Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Door Latching Mechanism
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for door latching mechanism
Navigating the complexities of the global market for door latching mechanisms is essential for international B2B buyers seeking reliable and secure solutions. Door latching mechanisms serve as a critical component in various industries, ensuring safety and accessibility in both commercial and residential settings. From Africa to South America, the Middle East to Europe, understanding the nuances of latches—from their diverse types to the materials used—is vital for making informed procurement decisions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of door latching mechanisms, delving into essential topics such as types of latches, manufacturing and quality control standards, supplier identification, and cost analysis. Each segment is designed to equip buyers with the knowledge necessary to evaluate their options effectively. Whether you are sourcing for industrial applications in Egypt, enhancing security in South Africa, or ensuring compliance in European markets, this guide provides actionable insights tailored to your needs.
By empowering buyers with detailed information and expert analysis, this resource aims to facilitate informed sourcing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and security. With a focus on practicality and real-world applications, you will be better positioned to select the right latching solutions that meet both your functional and budgetary requirements.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
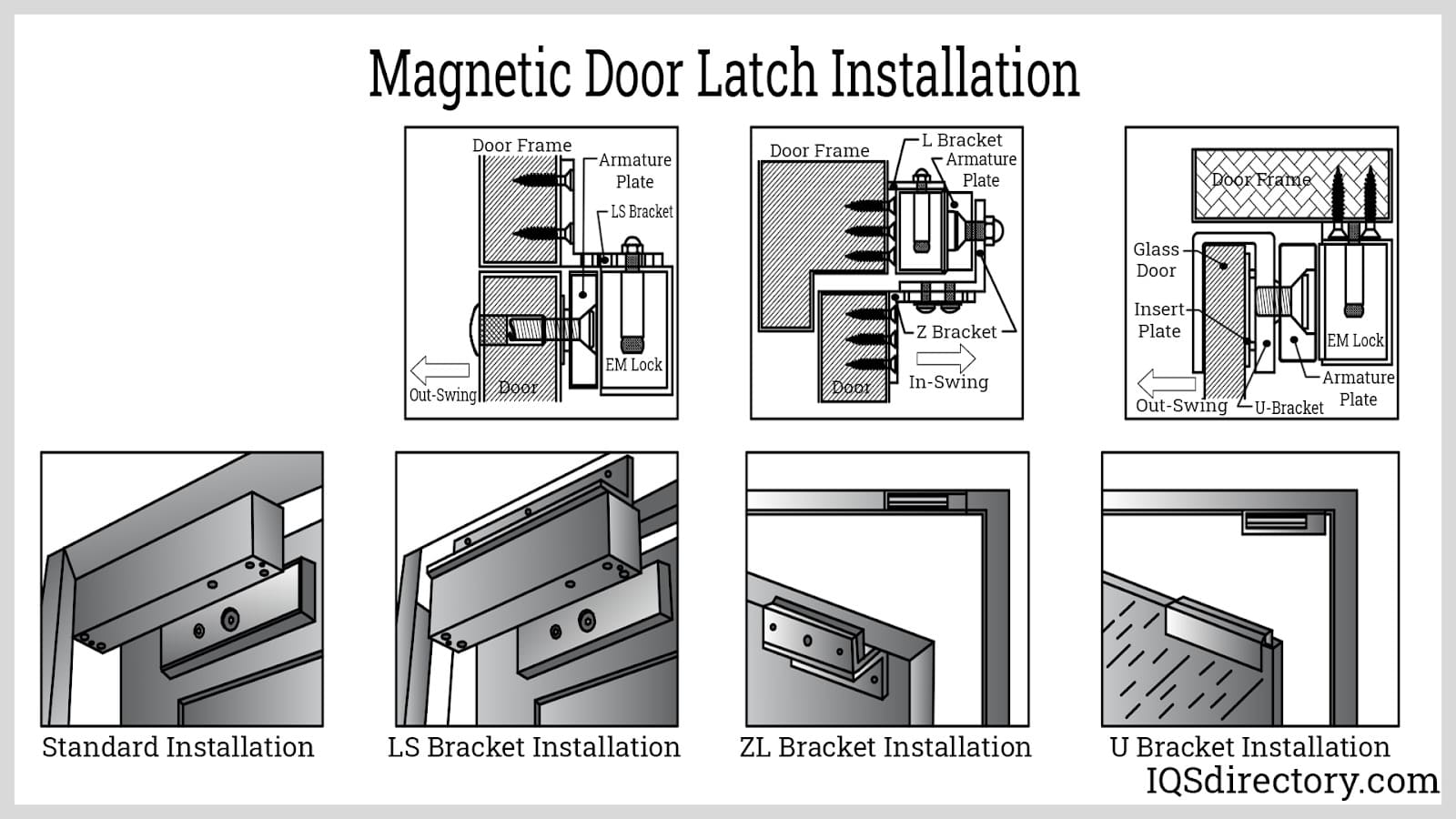
Understanding door latching mechanism Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Latch | Provides a secure, sealed closure through compressive force. | Electrical enclosures, HVAC systems, transport. | Pros: Excellent sealing, prevents dust/moisture. Cons: May require specific installation. |
| Draw Latch | Engages through a lever mechanism that pulls surfaces tightly. | Machinery enclosures, cargo containers, HVAC. | Pros: Strong closure, vibration-resistant. Cons: Can be complex to operate in tight spaces. |
| Slide-to-Open Latch | Utilizes a linear sliding motion for quick access. | Industrial machinery, storage units, cabinets. | Pros: Fast operation, easy access. Cons: Limited to applications with sliding access. |
| Pull Latch | Operates via a handle that pulls surfaces together. | Toolboxes, cabinets, transport vehicles. | Pros: Easy to operate, reliable fastening. Cons: Requires space for handle operation. |
| Cam Latch | Utilizes a rotating mechanism to secure surfaces. | Access panels, enclosures, vehicle doors. | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Less secure than compression latches. |
Compression Latch
Compression latches are designed to provide a secure closure by applying compressive force between two surfaces. This mechanism is particularly suitable for applications where sealing is crucial, such as in electrical enclosures, HVAC systems, and transportation equipment. When considering a compression latch, buyers should evaluate the environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture or dust, as these latches excel in preventing contaminants from entering sensitive areas. Additionally, installation requirements should be assessed, as some models may necessitate specific mounting techniques.
Draw Latch
The draw latch, also known as a tension latch, employs a lever mechanism that pulls two surfaces together, creating a tight seal. This type of latch is commonly used in machinery enclosures and cargo containers, where vibration resistance is essential. Buyers should consider the operational environment when selecting draw latches, especially if they will be used in high-vibration settings. While they offer robust closure capabilities, the complexity of operation in confined spaces may be a drawback for some applications.
Slide-to-Open Latch
Slide-to-open latches are characterized by their straightforward sliding action, making them ideal for applications requiring quick access, such as industrial machinery and storage cabinets. Their design allows for rapid engagement and disengagement, which can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Buyers should ensure that the installation area accommodates the necessary sliding motion, as this latch type is not suitable for traditional hinged doors. Additionally, while they provide ease of use, they may lack the security features of more complex latching systems.
Pull Latch
Pull latches function by using a handle or lever to pull surfaces together, providing reliable fastening for various applications, including toolboxes and transport vehicles. Their design emphasizes user-friendliness, making them easy to operate in many settings. When purchasing pull latches, buyers should assess the space available for handle operation, as this could impact usability. While they offer dependable performance, their effectiveness can be limited in applications requiring a high degree of security.
Cam Latch
Cam latches utilize a simple rotating mechanism to secure surfaces, making them a cost-effective solution for access panels and enclosures. They are easy to install and operate, which appeals to many buyers. However, while cam latches are economical, they may not provide the same level of security as more advanced latching mechanisms like compression latches. Buyers should consider the security requirements of their specific applications when choosing cam latches, as they may be better suited for low-security environments.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of door latching mechanism
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of door latching mechanism | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Cargo containers and truck bodies | Ensures secure transport of goods, reducing theft risk | Durability, resistance to vibrations, and ease of access |
| Industrial Machinery | Machinery enclosures and access panels | Facilitates maintenance access while ensuring safety | Robust design, weather resistance, and compliance with safety standards |
| HVAC Systems | Access panels for HVAC units | Maintains efficiency and performance by preventing leaks | Sealing capability, material compatibility, and ease of installation |
| Food Processing | Equipment doors and access covers | Ensures hygiene and prevents contamination | Compliance with food safety regulations, ease of cleaning, and durability |
| Telecommunications | Enclosures for telecom equipment | Protects sensitive equipment from environmental factors | Weatherproofing, locking mechanisms, and quick access features |
Transportation
In the transportation sector, door latching mechanisms are critical for securing cargo containers and truck bodies. These latches prevent unauthorized access and theft during transit, ensuring that goods arrive safely at their destinations. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable latching solutions that can withstand harsh environmental conditions is essential. Buyers should prioritize latches that offer resistance to vibrations and are easy to operate, as these features enhance both security and efficiency.
Industrial Machinery
Door latching mechanisms are extensively used in machinery enclosures and access panels within the industrial machinery sector. These latches provide secure closures that facilitate safe maintenance access while preventing accidental openings during operation. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it is crucial to consider latches that meet specific safety standards and are made from robust materials to withstand industrial environments. Additionally, ensuring that the latching mechanisms are weather-resistant can prolong their lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, door latching mechanisms are employed for access panels that need to maintain an airtight seal. This is vital for the efficiency and performance of heating and cooling units, as leaks can lead to increased energy consumption and operational costs. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions with extreme climates, sourcing latches that provide excellent sealing capabilities and are easy to install can significantly enhance system reliability. Buyers should also consider the materials used in latches to ensure compatibility with various HVAC systems.
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, door latching mechanisms are crucial for equipment doors and access covers that need to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination. These latches must comply with stringent food safety regulations, making it essential for buyers to select latching solutions that are easy to clean and resistant to corrosion. For international buyers, understanding local regulations regarding food safety can guide the sourcing of appropriate latching mechanisms that not only secure but also protect food products throughout the processing cycle.
Telecommunications
For telecommunications, door latching mechanisms are vital for enclosures that protect sensitive equipment from environmental factors such as dust and moisture. These latches ensure that equipment remains secure and operational, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. B2B buyers in regions with varying weather conditions should prioritize sourcing latches that offer weatherproofing features and robust locking mechanisms. Additionally, latches that allow for quick access can enhance service efficiency, making them an ideal choice for telecommunications applications.
Related Video: Door Latch
Strategic Material Selection Guide for door latching mechanism
When selecting materials for door latching mechanisms, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of door latching mechanisms, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand elevated temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and can handle pressures in industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: Highly durable and resistant to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications. It also offers a polished finish, enhancing aesthetic appeal.
– Disadvantages: Higher manufacturing costs compared to other materials and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, ensuring longevity and reliability in door latching mechanisms.
Considerations for Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel is crucial. Buyers should also consider local availability and cost implications in regions where stainless steel is less common.
2. Zinc Die-Cast
Key Properties: Zinc die-cast materials exhibit good corrosion resistance and can withstand moderate temperatures (up to 150°C). They are often used in applications requiring intricate shapes and designs.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: Cost-effective and allows for high-volume production with complex shapes. The material is lightweight, which can reduce shipping costs.
– Disadvantages: Less durable than stainless steel and can be prone to cracking under extreme stress or temperature fluctuations.
Impact on Application: Suitable for indoor applications where aesthetic design is important but may not be the best choice for high-stress environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the zinc die-cast products meet local standards, such as EN 1386 in Europe, and evaluate the potential for corrosion in humid climates.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency. It can operate effectively at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: Lightweight and easy to mold into various shapes, making it ideal for innovative designs. It also has good UV resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
– Disadvantages: Less durable than metals and can be affected by chemicals, which may limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Best used in applications where visibility is important, such as security doors, but may not be suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Considerations for Buyers: Compliance with safety standards like ISO 7391 is essential, especially in regions with stringent regulations. Buyers should also assess the environmental impact of using plastics in their applications.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It can handle temperatures up to 200°C and is often used in various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: Offers a good strength-to-weight ratio and is easier to machine than stainless steel. Its natural corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor use.
– Disadvantages: While durable, it is not as strong as stainless steel and may deform under heavy loads.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications requiring lightweight solutions without compromising too much on strength, such as in commercial buildings and residential doors.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum products comply with standards like ASTM B221. Additionally, they should consider the local market for aluminum and its availability, particularly in emerging markets.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for door latching mechanism | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Outdoor gates, industrial doors | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Zinc Die-Cast | Indoor decorative latches | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable under stress | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Security doors, display cases | High impact resistance and UV stability | Prone to chemical damage | Low |
| Aluminum | Commercial and residential doors | Good strength-to-weight ratio | Not as strong as stainless steel | Medium |
This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for door latching mechanisms, ensuring informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for door latching mechanism
Manufacturing Processes for Door Latching Mechanisms
The manufacturing of door latching mechanisms involves a systematic approach that includes several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage utilizes specific techniques to ensure that the final product meets the required standards for performance and durability.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is selecting the appropriate materials. Common materials for door latching mechanisms include stainless steel, zinc alloy, and plastic composites. These materials are chosen for their strength, corrosion resistance, and overall durability.
- Material Inspection: Before processing, incoming materials undergo rigorous inspection to confirm compliance with specified standards, ensuring they meet quality and safety requirements.
Forming
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into specific shapes and components using various techniques:
-
Stamping: This technique is often used for producing metal parts. A stamping press shapes the metal into desired forms, such as brackets or latches, through a process involving dies and molds.
-
Casting: For more complex shapes, casting methods may be employed. Molten metal is poured into molds, allowing for intricate designs that are difficult to achieve through stamping.
-
Injection Molding: For plastic components, injection molding is commonly used. This method injects molten plastic into molds, creating precise and consistent shapes for parts like housing or levers.
Assembly
After forming, the various components are assembled into a complete door latching mechanism. This stage may involve:
-
Mechanical Fastening: Parts are often joined using screws, bolts, or rivets, ensuring a secure fit.
-
Adhesive Bonding: In some cases, adhesives are utilized for additional strength or to bond different materials together.
-
Quality Checks: During assembly, periodic checks are conducted to ensure alignment and fit, which is crucial for the functionality of the latch.
Finishing
The finishing stage involves applying surface treatments to enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of the latch mechanisms:
-
Coating: Components may receive coatings such as powder coating or electroplating, providing protection against corrosion and wear.
-
Polishing: Aesthetic finishes are achieved through polishing, which not only improves appearance but also reduces friction in moving parts.
-
Final Inspection: Each finished product undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets the required specifications and quality standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of manufacturing door latching mechanisms, ensuring that products are reliable and meet international standards.
International Standards
Several international standards guide quality assurance in manufacturing:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Adhering to ISO 9001 helps manufacturers ensure consistent quality in their products and services.
-
CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Specifications: In specific industries, such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) specifications may be necessary, particularly for latches used in hazardous environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that any deviations from the set standards are identified and rectified promptly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection assesses the completed products against quality standards and specifications before they are shipped to customers.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are essential for verifying the performance and safety of door latching mechanisms:
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing the latch under various conditions to ensure it performs as expected, including checking its locking and unlocking mechanisms.
-
Durability Testing: Products are subjected to stress tests that simulate long-term use, assessing their ability to withstand wear and tear.
-
Environmental Testing: Latches may be exposed to extreme temperatures, humidity, or corrosive environments to evaluate their resilience.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is vital for maintaining standards in their supply chains. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality assurance systems. This can reveal potential risks and ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers, including metrics on defect rates, compliance with international standards, and results from testing.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspection services to conduct assessments of suppliers’ facilities and products. This provides an unbiased evaluation of quality practices.
Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from different regions face unique challenges in ensuring quality in their supply chains:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can affect communication and expectations regarding quality standards.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must be aware of varying regulations in their regions concerning product safety and quality, especially when importing goods.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Effective logistics planning is crucial, as delays or issues in transportation can affect product quality. Close collaboration with suppliers can help mitigate these risks.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for door latching mechanisms is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production and implementing effective quality control measures, buyers can ensure that they procure reliable and high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for door latching mechanism Sourcing
When sourcing door latching mechanisms, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will cover essential cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic buyer tips tailored for regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic. High-quality materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to enhanced durability and longevity, reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Labor: Labor costs are affected by the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but might compromise on quality. It’s vital to assess the skill level and training of the workforce, particularly in regions like South Africa or Egypt, where labor quality can vary.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overheads, impacting the price point favorably.
-
Tooling: Custom latches may require specialized tooling, which can be a significant initial investment. Buyers should consider whether suppliers have the capability to produce custom solutions without incurring excessive tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability. While this may increase costs, it is essential for maintaining standards, especially in industries where safety and compliance are critical.
-
Logistics: The transportation of latching mechanisms can be complex, especially for international shipments. Costs can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and customs regulations. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for clarifying responsibilities and potential cost implications.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market conditions. Buyers should be aware of standard margins in the industry to identify reasonable pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders usually lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their budget and inventory strategies.
-
Specifications/Customization: Tailored products may come at a premium. Clearly defining requirements can help avoid unnecessary costs associated with redesigns.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) can increase costs but may offer better performance and compliance, making them worthwhile investments.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for determining who bears the shipping costs and risks, which can significantly affect the final price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to understand their cost structures. This knowledge can empower buyers to negotiate better terms and prices.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider long-term benefits, such as reduced maintenance costs and increased durability.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, imports to South America may incur higher tariffs compared to European countries, affecting overall costs.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into upcoming product innovations.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices and trends. This will help in benchmarking offers and making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for door latching mechanisms can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers are encouraged to seek multiple quotes and conduct due diligence to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential door latching mechanism Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘door latching mechanism’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for door latching mechanism
Key Technical Properties for Door Latching Mechanisms
When selecting door latching mechanisms, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring reliability, security, and functionality. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material significantly impacts the durability and corrosion resistance of the latch. Common materials include stainless steel, zinc alloys, and plastic composites. Stainless steel offers superior strength and is ideal for outdoor applications, while plastic latches may be suitable for lighter-duty, indoor use. Selecting the right material can prevent premature failure and minimize maintenance costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during manufacturing. High tolerance levels ensure that components fit together correctly, which is critical for the functionality of the latch. Poor tolerance can lead to misalignment, causing operational failures or security vulnerabilities. Buyers should request tolerance specifications to ensure that the latches will perform as intended in their specific applications. -
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum weight or force a latch can withstand without deforming or failing. Load capacity is particularly important in industrial settings where latches may be subjected to significant stress. Buyers should assess the load requirements of their application to ensure that the selected latch can handle the expected forces, which will help in avoiding safety hazards or operational disruptions. -
Corrosion Resistance
In environments where moisture and chemicals are prevalent, corrosion resistance is a vital property. Latches should be treated or constructed from materials that can withstand environmental stressors. Buyers operating in humid climates or industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals should prioritize latches with high corrosion resistance to ensure longevity and compliance with health standards. -
Operating Temperature Range
Different latching mechanisms can perform optimally within specific temperature ranges. For instance, some materials may become brittle in extreme cold or lose their integrity at high temperatures. Understanding the operating environment is essential for selecting a latch that will perform reliably under varying thermal conditions, especially in regions with extreme weather. -
Actuation Mechanism
The actuation mechanism determines how the latch is engaged or disengaged. Options include manual, electronic, and pneumatic actuation. Understanding the actuation type is crucial for integration into existing systems, particularly for automated or secure environments. This can impact user convenience and overall security.
Common Trade Terminology in Door Latching Mechanisms
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some common terms related to door latching mechanisms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of latches, an OEM might provide custom latch solutions tailored to specific industrial needs. Knowing the OEM can facilitate better understanding of product quality and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is critical for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for international buyers who may face additional shipping costs on smaller orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. This is a standard practice in B2B transactions, allowing buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers to clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ultimately influencing the total landed cost of products. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For latching mechanisms, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the product and the supplier’s capacity. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning projects to avoid delays in installation or production. -
Certification Standards
These are industry-specific standards that ensure products meet safety and quality requirements. Common certifications for latches include ISO, ANSI, and UL. Buyers should verify that the latches they intend to purchase comply with relevant certifications to ensure product reliability and adherence to local regulations.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and security of their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the door latching mechanism Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The door latching mechanism sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by globalization and technological advancements. Key market drivers include the increasing demand for secure access solutions across various industries, notably in construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. As urbanization accelerates in regions like Africa and South America, the need for reliable and efficient latching mechanisms is paramount.
Emerging B2B tech trends such as smart latching systems that integrate IoT capabilities are gaining traction. These technologies not only enhance security but also offer remote monitoring and control, aligning with the growing trend of automation in industrial applications. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has stimulated demand for innovative latching solutions that facilitate quick assembly and disassembly, catering to logistics and shipping needs.
Market dynamics for international buyers are shaped by regional variations in standards and regulations. For instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize compliance with stringent safety standards, while those in Africa might focus on cost-effectiveness and durability due to varying infrastructure conditions. Understanding these nuances is crucial for successful sourcing. Furthermore, partnerships with local suppliers can enhance supply chain resilience, ensuring timely access to essential components.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the door latching mechanism sector. The environmental impact of production processes is under scrutiny, prompting manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices. This includes utilizing recycled materials and minimizing waste during production.
Ethical sourcing has gained prominence as buyers increasingly prefer suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. This involves ensuring fair labor practices and transparency in supply chains. Green certifications such as ISO 14001 or materials like recycled metals and biodegradable plastics are becoming essential criteria for procurement decisions. Buyers should actively seek out manufacturers who prioritize sustainability, as this not only enhances corporate responsibility but also appeals to an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base.
Adopting a sustainable sourcing strategy can also lead to cost savings in the long run. Companies that invest in energy-efficient production and sustainable materials often see reductions in operational costs, making them more competitive in the market.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of door latching mechanisms reflects broader technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Initially, latches were simple mechanical devices designed to secure doors and gates. Over time, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes led to the development of more sophisticated latching systems, including those that offer better security and ease of use.
The introduction of electronic latching systems marked a significant turning point, allowing for integration with security systems and smart home technologies. Today, the focus has shifted towards creating latches that not only provide security but also enhance user convenience and efficiency. This historical progression illustrates the industry’s adaptability and responsiveness to market demands, making it crucial for international B2B buyers to stay informed about ongoing innovations and trends.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of door latching mechanism
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers of door latching mechanisms?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, product range, and reputation. Request references and verify their certifications, particularly ISO standards relevant to manufacturing quality. Assess their production capabilities, including technology and equipment, to ensure they meet your specifications. Finally, consider their customer service responsiveness and ability to provide support in your time zone, which is crucial for effective communication. -
Can I customize door latching mechanisms to meet specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for door latching mechanisms, including dimensions, materials, and finishes. When inquiring about customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements. Discuss potential design modifications and ensure that the supplier has experience with similar requests. Understand the implications of customization on lead times and costs, as more complex changes may require additional resources and longer production periods. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for door latching mechanisms?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the complexity of the product and the supplier’s production capacity. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors such as customization requests and current order volumes. Always confirm these details during negotiations and factor in potential delays in logistics, especially for international shipments. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing door latching mechanisms internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include 30% upfront and 70% upon delivery, or payment in full before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms based on established relationships. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms and conditions before finalizing your order to avoid disputes later. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for my door latching mechanisms?
Request documentation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Conduct factory audits, if possible, to observe their manufacturing practices. Consider third-party quality inspections prior to shipment to verify compliance with your specifications and industry standards. Establish clear quality expectations in your contract to hold suppliers accountable. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing door latching mechanisms?
Logistics involve several considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in international shipments. Be aware of import regulations and tariffs specific to your country to avoid unexpected costs. Plan for potential delays in customs and ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, is prepared to facilitate smooth transit. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding door latching mechanisms?
Start by addressing issues directly with the supplier through open communication, aiming for a resolution. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution processes. Consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, which can be costly and time-consuming. Document all communications and agreements to support your case should escalation be needed. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with suppliers?
Building a strong partnership involves regular communication, transparency, and feedback. Schedule periodic reviews to discuss performance, quality, and any emerging needs. Acknowledge good service and timely delivery, which fosters goodwill. By demonstrating loyalty and willingness to collaborate on improvements, you can enhance your supplier relationships, leading to better pricing, priority service, and innovative solutions tailored to your business.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for door latching mechanism
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of door latching mechanisms is essential for ensuring security, durability, and efficiency across various applications. B2B buyers should prioritize understanding the diverse types of latches available—such as compression, draw, and slide-to-open latches—and their specific applications to make informed purchasing decisions. Leveraging reliable suppliers that offer high-performance products will not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to long-term cost savings.
Key Takeaways:
– Evaluate Needs: Assess the specific requirements of your applications to choose the most suitable latch type.
– Supplier Reliability: Partner with reputable manufacturers who prioritize quality and innovation in their latch solutions.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and longevity, rather than just the initial purchase price.
As the global market continues to evolve, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must remain proactive in sourcing strategies. Engaging in partnerships that foster innovation and sustainability will be crucial for staying competitive. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operational frameworks by investing in high-quality door latching mechanisms today.