Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Conveying System
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for conveying system
In today’s globalized economy, the efficiency and reliability of material handling systems are paramount for businesses aiming to enhance their operational performance. Conveying systems play a crucial role in this landscape, acting as the backbone of manufacturing and logistics across various industries. From automating the movement of bulk materials to streamlining production lines, these systems not only improve productivity but also reduce labor costs and minimize the risk of contamination.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of conveying systems, offering international B2B buyers—particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—a detailed exploration of essential topics. You will gain insights into the various types of conveying systems, including belt, screw, and pneumatic systems, each tailored to specific applications and material types. Additionally, the guide covers key aspects of manufacturing quality control, supplier evaluation, and cost considerations, empowering you to make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
By navigating the intricacies of the global market for conveying systems, you will be equipped with the knowledge to optimize your sourcing strategy. This guide addresses common questions and provides actionable insights, ensuring that you can select the right solutions to meet your operational needs while enhancing your competitive edge in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Understanding conveying system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt Conveyors | Continuous loop of flexible material; versatile incline or horizontal operation. | Manufacturing, logistics, and food processing. | Pros: Low maintenance, easy to customize. Cons: Limited to certain materials and may require more space. |
| Screw Conveyors | Helical screw blade for pushing materials; enclosed design to prevent spillage. | Agriculture, chemical processing, and construction. | Pros: Efficient for granular materials, customizable length. Cons: Limited to specific materials; can be less efficient for bulk. |
| Bucket Elevators | Vertical transport using buckets; designed for bulk materials. | Grain handling, mining, and fertilizer distribution. | Pros: High capacity, effective for vertical movement. Cons: Higher initial costs; requires more space for installation. |
| Pneumatic Conveying Systems | Utilizes air to move materials through pipelines; enclosed system reduces dust. | Food processing, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. | Pros: Clean operation, reduced contamination risk. Cons: Higher energy costs; requires precise control for efficiency. |
| Magnetic Conveyors | Uses magnetic forces to move ferrous materials; flexible configurations. | Automotive, electronics, and metal processing. | Pros: Effective for small parts, minimal wear. Cons: Limited to magnetic materials; may require specialized maintenance. |
Belt Conveyors
Belt conveyors are one of the most recognized types of conveying systems, featuring a continuous loop of flexible material driven by pulleys. They can be adapted for horizontal or inclined transport, making them suitable for a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, logistics, and food processing. Buyers should consider the specific material types and sizes they will be handling, as well as the available space for installation.
Screw Conveyors
Screw conveyors employ a helical screw blade that rotates to push materials forward, often encased to prevent spillage. They are particularly effective for granular materials and liquids, commonly used in agriculture, chemical processing, and construction. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the material’s characteristics, such as abrasiveness and moisture content, to ensure compatibility with the screw design.
Bucket Elevators
Bucket elevators are designed to transport bulk materials vertically using a series of buckets attached to a belt or chain. This system is ideal for applications in grain handling, mining, and fertilizer distribution due to its high capacity and efficiency in moving materials against gravity. Buyers should assess the initial investment and space requirements, as these systems can be more costly and require a larger footprint.
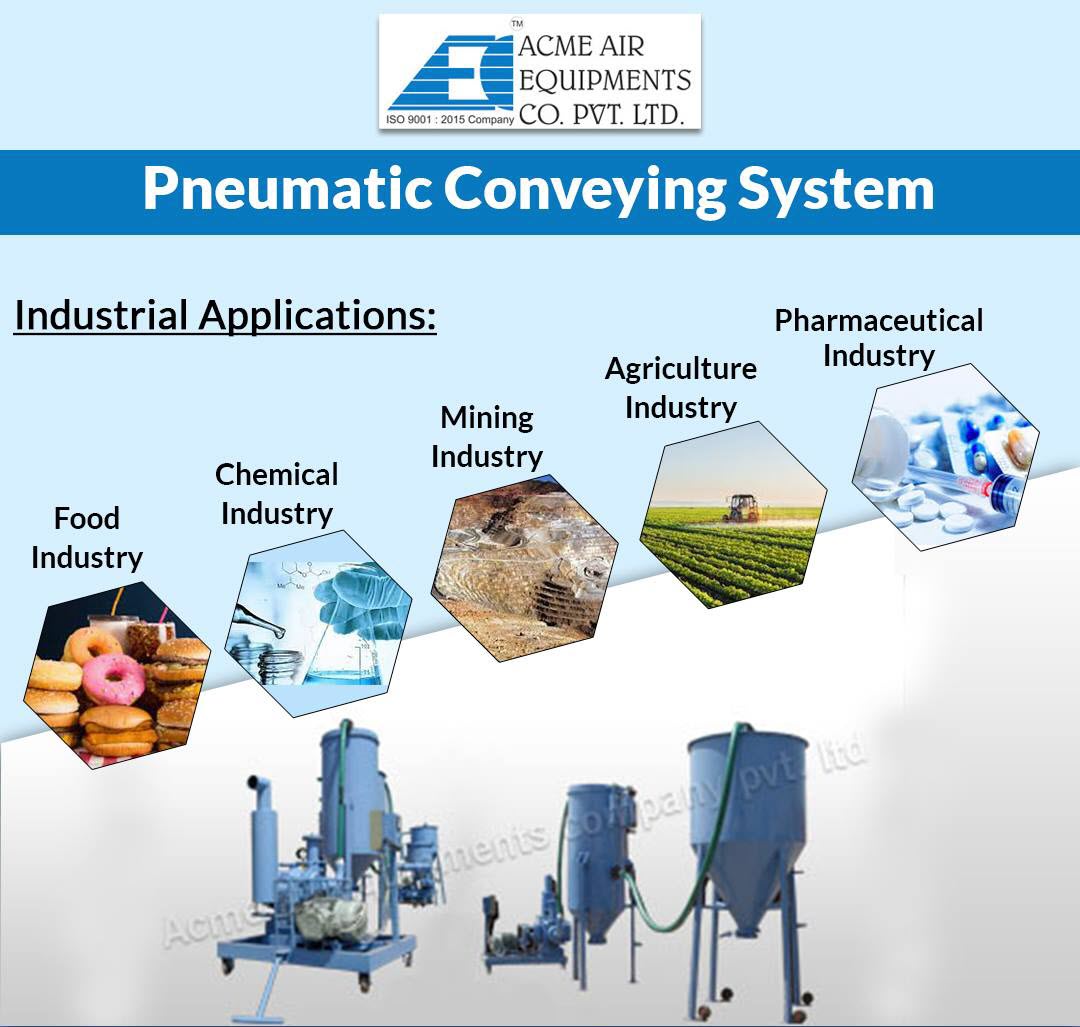
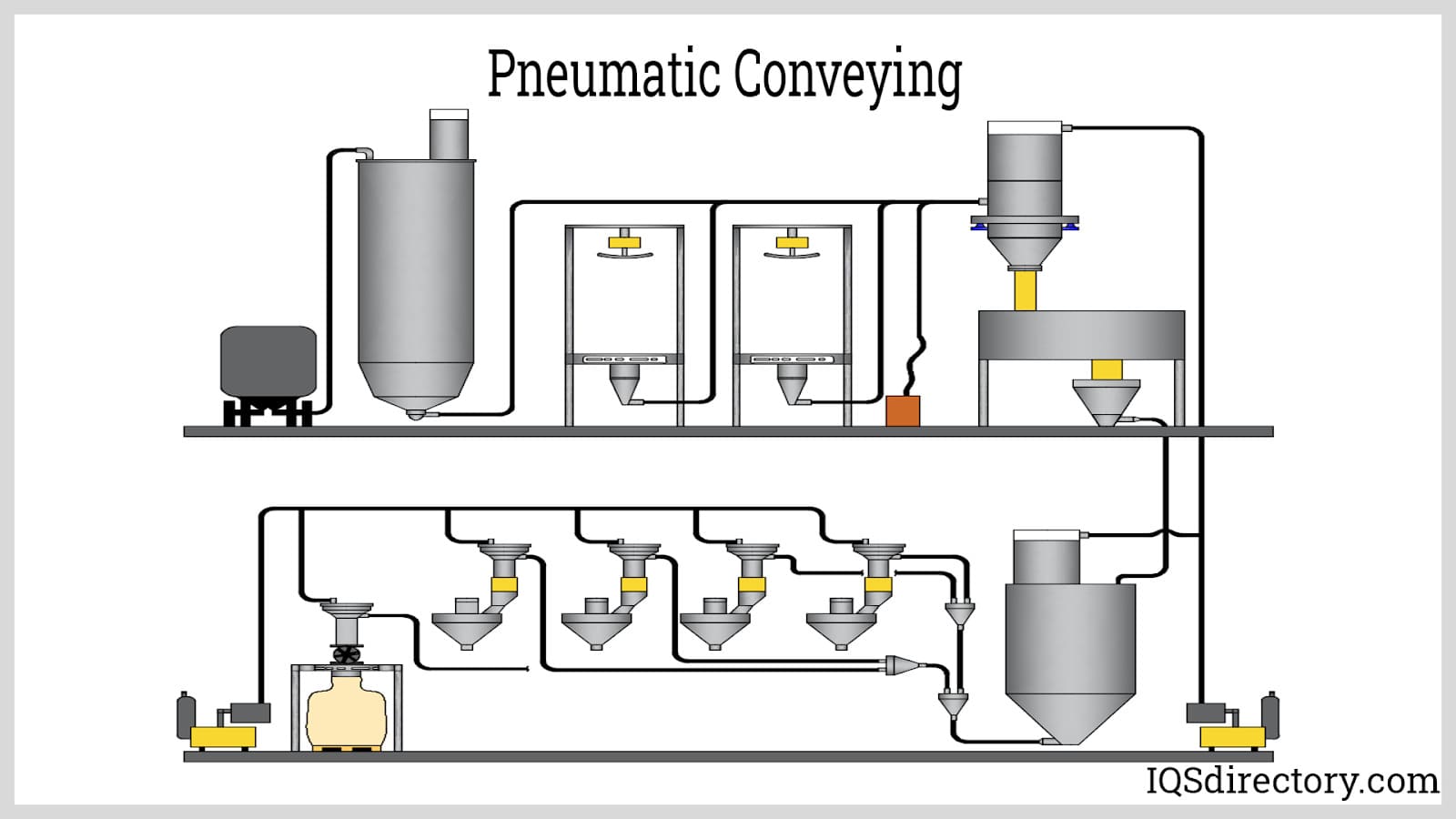
Pneumatic Conveying Systems
Pneumatic conveying systems leverage air to move bulk solids or powders through enclosed pipelines, providing a clean and efficient transport method. They are widely used in food processing, plastics, and pharmaceuticals, where contamination control is critical. Buyers should consider the energy costs associated with these systems, as well as the need for precise control mechanisms to maintain efficiency and minimize product degradation.
Magnetic Conveyors
Magnetic conveyors utilize magnetic forces to transport ferrous materials along a belt. This system offers flexibility in configurations and is particularly effective for handling small parts in industries such as automotive and electronics. Buyers must keep in mind that these conveyors are limited to magnetic materials and may require specialized maintenance, which can impact long-term operational costs.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of conveying system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of conveying system | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Transporting bulk ingredients like grains and sugar | Enhanced efficiency, reduced contamination risk | Compliance with food safety standards, material durability |
| Mining and Minerals | Moving ores and aggregates | Increased productivity, minimized manual handling | Equipment robustness, ability to handle heavy loads |
| Pharmaceuticals | Handling powders and granules | Improved accuracy, reduced contamination | Precision engineering, compliance with regulatory standards |
| Agriculture | Conveying fertilizers and seeds | Streamlined operations, reduced waste | Material compatibility, weather resistance |
| Packaging | Automated sorting and packaging of products | Enhanced throughput, reduced labor costs | Customization options, scalability for production needs |
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, conveying systems are utilized to transport bulk ingredients such as grains, sugar, and flour from storage to processing areas. These systems help streamline operations by facilitating continuous flow, reducing manual labor, and minimizing contamination risks. For international buyers, it’s crucial to ensure that the conveying systems comply with local food safety regulations and standards. Additionally, the durability of materials used in construction can significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of the systems.
Mining and Minerals
Conveying systems play a vital role in the mining and minerals sector, where they are employed to move ores, aggregates, and other heavy materials. These systems enhance productivity by automating the transport process, thus minimizing the need for manual handling and reducing labor costs. When sourcing equipment, international buyers should consider the robustness of the systems to handle heavy loads and the environmental conditions of the operational site, ensuring that the equipment can withstand harsh mining environments.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, conveying systems are essential for handling powders and granules with precision. These systems improve accuracy in material transfer and significantly reduce contamination risks, which is critical in maintaining product integrity. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing systems that adhere to stringent regulatory standards, such as GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice), to ensure compliance and safety. Precision engineering is also a key consideration, as it impacts the system’s performance and reliability.
Agriculture
In agriculture, conveying systems are commonly used for transporting fertilizers and seeds from storage to application points. This automation streamlines operations, reduces waste, and enhances efficiency in farming practices. For international buyers, it is important to assess the material compatibility of the conveying systems, particularly in terms of handling different types of fertilizers and seeds. Additionally, sourcing equipment that can withstand various weather conditions is essential to ensure consistent operation.
Packaging
The packaging industry benefits significantly from automated conveying systems, which are employed for sorting and packaging products efficiently. These systems enhance throughput, reduce labor costs, and improve the overall efficiency of production lines. Buyers should look for customizable options that can adapt to varying production needs and scalability, ensuring that the systems can grow alongside their business. It is also vital to consider the integration capabilities with existing machinery to optimize workflow.
Related Video: Pneumatic Conveying System (Dilute Phase)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for conveying system
When selecting materials for conveying systems, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in conveying systems, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand elevated temperatures (up to 870°C). It is also non-reactive, making it suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can endure harsh environments without degrading. However, its high cost compared to other materials can be a drawback, particularly for large-scale operations. Manufacturing complexity can also increase due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for conveying systems that handle corrosive materials or require stringent hygiene standards, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local food safety regulations and standards such as ASTM or ISO. In regions like Europe, adherence to EU regulations for food-grade materials is crucial.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel offers good strength and wear resistance, with a temperature rating of up to 500°C. It is generally less expensive than stainless steel but is prone to rusting if not properly coated.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects. However, its susceptibility to corrosion limits its use in wet or corrosive environments, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in bulk material handling systems for aggregates, coal, and other non-corrosive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the local availability of protective coatings and maintenance services to prevent rust and extend the life of carbon steel components.
3. Polypropylene
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a lightweight, chemical-resistant thermoplastic that can operate effectively within a temperature range of -20°C to 100°C. It is particularly resistant to acids and bases.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of polypropylene is its low weight and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for transporting various materials, including chemicals and food products. However, it has a lower strength compared to metals and may not be suitable for high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is ideal for pneumatic conveying systems that handle powders and granules, especially in the chemical and food industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected polypropylene grades comply with local regulations regarding food safety and chemical handling, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a temperature rating of up to 400°C. Its strength-to-weight ratio makes it a popular choice for various conveying applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier installation and reduced energy costs in conveying systems. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and may require additional maintenance to prevent corrosion in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications requiring lightweight components, such as in packaging and food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet local standards for food safety and environmental regulations, particularly in regions where recycling and sustainability are prioritized.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for conveying system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Bulk material handling (non-corrosive) | Cost-effective, good strength | Prone to rust, requires protective coatings | Medium |
| Polypropylene | Chemical and food product handling | Lightweight, chemical resistance | Lower strength, not suitable for heavy loads | Low |
| Aluminum | Packaging, food processing | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Higher cost, requires maintenance | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for conveying systems, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for conveying system
In the realm of manufacturing conveying systems, understanding the production processes and quality assurance measures is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only facilitates informed purchasing decisions but also helps in establishing reliable partnerships with suppliers across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes for Conveying Systems
The manufacturing of conveying systems involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality raw materials, which can include metals such as steel or aluminum, polymers for certain components, and specialized materials that may be needed for specific applications.
- Material Selection: Buyers should prioritize suppliers that use sustainable materials and have a proven track record of sourcing from reputable vendors. This not only ensures product durability but also aligns with eco-friendly practices.
- Pre-Processing: Materials are often cut, shaped, or treated to prepare them for the next stage. Techniques such as laser cutting or water jet cutting are commonly employed for precision.
2. Forming
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the necessary components of the conveying system.
- Techniques Used: Common forming techniques include:
- Welding: For joining metal parts, ensuring structural integrity.
- Molding: For plastic components, where materials are heated and shaped into molds.
-
Bending and Stamping: To create specific shapes and features in metal components.
-
Technology Integration: Advanced manufacturing technologies such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are utilized to enhance accuracy and repeatability in forming components.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they undergo assembly. This stage is crucial as it integrates various parts into a functional conveying system.
- Assembly Techniques:
- Modular Assembly: Allows for easier assembly and maintenance, accommodating customization based on client needs.
-
Automated Assembly: Utilizes robotics for efficiency, particularly in high-volume production environments.
-
Customization Options: Buyers should inquire about the ability to customize systems to meet specific operational needs, such as material type, capacity, and dimensions.
4. Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which enhances the appearance and functionality of the conveying system.
- Finishing Processes:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as powder coating or galvanizing are applied to enhance corrosion resistance and durability.
- Quality Checks: Each finished product undergoes stringent inspection to ensure it meets design specifications.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product is safe, reliable, and meets international standards.
International Standards
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to recognized quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001:2015: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Indicates that a product meets European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for suppliers in the petroleum and natural gas industries, ensuring products meet specific technical requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducts assessments during the manufacturing process, allowing for immediate corrections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Involves comprehensive testing of the finished product before it is shipped, ensuring it functions as intended.
Common Testing Methods
Buyers should be aware of standard testing methods that suppliers may employ:
- Functional Testing: Ensures the conveying system operates correctly under expected conditions.
- Stress Testing: Assesses the durability and strength of materials under extreme conditions.
- Safety Testing: Verifies compliance with safety standards, particularly for systems handling hazardous materials.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential to minimize risks associated with product failure or compliance issues.
Recommended Verification Strategies
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their quality management systems and manufacturing processes. This can include on-site visits or remote evaluations.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for detailed quality assurance reports, which should outline their QA processes, testing results, and certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to independently verify compliance with quality standards and specifications.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the following nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understand the regional manufacturing practices and quality expectations. Building relationships with local suppliers can lead to better communication and quality outcomes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Be aware of the specific regulations that may apply in different regions, as these can impact product design and quality standards.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Ensure that quality control measures extend beyond manufacturing to include shipping and handling processes, as these can significantly affect product integrity.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for conveying systems, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. This knowledge not only fosters successful partnerships but also enhances the overall efficiency of their operations.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for conveying system Sourcing
Cost Structure of Conveying Systems
When sourcing conveying systems, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary components influencing the cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall price. Higher-quality materials or specialized components (e.g., abrasion-resistant steel) will increase costs but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both manufacturing and installation. In regions with high labor costs, such as parts of Europe, this can be a significant factor. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs might reduce expenses, but be mindful of quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturers may offer competitive pricing due to optimized overhead.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can add to upfront costs. However, investing in the right tooling can lead to better quality and efficiency in production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability. Suppliers with ISO certifications, for example, may charge more due to their commitment to quality, but this can save costs in the long run by reducing failures and maintenance.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting equipment, especially internationally, can be substantial. Consider shipping routes, freight charges, and any potential tariffs that could affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers’ profit margins can vary widely. Understanding a supplier’s business model can provide insights into their pricing structure.
Price Influencers
Several factors can affect pricing dynamics in the conveying system market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically result in better pricing due to economies of scale. International buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs while maximizing cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed systems tailored to specific processes may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Choices: The selection between standard and premium materials directly influences price. Assess the trade-off between cost and the longevity of materials.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet stringent international certifications (like ISO 9001) may be priced higher but can provide assurance of quality and compliance, which is vital in regulated industries.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and service levels can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and support.
-
Incoterms: The shipping terms agreed upon (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect pricing. Understanding these terms is essential for international buyers to manage logistics costs effectively.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
To optimize sourcing strategies, international B2B buyers should consider the following:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms and pricing. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with a conveying system, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment might lead to lower operational costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, local taxes, and import duties that can affect total costs. Additionally, consider the implications of different shipping methods on lead times and costs.
-
Supplier Research: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for reviews, case studies, and testimonials from similar markets or industries to gauge their reliability.
-
Collaboration with Suppliers: Engage suppliers early in the design phase. Collaborative efforts can lead to innovative solutions that optimize both performance and cost.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost components discussed are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions, geographical location, and specific project requirements. Always consult with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing for your needs.
Spotlight on Potential conveying system Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘conveying system’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for conveying system
Key Technical Properties of Conveying Systems
Understanding the essential technical properties of conveying systems is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of material used to construct the conveying system, which can range from stainless steel to high-density polyethylene. Choosing the right material is crucial for durability, resistance to corrosion, and compatibility with the materials being conveyed. For example, stainless steel is often preferred in food processing due to its hygienic properties. -
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum weight or volume of materials that the conveying system can handle. Load capacity is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and preventing equipment failure. Buyers should assess their material handling requirements to select a system that meets or exceeds their needs. -
Speed and Throughput
Speed refers to how quickly materials can be transported through the system, while throughput indicates the volume of materials moved within a specific timeframe. These factors are critical for optimizing production processes. A higher throughput can significantly enhance productivity, especially in high-demand industries. -
Operational Temperature Range
Different materials and processes require specific temperature tolerances. The operational temperature range defines the conditions under which the conveying system can function effectively. Selecting a system that can withstand extreme temperatures is vital for industries such as food processing or chemicals. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the permissible deviation from specified dimensions in the components of the conveying system. Precision in manufacturing is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of the system. Buyers should inquire about tolerance specifications to avoid performance issues down the line.
Common Trade Terms in the Conveying Systems Industry
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces components or systems that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers seeking reliable suppliers that adhere to industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it can affect overall purchasing costs and lead times. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It is a key step in the procurement process and helps buyers compare offers from multiple vendors. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are received. Understanding lead times is critical for effective project planning and inventory management, especially in industries with tight production schedules.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting conveying systems that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the conveying system Sector
The conveying system sector has experienced significant transformation in recent years, driven by various global dynamics and technological advancements. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must stay attuned to these trends to make informed sourcing decisions.
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global conveying systems market is largely influenced by the rise in automation across industries, the need for efficient material handling, and the growth of e-commerce. As manufacturing processes become increasingly automated, the demand for reliable and flexible conveying systems is surging. Key trends include:
-
Integration of IoT and AI: Smart conveying systems equipped with IoT sensors are becoming mainstream, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This capability enhances operational efficiency and minimizes downtime, which is crucial for industries in fast-paced regions such as South America and Africa.
-
Increased Customization: Buyers are seeking tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs. Manufacturers are responding by offering customizable systems that can handle diverse materials and integrate seamlessly with existing operations.
-
Shift Towards Pneumatic Systems: Pneumatic conveying systems are gaining traction due to their ability to reduce contamination and improve safety. These systems are particularly beneficial in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness and efficiency are paramount.
-
Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage: As global awareness of environmental issues grows, companies are increasingly prioritizing sustainability. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe, where regulations are stringent, and consumers demand responsible practices.
B2B buyers should leverage these trends by engaging with suppliers who can offer innovative, sustainable solutions while ensuring that systems are adaptable to varying operational contexts.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a choice but a necessity in the conveying systems sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing and transporting materials necessitates a shift towards greener practices. Key considerations include:
-
Use of Eco-Friendly Materials: Suppliers are increasingly sourcing sustainable materials that reduce the carbon footprint of conveying systems. Buyers should prioritize vendors who use recycled or biodegradable components in their systems.
-
Energy Efficiency: Many modern conveying systems are designed to optimize energy consumption. Investing in energy-efficient solutions not only lowers operational costs but also aligns with corporate sustainability goals.
-
Certification and Compliance: Look for manufacturers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. These certifications reflect a commitment to sustainable practices and can enhance a company’s reputation in the marketplace.
-
Ethical Supply Chains: Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices is crucial. Buyers should conduct due diligence to verify that their suppliers engage in fair labor practices and sustainable sourcing, thereby contributing to a more responsible supply chain.
By focusing on sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can enhance their brand image while contributing to global environmental efforts.
Brief Evolution/History
The conveying system sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally reliant on manual labor, the introduction of mechanical systems revolutionized material handling, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. The assembly line concept popularized by Henry Ford exemplified this shift, laying the groundwork for modern manufacturing.
As technology advanced, so did the sophistication of conveying systems. The late 20th century saw the rise of automation and computerization, leading to the development of smart, integrated systems. Today, with the advent of IoT and AI, the industry is on the cusp of another transformation, promising even greater efficiencies and capabilities for international B2B buyers.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of conveying system
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of conveying systems?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their experience, reputation, and industry certifications. Look for companies with a proven track record in delivering similar systems in your sector. Check for ISO certifications and customer testimonials, as these indicate reliability and quality. Additionally, assess their technical capabilities to customize solutions to your needs. Engage in discussions about their manufacturing processes and after-sales support to ensure they align with your expectations. -
Can conveying systems be customized to fit specific operational needs?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for conveying systems to meet unique operational requirements. This can include adjustments in size, materials, and configurations to suit specific production processes. Discuss your needs in detail with potential suppliers, providing information on the materials to be conveyed, the layout of your facility, and any regulatory requirements. A collaborative approach can lead to a tailored solution that enhances efficiency and productivity. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for conveying systems?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly based on the type of conveying system and the supplier. For standard systems, MOQs may range from one unit to several, while custom solutions typically have higher MOQs. Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capacity. Always clarify these details upfront to align your procurement schedule with your operational needs. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of conveying systems?
Payment terms can differ by supplier, but common arrangements include upfront deposits followed by balance payments upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms based on your credit history and relationship with them. Always negotiate payment terms that protect your cash flow while ensuring you meet the supplier’s requirements. It’s advisable to have these terms documented in the purchase agreement to avoid disputes. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and compliance with industry standards?
To ensure quality, request detailed information about the supplier’s quality assurance processes and certifications. Suppliers should adhere to international standards, such as ISO 9001:2015, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Inquire about their testing procedures, material sourcing, and compliance with safety regulations. Additionally, consider conducting factory visits or audits to evaluate their manufacturing capabilities and quality control measures firsthand.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing conveying systems?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of conveying systems. Consider the supplier’s ability to handle international shipping and customs clearance, as this can impact lead times. Discuss transportation options, including air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for cost-effective solutions. Additionally, clarify the supplier’s packaging practices to prevent damage during transit and ensure that all documentation is in order to facilitate smooth customs processing. -
How can I address disputes that may arise during the procurement process?
Disputes can arise from misunderstandings regarding specifications, delivery timelines, or payment terms. To mitigate this, ensure that all agreements are clearly documented in a contract. Include clauses that outline dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration, to handle conflicts amicably. Establish regular communication with the supplier to address any issues as they arise, fostering a collaborative relationship that can help prevent disputes from escalating. -
What are the best practices for maintaining conveying systems post-installation?
Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and efficiency of conveying systems. Establish a maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections, cleaning, and part replacements as needed. Training your staff on proper operation and troubleshooting can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems. Additionally, maintain an open line of communication with your supplier for technical support and access to replacement parts, ensuring that your systems remain operational and efficient.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for conveying system
In the evolving landscape of global manufacturing, the importance of strategic sourcing for conveying systems cannot be overstated. By leveraging advanced technologies such as pneumatic and mechanical conveying solutions, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce contamination, and ensure consistent material handling. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize sourcing partners that demonstrate a commitment to quality, sustainability, and innovation.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Investing in reliable conveying systems not only optimizes production processes but also aligns with broader goals of cost reduction and environmental stewardship. As competition intensifies, companies that embrace strategic sourcing will gain a significant advantage, enabling them to respond swiftly to market demands and operational challenges.
Looking ahead, the future of conveying systems is bright, with innovations poised to transform material handling practices further. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who offer tailored solutions and ongoing support. By doing so, they can ensure their operations remain agile, efficient, and ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—partner with leading manufacturers to drive your business forward.