Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Copper Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for copper suppliers
In an era marked by rapid urbanization and a global shift towards renewable energy, copper has emerged as a critical material across various industries. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the dynamics of the copper supply market is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. Copper suppliers play a vital role in providing high-quality materials necessary for construction, electrical applications, and advanced technologies, including electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate landscape of copper suppliers, offering insights into the different types of copper products, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards. It explores various materials and their applications, equipping buyers with knowledge about cost structures and market trends that can impact procurement strategies. With the copper market projected to grow significantly in the coming years, understanding how to navigate supplier relationships is more critical than ever.
By addressing frequently asked questions and providing actionable insights, this guide empowers international buyers to optimize their sourcing processes. Whether you are looking to establish long-term partnerships or seeking reliable suppliers for immediate needs, our guide serves as an indispensable resource, ensuring that you make strategic decisions that enhance your business’s competitive edge. Engage with this guide to unlock the potential of copper in your supply chain.
Understanding copper suppliers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Copper Suppliers | Focus on raw copper extraction and refining; often large-scale operations | Electrical wiring, construction, automotive | Pros: High volume availability; competitive pricing. Cons: Long lead times; may lack customization. |
| Copper Fabricators | Specialize in processing copper into finished products; often offer custom solutions | HVAC systems, plumbing, electrical components | Pros: Customization options; expertise in applications. Cons: Higher costs; potential for longer delivery times. |
| Copper Recycling Firms | Source copper from scrap materials; focus on sustainability | Electrical components, construction materials | Pros: Eco-friendly; cost-effective. Cons: Quality may vary; potential supply limitations. |
| Copper Alloys Suppliers | Provide copper mixed with other metals for enhanced properties | Aerospace, automotive, electronics | Pros: Specialized properties; tailored solutions. Cons: May require higher investment; limited availability. |
| Wholesale Copper Distributors | Serve as intermediaries; stock various copper products from multiple suppliers | General construction, electrical installations | Pros: Quick access to diverse products; lower minimum orders. Cons: Margins may affect pricing; less control over quality. |
Primary Copper Suppliers
These suppliers are at the forefront of copper extraction and refining, typically operating large-scale mines and processing facilities. They play a crucial role in the copper supply chain by providing raw materials for various industries. Buyers should consider their ability to meet large volume demands, but may encounter longer lead times and less flexibility in product customization.
Copper Fabricators
Copper fabricators transform raw copper into finished products, including pipes, sheets, and components. They often provide tailored solutions to meet specific application needs, making them ideal for projects requiring specialized copper products. Buyers should evaluate their fabrication capabilities and expertise, but be aware of potentially higher costs and extended delivery times.
Copper Recycling Firms
These firms focus on sourcing copper from scrap materials, promoting sustainability and circular economy practices. They can offer cost-effective solutions while contributing to environmental goals. However, buyers must be cautious about quality variations and potential supply constraints, especially if relying heavily on recycled materials.
Copper Alloys Suppliers
Specializing in copper mixed with other metals, these suppliers provide materials that enhance specific properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity. They are critical for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where performance is paramount. While they offer tailored solutions, buyers may face higher costs and limited availability.
Wholesale Copper Distributors
These distributors act as intermediaries, stocking a wide range of copper products from various suppliers. They provide quick access to diverse inventory, making them suitable for general construction and electrical installations. However, buyers should consider the potential impact of distributor margins on pricing and the trade-off between product quality and availability.
Related Video: What Makes Large Language Models Expensive?
Key Industrial Applications of copper suppliers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of copper suppliers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Electrical wiring and plumbing systems | Ensures safety and efficiency in infrastructure projects | Quality certifications, compliance with local codes |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panels and wind turbine components | Supports sustainable energy initiatives and reduces emissions | Supplier reliability, innovation in product design |
| Automotive | Electric vehicle (EV) components | Enhances performance and sustainability of vehicles | Advanced technology compatibility, bulk supply capabilities |
| Electronics | Circuit boards and semiconductors | Improves efficiency and reduces electronic failures | Quality control processes, technical support availability |
| Telecommunications | 5G infrastructure and IoT devices | Facilitates high-speed connectivity and supports smart technology | Scalability of supply, adherence to international standards |
Construction
In the construction industry, copper is essential for electrical wiring and plumbing systems due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Copper suppliers provide high-quality materials that meet safety standards, which is crucial for the integrity of infrastructure projects. International buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers with robust quality certifications and a proven track record of compliance with local building codes to ensure project success.
Renewable Energy
Copper plays a pivotal role in the renewable energy sector, particularly in the manufacturing of solar panels and wind turbine components. Its high conductivity makes it an ideal choice for energy transmission, supporting the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions. B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing from suppliers that demonstrate reliability and innovation in product design, as these factors can significantly impact the efficiency and longevity of renewable energy installations.
Automotive
The automotive industry, especially with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), demands substantial amounts of copper for components such as batteries, wiring harnesses, and electric motors. As EV technology evolves, the need for high-quality copper components becomes more critical to enhance vehicle performance and sustainability. Buyers must consider suppliers that offer advanced technology compatibility and can meet bulk supply requirements to support large-scale production.
Electronics
In electronics, copper is integral to the manufacturing of circuit boards and semiconductors, where it enhances performance and reduces the risk of electronic failures. Given the increasing complexity of electronic devices, sourcing from suppliers that maintain stringent quality control processes and provide technical support is essential for B2B buyers. This is particularly important for companies in Europe and South America, where innovation is a key competitive factor.
Telecommunications
Copper is fundamental to the development of 5G infrastructure and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling high-speed connectivity and the deployment of smart technologies. As demand for faster and more reliable communication grows, international buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to scale production and adhere to international standards. This ensures that the components sourced can support the rapid advancements in telecommunications technology.
Related Video: Uses of Metal – Gold, Copper, Aluminium & Steel | Properties of Matter| Chemistry | FuseSchool
Strategic Material Selection Guide for copper suppliers
When selecting materials from copper suppliers, international B2B buyers should consider several common copper alloys and their properties. The choice of material can significantly impact product performance, manufacturing processes, and overall project success. Below are analyses of four prevalent copper materials, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Copper C11000 (Electrolytic Tough Pitch Copper)
Key Properties:
Copper C11000 is known for its excellent electrical conductivity (around 101% IACS) and good thermal conductivity. It has a melting point of approximately 1,083°C and is highly resistant to corrosion in non-oxidizing environments.
Pros & Cons:
This material is durable and easy to work with, making it suitable for various applications, including electrical wiring and plumbing. However, its susceptibility to oxidation in harsh environments can limit its use without proper coatings or treatments. Additionally, while it is cost-effective, the manufacturing process can be complex due to its need for precise handling.
Impact on Application:
Copper C11000 is particularly compatible with electrical applications where high conductivity is essential. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for plumbing systems but may not perform well in coastal or industrial environments without protective measures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 and consider local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact. Understanding the specific corrosion resistance needs based on regional climates is also crucial.
Copper C26000 (Brass)
Key Properties:
Copper C26000, also known as cartridge brass, contains about 30% zinc. It offers good corrosion resistance, moderate strength, and excellent machinability. Its melting point is around 900°C.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of C26000 is its versatility; it can be used in various applications, from plumbing fittings to electrical connectors. However, it is less conductive than pure copper and can be more expensive due to the alloying process. The manufacturing complexity increases with the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application:
C26000 is suitable for applications requiring good strength and corrosion resistance, such as in plumbing and electrical components. Its compatibility with different media makes it a popular choice in diverse industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable to brass in their regions, such as ASTM B36 and JIS H3250. Additionally, understanding the local market for brass components can help in negotiating better pricing.
Copper C70250 (Nickel Silver)
Key Properties:
Copper C70250, or nickel silver, is an alloy containing copper, nickel, and zinc. It is characterized by its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, with a melting point around 1,050°C.
Pros & Cons:
This alloy is highly durable and resistant to tarnishing, making it suitable for decorative applications. However, it is more expensive than other copper alloys and can be challenging to machine due to its hardness.
Impact on Application:
C70250 is often used in applications where appearance and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in jewelry, cutlery, and musical instruments. Its compatibility with various environments makes it a preferred choice for decorative items.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with local standards such as ASTM B171 and consider the aesthetic preferences of their target markets. Understanding the cost implications of using higher-grade materials is essential for budgeting.
Copper C19400 (Beryllium Copper)
Key Properties:
Copper C19400 is an alloy that includes beryllium, providing high strength and excellent fatigue resistance. It has a melting point of approximately 900°C and is known for its good electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
This material is incredibly durable and suitable for high-stress applications, such as tools and connectors. However, it is more expensive and requires careful handling due to the toxicity of beryllium dust during machining.
Impact on Application:
C19400 is ideal for applications requiring high strength and conductivity, including aerospace and military applications. Its performance in high-stress environments makes it a valuable choice for demanding industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider the stringent regulations regarding beryllium handling and disposal in their regions. Compliance with standards like ASTM B194 is crucial, especially in markets with strict environmental regulations.
| Material | Typical Use Case for copper suppliers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper C11000 | Electrical wiring, plumbing | Excellent conductivity | Susceptible to oxidation | Medium |
| Copper C26000 | Plumbing fittings, electrical connectors | Versatile and good machinability | Less conductive than pure copper | Medium |
| Copper C70250 | Decorative items, jewelry | High corrosion resistance | More expensive, harder to machine | High |
| Copper C19400 | Aerospace, military applications | High strength and fatigue resistance | Expensive, requires careful handling | High |
This selection guide should assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding copper materials, ensuring they align with their operational needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for copper suppliers
Manufacturing Processes for Copper Suppliers
The manufacturing processes for copper products are crucial for ensuring quality and performance, especially for international B2B buyers. Understanding these processes can help buyers make informed decisions when sourcing copper materials.
Main Stages of Copper Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– The first stage involves sourcing high-quality raw copper, typically in the form of copper ore. Suppliers often conduct thorough inspections of the ore to ensure it meets specified standards.
– Key Techniques: Advanced extraction methods such as hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are employed to separate copper from the ore. This is followed by refining processes that enhance purity levels, often exceeding 99.9%. -
Forming
– Once purified, the copper undergoes various forming processes to create products such as wires, sheets, and tubes. Common methods include casting, rolling, and extrusion.
– Key Techniques:- Casting: Molten copper is poured into molds to create ingots or custom shapes.
- Rolling: Copper ingots are rolled into sheets or strips using heavy machinery, which can be further processed into wires.
- Extrusion: Copper is forced through a die to create specific cross-sectional shapes, such as rods and tubes.
-
Assembly
– In this stage, different copper components are assembled to create final products. This may involve soldering, welding, or mechanical fastening.
– Key Techniques: Automated assembly lines are often utilized to enhance efficiency and ensure uniformity. -
Finishing
– The final step involves surface treatments to improve durability and aesthetic appeal. Processes may include plating, polishing, and coating.
– Key Techniques: Electroplating and anodizing are common methods that provide corrosion resistance and enhance surface properties.
Quality Assurance in Copper Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is essential to maintaining high standards in copper production. International B2B buyers must be aware of the various standards and checkpoints involved in QA processes.
International Standards and Certifications
-
ISO 9001
– This widely recognized standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Suppliers must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. -
Industry-Specific Standards
– Depending on the application, additional certifications may be required:- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Applicable to suppliers providing copper components for the oil and gas industry, ensuring products meet specific safety and quality benchmarks.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before processing begins. This includes checking for defects, composition, and dimensions. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Throughout the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor quality. This can involve measuring dimensions, testing material properties, and ensuring process parameters are met.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Final Quality Control (FQC)
– At the end of the production process, finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify they meet all specifications. This may include stress tests, electrical conductivity tests, and surface quality assessments.
Common Testing Methods
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, elongation, and hardness.
- Chemical Analysis: Ensuring the copper alloy composition meets specified standards.
- Electrical Conductivity Testing: Verifying that the copper meets required conductivity levels, critical for electrical applications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must employ strategies to verify supplier quality control measures effectively. Here are key approaches:
-
Supplier Audits
– Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards. This is particularly important for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulations may vary. -
Quality Reports
– Requesting regular quality reports from suppliers can help buyers monitor product quality over time. These reports should detail inspection results, quality metrics, and any corrective actions taken. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide unbiased assessments of supplier quality practices. These agencies can conduct audits and tests to ensure products meet required standards before shipment.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should be familiar with local regulations in their regions, as well as international standards that may apply to their sourced copper products.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural nuances in communication and business practices can enhance supplier relationships and ensure smoother quality verification processes.
- Sustainability Practices: Increasingly, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that adopt sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes. This includes efficient resource use and responsible waste management, which can be verified through certifications and audits.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures of copper suppliers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right suppliers but also fosters long-term partnerships built on trust and reliability.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for copper suppliers Sourcing
In the competitive landscape of copper sourcing, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing mechanisms is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips that are particularly relevant for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Copper Sourcing
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in copper sourcing is the raw copper itself. Prices fluctuate based on market demand, geopolitical factors, and mining output. Buyers should monitor these trends to anticipate pricing shifts.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and can impact the overall pricing. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, the manufacturing expenses may be elevated compared to regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and maintenance. Efficient operations can lead to lower overhead, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in machinery and tools required for production can be substantial. This cost is typically amortized over the production volume, impacting unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality products involves rigorous testing and compliance with international standards. The cost of QC processes can be significant, particularly for suppliers seeking certifications that meet buyer requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs play a crucial role, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and customs duties can significantly affect the total cost of copper sourcing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate a profit margin, which can vary based on their market positioning and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can aid buyers in negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) and the volume of copper purchased can greatly influence pricing. Larger orders often result in better per-unit pricing due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications may lead to higher costs due to additional processing and testing requirements. Standard products are generally more cost-effective.
-
Materials: The type of copper (e.g., primary vs. recycled) and any additional alloying elements can affect prices. Buyers should clarify material specifications upfront to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers offering higher quality and certified materials (like ISO standards) may charge a premium. Buyers must weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and financial stability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better service but at a higher cost.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact total costs, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
Buyer Tips for Effective Sourcing
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation is crucial. Buyers should be prepared with market data and comparable quotes to leverage better terms. Establishing long-term relationships can also yield benefits like volume discounts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider logistics, potential tariffs, and lifecycle costs of the copper products.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, copper prices in South America may differ from those in Europe due to local demand and supply dynamics.
-
Market Intelligence: Stay informed about market trends, geopolitical influences, and technological advancements that can impact copper pricing. Regularly consult industry reports and analyses to make informed decisions.
Disclaimer
This analysis provides indicative pricing insights and cost structures that can vary based on specific circumstances, including supplier relationships, market conditions, and regional economic factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to secure the best possible terms for their copper sourcing needs.
Spotlight on Potential copper suppliers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘copper suppliers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for copper suppliers
Essential Technical Properties of Copper
Understanding the technical properties of copper is crucial for international B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade:
– Copper is categorized into various grades based on its purity and alloying elements. Common grades include C11000 (pure copper) and C10200 (oxygen-free copper).
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right grade affects conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength, which are critical for applications in electrical wiring and construction. -
Conductivity:
– This measures how well copper can conduct electricity, typically expressed in percentage IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). Pure copper has a conductivity of 100% IACS.
– B2B Importance: High conductivity is essential for minimizing energy loss in electrical applications, making it a key factor in the selection process for suppliers. -
Tolerance:
– Tolerance refers to the acceptable limits of variation in dimensions or properties of copper products. For example, wire gauges have specific tolerances for diameter.
– B2B Importance: Accurate tolerances ensure compatibility with other components in assemblies, reducing the risk of operational failures and improving overall system reliability. -
Mechanical Properties:
– This includes tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. For instance, copper typically exhibits high ductility, allowing it to be drawn into wires.
– B2B Importance: Understanding mechanical properties helps buyers select the right type of copper for specific applications, especially in industries like construction and automotive. -
Thermal Conductivity:
– This property measures copper’s ability to conduct heat, with pure copper exhibiting high thermal conductivity.
– B2B Importance: High thermal conductivity is vital for applications in heat exchangers and electronic components, ensuring efficient thermal management. -
Corrosion Resistance:
– Copper’s ability to resist corrosion varies depending on its environment. For example, copper exposed to air will develop a patina, which protects the underlying metal.
– B2B Importance: Assessing corrosion resistance helps buyers determine the longevity and maintenance requirements of copper products in specific applications.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with trade terminology can enhance communication and negotiation effectiveness in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
– Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source components for manufacturing processes or assemblies. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
– This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies and manage inventory effectively, particularly in bulk orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
– An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– B2B Importance: Sending out RFQs allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better negotiation outcomes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
– These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, such as shipping and insurance.
– B2B Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs and risks, ensuring clarity in contracts and agreements. -
Lead Time:
– This refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the lead time is essential for supply chain management and helps buyers schedule production processes without delays. -
Certification:
– This involves a formal recognition that a product meets certain standards or regulations, often verified by a third party.
– B2B Importance: Certifications can impact buyer confidence and compliance, particularly in regulated industries where quality and safety are paramount.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the copper supply landscape more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the copper suppliers Sector
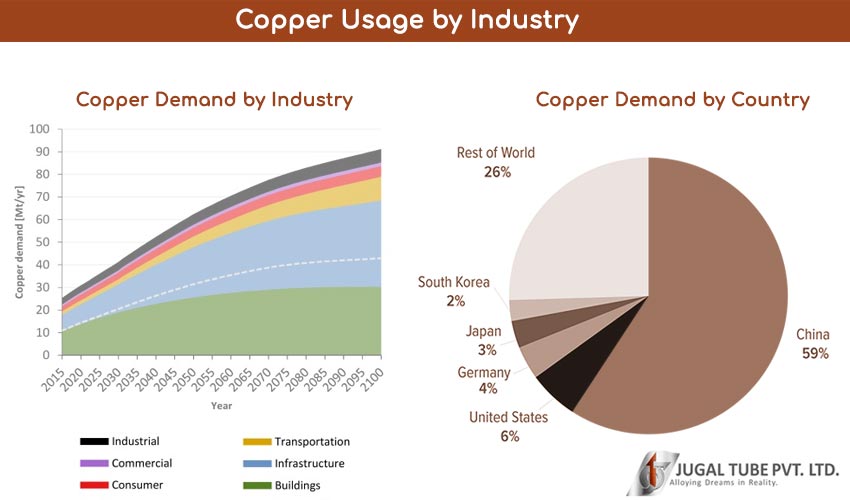
Global copper consumption is on an upward trajectory, driven by increasing urbanization, renewable energy initiatives, and technological advancements. The market is projected to grow from USD 241.88 billion in 2024 to USD 339.95 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these market dynamics is crucial.
Market Overview & Key Trends
The demand for copper is significantly influenced by the construction sector, which accounted for 26.4% of market share in 2024. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in rapidly developing regions such as Africa and South America, where infrastructure projects are booming. The rising installation of solar and wind energy systems is another major driver, as these technologies rely heavily on copper for efficient energy transmission. Additionally, the automotive industry’s shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping demand, as EVs utilize substantially more copper than traditional vehicles for wiring and battery systems.
Emerging technologies are also transforming sourcing practices. B2B buyers should leverage digital procurement platforms and data analytics to enhance supplier selection processes. As the market evolves, the focus on transparency and traceability in supply chains becomes paramount. Buyers are encouraged to establish strong relationships with suppliers who can demonstrate not just reliability but also an understanding of the specific needs of their respective markets.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer optional; it’s a critical factor for B2B buyers in the copper sector. The environmental impact of copper mining is significant, with concerns about land degradation and water usage. As a result, companies are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing to mitigate these impacts. Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to recognized green certifications, such as the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) and ISO 14001, which indicate compliance with environmental management standards.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Moreover, the push for circular economy practices is gaining momentum. Engaging with suppliers who focus on copper recycling can not only help reduce environmental footprints but also ensure a stable supply chain amid fluctuating raw material prices. By prioritizing suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices, buyers can align their sourcing strategies with global sustainability goals and enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles.
Brief Evolution/History
The copper industry has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, but its transformation in the last few decades is particularly noteworthy for B2B buyers. The advent of globalization and advancements in mining technology have reshaped supply chains, allowing for more efficient extraction and distribution. In recent years, the industry’s focus has shifted towards sustainable practices and ethical sourcing, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures. This evolution presents opportunities for B2B buyers to partner with suppliers who not only meet their material needs but also align with modern sustainability standards.
In conclusion, international B2B buyers in the copper sector should remain vigilant about market dynamics, embrace sustainability, and leverage technological advancements in sourcing to enhance their procurement strategies.
Related Video: Selling stuff to other countries: global trade explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of copper suppliers
-
What criteria should I use to vet copper suppliers?
When vetting copper suppliers, consider several key criteria. First, assess their financial stability to ensure they can support long-term contracts. Next, evaluate their operational capability, including production capacity and technology used. Look for certifications such as ISO and compliance with international standards, which indicate quality assurance. Additionally, investigate their reputation in the market through client reviews and references. Finally, consider their logistical capabilities, especially if you are importing from different regions, to ensure timely delivery. -
Can copper suppliers customize their products to meet my specifications?
Many copper suppliers offer customization options, including variations in alloy composition, size, and form (e.g., wire, sheets, or tubes). When discussing customization, clearly articulate your requirements, including tolerances and specifications. It’s essential to confirm that the supplier has the technological capability and expertise to meet your needs. Be prepared to discuss minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, as these may differ from standard offerings. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for copper orders?
MOQs for copper orders can vary significantly depending on the supplier, product type, and customization. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons. Lead times also vary based on the supplier’s inventory and production capabilities, but you can expect anywhere from 2 to 12 weeks for standard orders. For customized products, lead times may be longer. Always confirm these details in advance to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing copper internationally?
Payment terms for international copper sourcing often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment on delivery. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms with your supplier early in negotiations. For new suppliers, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit to mitigate risks. Always review the terms of payment in the context of the entire deal, including currency fluctuations and potential import duties, to ensure favorable conditions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications from my copper supplier?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO 9001, which reflects quality management practices. It’s also beneficial to ask for product specifications and test reports that demonstrate compliance with international standards. Conducting factory audits or third-party inspections can further validate the supplier’s quality control processes. Establishing a clear quality assurance agreement in your contract can protect your interests and ensure adherence to agreed standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing copper?
Logistics are critical when sourcing copper, particularly for international shipments. Ensure your supplier has robust logistics capabilities, including handling customs clearance and freight forwarding. Discuss shipping methods (air, sea, or land) and associated costs, as these can impact your total expenses. Additionally, consider the supplier’s experience with international trade regulations and documentation requirements to avoid delays. Establishing a clear logistics plan will help streamline the import process and minimize disruptions. -
How can disputes with copper suppliers be effectively resolved?
To resolve disputes with copper suppliers effectively, start with open communication to address the issue directly. It’s advisable to have a clear dispute resolution clause in your contract, outlining steps for mediation or arbitration. Documentation is key; keep records of all communications, agreements, and transactions. If the dispute escalates, consider involving a third-party mediator or legal counsel familiar with international trade laws. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations in case of conflicts. -
What are the environmental and sustainability practices I should look for in copper suppliers?
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, evaluate your copper suppliers based on their environmental practices. Look for certifications related to sustainable mining and recycling processes, such as those from the Responsible Minerals Initiative. Suppliers that invest in eco-friendly technologies and adhere to local and international environmental regulations demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. Engaging with suppliers on their sustainability policies can also enhance your corporate responsibility profile and appeal to environmentally-conscious customers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for copper suppliers
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of copper is pivotal for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their supply chain resilience and capitalize on emerging market opportunities. As the demand for copper continues to surge, driven by the global shift towards renewable energy, electric vehicles, and advanced technologies, buyers must prioritize establishing strong partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Key takeaways for international buyers include the importance of evaluating suppliers not just on cost, but also on their operational capabilities, cultural alignment, and financial stability. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate transparency and a commitment to sustainability can significantly enhance your competitive edge in the marketplace.
Looking ahead, the copper market is poised for robust growth, with projections indicating a significant increase in demand through 2030. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this momentum by investing in strategic sourcing initiatives that align with their long-term business goals. Now is the time to take action—explore diverse supplier networks, embrace innovative sourcing strategies, and position your business for success in a rapidly evolving landscape.