas with limited expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including facility costs, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Understanding the local manufacturing environment can help buyers anticipate these costs. For instance, countries with higher energy costs may see increased overhead.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom broaches. The complexity of the tooling design, along with the need for precise engineering, can lead to higher initial costs. Buyers should consider whether standard tooling can suffice for their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring quality through rigorous QC processes is essential. This can add to the cost, particularly if certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) are required. Buyers should assess the supplier’s QC capabilities to avoid future costs associated with defects or non-compliance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary based on the shipping distance, method, and volume. Incoterms play a critical role here, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin in the pricing, which can range from 10% to 40% depending on market conditions and the supplier’s positioning. Understanding the typical margins in the broach machine market can help buyers identify fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Buying in bulk can significantly reduce the per-unit cost. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized machines will generally incur higher costs due to the additional design and manufacturing processes required. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality: High-quality materials and certifications typically come with a higher price tag. Buyers must weigh the benefits of investing in better quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and proven quality, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the total cost of ownership. Terms like DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) can simplify logistics but might come with higher costs compared to FOB (Free on Board), where the buyer assumes more responsibility.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Buyers should not hesitate to negotiate pricing, especially when placing large orders. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assessing the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs, is crucial. Sometimes a higher upfront cost can lead to lower long-term expenses due to better durability or efficiency.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Additionally, understanding local market dynamics can help in assessing fair pricing.
-
Regional Considerations: Different regions may have varying standards and practices. Buyers from Africa and South America, for instance, may face different logistics challenges than their European counterparts, impacting overall costs.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific supplier agreements, market conditions, and additional factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for accurate pricing.
Spotlight on Potential broach machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘broach machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for broach machine
Key Technical Properties of Broach Machines
When considering the procurement of broach machines, understanding their technical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical properties to evaluate:
-
Material Grade:
– Definition: The quality and type of materials used in the construction of the broaching machine, typically high-speed steel (HSS) or alloy steel.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials ensure durability and resistance to wear, which is vital for maintaining precision and reducing downtime. For international buyers, verifying material grade can prevent costly replacements and ensure compatibility with local manufacturing standards. -
Tolerance:
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, crucial for ensuring parts fit together correctly.
– Importance: Tight tolerances are necessary for high-precision applications. In markets where quality control is paramount, such as in automotive or aerospace sectors, understanding tolerance specifications can be a deciding factor in machine selection. -
Broaching Stroke Length:
– Definition: The maximum distance the broach can travel during the cutting process.
– Importance: A longer stroke length allows for processing larger workpieces, which can be a significant advantage in high-volume production environments. Buyers should assess the stroke length in relation to their typical workpiece dimensions. -
Drive Mechanism:
– Definition: The system that powers the broaching process, commonly hydraulic or electro-mechanical.
– Importance: Different drive mechanisms offer varying levels of control and efficiency. Hydraulic systems tend to be more economical, while electro-mechanical systems may provide greater precision. Understanding these options helps buyers align machine capabilities with operational needs. -
Production Rate:
– Definition: The number of parts a broaching machine can produce in a given time frame, often measured in parts per hour.
– Importance: A higher production rate can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness, particularly for large-scale manufacturers. Buyers should consider their production requirements and match them with the machine’s capabilities. -
Cooling System:
– Definition: The method employed to manage heat during the broaching process, usually involving cutting fluids.
– Importance: An efficient cooling system prolongs tool life and enhances cutting performance. Buyers should inquire about the compatibility of cooling systems with their operational environment and materials.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the broaching machine market. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
– Refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess product quality and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
– The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for smaller businesses or new entrants in the market. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
– A formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This is a critical step in procurement, enabling buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple vendors. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
– A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, risk, and insurance. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for international transactions to avoid misunderstandings regarding shipping costs and liability. -
Lead Time:
– The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules and manage inventory effectively. -
Service Level Agreement (SLA):
– A contract that outlines the expected service standards between a supplier and a buyer. SLAs are crucial for establishing clear expectations regarding product support, maintenance, and response times, ensuring reliability in operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and establish more fruitful relationships with suppliers in the broaching machine industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the broach machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global broach machine market is witnessing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and machinery. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to industrialize, the need for high-efficiency machining processes is becoming paramount. Key trends include the adoption of advanced automation technologies, which enhance the efficiency and accuracy of broaching operations. Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles is leading to smarter broach machines that can provide real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and improved operational flexibility.
Sourcing trends are also evolving, with international buyers increasingly looking for suppliers that offer customized solutions tailored to specific production needs. The rise of digital platforms for sourcing equipment is making it easier for buyers to connect with manufacturers worldwide. Additionally, there is a noticeable shift towards local sourcing in certain regions, driven by the desire to reduce lead times and transportation costs, particularly in emerging markets.
Buyers should also be aware of geopolitical factors that can influence market dynamics, such as trade agreements and tariffs, which may affect pricing and availability. Understanding these trends is essential for making informed purchasing decisions and optimizing supply chains.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the broach machine sector, with increasing pressure on manufacturers to minimize their environmental impact. The production and operation of broaching machines can generate significant waste, including metal shavings and cutting fluids, which necessitates effective waste management and recycling strategies. International B2B buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and implementing energy-efficient technologies in their manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where supply chain transparency is gaining traction. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations, as this not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Moreover, the use of bio-based cutting fluids and recyclable broach materials is becoming increasingly common. These innovations not only reduce environmental impact but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Brief Evolution/History
The broaching machine has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-19th century. Initially, broaching tools were rudimentary and operated manually. The introduction of hydraulic and electric drives in the 20th century revolutionized the sector, allowing for greater precision and efficiency. Over time, advancements in materials science, particularly the development of high-speed steel and carbide tools, have further enhanced the capabilities of broaching machines.
Today, modern broach machines are equipped with sophisticated control systems, enabling manufacturers to perform complex machining tasks with minimal human intervention. This evolution reflects the broader trends in manufacturing towards automation, precision, and sustainability, making broaching an essential process in contemporary production environments. International buyers should leverage this historical context to appreciate the technological advancements that impact the performance and reliability of broach machines.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of broach machine
-
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing broach machines internationally?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their company history, production capabilities, and customer reviews. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate quality management systems. Engage with previous clients to understand their experiences and request samples of their work. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facility if possible or utilizing third-party inspection services to evaluate the equipment and processes firsthand. -
What customization options are typically available for broach machines?
Many manufacturers offer customization to meet specific operational needs. This may include adjustments in size, tooling specifications, and operational speed. Discuss your particular application with potential suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your requirements, such as tailored broach designs for unique shapes or materials. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of integrating automation features to enhance production efficiency. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for broach machines?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier’s production capacity and the complexity of the machine. Generally, established manufacturers may have a minimum order of 1-5 units, while custom machines may require larger orders. Lead times typically range from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the machine’s specifications and the supplier’s workload. Always confirm these details upfront to align your production schedules with the supplier’s capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing broach machines?
Payment terms vary by supplier but generally include options such as a deposit followed by a balance payment upon delivery or installation. Be prepared to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow, but ensure that they are secure. Consider using escrow services for larger transactions to protect your investment. Additionally, verify whether the supplier accepts international payment methods such as letters of credit or bank transfers. -
What quality assurance certifications should I look for in broach machines?
Look for suppliers who have quality assurance certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Additionally, check if the machines come with CE marking for compliance with European safety standards, especially if you are sourcing from Europe. Request documentation of quality control processes and any test reports related to the machines’ performance and durability. -
How can I manage logistics when importing broach machines?
Engage a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping regulations to facilitate the import process. Understand the total landed cost, which includes shipping, customs duties, and insurance. Ensure that your supplier provides appropriate documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, to streamline customs clearance. Consider shipping insurance to mitigate risks during transit, and plan for potential delays in delivery due to customs or logistical issues. -
What should I do in case of disputes with my supplier?
Establish clear communication channels and document all agreements, including specifications and timelines, to prevent misunderstandings. If disputes arise, attempt to resolve them amicably through direct negotiation. If that fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution methods, such as mediation or arbitration. Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations that may apply, and consider involving legal counsel if necessary. -
How can I ensure the machines are delivered as specified?
To ensure that the machines meet your specifications upon delivery, conduct a thorough inspection upon receipt. Utilize checklists based on the agreed specifications and quality standards. If possible, arrange for a pre-shipment inspection by a third party to confirm that the machines meet the agreed-upon criteria before shipping. Document any discrepancies immediately and communicate them to the supplier to resolve issues swiftly.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for broach machine
In summary, the strategic sourcing of broach machines presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various types of broaching machines—horizontal, vertical, surface, and continuous—along with their specific applications can lead to better procurement decisions. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that utilize high-quality materials and advanced technologies, ensuring durability and precision in their machining processes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic sourcing not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to cost savings and improved product quality. As global supply chains evolve, buyers must remain agile, exploring partnerships that offer both innovation and reliability.
Looking ahead, the demand for broach machines is expected to grow as industries increasingly adopt automation and precision engineering techniques. International B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage this momentum by actively seeking suppliers that align with their strategic goals. By doing so, they can position themselves to capitalize on emerging market trends and secure a competitive advantage in their respective sectors.