Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Electric Heating Elements
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric heating elements
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, electric heating elements play a pivotal role in various applications, from manufacturing and food processing to chemical production and HVAC systems. As global demand for energy-efficient solutions grows, understanding the nuances of electric heating elements becomes essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These components not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing energy consumption.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed sourcing decisions. We will explore the various types of electric heating elements, including cartridge, tubular, and immersion heaters, alongside the materials used in their construction, such as stainless steel and silicone. Additionally, we will delve into manufacturing processes and quality control standards to ensure reliability and safety.
Buyers will also find valuable insights on leading suppliers in the market, cost considerations, and emerging trends that could impact procurement strategies. The guide addresses frequently asked questions, providing clarity on critical aspects that influence purchasing decisions. By empowering B2B buyers with this knowledge, we aim to facilitate successful partnerships and optimize operational efficiency in diverse industries across the globe.
Understanding electric heating elements Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cartridge Heating Element | Compact design, high thermal efficiency | Medical devices, plastic molding | Pros: Space-saving, quick heat-up. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Immersion Heater Element | Submerged in liquids, effective for direct heating | Water heating, food processing | Pros: High efficiency, precise temperature control. Cons: Requires careful installation. |
| Tubular Heating Element | Versatile shape, suitable for various applications | HVAC systems, industrial ovens | Pros: Customizable lengths, robust. Cons: May require specialized fittings. |
| Ceramic Heating Element | High-temperature resistance, durable | Space heaters, industrial processes | Pros: Long lifespan, energy-efficient. Cons: Generally more expensive. |
| Flexible Heating Element | Thin, lightweight, and adaptable | Aerospace, automotive applications | Pros: Easy installation, versatile. Cons: Limited maximum temperature range. |
Cartridge Heating Element
Cartridge heating elements are compact and designed for high thermal efficiency. They are commonly used in applications such as medical devices and plastic molding. B2B buyers should consider their space-saving capabilities and rapid heat-up times, which can enhance productivity. However, these elements are typically limited to specific applications, so thorough compatibility checks are essential before purchase.
Immersion Heater Element
Immersion heater elements are designed to be submerged in liquids, making them effective for direct heating applications. They find extensive use in water heating and food processing. Buyers benefit from their high efficiency and precise temperature control, which is crucial in industrial settings. However, careful installation is necessary to avoid operational issues or hazards, necessitating skilled labor.
Tubular Heating Element
Versatile and robust, tubular heating elements can be customized in length and diameter, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including HVAC systems and industrial ovens. B2B buyers appreciate their durability and adaptability, which can reduce overall maintenance costs. However, the need for specialized fittings and configurations may increase installation complexity.
Ceramic Heating Element
Ceramic heating elements are known for their high-temperature resistance and durability, making them ideal for applications like space heaters and various industrial processes. Their long lifespan and energy efficiency are significant advantages for B2B buyers looking to minimize operational costs. However, the initial investment is generally higher compared to other types, which may affect budget considerations.
Flexible Heating Element
These elements are thin, lightweight, and adaptable, making them ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive industries. The ease of installation and versatility are key benefits for B2B buyers, enabling integration into complex systems. However, they typically have a limited maximum temperature range, which may restrict their use in high-heat applications. Buyers should evaluate their specific heating requirements to ensure compatibility.
Key Industrial Applications of electric heating elements
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electric Heating Elements | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Heating of cooking vessels and food transport systems | Ensures consistent temperature control for food safety, enhancing product quality and compliance. | Material compatibility, watt density, and energy efficiency ratings. |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Process heating for reactors and mixing tanks | Optimizes reaction rates, reducing processing time and energy costs. | Customization options for size and shape, and resistance to corrosive environments. |
| Textile Industry | Heating elements for dyeing and finishing processes | Improves dye uptake and fabric quality, leading to reduced waste and rework. | Temperature control precision, flexibility in design, and compliance with safety standards. |
| Plastics and Polymer Production | Preheating of materials for molding processes | Enhances material flow and reduces defects in finished products. | Durability under high temperatures, compatibility with various polymers, and reliability in performance. |
| HVAC Systems | Electric duct heaters and unit heaters | Provides efficient heating solutions, improving energy savings and comfort in commercial spaces. | Voltage compatibility, safety certifications, and maintenance requirements. |
Food Processing
Electric heating elements play a crucial role in the food processing sector, particularly in the heating of cooking vessels and food transport systems. These elements ensure consistent temperature control, which is vital for food safety and quality. For international buyers, especially those in regions with strict food safety regulations, sourcing elements that comply with local standards and are made from food-grade materials is essential. Additionally, energy efficiency ratings can significantly impact operational costs, making them a key consideration in procurement.
Chemical Manufacturing
In the chemical manufacturing industry, electric heating elements are used for process heating in reactors and mixing tanks. They optimize reaction rates and enhance the efficiency of chemical processes, ultimately reducing processing time and energy costs. Buyers from Africa and South America should focus on sourcing elements that can withstand corrosive environments and offer customization options to fit specific reactor designs. Ensuring reliable performance is crucial, as any downtime can lead to significant losses.
Textile Industry
The textile industry utilizes electric heating elements primarily in dyeing and finishing processes. These elements facilitate precise temperature control, which is essential for improving dye uptake and fabric quality. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it’s important to consider the flexibility in design and the elements’ compliance with safety standards. This ensures not only the quality of the final product but also adherence to environmental regulations.
Plastics and Polymer Production
Electric heating elements are integral in the preheating of materials for molding processes in the plastics and polymer production sector. By enhancing material flow, these elements help reduce defects in finished products, leading to higher quality outputs. Buyers should prioritize sourcing durable elements that can withstand high temperatures and are compatible with various polymers. Reliability in performance is also a vital factor, as it directly affects production efficiency.
HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, electric heating elements are commonly employed in electric duct heaters and unit heaters. They provide efficient heating solutions that enhance energy savings and comfort in commercial spaces. International buyers should pay attention to voltage compatibility and safety certifications when sourcing these elements, particularly in regions with varying electrical standards. Additionally, understanding maintenance requirements can help in selecting the right components for long-term reliability.
Related Video: Ultimate DIY Electric Kiln Guide – The Heating Elements (part 2)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric heating elements
When selecting materials for electric heating elements, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in electric heating elements: Nickel-Chromium Alloys, Copper, Stainless Steel, and Silicone Rubber. Each material presents unique characteristics that can significantly impact performance and application.
Nickel-Chromium Alloys
Key Properties: Nickel-chromium alloys, often referred to as nichrome, offer excellent resistance to oxidation and high temperatures, typically rated up to 1200°C (2192°F). They maintain their strength and resist scaling, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of nichrome is a significant advantage, as it can withstand prolonged use without degradation. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which can impact overall production costs. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specialized equipment for shaping and forming.
Impact on Application: Nichrome is ideal for applications involving air, gases, and some liquids, but it may not be suitable for corrosive environments without additional protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide certification for the alloys used, particularly in regions with strict regulations.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal efficiency, with a melting point around 1085°C (1985°F). It is highly malleable, allowing for easy shaping into various forms.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its cost-effectiveness and high performance in heat transfer applications. However, it is prone to oxidation and corrosion, which can limit its lifespan in certain environments. Thus, it may require protective coatings or alloys for durability.
Impact on Application: Copper is best suited for low to moderate temperature applications, such as heating elements in household appliances. Its compatibility with water and non-corrosive fluids makes it a popular choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards for copper products across regions. Ensuring compliance with local regulations can mitigate risks related to material quality.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 800°C (1472°F). It is strong and durable, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is a significant advantage for applications involving moisture or aggressive chemicals. However, it has lower thermal conductivity compared to copper and nichrome, which can affect efficiency. The manufacturing process can also be more complex, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for heating elements in food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries due to its hygienic properties. It is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards and material certifications is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where regulations are stringent. Buyers should verify that suppliers meet these standards.
Silicone Rubber
Key Properties: Silicone rubber can withstand temperatures ranging from -60°C to 230°C (-76°F to 446°F). It is flexible and can be molded into various shapes, making it versatile for different applications.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility and high-temperature resistance of silicone rubber are significant advantages, allowing it to conform to various surfaces. However, it has lower thermal conductivity compared to metal options, which may limit its use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Silicone rubber is commonly used for heating pads and blankets, where flexibility and even heat distribution are essential. It is compatible with a variety of applications, including medical and consumer products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that silicone products meet relevant safety and performance standards, particularly in the medical and food sectors. Understanding local regulations regarding silicone materials is essential.
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric heating elements | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium Alloys | High-temperature industrial applications | Excellent oxidation resistance | Higher cost and moderate complexity | High |
| Copper | Household appliances and low-temp applications | Cost-effective and highly conductive | Prone to oxidation and corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and chemical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower thermal conductivity | Medium to High |
| Silicone Rubber | Heating pads and flexible applications | Flexibility and high-temp resistance | Lower thermal conductivity | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric heating elements
Electric heating elements are crucial components in various industrial applications, necessitating a detailed understanding of their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of these aspects to ensure they are sourcing reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Manufacturing Processes for Electric Heating Elements
The manufacturing of electric heating elements involves several critical stages, each of which requires precision and adherence to industry standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing electric heating elements is the selection and preparation of materials. Typically, high-resistance metals such as nichrome (nickel-chromium alloy) are used due to their excellent heat-generating properties. The preparation process includes:
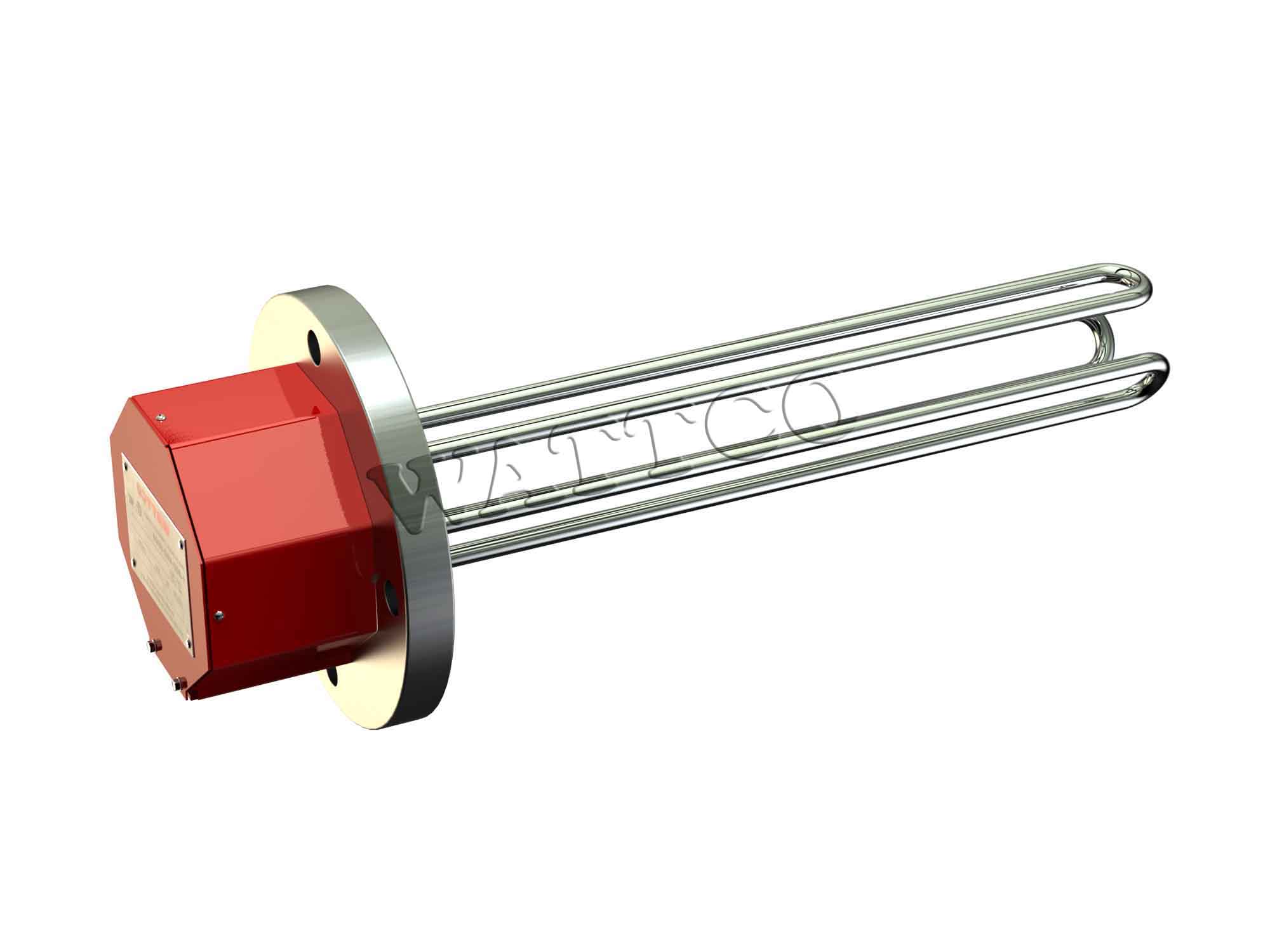
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Material Sourcing: B2B buyers should verify the provenance of materials to ensure quality and compliance with regulations.
- Testing Raw Materials: Before processing, materials undergo tests for composition and resistance to guarantee they meet specifications.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, they are formed into the desired shapes. This process can vary based on the type of heating element being manufactured:
- Winding: For coil-type elements, wires are wound around a core or framework.
- Molding: Ceramic or silicone heating elements are formed using molds to achieve specific dimensions and shapes.
- Tubular Formation: Tubular heating elements are created by shaping metal tubes and inserting heating wires.
3. Assembly
After forming, the elements are assembled. This stage may include:
- Connecting Terminals: Electrical connections are made, ensuring that the terminals are securely attached to prevent failure during operation.
- Insulation Application: Insulating materials are applied to prevent electrical leaks and enhance safety.
4. Finishing
The final stage in the manufacturing process involves finishing touches that improve performance and aesthetics:
- Coating: Elements may be coated with protective materials to resist corrosion and enhance durability.
- Quality Checks: Visual inspections and measurements are conducted to ensure compliance with specifications.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance is vital in the production of electric heating elements to ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency. Here are key aspects of quality assurance that B2B buyers should consider:
International and Industry-Specific Standards
- ISO 9001: This international standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, adherence to API standards ensures that heating elements can withstand harsh environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is integrated at various stages of manufacturing:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are performed during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the required specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of the testing methods used to ensure product quality:
- Electrical Testing: This includes resistance measurement and dielectric strength testing to ensure safety and functionality.
- Thermal Testing: Elements are tested under operating conditions to ensure they can handle specified temperatures without failure.
- Durability Testing: Products may undergo stress tests to assess their longevity and reliability in real-world applications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can implement several verification strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the operational processes and quality control measures in place.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can validate supplier claims regarding product quality and compliance with standards.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from different regions must navigate various nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Certifications: Familiarize yourself with local standards and certifications applicable in your region. For example, buyers in Africa may need to consider the SABS (South African Bureau of Standards) certifications, while those in Europe should focus on CE compliance.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understand that manufacturing practices and quality expectations may vary significantly across different countries. Building strong relationships with suppliers and regularly communicating quality expectations can help mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for electric heating elements is crucial for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with these aspects, especially in the context of international standards and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet their operational requirements. This diligence not only enhances operational efficiency but also minimizes the risk of costly failures and downtime.
Related Video: How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric heating elements Sourcing
When sourcing electric heating elements, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge helps in making informed purchasing decisions and maximizing cost efficiency.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of materials is a significant component in the pricing of electric heating elements. Common materials include nickel, copper, stainless steel, and ceramic. Prices fluctuate based on global market conditions and the purity or grade of the materials used. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with abundant material resources to reduce costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely across different regions. In countries with higher wage standards, labor costs can significantly impact the overall price of heating elements. However, in regions such as Africa and South America, where labor might be more affordable, buyers may find competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with running a factory, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes and modern machinery can help reduce these costs, which can be passed on to the buyer.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for manufacturing specific heating elements can be substantial. For custom orders, this cost can increase significantly, affecting the overall price. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs upfront, especially when ordering customized or specialized products.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control processes ensures that the heating elements meet industry standards. While this may add to the cost, it is crucial for avoiding costly defects and ensuring product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on distance, volume, and the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should consider both shipping and potential tariffs, especially when sourcing from different continents.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in larger quantities can often lead to significant discounts. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can facilitate better pricing structures based on volume.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom heating elements that require specific designs or materials may come at a premium. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and certifications (like ISO or CE) can influence pricing. High-quality materials and certified products may be more expensive but can lead to lower failure rates and better performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but provide added assurance of product performance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (like FOB or CIF) can significantly impact costs. Buyers should clarify these terms to understand who bears the shipping costs and risks during transit.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate. Understanding the cost components can give buyers leverage during discussions with suppliers.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of local market conditions and currency fluctuations, which can affect pricing. It’s advisable to stay informed about trends in both the supplier’s and buyer’s regions.
In conclusion, while indicative prices can vary widely, understanding the cost structure and key price influencers can empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Consider these factors carefully to optimize sourcing strategies for electric heating elements, ensuring both quality and cost-effectiveness.
Spotlight on Potential electric heating elements Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electric heating elements’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric heating elements
Electric heating elements are integral components in various industrial applications, and understanding their technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers. Below are some key specifications and industry terms that will aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
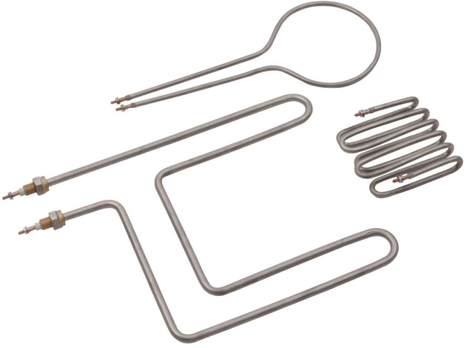
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Technical Properties of Electric Heating Elements
-
Material Grade
– The material used in electric heating elements significantly influences performance and durability. Common materials include nickel-chromium alloys for resistance wire, stainless steel for housing, and ceramics for insulation. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures optimal heat transfer, corrosion resistance, and longevity, which are vital for minimizing operational downtime and maintenance costs. -
Watt Density
– This property refers to the amount of power (in watts) delivered per unit area of the heating element. High watt density can lead to faster heating times but may also increase the risk of overheating or premature failure if not managed properly. Understanding watt density helps buyers choose elements that meet their specific heating requirements without compromising safety. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance indicates the allowable variation in dimensions or performance of the heating element. It is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and meeting precise operational standards. A tight tolerance can enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of failures, making it a critical consideration for buyers seeking reliability. -
Voltage Rating
– The voltage rating of a heating element determines its operational capacity and compatibility with electrical systems. Choosing the correct voltage rating is essential to prevent overheating and potential damage to the element. Buyers must match the voltage rating with their power supply specifications to ensure optimal performance. -
Insulation Class
– Insulation class defines the thermal limits of the materials used to insulate the heating element. Classes range from A to H, with higher classes indicating better thermal resistance. Selecting the right insulation class is important for safety and operational efficiency, especially in high-temperature environments. -
Response Time
– Response time measures how quickly a heating element can reach its operating temperature. Faster response times lead to improved process control and energy efficiency. Buyers should evaluate their process requirements to select elements that provide suitable response times for their applications.
Common Trade Terms in Electric Heating Elements
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing high-quality components that are designed for specific applications, ensuring compatibility and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory and budget effectively. It is crucial for negotiating terms with suppliers, especially for small to medium enterprises looking to maintain cost efficiency. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal process used to invite suppliers to submit pricing and terms for specific products. Submitting an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better terms, making it an essential step for buyers looking to procure heating elements at favorable rates. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is vital for clarifying shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery timelines, which can significantly impact the overall cost of procurement. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the amount of time between placing an order and receiving the product. For international buyers, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management, as longer lead times can affect production schedules. -
Certification Standards
– These are industry-specific standards that ensure products meet safety, quality, and environmental regulations. Familiarity with relevant certification standards (such as CE, UL, or ISO) helps buyers ensure compliance and quality assurance in their procurement processes.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and support their business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electric heating elements Sector
Electric heating elements are vital components in various industrial applications, providing efficient heating solutions for processes ranging from manufacturing to food production. As global demand for energy-efficient technologies rises, buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must stay informed about market dynamics and emerging trends.
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electric heating elements market is driven by several global factors, including increasing energy efficiency regulations, the transition towards renewable energy sources, and growing industrial automation. In particular, countries in Africa and South America are investing heavily in infrastructure, which boosts the demand for electric heating solutions in construction and manufacturing.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the adoption of smart heating elements equipped with IoT capabilities. These advanced systems allow for real-time monitoring and control, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Moreover, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on customizable heating solutions to meet the specific needs of diverse industries, from automotive to pharmaceuticals.
Market dynamics for international buyers are influenced by geopolitical factors and trade regulations. Buyers should be aware of fluctuations in material costs, particularly metals used in heating elements, and consider sourcing from regions with stable supply chains. Additionally, partnering with manufacturers that offer comprehensive technical support can provide a competitive edge, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of heating solutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the electric heating elements sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the use of non-renewable materials poses significant challenges. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing from suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as minimizing waste and reducing carbon emissions during production.
Ethical supply chains are paramount, especially as consumers increasingly demand transparency regarding the origins of products. Buyers should look for suppliers that hold recognized certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or certifications for the use of recycled materials. Utilizing ‘green’ materials in the production of electric heating elements not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, investing in energy-efficient heating solutions can significantly lower operational costs and reduce environmental footprints. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and attract a broader customer base.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electric heating elements can be traced back to the late 19th century, with early designs primarily focused on basic heating applications. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering led to the development of more efficient and durable heating solutions. The introduction of tubular and immersion heaters revolutionized the industry, allowing for more precise temperature control and faster heating times.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies has transformed the sector, enabling manufacturers to create smarter, more adaptable heating solutions. As the market continues to evolve, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into the future trajectory of electric heating elements and their applications across various industries.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric heating elements
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of electric heating elements?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Check for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance certifications, which indicate adherence to international standards. Request references or case studies from previous clients, especially those in your region. Additionally, assess their production capacity and technological capabilities to ensure they can meet your specific needs. -
Can I customize electric heating elements for my specific application?
Many manufacturers offer customization options tailored to unique applications. Discuss your requirements in detail, including size, wattage, and material specifications. Ensure the supplier has experience with custom projects and can provide examples of similar customizations. Request prototypes or samples to verify that the final product meets your expectations before placing a larger order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electric heating elements?
MOQs can vary widely depending on the supplier and the type of heating element. Generally, manufacturers may require a minimum order of 100-500 units for standard products, while custom orders may have higher MOQs. Lead times typically range from 2 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors like complexity, customization, and supplier location. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid delays in your project timeline. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric heating elements internationally?
Payment terms often vary by supplier and geographical region. Common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 terms. It’s essential to negotiate clear payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Ensure you understand any potential tariffs or import duties that may affect the total cost. Utilizing secure payment methods can also help protect your investment. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in electric heating elements?
Ensure that the supplier adheres to strict quality control processes, including testing procedures for their heating elements. Ask for documentation of quality assurance practices, such as material certifications and performance testing results. Inquire about the warranty terms and what recourse you have if the product does not meet specified standards. Regular audits and compliance with international standards are also critical indicators of product quality. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of electric heating elements?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Consider shipping methods, costs, and transit times when planning your order. Work with suppliers who have experience in shipping to your region and can navigate customs regulations efficiently. Discuss who will bear the cost of shipping and insurance, and ensure there is a clear plan for handling potential delays or issues during transit. -
What should I do if I encounter disputes with my supplier?
Establish clear communication channels with your supplier to address any issues that arise promptly. Document all agreements and communications to have a record in case of disputes. If disagreements cannot be resolved amicably, refer to the contract for dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration. Engaging legal counsel familiar with international trade laws can also be beneficial in complex situations. -
Are there specific certifications or standards I should verify for electric heating elements?
Yes, certain certifications can indicate the quality and safety of electric heating elements. Look for compliance with international standards such as IEC, UL, or CE, depending on your market. These certifications ensure that products meet safety and performance requirements. Additionally, consider any local regulations or standards that may apply in your region, as compliance can affect marketability and legal liability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric heating elements
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of electric heating elements is not just a procurement decision; it is a pivotal factor in enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring product reliability. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of supply chains, understanding the diverse range of heating elements—such as tubular, immersion, and cartridge types—becomes essential. Prioritizing suppliers with a proven track record in quality, compliance with international standards, and the ability to customize products to specific needs can lead to significant cost savings and improved performance.
Moreover, leveraging technology for supplier evaluation and performance monitoring can facilitate informed decision-making and foster long-term partnerships. As the demand for sustainable and energy-efficient heating solutions grows, aligning sourcing strategies with innovative manufacturers who are investing in eco-friendly technologies will be crucial.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with suppliers, attend industry trade shows, and utilize digital platforms to stay informed about the latest advancements in electric heating technology. By doing so, they can position their businesses for success in a competitive landscape and contribute to a more sustainable industrial future.