Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Electrical Prongs
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrical prongs
In today’s global marketplace, understanding the intricacies of electrical prongs is paramount for international B2B buyers. These seemingly simple components play a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient power connectivity across diverse applications and regions. From the specialized prongs used in industrial machinery to those suited for consumer electronics, the significance of selecting the right electrical prongs cannot be overstated.
This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource, offering insights into various types of electrical prongs, including their designs and functionalities. It delves into the materials used in manufacturing, quality control standards, and the factors influencing sourcing decisions. Additionally, buyers will find valuable information on key suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends that can impact procurement strategies.
By equipping decision-makers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with the knowledge to navigate this complex landscape, this guide empowers them to make informed sourcing choices. Whether you are a buyer in South Africa looking for reliable suppliers or an importer in Italy seeking cost-effective solutions, understanding the nuances of electrical prongs will enhance your ability to secure high-quality products that meet safety and performance standards. Prepare to optimize your procurement processes and boost operational efficiency as you explore the dynamic world of electrical prongs.
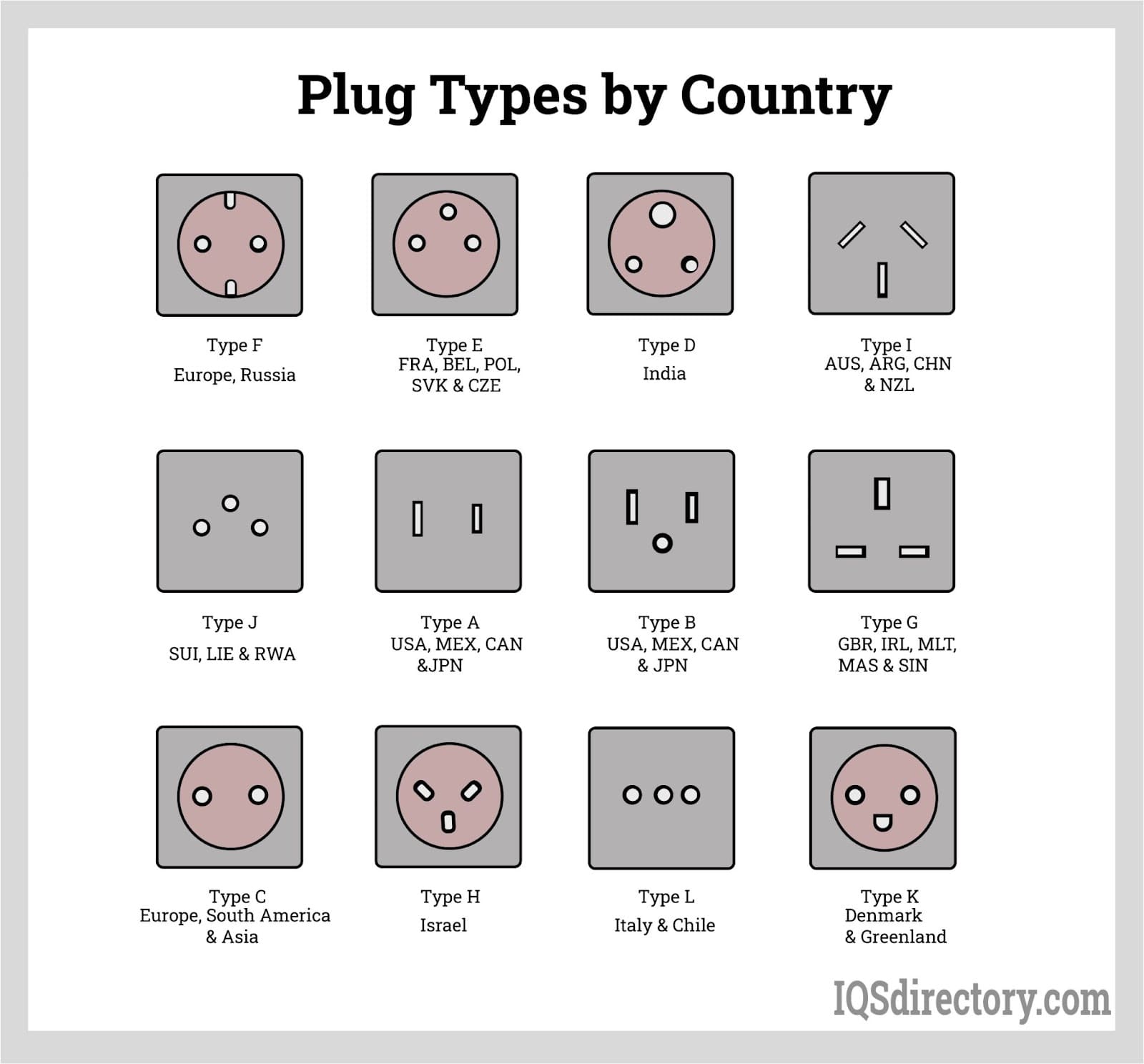
Understanding electrical prongs Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Two flat parallel prongs; non-polarized | General appliances, electronics | Pros: Widely used; Cons: Limited grounding. |
| Type B | Two flat prongs plus a round grounding prong | Heavy-duty appliances, industrial use | Pros: Enhanced safety; Cons: Bulkier design. |
| Type C | Two round prongs; commonly used in Europe and Asia | Lightweight devices, travel adapters | Pros: Compact size; Cons: Not grounded. |
| Type D | Three large round prongs; primarily used in India | High-power equipment, industrial tools | Pros: High current capacity; Cons: Less common globally. |
| Type G | Three rectangular prongs forming a triangular pattern | UK appliances, power tools | Pros: Secure connection; Cons: Requires adapter in other regions. |
Type A
Type A plugs feature two flat parallel prongs and are non-polarized, making them easy to insert into sockets without regard for orientation. Commonly found in North America and parts of Asia, they are primarily used for general appliances and electronics. Buyers should consider their widespread availability and compatibility with devices, but note that the lack of a grounding feature may pose safety concerns for sensitive electronics.
Type B
Type B plugs are characterized by two flat prongs and an additional round grounding prong, providing a secure connection and enhanced safety. They are commonly used in heavy-duty appliances and industrial applications that require higher power levels. B2B buyers should appreciate the grounding feature which protects against electrical surges, although the bulkier design may limit compatibility with some devices.
Type C
Type C plugs consist of two round prongs and are widely used across Europe, Asia, and Africa. They are typically found in lightweight devices and travel adapters. The compact design is advantageous for portable applications, but the absence of a grounding prong may limit their use with high-power devices. Buyers should consider the regional compatibility when sourcing Type C plugs.
Type D
Type D plugs are distinguished by three large round prongs and are primarily utilized in India and some African countries. They are designed for high-power equipment and industrial tools, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. The high current capacity is a significant advantage for buyers; however, Type D plugs are less common globally, which may pose challenges in sourcing and compatibility.
Type G
Type G plugs feature three rectangular prongs arranged in a triangular pattern and are predominantly used in the United Kingdom and its former colonies. They are known for providing a secure connection and are often used in UK appliances and power tools. B2B buyers should be aware that while Type G plugs are robust and safe, they may require adapters for use in regions with different plug types, potentially complicating international transactions.
Key Industrial Applications of electrical prongs
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electrical Prongs | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Power supply connections for appliances | Ensures reliable operation and safety of devices | Compatibility with local standards, voltage ratings, and certifications |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Machinery and equipment connections | Facilitates efficient operation and reduces downtime | Durability, load capacity, and compliance with safety standards |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panel installations | Enhances energy efficiency and system reliability | Resistance to environmental factors and compatibility with existing systems |
| Automotive | Charging stations for electric vehicles | Supports the growth of EV infrastructure and consumer adoption | Adaptability to various vehicle models and safety certifications |
| Telecommunications | Network equipment power connections | Maintains uptime and reliability of communication systems | Compliance with international electrical standards and quality assurance |
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics sector, electrical prongs are crucial for power supply connections in appliances such as refrigerators, microwaves, and televisions. These prongs ensure reliable operation, facilitating a snug fit in outlets to prevent accidental disconnection. For international buyers, it is essential to consider the compatibility of prong designs with local electrical standards and voltage ratings. Additionally, certifications for safety and energy efficiency can enhance product appeal in diverse markets.
Industrial Manufacturing
Electrical prongs are integral in connecting machinery and equipment within industrial manufacturing environments. They facilitate efficient operation, which can significantly reduce downtime due to electrical failures. Buyers in this sector should prioritize durability and load capacity when sourcing prongs, as well as ensure compliance with relevant safety standards. Understanding local regulations and industrial requirements can also aid in selecting the right prong specifications.
Renewable Energy
In renewable energy applications, such as solar panel installations, electrical prongs play a vital role in enhancing energy efficiency and system reliability. They connect various components within the solar power system, ensuring that energy flows smoothly from panels to inverters and batteries. International buyers must consider environmental resistance and compatibility with existing systems when sourcing prongs, as these factors can impact the longevity and performance of renewable energy solutions.
Automotive
The automotive industry increasingly relies on electrical prongs for charging stations dedicated to electric vehicles (EVs). These connections support the growing infrastructure for EVs, making them essential for consumer adoption. When sourcing prongs for automotive applications, buyers should focus on adaptability to various vehicle models and ensure that they meet rigorous safety certifications. This consideration is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of charging systems.
Telecommunications
In the telecommunications sector, electrical prongs are used for powering network equipment, ensuring that systems remain operational and reliable. The performance of communication systems heavily depends on the quality of electrical connections, making it critical for businesses to source high-quality prongs. Buyers should ensure that sourced products comply with international electrical standards and undergo rigorous quality assurance processes to maintain system uptime and reliability.
Related Video: The Electrical Distribution System
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrical prongs
When selecting materials for electrical prongs, it is crucial to consider various factors such as conductivity, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of electrical prongs, tailored for international B2B buyers.
1. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m. It also has a melting point of 1,984°F (1,085°C), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons:
Copper prongs are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, especially when plated with nickel. However, the cost of copper can be high, and it may require additional treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as copper can be easily shaped and formed.
Impact on Application:
Copper is compatible with a wide range of electrical media, making it suitable for both residential and industrial applications. However, in humid environments, copper may oxidize, which can affect performance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B187 and IEC 60998. In regions like Europe and South Africa, copper is widely accepted and preferred for its reliability.
2. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers good electrical conductivity (around 28% of copper) and has a melting point of approximately 1,650°F (900°C). It is also known for its resistance to corrosion and tarnishing.
Pros & Cons:
Brass prongs are less expensive than pure copper and are easier to manufacture due to their malleability. However, they have lower conductivity compared to copper, which may limit their use in high-power applications.
Impact on Application:
Brass is suitable for general-purpose electrical connections but may not be ideal for high-load applications where maximum conductivity is required.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Brass components must comply with standards like ASTM B16 and DIN 17660. In regions such as South America and the Middle East, brass is often favored for its cost-effectiveness and performance in moderate conditions.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, with a melting point of around 2,500°F (1,370°C). Its electrical conductivity is lower than that of copper and brass.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to environmental factors, its lower conductivity makes it less suitable for high-current applications. The manufacturing process can be more complex due to its hardness.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel prongs are ideal for harsh environments, such as outdoor or industrial settings, where corrosion is a concern. However, their reduced conductivity may limit their use in certain electrical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 and ISO 9445 is essential. In Europe, stainless steel is often used in applications requiring high durability and corrosion resistance.
4. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum has a conductivity rating of about 37% of copper and a melting point of 1,221°F (660°C). It is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is cost-effective and lightweight, making it an attractive option for many applications. However, its lower conductivity can be a drawback for high-power devices, and it may require special connectors to ensure secure connections.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum prongs are suitable for lightweight devices and applications where weight reduction is critical. However, they may not be suitable for high-load applications without proper design considerations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 and IEC 60884. In regions like Africa and South America, aluminum is increasingly adopted due to its cost-effectiveness and lightweight properties.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electrical prongs | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-performance electrical devices | Excellent conductivity | High cost; requires corrosion treatment | High |
| Brass | General-purpose electrical connections | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environment applications | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Lower conductivity; complex to manufacture | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight devices | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity; special connectors needed | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for electrical prongs, aimed at facilitating informed decisions for international B2B buyers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrical prongs
Manufacturing Processes for Electrical Prongs
The manufacturing of electrical prongs involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets both performance and safety standards. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers from diverse regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions when sourcing electrical components.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing electrical prongs is material preparation. Typically, high-conductivity metals such as brass or copper are chosen for their excellent electrical properties. The selected materials undergo the following:
- Material Sourcing: Ensure that suppliers provide materials that comply with international standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials).
- Inspection: Before production, raw materials are subjected to incoming quality control (IQC) checks to verify their quality and specifications.
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into manageable sizes, often using precision cutting tools, to prepare for the forming stage.
2. Forming
Forming is a crucial stage where the raw material is shaped into prongs. This can involve several techniques:
- Stamping: This method utilizes a die to cut and shape the metal into prongs, allowing for high-volume production with consistent quality.
- Forging: In some cases, prongs are forged to enhance their mechanical properties, providing added strength and durability.
- Machining: Additional machining may be necessary to achieve precise dimensions or specific features, such as holes for padlocks or ties.
3. Assembly
Once the individual prongs are formed, the next step is assembly:
- Joining Components: If the prongs are part of a more complex plug assembly, they are joined with other components (e.g., housings, insulation) using techniques such as soldering or crimping.
- Integration of Safety Features: During assembly, manufacturers often incorporate safety features such as grounding prongs to prevent electrical surges, which is critical for compliance with safety standards.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage is essential for ensuring the prongs are ready for market:
- Surface Treatment: This may include plating with nickel or tin to enhance corrosion resistance and improve conductivity.
- Quality Coating: A non-conductive coating may be applied to certain parts to prevent accidental contact with live electrical components.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components meet quality and safety specifications.
Quality Assurance for Electrical Prongs
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of electrical prongs, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards
Buyers should be familiar with the following standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For prongs used in specific industries, such as oil and gas, adherence to API standards may be necessary.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for defects and compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are conducted to monitor the production process and ensure adherence to standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, final inspections are performed to verify the functionality and safety of the electrical prongs.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should expect the following testing methods as part of the QC process:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that prongs meet required electrical specifications.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the strength and durability of the prongs under various conditions.
- Environmental Testing: Evaluates performance in different environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature extremes.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers adhere to high-quality standards, buyers should consider the following strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can provide insights into their operational practices and adherence to standards.
- Review of Quality Reports: Request access to quality reports that detail inspections and testing results. This transparency can build confidence in the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices.
Navigating Quality Certification Nuances
International B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa and South America, should be aware of the following nuances:
- Certification Variances: Different regions may have varying certification requirements. Understanding local regulations can help in choosing compliant suppliers.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Quality expectations may differ by region. Buyers should communicate their specific requirements clearly to avoid misunderstandings.
- Local Representation: Having local representatives can facilitate better communication and quality oversight, especially when sourcing from regions with different regulatory landscapes.
Conclusion
For B2B buyers, a deep understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electrical prongs is essential. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, and robust quality control measures, buyers can ensure they source high-quality products that meet international standards. Being proactive in verifying supplier practices through audits and inspections can further mitigate risks associated with sourcing electrical components globally.
Related Video: Cell Production | Battery Manufacturing Automation
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrical prongs Sourcing
In the sourcing of electrical prongs, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. The following analysis breaks down the key components that affect pricing and offers actionable insights for negotiating better deals.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in electrical prong production include copper, brass, and various plastics. The choice of materials directly influences both the cost and quality of the final product. Copper, for instance, is more conductive but also more expensive than aluminum.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region of manufacture. Countries with lower labor costs can provide more competitive pricing, but this may sometimes compromise quality. Buyers should consider the skill level of the workforce and the potential need for additional quality control.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs of running a manufacturing facility, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. These costs are typically spread across all products manufactured, influencing the final price of electrical prongs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom designs can be substantial. If specific prong specifications or customizations are required, it’s essential to factor in these costs when assessing the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that electrical prongs meet safety and performance standards is vital. Enhanced QC processes can increase production costs but are necessary for minimizing defects and ensuring compliance with international standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and customs duties, can impact the final price significantly, especially for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms is essential, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and profit. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position and the competitiveness of their pricing strategy.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that allow for cost savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs often entail higher costs. Buyers should balance the need for specific features with the potential price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., UL, CE) can elevate costs. Buyers should determine the necessary certifications for their markets to avoid overpaying.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their quality assurance and service reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding which Incoterms apply can help buyers manage shipping costs and risks effectively.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough discussions with suppliers. Being well-informed about market prices and competitors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Cost Efficiency: Calculate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as durability, warranty, and potential replacements over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that may impact overall costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these risks.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding costs and pricing dynamics, actual prices can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotations to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential electrical prongs Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electrical prongs’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrical prongs
Key Technical Properties of Electrical Prongs
When sourcing electrical prongs, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility, safety, and performance. Below are essential properties that buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Electrical prongs are typically made from conductive metals like brass or copper, often plated with nickel or tin to enhance corrosion resistance.
– B2B Importance: The choice of material affects conductivity, durability, and overall safety. High-quality materials ensure a reliable connection and minimize the risk of overheating. -
Prong Size and Shape
– Definition: Different regions use various prong configurations, such as flat, round, or octagonal shapes, with specific dimensions for width and length.
– B2B Importance: Understanding regional standards (e.g., Type A, Type C) is vital for compliance and compatibility with local electrical systems. This knowledge can prevent costly shipping errors and product returns. -
Electrical Rating (Amperage and Voltage)
– Definition: This specification indicates the maximum current (in amps) and voltage (in volts) that the prong can safely handle.
– B2B Importance: Selecting prongs with the appropriate rating is essential to prevent electrical failures and ensure that devices operate safely within their limits. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in prong dimensions, ensuring a snug fit within sockets.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are crucial for maintaining a secure connection, reducing the risk of arcing or electrical shorts, which can lead to device damage or safety hazards. -
Insulation Type
– Definition: Some prongs come with insulation to prevent accidental contact with live components.
– B2B Importance: Insulated prongs enhance safety by reducing the risk of electrical shock, making them suitable for various applications, especially in industrial settings. -
Compliance Standards
– Definition: Many regions have specific electrical safety standards (e.g., IEC, UL) that prongs must meet.
– B2B Importance: Ensuring that prongs comply with local regulations is critical for market entry and can significantly affect liability and product safety.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the electrical prong market. Here are some key terms:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Knowing OEM specifications helps buyers source compatible components that meet their production requirements.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is vital for budgeting and inventory management, allowing buyers to balance cost-efficiency with supply needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that buyers send to suppliers to request price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, terms, and capabilities from multiple suppliers, leading to informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms helps buyers navigate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and payment terms, crucial for international transactions. -
Certification
– Definition: A process by which a product is tested and verified to meet specific standards.
– Importance: Certification assures buyers of product quality and safety, providing confidence in compliance with local regulations and market acceptance. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times aids in planning and ensures that production schedules align with supply availability, minimizing disruptions.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right electrical prongs for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electrical prongs Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global electrical prongs market is witnessing significant transformation driven by several key factors. The increasing demand for electrical appliances across various sectors, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, is propelling the growth of this sector. As urbanization accelerates, the need for reliable and safe electrical connections becomes paramount. Additionally, the shift towards smart technology integration in homes and businesses is influencing the design and functionality of electrical prongs, fostering innovation and increasing the complexity of sourcing requirements.
B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on sourcing trends that emphasize quality and compliance with international safety standards. The rise of online B2B platforms, such as DirectIndustry, facilitates access to a wider range of suppliers and products, enabling buyers to compare offerings effectively. Moreover, the trend towards customization is gaining traction, with manufacturers offering tailored solutions to meet specific regional needs, such as varying voltage and current specifications prevalent in different countries.
Another notable trend is the increasing importance of transparency in supply chains. Buyers are now more informed about the source and manufacturing processes of electrical components, compelling suppliers to provide detailed information regarding their production practices. This shift towards transparency is essential for mitigating risks associated with non-compliance and ensuring that products meet the necessary regulatory standards.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical concern within the electrical prongs sector, reflecting a broader global movement towards environmentally responsible practices. The production of electrical prongs often involves materials that can have significant environmental impacts, including metal extraction and plastic production. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and energy consumption during manufacturing.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence, as buyers seek to partner with manufacturers that uphold fair labor practices and ensure safe working conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming prerequisites for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in the market. Additionally, the use of “green” materials, such as recycled plastics and sustainably sourced metals, is becoming a competitive advantage for manufacturers.
Incorporating sustainability into sourcing strategies not only enhances brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings in the long term. Companies that invest in sustainable practices often find that they can reduce operational costs through improved efficiency and waste reduction, ultimately providing better value to their customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The design and functionality of electrical prongs have evolved significantly since their inception. Initially, plugs and sockets were rudimentary, with little standardization, leading to safety hazards and compatibility issues. The introduction of standardized plug types in the early 20th century marked a pivotal moment, as it allowed for greater safety and efficiency in electrical connections.
As technology progressed, the need for grounded plugs became apparent, leading to the development of three-prong designs that provided enhanced safety for users. Today, the evolution continues with the integration of smart technologies and energy-efficient designs, reflecting the ongoing demand for innovation in the electrical prongs sector. This historical context underscores the importance of understanding the dynamics of the market as international B2B buyers navigate sourcing decisions in an increasingly complex landscape.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrical prongs
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of electrical prongs?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their certifications and compliance with international safety standards, such as ISO or IEC. Request samples to assess the quality of their products. Additionally, check for reviews and ratings from other buyers, and ask for references to understand their reliability. Ensure they have a clear return policy and customer support in case of disputes. Finally, consider their manufacturing capabilities and whether they can meet your specific needs, such as customization or bulk orders. -
Can electrical prongs be customized to fit specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electrical prongs. You can request changes in size, shape, or material to meet your application needs. Discuss your specifications with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Ensure they provide a prototype for testing before finalizing the order. Customization may impact lead times and costs, so clarify these details upfront to avoid surprises. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electrical prongs?
MOQs for electrical prongs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Generally, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 100 to several thousand units. Lead times can also vary, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks depending on the supplier’s production capacity and your order’s customization requirements. Always confirm these details before placing an order to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted for international purchases of electrical prongs?
Most suppliers accept various payment methods, including wire transfers, letters of credit, and online payment platforms like PayPal. For large orders, letters of credit can provide security for both parties. Always clarify payment terms, including deposits and final payment schedules. Ensure that you understand any currency exchange implications, especially when dealing with suppliers in different regions, to avoid unexpected costs. -
How can I ensure the quality of electrical prongs before shipping?
To ensure quality, ask suppliers for detailed quality assurance (QA) processes, including testing procedures and certifications. Request inspection reports or third-party testing results for the products you intend to purchase. Consider conducting a factory audit or hiring a quality control service to inspect the goods before shipment. This proactive approach can help mitigate risks associated with defective products. -
What certifications should I look for in electrical prongs?
Look for certifications that confirm compliance with international safety and quality standards. Common certifications include UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CE marking in Europe, and IEC standards. These certifications ensure that the electrical prongs meet specific safety requirements and performance standards. Always request copies of these certifications from suppliers before finalizing your purchase. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing electrical prongs?
When sourcing electrical prongs, consider the logistics of shipping, including freight costs, delivery timelines, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in international shipping to handle your orders. Be aware of the import duties and taxes applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, ensure the packaging is robust to prevent damage during transit. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers regarding electrical prongs?
To resolve disputes, first, engage in direct communication with your supplier to discuss the issue. Provide clear evidence and documentation to support your claim. If resolution is not achieved, refer to the terms outlined in your contract, which may specify mediation or arbitration processes. Consider involving a third-party mediator if necessary. Maintaining open communication and a professional demeanor can often lead to a more amicable resolution.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrical prongs
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of electrical prongs is a critical component for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance their operational efficiency and product safety. Understanding the various types of electrical prongs, their specifications, and compliance standards is paramount. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers who adhere to industrial safety standards, ensuring the durability and reliability of the products.
Key Takeaways:
– Diversity in Specifications: Different regions utilize various prong sizes and configurations, impacting compatibility and safety. Familiarizing yourself with local standards is essential.
– Cost Efficiency: Opting for suppliers that utilize innovative designs, such as prong holes for material savings, can lead to significant cost reductions without compromising quality.
– Long-Term Partnerships: Building relationships with manufacturers can provide insights into upcoming trends and technologies, ensuring a competitive edge.
As we look to the future, the demand for reliable electrical components will continue to rise, particularly in developing markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Now is the time to engage with suppliers who can meet your specific needs while also providing quality assurance. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your procurement strategy and ensure your business is prepared for the evolving landscape of electrical safety and efficiency.