Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Electrical Heating Element
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrical heating element
In today’s increasingly interconnected world, the demand for efficient and reliable heating solutions has never been greater. Electrical heating elements play a crucial role across various industries, from manufacturing and food processing to healthcare and energy production. These components are not just integral to operational efficiency; they also significantly impact energy consumption and overall product quality. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the complexities of sourcing electrical heating elements is vital for informed decision-making.
This guide serves as an essential resource, offering a comprehensive overview of the electrical heating element market. It covers the different types of heating elements available, including tubular, cartridge, and immersion variants, and delves into material selection, discussing the properties and applications of various resistive materials. Additionally, we will explore manufacturing and quality control processes, helping buyers assess supplier capabilities and product reliability.
Buyers will also gain insights into cost considerations, market trends, and a curated list of reputable suppliers, ensuring they can navigate the global marketplace with confidence. The guide concludes with a detailed FAQ section addressing common queries, thus empowering businesses to make strategic sourcing decisions. By leveraging this information, international buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they secure the best solutions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Understanding electrical heating element Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular Heating Elements | Versatile, can be bent into various shapes; high thermal efficiency | Food processing, plastics, ceramics | Pros: Customizable shapes, high efficiency. Cons: Installation may require specialized skills. |
| Cartridge Heating Elements | Compact design, often used in tight spaces; excellent for localized heating | Industrial machinery, medical devices | Pros: Space-saving, quick heat-up time. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Immersion Heating Elements | Directly heated by submerging in liquids; efficient heat transfer | Water heating, chemical processing | Pros: High efficiency, effective for large volumes. Cons: Requires careful installation to avoid damage. |
| Coil Heating Elements | Flexible, can be used in various configurations; suitable for radiant heating | Ovens, furnaces, and industrial heaters | Pros: Versatile, easy to replace. Cons: May have lower durability in harsh environments. |
| Infrared Heating Elements | Emits infrared radiation for heating; effective for surface heating | Automotive, food service, drying applications | Pros: Fast heating, energy-efficient. Cons: Limited penetration depth; not suitable for all materials. |
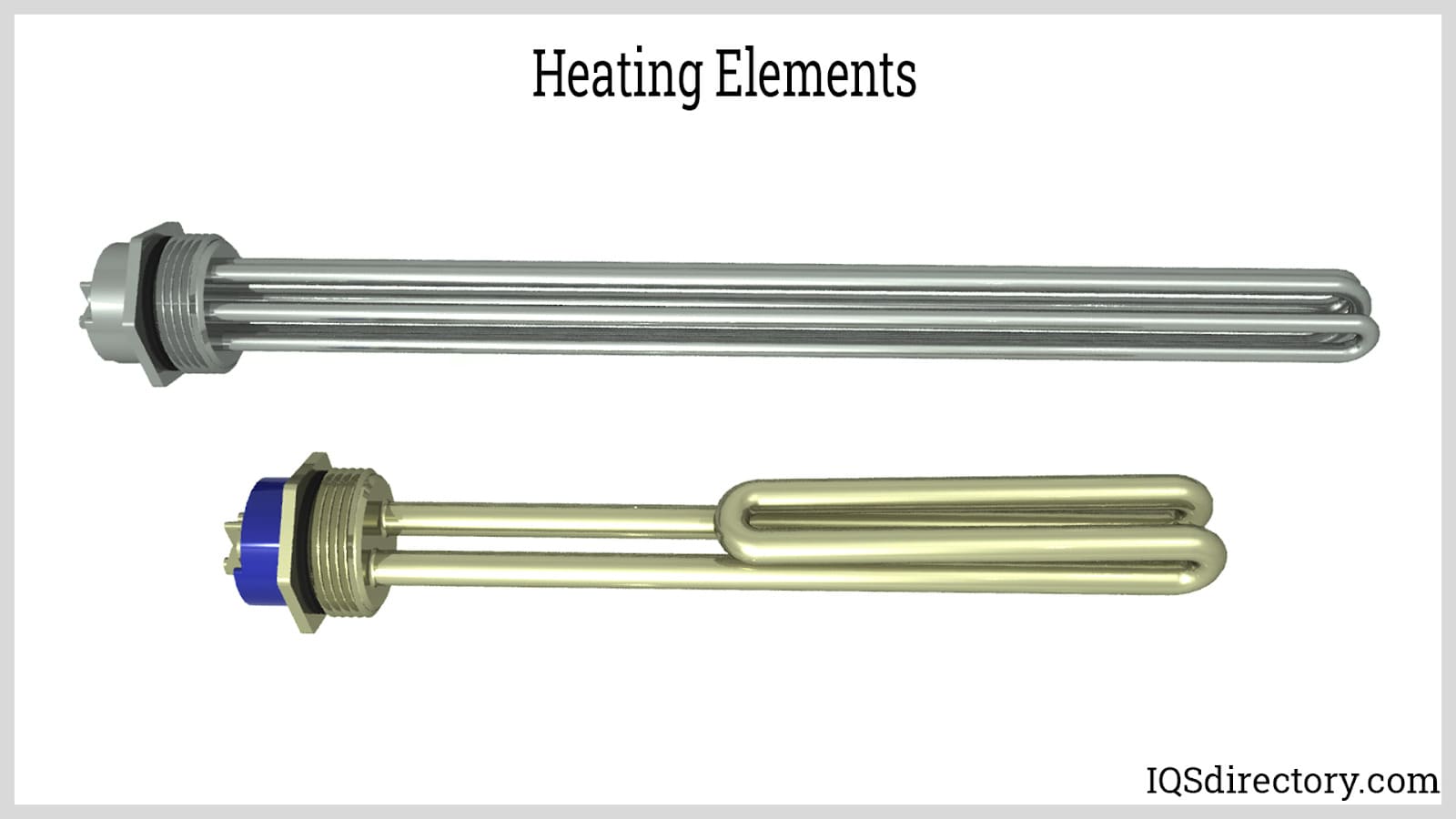
Tubular Heating Elements
Tubular heating elements are highly versatile and can be manufactured in various shapes to fit specific applications. Their high thermal efficiency makes them ideal for industries such as food processing, plastics, and ceramics. B2B buyers should consider customization options, installation requirements, and the thermal capacity needed for their specific applications when selecting tubular heating elements.
Cartridge Heating Elements
Cartridge heating elements are compact and designed for use in tight spaces, making them ideal for industrial machinery and medical devices. Their localized heating capability allows for quick heat-up times, which is essential in many applications. Buyers should evaluate the space constraints of their equipment and the specific heating requirements to ensure compatibility with cartridge heating elements.
Immersion Heating Elements
Immersion heating elements are designed to be submerged in liquids, providing efficient heat transfer for applications such as water heating and chemical processing. Their ability to heat large volumes of liquid quickly makes them a popular choice in various industries. B2B buyers must consider the installation environment and ensure that the elements are protected against corrosion and other potential damage.
Coil Heating Elements
Coil heating elements are flexible and can be configured in various ways, making them suitable for ovens, furnaces, and industrial heaters. Their versatility and ease of replacement are significant advantages. However, buyers should be aware that coil elements may not perform as well in harsh environments, and careful selection based on the application is crucial.
Infrared Heating Elements
Infrared heating elements work by emitting infrared radiation, making them effective for surface heating applications such as automotive, food service, and drying processes. They provide fast heating and energy efficiency, but their limited penetration depth means they may not be suitable for all materials. Buyers should assess the specific heating needs and the materials involved to determine the appropriateness of infrared heating solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of electrical heating element
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electrical heating element | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Industrial Ovens for Material Processing | Ensures uniform heating, enhancing product quality | Material compatibility, energy efficiency, and safety certifications. |
| Food and Beverage | Food Processing Equipment (e.g., fryers, ovens) | Improved cooking efficiency and consistent food quality | Hygiene standards, temperature control, and energy consumption. |
| Chemical Processing | Heating Reactors for Chemical Reactions | Accelerates reaction times, improving production rates | Resistance to corrosive environments and precise temperature control. |
| Textiles | Drying Machines for Fabric Treatment | Reduces drying time, enhancing throughput | Temperature uniformity, energy efficiency, and compliance with safety regulations. |
| Energy and Utilities | Heat Exchangers in Power Generation | Increases energy efficiency and lowers operational costs | Durability under high temperatures and compatibility with various fluids. |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, electrical heating elements are integral to industrial ovens used for material processing. These elements provide uniform heating, which is critical for ensuring product quality and consistency. Buyers should consider the material compatibility of heating elements with the substances being processed, the energy efficiency of the heating solution, and the necessary safety certifications to comply with local regulations, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East where industrial standards can vary significantly.
Food and Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, electrical heating elements are widely used in equipment such as fryers and ovens. These elements enhance cooking efficiency and ensure consistent food quality, crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and compliance with food safety regulations. When sourcing, businesses should prioritize hygiene standards, precise temperature control, and energy consumption metrics to optimize operational costs, particularly in competitive markets in South America and Europe.
Chemical Processing
Electrical heating elements are essential in chemical processing, particularly in heating reactors where chemical reactions occur. These elements facilitate faster reaction times, leading to improved production rates. For international buyers, sourcing considerations include the elements’ resistance to corrosive environments and their ability to maintain precise temperature controls, which are vital for safety and efficiency in regions with stringent chemical handling regulations.
Textiles
In the textile industry, electrical heating elements are utilized in drying machines for fabric treatment. These elements significantly reduce drying time, thereby enhancing throughput and productivity. Buyers should focus on ensuring temperature uniformity across the heating elements, energy efficiency to reduce operational costs, and compliance with safety regulations, especially in regions like Europe where environmental standards are stringent.
Energy and Utilities
In the energy sector, electrical heating elements are employed in heat exchangers used in power generation. They play a crucial role in increasing energy efficiency and lowering operational costs. When sourcing these elements, businesses need to ensure their durability under high temperatures and compatibility with various fluids, which is especially important in regions experiencing rapid industrial growth, such as Africa and the Middle East.
Related Video: How PTC Heating Element Technology Works
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrical heating element
When selecting materials for electrical heating elements, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in electrical heating elements, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Nickel-Chromium Alloys
Key Properties:
Nickel-chromium alloys are known for their high heat resistance and excellent corrosion resistance. They can operate at temperatures exceeding 1000°C and exhibit high electrical resistivity, making them suitable for various heating applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of nickel-chromium alloys is their durability, which leads to a longer lifespan for heating elements. However, they are relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can impact overall project costs. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for precise alloying.
Impact on Application:
These alloys are ideal for high-temperature applications, such as industrial furnaces and ovens. They are compatible with various media, including air and gases, but may not perform well in highly corrosive environments without additional protective measures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM and DIN, particularly in industries like oil and gas where safety is paramount. Understanding the specific alloy composition is crucial for ensuring compatibility with local environmental conditions.
Silicon Carbide
Key Properties:
Silicon carbide is renowned for its exceptional high-temperature resistance, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 2700°C. It also possesses excellent oxidation resistance and thermal shock resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of silicon carbide is its ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions, making it suitable for high-temperature furnaces and kilns. However, it is more brittle than other materials, which can lead to failure under mechanical stress. The cost is generally high due to the specialized manufacturing processes required.
Impact on Application:
Silicon carbide is particularly effective in applications involving molten metals or aggressive atmospheres. It is important for buyers to consider the mechanical stresses involved in their specific applications to avoid premature failure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and South America should be aware of the specific certifications required for silicon carbide heating elements, especially in industries that demand high safety standards. Familiarity with local regulations regarding material sourcing can also influence procurement strategies.
Molybdenum Disilicide
Key Properties:
Molybdenum disilicide can withstand temperatures up to 1700°C and forms a protective oxide layer, enhancing its durability in high-temperature environments. It has good thermal conductivity and is resistant to oxidation.
Pros & Cons:
This material offers a balance of performance and cost, making it an attractive option for many industrial applications. However, it may require careful handling during installation due to its brittleness, and its performance can be compromised in reducing atmospheres.
Impact on Application:
Molybdenum disilicide is commonly used in ceramic kilns and industrial furnaces, where high temperatures are essential. Its compatibility with various heating media makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in regions such as Africa and the Middle East, understanding the local market’s demand for high-temperature applications is essential. Compliance with international standards can facilitate smoother transactions and ensure product reliability.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it a popular choice for sheath materials in heating elements. It can operate effectively at moderate temperatures, typically up to 600°C.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which extends the lifespan of heating elements. However, its thermal conductivity is lower than that of other materials, which may impact heating efficiency. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to high-performance alloys.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is widely used in applications requiring moderate heat, such as water heating and food processing. Its compatibility with various media, including water and oils, makes it a versatile option.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe should focus on the specific grade of stainless steel to ensure compliance with food safety regulations, particularly in food processing applications. Understanding local standards for corrosion resistance can also influence material selection.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electrical heating element | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium Alloys | Industrial furnaces, high-temperature ovens | High durability and lifespan | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Silicon Carbide | High-temperature furnaces, kilns | Exceptional high-temperature performance | Brittle and high cost | High |
| Molybdenum Disilicide | Ceramic kilns, industrial furnaces | Good thermal conductivity and oxidation resistance | Brittle and sensitive to reducing atmospheres | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Water heating, food processing | Corrosion resistance and mechanical strength | Lower thermal conductivity | Low |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, emphasizing the importance of material selection based on performance, application, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrical heating element
Manufacturing Processes for Electrical Heating Elements
The manufacturing of electrical heating elements is a complex process that involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer requirements. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
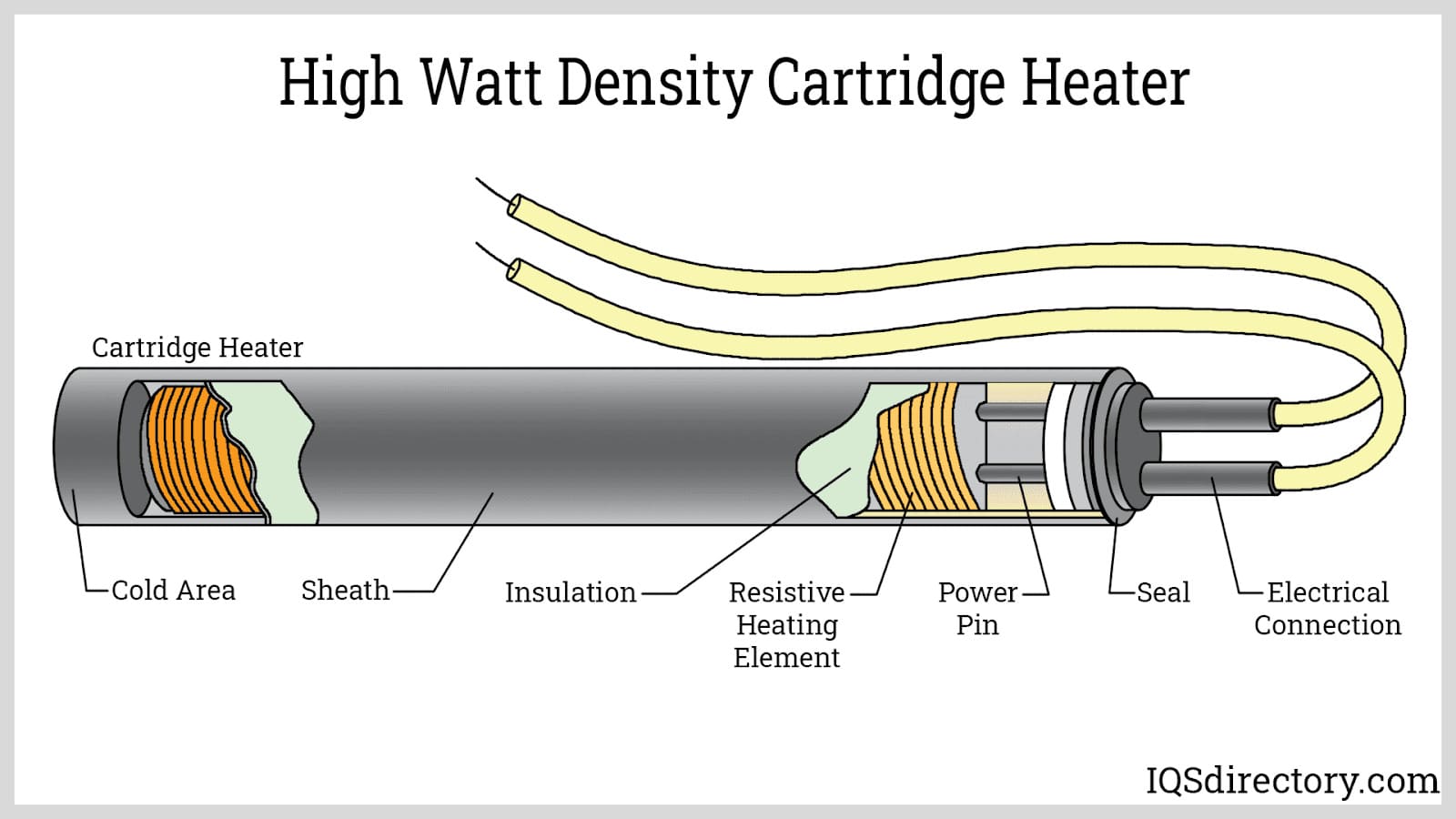
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate resistive materials (such as nickel-chromium alloys or copper) and insulating materials (like magnesium oxide or ceramics). The choice of materials directly impacts the efficiency, longevity, and safety of the heating elements.
- Material Sourcing: Suppliers should ensure that the materials are sourced from reputable manufacturers who provide certification of quality and origin.
- Testing: Incoming materials undergo rigorous testing to verify their properties, such as electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity, ensuring they meet predefined specifications.
Forming
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into the desired configurations.
- Wire Drawing: Resistive wire is drawn to the required diameter, which is essential for achieving the desired resistance and heat output.
- Tube Formation: For tubular heating elements, metal tubes are formed to encase the resistive wire. This can involve processes such as extrusion or rolling, depending on the design specifications.
Assembly
The assembly stage is where the components are brought together to create the heating element.
- Winding: The resistive wire is wound into coils or rods, depending on the type of heating element being produced.
- Encapsulation: The wound wire is then placed within the insulating sheath, typically made from materials like magnesium oxide, which provides thermal insulation and protects the wire from oxidation.
- Sealing: End fittings or terminals are attached to ensure a secure connection to the power supply, while also providing mechanical stability.
Finishing
The finishing stage includes any additional processes required to ensure the heating elements are ready for use.
- Testing: Each batch undergoes extensive testing to check for defects, electrical continuity, and insulation integrity.
- Coating: Some heating elements may receive a protective coating to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Packaging: Finally, the elements are packaged in a manner that protects them during transit and storage.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of electrical heating elements to ensure they meet both international and industry-specific standards. Effective QA processes can significantly reduce the risk of product failure and enhance customer satisfaction.
International Standards
Compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001, is essential for manufacturers aiming to export their products globally. ISO 9001 provides a framework for quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- ISO Certification: B2B buyers should verify if suppliers hold ISO certification, which demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Industry-Specific Standards
In addition to international standards, many industries have specific regulations that manufacturers must adhere to. For example, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has standards for heating elements used in oil and gas applications.
- API Certification: Suppliers serving the oil and gas sector should be certified by API, indicating that their products meet stringent industry requirements.
Quality Checkpoints
Throughout the manufacturing process, various quality checkpoints are implemented to catch defects early and ensure compliance with standards.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Checks are performed on raw materials as they arrive to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify issues in real-time, allowing for corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished products undergo a final inspection to verify they meet all quality criteria.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of electrical heating elements:
- Electrical Testing: Measures resistance, insulation resistance, and continuity to ensure proper functionality.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluates the heat output and temperature stability under operational conditions.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses durability and strength, particularly for elements that will be subjected to mechanical stress.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can help buyers assess the reliability of the supplier’s products.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for electrical heating elements is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, forming techniques, assembly methods, and rigorous quality control, buyers can ensure they partner with manufacturers who deliver high-quality, reliable products. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also fosters long-term business relationships based on trust and quality assurance.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrical heating element Sourcing
When sourcing electrical heating elements, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will break down the key cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable tips for maximizing cost efficiency.
Cost Components
-
Materials
The primary cost driver in electrical heating elements is the raw materials used, including resistive materials like nickel-chromium alloys and insulating materials such as magnesium oxide. The quality and specifications of these materials can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with lower material costs but maintain quality standards. -
Labor
Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of manufacturing processes. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, manufacturers may invest in automation to reduce these expenses. Buyers should assess whether labor costs influence the overall pricing and factor this into their sourcing decisions. -
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Manufacturers often pass these costs onto buyers, so understanding the overhead structure can aid in negotiations. -
Tooling
Custom tooling for specialized heating elements can add to upfront costs. If a buyer requires specific designs, this should be discussed early in the negotiation to avoid unexpected expenses later. -
Quality Control (QC)
Investments in quality control processes ensure that the heating elements meet industry standards and certifications. While this may increase the initial price, it can lead to long-term savings by reducing failure rates and warranty claims. -
Logistics
Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and customs duties should be evaluated to get a clearer picture of the total landed cost. -
Margin
Suppliers typically include a margin to cover their risks and profit. Buyers should understand the typical margins in the industry to gauge whether a quote is competitive.
Price Influencers
- Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom heating elements tailored to specific applications will generally incur higher costs. Clearly defining requirements can help manage these expenses.
- Materials: The choice of materials directly influences pricing; premium materials will drive up costs. Buyers should balance quality with budget constraints.
- Quality/Certifications: Elements that meet stringent quality standards or certifications may carry a higher price tag. However, investing in certified products can reduce risks in the long run.
- Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and geographic location can impact pricing. Building strong relationships can yield better terms.
- Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms can help buyers assess risks and costs associated with transportation and customs.
Buyer Tips
- Negotiation: Engage suppliers in open discussions about pricing structures. Understanding the breakdown of costs can provide leverage during negotiations.
- Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the purchase price. Consider total cost of ownership, including maintenance, efficiency, and potential downtime costs.
- Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing variations and potential hidden costs due to tariffs or local taxes.
- Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Always approach quotes with the understanding that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, material costs, and geopolitical factors.
By carefully analyzing these components and influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that balance cost with quality, ultimately leading to successful sourcing of electrical heating elements.
Spotlight on Potential electrical heating element Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electrical heating element’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrical heating element
Critical Technical Properties of Electrical Heating Elements
When sourcing electrical heating elements, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with your applications. Here are some key properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material greatly influences the performance and longevity of heating elements. Common materials include nickel-chromium alloys for high-temperature applications and stainless steel for corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate material grade can enhance efficiency and reduce downtime due to equipment failures. -
Watt Density
Watt density, measured in watts per square inch, indicates how much power a heating element can deliver over a specific area. Higher watt densities allow for faster heating but can also lead to overheating if not managed properly. Understanding watt density is vital for applications requiring precise temperature control to prevent damage to materials being heated. -
Temperature Rating
Each heating element is designed to operate within a specific temperature range. The maximum operating temperature should match the requirements of your application. Failure to adhere to these ratings can lead to premature failure of the element or even safety hazards. -
Resistance Tolerance
This specification refers to the allowable variation in the resistance of the heating element. Lower tolerance values indicate higher precision in performance, which is essential for applications that require consistent heat output. Understanding resistance tolerance helps ensure that the heating element will perform reliably within the expected operational parameters.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how effectively a material can transfer heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity promote efficient heating, reducing energy consumption and improving performance. This property is essential for applications where energy efficiency is a priority. -
Insulation Type
The insulation surrounding the heating element plays a critical role in safety and efficiency. Common insulation materials include magnesium oxide and ceramic, which prevent heat loss and protect against electrical shorts. Selecting the right insulation can enhance the element’s performance and lifespan while ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Common Trade Terms in Electrical Heating Element Procurement
Navigating the procurement of electrical heating elements involves familiarity with specific industry terminology. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term defines the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is important for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for smaller companies or those testing new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of goods. Submitting an RFQ is a standard practice in B2B transactions, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with delivery. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving it. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and avoiding delays in production, especially in industries with tight schedules. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the performance and longevity of the product. Knowing the terms of the warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment in the event of product failure.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make informed decisions when sourcing electrical heating elements, ensuring they meet your operational needs and standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electrical heating element Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electrical heating element sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. The increased demand for energy-efficient heating solutions is a primary market driver, particularly as industries seek to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Technological advancements are also reshaping the landscape, with innovations such as smart heating elements that integrate with IoT systems for enhanced control and efficiency.
International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing customization and flexibility in sourcing heating elements. Suppliers are responding by offering tailored solutions that meet specific industry requirements, such as varying voltage and wattage specifications. Additionally, regional sourcing trends are emerging, with countries in Africa and South America looking to localize their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with global logistics disruptions. This shift not only supports local economies but also ensures quicker turnaround times.
Sustainability is becoming a significant consideration in purchasing decisions. Buyers are more inclined to choose suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. The European market, in particular, is leading the way in enforcing stringent regulations regarding energy efficiency and waste management, prompting suppliers to adapt swiftly.
Overall, the electrical heating element market is characterized by a dynamic interplay of technological innovation, sustainability imperatives, and evolving buyer preferences, creating a fertile ground for B2B opportunities across continents.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of electrical heating elements cannot be understated. Traditional manufacturing processes often involve materials and practices that contribute to pollution and resource depletion. As a result, the industry is witnessing a shift towards sustainable practices that minimize ecological footprints. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing, ensuring that raw materials are obtained from responsible sources that adhere to fair labor practices and environmental stewardship.
Incorporating green certifications into the sourcing process is becoming a norm. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Energy Star are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, the use of materials like recycled metals and innovative alternatives such as biodegradable insulation is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce the environmental impact but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
As international B2B buyers navigate their sourcing decisions, understanding the sustainability credentials of suppliers is vital. Engaging with manufacturers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and compliance with environmental regulations can enhance a company’s brand reputation and foster long-term partnerships.
Brief Evolution/History
The electrical heating element sector has evolved significantly over the decades, driven by advancements in materials science and manufacturing technologies. Initially, heating elements were primarily made from simple metals like iron and copper, which were limited by their thermal efficiency and lifespan. The introduction of nickel-chromium alloys in the mid-20th century marked a turning point, offering higher resistance to oxidation and improved durability.
As energy efficiency became a priority, the late 20th century saw the rise of ceramic and silicon carbide materials, which enabled higher temperature applications while maintaining energy efficiency. The digital age has further transformed the sector, with smart technology integration allowing for real-time monitoring and control of heating elements, enhancing both efficiency and user experience. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards innovation and sustainability, shaping the future of electrical heating elements in various industries.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrical heating element
-
How do I vet suppliers for electrical heating elements?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Start by checking their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001. Request references from existing clients and evaluate their reputation in the market. Conduct factory visits if possible, or utilize third-party auditing services. Additionally, assess their production capacity and technology to ensure they can meet your demands consistently. -
Can I customize electrical heating elements for my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to meet your specific operational requirements. Discuss your needs regarding dimensions, wattage, and materials with potential suppliers. It is essential to provide detailed specifications and applications to ensure the manufacturer can meet your expectations. Request samples to evaluate the performance of customized elements before placing a larger order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the heating elements. Generally, expect MOQs ranging from 50 to several hundred units. Lead times can also vary; standard products may be available within 2-4 weeks, while customized elements could take longer. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid supply chain disruptions. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing heating elements internationally?
Payment terms often depend on the supplier’s policies and your negotiating power. Common terms include a 30% deposit with the order and the balance before shipment. For larger orders, consider using letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings later. -
What quality assurance processes should suppliers have?
Quality assurance is vital in manufacturing electrical heating elements. Suppliers should have robust QA processes, including incoming material inspections, in-process quality checks, and final product testing. Request documentation of their QA procedures and any relevant certifications, such as CE or UL. Understanding their testing methods will give you confidence in the reliability and safety of the products. -
How do I handle logistics for international shipments?
Logistics can be complex when dealing with international suppliers. Ensure that you understand the Incoterms used in your contract, as they define responsibilities for shipping costs, risk, and insurance. Collaborate with logistics providers familiar with customs regulations in your region. Additionally, consider insurance for high-value shipments to protect against loss or damage during transit. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In case of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue directly with the supplier through open communication. Document all correspondences and agreements. If an agreement cannot be reached, refer to the dispute resolution clause in your contract, which may include mediation or arbitration. Legal avenues can be pursued, but they are often time-consuming and costly, so consider all alternatives before proceeding. -
What certifications should electrical heating elements have?
Certifications are essential to ensure that the heating elements comply with safety and performance standards. Look for certifications such as CE (European Conformity), UL (Underwriters Laboratories), or RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) depending on your market requirements. These certifications not only ensure product safety but also facilitate smoother customs clearance when importing. Always request certification documents from suppliers before finalizing your order.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrical heating element
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of electrical heating elements is crucial for international buyers seeking efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in their operations. Understanding the diverse materials and technologies available allows businesses to select heating elements that best fit their specific applications, whether in industrial manufacturing, food processing, or energy sectors.
Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating resistive and sheath materials, as well as insulation properties, to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, engaging with reputable suppliers who offer tailored solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiencies and reduce downtime.
As the global market evolves, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are encouraged to leverage digital platforms for sourcing and collaboration. This approach not only opens doors to innovative technologies but also fosters partnerships that can drive competitive advantages.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers must remain proactive in adapting to emerging trends and sustainability practices within the electrical heating sector. By doing so, they can ensure their businesses not only thrive today but are also well-prepared for future challenges. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy today—explore new suppliers, technologies, and opportunities that align with your operational goals.