Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Ceramic Heater
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ceramic heater
Navigating the global market for ceramic heaters is essential for businesses seeking reliable, efficient heating solutions. Ceramic heaters are increasingly favored for their high thermal efficiency, durability, and ability to operate in extreme environments. These heaters not only provide rapid heat-up times but also ensure precise temperature control, making them indispensable across various industries, from manufacturing and construction to medical applications.
This guide aims to empower international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, by offering a comprehensive overview of ceramic heaters. We will delve into the different types of ceramic heating elements, explore the materials used, and examine the manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure product reliability. Additionally, we will provide insights into sourcing strategies, cost considerations, and key market trends, alongside a detailed FAQ section to address common queries.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and up-to-date information, this guide will facilitate informed sourcing decisions, helping businesses optimize their heating solutions while navigating the complexities of the global market. Whether you are a manufacturer, distributor, or end-user, understanding the nuances of ceramic heaters will enhance your procurement strategy and ultimately drive operational efficiency.
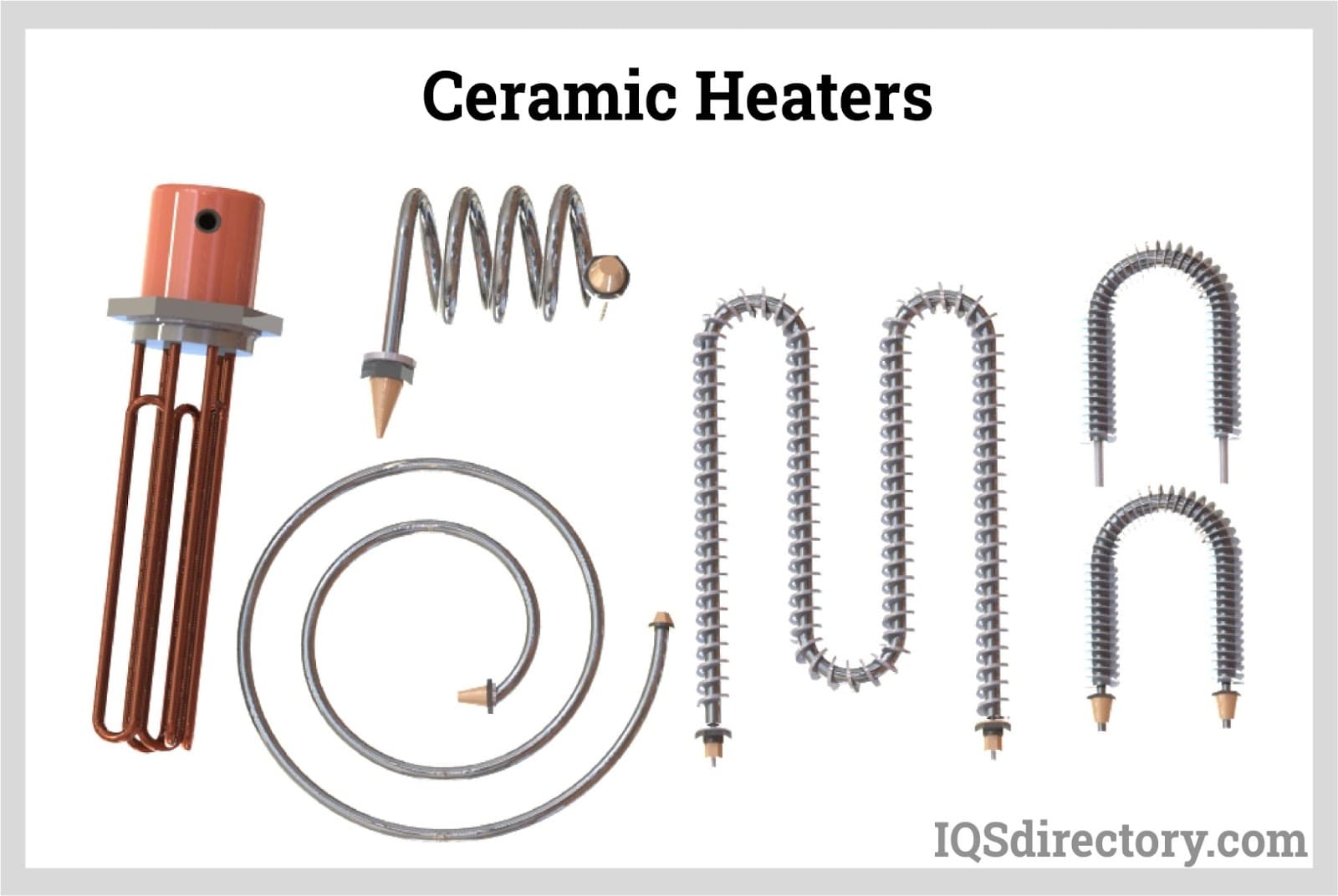
Understanding ceramic heater Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCH Ceramic Heaters | Metal-Ceramic hybrid, rapid heating, precise temperature control | Electronics, Medical Devices | Pros: Fast response, compact design. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| PTC Ceramic Heaters | Positive Temperature Coefficient technology, self-regulating | HVAC systems, Home Appliances | Pros: Energy-efficient, safe operation. Cons: Limited high-temperature applications. |
| Infrared Ceramic Heaters | Emit infrared radiation, quick heat-up time | Industrial heating, Food processing | Pros: Direct heating, energy-efficient. Cons: Can be costly upfront. |
| Fan-Forced Ceramic Heaters | Integrated fan for enhanced heat distribution | Workshops, Warehouses | Pros: Efficient air circulation, fast heating. Cons: Noisy operation. |
| Tubular Ceramic Heaters | Cylindrical shape, versatile installation options | Manufacturing, Chemical processing | Pros: Durable, high thermal efficiency. Cons: Bulkier design. |
MCH Ceramic Heaters
MCH (Metal-Ceramic Heater) elements are notable for their combination of ceramic insulation and embedded metal circuits. This design allows for rapid heating and precise temperature control, making them ideal for applications in electronics, such as soldering irons and medical devices. When purchasing MCH heaters, buyers should consider factors like thermal efficiency, size constraints, and the specific heating requirements of their applications, as these elements tend to have a higher initial cost but provide exceptional performance.
PTC Ceramic Heaters
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) ceramic heaters leverage self-regulating technology, which means they automatically adjust their resistance as the temperature changes. This feature makes them particularly suitable for HVAC systems and home appliances, where energy efficiency and safety are paramount. B2B buyers should evaluate the operating temperature range and energy consumption of PTC heaters, as they are highly efficient but may not perform well in extreme heat environments.
Infrared Ceramic Heaters
Infrared ceramic heaters operate by emitting infrared radiation, which directly heats objects rather than warming the air. This characteristic makes them highly effective for industrial heating applications and food processing, where quick heat-up times are crucial. When sourcing infrared heaters, buyers should assess the energy efficiency and installation requirements, as these systems may involve higher upfront costs but can lead to significant long-term savings through energy use.
Fan-Forced Ceramic Heaters
Fan-forced ceramic heaters incorporate a built-in fan to distribute heat evenly across larger spaces, making them suitable for workshops and warehouses. Their ability to circulate warm air quickly allows for efficient heating in commercial settings. Buyers should consider the noise level and maintenance requirements when selecting fan-forced heaters, as these units can be noisier than other types, potentially affecting the work environment.
Tubular Ceramic Heaters
Tubular ceramic heaters feature a cylindrical design that allows for versatile installation options, making them popular in manufacturing and chemical processing applications. These heaters are known for their durability and high thermal efficiency. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the heater’s size, wattage, and compatibility with existing systems, as their bulkier design may require more space and specific mounting arrangements.
Related Video: What’s In an Electric Heater? Test & Teardown of 4 Heater Types
Key Industrial Applications of ceramic heater
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Ceramic Heater | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics Manufacturing | Soldering and PCB Assembly | Precise temperature control for soldering processes | Need for high thermal efficiency and rapid heat-up times |
| Automotive | Engine Block Heating | Enhanced efficiency in engine testing | Durability under extreme conditions and resistance to corrosion |
| Food Processing | Industrial Ovens and Food Drying | Uniform heating for consistent product quality | Compliance with food safety standards and energy efficiency |
| HVAC Systems | Duct Heaters and Air Handlers | Improved air temperature regulation | Compatibility with various HVAC systems and energy ratings |
| Medical Equipment | Sterilization and Heating in Medical Devices | Reliable operation for critical medical applications | High precision and compliance with medical standards |
Electronics Manufacturing
In the electronics sector, ceramic heaters are integral to soldering and PCB assembly processes. They provide precise temperature control essential for soldering components without damaging sensitive electronic parts. These heaters resolve issues related to inconsistent heating, which can lead to poor solder joints and product failures. Buyers should prioritize sourcing ceramic heaters that offer high thermal efficiency and rapid heat-up times to enhance production rates and minimize energy consumption.
Automotive
Ceramic heaters are used in automotive applications, particularly in engine block heating. This technology ensures that engines reach optimal operating temperatures quickly, improving efficiency during testing and reducing wear on components. The main challenge addressed is the need for reliable heating under extreme conditions. When sourcing, buyers should look for heaters that demonstrate durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments.
Food Processing
In food processing, ceramic heaters are utilized in industrial ovens and food drying equipment. They provide uniform heating, which is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety. This application solves problems related to uneven cooking and drying, which can lead to spoilage or safety concerns. Buyers should ensure that the heaters comply with food safety standards and emphasize energy efficiency to reduce operational costs.
HVAC Systems
Ceramic heaters play a vital role in HVAC systems, particularly in duct heaters and air handlers. They enhance air temperature regulation, providing comfort in residential and commercial spaces. The challenge of maintaining consistent temperatures can be effectively addressed with these heaters. Buyers should consider compatibility with various HVAC systems and look for energy ratings that indicate efficiency, as this can significantly impact operational costs.
Medical Equipment
In the medical field, ceramic heaters are essential for sterilization processes and heating in medical devices. Their reliable operation is critical for ensuring patient safety and equipment functionality. The use of ceramic heaters addresses the need for precise temperature control in sensitive applications. Buyers in this sector must focus on sourcing heaters that meet high precision standards and comply with stringent medical regulations to ensure safety and efficacy.
Related Video: A1321 ceramic heater (Hakko clone) for soldering iron /pinout/installation/tests
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ceramic heater
When selecting materials for ceramic heaters, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze several common materials used in ceramic heaters, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, and implications for specific applications.
Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Key Properties: Alumina is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and high-temperature resistance, typically rated up to 1,600°C. It also exhibits good electrical insulation and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The durability of alumina is one of its key strengths, as it can withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress. However, it can be relatively expensive to manufacture, particularly for high-purity grades. Its brittleness may pose challenges during handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Alumina’s compatibility with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, makes it ideal for industrial applications such as furnaces and kilns. However, its brittleness may limit its use in applications where mechanical impact is a concern.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM or DIN) when sourcing alumina-based heaters. Understanding the availability of high-purity alumina in local markets can also influence purchasing decisions.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Key Properties: Silicon carbide offers high thermal conductivity and exceptional thermal shock resistance, with operating temperatures exceeding 1,600°C. It is also highly resistant to oxidation and chemical corrosion.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of SiC is its durability and ability to operate in extreme conditions, making it suitable for high-performance applications. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, leading to higher prices compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: SiC is particularly effective in applications involving high temperatures and aggressive environments, such as semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature furnaces. Its compatibility with various media enhances its versatility.
Considerations for Buyers: International buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, should be aware of the specific standards governing SiC materials. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to quality certifications can mitigate risks associated with performance and safety.
Zirconia (ZrO₂)
Key Properties: Zirconia is known for its high thermal insulation properties and can withstand temperatures up to 2,500°C. It also provides excellent mechanical strength and resistance to wear.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of zirconia is its ability to maintain structural integrity at extreme temperatures, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. However, it is relatively expensive and may not be as readily available as other materials.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is commonly used in applications requiring high thermal stability, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Its high cost may limit its use in less critical applications.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers in regions with stringent quality requirements, such as Turkey and Europe, should prioritize suppliers that can provide detailed material certifications. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance, is crucial when considering zirconia.
Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Key Properties: Magnesium oxide has good thermal conductivity and can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°C. It also offers excellent electrical insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: MgO is less expensive than alumina and zirconia, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive applications. However, it is less durable and can be prone to degradation in highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Magnesium oxide is suitable for applications where cost is a significant factor, such as in heating pads and low-temperature furnaces. Its limited resistance to harsh chemicals may restrict its use in more demanding settings.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers from South America and Africa may find magnesium oxide more accessible and cost-effective. However, they should be cautious about the material’s limitations in corrosive environments and ensure that it meets relevant safety standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for ceramic heater | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Industrial furnaces and kilns | Excellent thermal conductivity | Brittle and expensive | High |
| Silicon Carbide | Semiconductor manufacturing | High durability and thermal shock resistance | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Zirconia | Aerospace and automotive applications | High thermal stability | Expensive and less readily available | High |
| Magnesium Oxide | Heating pads and low-temperature furnaces | Cost-effective | Less durable and limited chemical resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on performance characteristics, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ceramic heater
The manufacturing of ceramic heaters involves several critical processes and stringent quality assurance measures that are essential for producing reliable and efficient heating elements. Understanding these processes and quality checks will enable B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to make informed decisions when sourcing ceramic heaters.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves selecting and preparing raw materials. High-quality ceramic powders, typically alumina (Al2O3), are mixed with additives to enhance properties such as thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. This mixture is carefully formulated to ensure consistency and performance.
Key Techniques:
– Mixing: Uniform blending of ceramic powders and additives to achieve the desired properties.
– Granulation: Converting the mixed powder into granules for easier handling and processing.
2. Forming
Once the material is prepared, it undergoes forming to create the desired shape of the ceramic heater. This can be achieved through various methods:
- Pressing: The powder is compacted into molds under high pressure. This method is common for producing bulk components.
- Injection Molding: Suitable for complex shapes, where the ceramic slurry is injected into a mold.
- Casting: Involves pouring the ceramic slurry into molds, allowing it to set before demolding.
Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the design and application requirements of the heater.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled. This may include integrating metal parts for electrical connections, such as terminals or heating elements. The assembly must be precise to ensure electrical and thermal efficiency.
Key Techniques:
– Sintering: A critical process where the formed components are heated to a temperature below their melting point, causing the particles to bond and strengthen the material.
– Coating: Applying protective coatings to enhance durability and thermal resistance.
4. Finishing
The final stage of the manufacturing process involves finishing operations that improve the heater’s performance and aesthetics. This may include:
- Surface Treatment: Enhancing surface properties for better thermal conductivity and resistance to oxidation.
- Quality Trimming and Polishing: Ensuring that all edges are smooth and that the heater meets the specified dimensions.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of ceramic heaters, as it directly impacts their performance and safety. The following international standards and industry-specific certifications are crucial:
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems and ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for ceramic heaters used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring reliability under extreme conditions.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product before shipment to confirm that it meets all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods for ceramic heaters include:
- Electrical Resistance Testing: Ensures that the heater operates within the specified resistance range.
- Thermal Performance Testing: Evaluates the heater’s efficiency and ability to reach and maintain required temperatures.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the durability and structural integrity of the ceramic materials under stress.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is critical to ensure reliable products. Here are some actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regular on-site audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the production processes and quality control measures.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports that document compliance with relevant standards and testing results.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspectors to verify quality claims can ensure objectivity and credibility in the supplier’s processes.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from diverse regions may face unique challenges regarding quality control and certification:
- Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards in their respective countries to ensure compliance.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that all documentation, including quality reports and certifications, is available in a language that can be understood by the buyer.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances can facilitate better communication with suppliers, ensuring that quality expectations are met.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for ceramic heaters, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Sintering Process |An Essential Step of Alumina Ceramic Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ceramic heater Sourcing
Ceramic heaters are essential components in various industrial applications, and understanding their cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will provide insights into the cost components involved, the factors influencing pricing, and practical tips for optimizing sourcing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary costs for ceramic heaters are driven by the raw materials used, including high-grade ceramics, metals for wiring, and insulation materials. The choice of materials significantly impacts the heater’s performance, durability, and ultimately, its cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be a significant portion of the total manufacturing cost. Skilled labor is often required for assembling complex heating elements, particularly in regions with higher wage standards.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance of equipment. Overhead can be substantial, especially for manufacturers operating in developed countries where operational costs are higher.
-
Tooling: Initial investment in tooling and machinery for producing ceramic heaters can be significant. This is especially true for custom or specialized designs, which require specific molds and production setups.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount, especially for heating elements that must meet safety and performance standards. QC processes add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining reliability and compliance.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and regional infrastructure. For international buyers, understanding the logistics involved is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market competition, supplier reputation, and the complexity of the product.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit prices. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specifications typically incur higher costs due to additional manufacturing processes and materials. Buyers should assess whether customization is necessary for their applications.
-
Materials: The quality of materials directly impacts the pricing. Premium materials can enhance performance but will also increase costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international standards and certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should consider the value of these certifications in relation to their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge a premium, but they also reduce risk for buyers.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage total costs effectively.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your requirements and market prices. Be prepared to discuss volume commitments for better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial purchase price. Factor in maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan when evaluating options.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and potential tariffs or duties that could affect the final pricing. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and priority in supply during high-demand periods.
Disclaimer
Prices for ceramic heaters can fluctuate based on market conditions, material costs, and regional factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are getting competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential ceramic heater Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘ceramic heater’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ceramic heater
Ceramic heaters are crucial components in various industrial and commercial applications, and understanding their technical properties and trade terminology is essential for effective procurement. Below are key specifications and terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with when sourcing ceramic heaters.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the composition and quality of the ceramic material used in the heater. Common grades include aluminum oxide and silicon carbide.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials typically offer better thermal conductivity, durability, and resistance to thermal shock. For international buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures the heater can withstand specific operational environments. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the allowable variation in dimensions or performance characteristics of the ceramic heater.
– Importance: A tight tolerance is crucial for applications requiring precise temperature control. Buyers must consider tolerance specifications to ensure compatibility with existing systems, especially in precision industries like electronics and medical equipment. -
Power Rating
– Definition: This is the maximum power input (measured in watts) the ceramic heater can handle without failure.
– Importance: Understanding the power rating is essential for ensuring that the heater can meet the energy demands of the application. Buyers need to match power ratings with operational requirements to optimize efficiency and performance. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Definition: This specification defines the maximum and minimum temperatures at which the ceramic heater can function effectively.
– Importance: Different applications require different temperature ranges. For instance, high-temperature applications in industrial settings necessitate heaters that can operate at elevated temperatures without degrading. -
Heating Element Type
– Definition: This refers to the specific design of the heating element, such as MCH (Metal-Ceramic Heater) or PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient).
– Importance: Different types of heating elements offer various benefits, such as faster heating times or self-regulating properties. Buyers should select the type that best fits their operational needs.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Significance: Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source reliable components that integrate seamlessly into existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning. Buyers should ensure that the MOQ aligns with their inventory and usage needs to avoid excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specified products or services.
– Significance: An RFQ is essential for comparing offers from multiple suppliers. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to receive accurate and competitive quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global transactions.
– Significance: Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping, insurance, and risk management. Buyers should ensure that terms are clearly defined to avoid disputes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Significance: Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules and inventory management effectively. It is particularly important in industries where timely delivery is critical.
By comprehending these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing ceramic heaters, ensuring they select the right products for their specific applications and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the ceramic heater Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The ceramic heater market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions across various industries. Global trends indicate a shift towards smart technology integration in heating systems, enhancing user control and energy management. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should note the rising interest in Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) technology, which offers automatic temperature regulation, improving safety and efficiency.
Additionally, the push for sustainability is reshaping sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly favoring manufacturers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes. For instance, ceramic heating elements known for their durability and long lifespan are becoming preferred choices due to their lower environmental impact over time. Emerging markets are witnessing a surge in demand for compact and portable heating solutions, particularly in the consumer electronics and automotive sectors.
International buyers should also be aware of fluctuating raw material prices, which can affect procurement strategies. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Furthermore, leveraging digital platforms for sourcing not only enhances transparency but also allows buyers to access a wider range of manufacturers, particularly those from emerging markets like Turkey and Brazil.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral consideration; it is central to the decision-making process in B2B procurement. The ceramic heater industry faces scrutiny regarding its environmental impact, particularly concerning the sourcing of raw materials and energy consumption during manufacturing. International buyers should prioritize ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that their suppliers adhere to environmental regulations and labor standards.
The use of green certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management can serve as a benchmark for assessing supplier sustainability. Additionally, opting for ceramic heaters made from recycled materials or those that utilize renewable energy sources during production can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with heating solutions.
Buyers should also consider manufacturers that actively engage in waste reduction initiatives and invest in innovative technologies to minimize emissions. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, businesses not only enhance their corporate image but also meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The ceramic heater industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, ceramic heating elements were primarily used in industrial applications due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and provide consistent heat. Over the years, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of more efficient and compact ceramic heaters suitable for residential and commercial applications.
Today, the integration of smart technology and a focus on sustainability are at the forefront of the industry’s evolution. As global energy demands increase, ceramic heaters are becoming synonymous with energy efficiency and environmental responsibility, making them a compelling choice for international B2B buyers looking to invest in future-proof heating solutions.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ceramic heater
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of ceramic heaters?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience, production capacity, and certifications such as ISO 9001. Check their previous client references and reviews to assess reliability. Request information about their quality control processes and inquire about their ability to meet international standards, especially if you are importing from regions like Asia or Europe. A site visit can also provide insight into their manufacturing practices and infrastructure. -
Can ceramic heaters be customized to meet specific industrial needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for ceramic heaters. You can specify dimensions, wattage, voltage, and even specific materials to suit your application. Discuss your requirements directly with the supplier to ensure they can accommodate your needs. Keep in mind that custom orders may affect lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs), so clarify these details upfront. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for ceramic heaters?
MOQs for ceramic heaters can vary significantly by supplier and product type, typically ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times generally span from 2 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production schedule. Always confirm these details before placing an order, especially if you have tight deadlines for your projects. -
What payment options should I expect when sourcing ceramic heaters internationally?
Payment terms can vary, but common options include letters of credit, bank transfers, or payment through platforms like PayPal. For larger orders, suppliers may offer flexible payment plans or deposits. Ensure you understand the supplier’s payment policies and any associated fees, particularly when dealing with international transactions, as currency exchange rates may also impact the final cost. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in ceramic heaters?
Effective quality assurance measures include certifications such as CE, UL, or RoHS, which indicate compliance with safety and environmental standards. Request detailed reports on testing procedures and results, as well as warranty terms. It’s advisable to ask for samples to evaluate the quality of the heaters before making a bulk purchase, as this can help prevent issues later on. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of ceramic heaters?
Logistics for international orders typically involve freight forwarding, customs clearance, and delivery to your specified location. Discuss with your supplier whether they handle shipping or if you need to arrange it yourself. Factor in shipping costs, lead times, and potential customs duties when budgeting. Working with a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the process and mitigate delays. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with my ceramic heater supplier?
In case of a dispute, start by communicating directly with the supplier to address the issue. Document all correspondence and agreements to reference later. If resolution is not reached, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract. Always ensure that your contracts include clear terms regarding dispute resolution and the governing law, especially for international agreements. -
What certifications are important for ceramic heater suppliers?
Important certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking for compliance with European safety standards, and RoHS compliance for environmental regulations. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to recognized industry practices. Additionally, check for any specific certifications relevant to your industry, such as UL for electrical safety in North America, to ensure that the products meet your operational requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ceramic heater
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of ceramic heaters presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the unique advantages of ceramic heating elements—such as their high efficiency, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures—buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational capabilities.
Key takeaways include:
- Supplier Diversification: Engage with multiple manufacturers to ensure a steady supply chain and to take advantage of competitive pricing.
- Quality Assurance: Prioritize suppliers that emphasize quality control, as this ensures reliability and longevity in performance.
- Technological Adoption: Consider advanced ceramic heating technologies like MCH for specific applications requiring precision and rapid heating.
As the demand for energy-efficient heating solutions grows, staying ahead of trends in the ceramic heating market will be crucial. By proactively sourcing innovative products and building strong supplier relationships, B2B buyers can position themselves for long-term success. Now is the time to explore these opportunities and invest in high-quality ceramic heaters that will support your business needs and drive future growth.