Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Electromagnetic
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electromagnetic interference filter
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic devices across various industries. As the demand for compact, efficient, and high-performance electronics continues to surge, the need for effective EMI shielding solutions becomes increasingly critical. Whether you’re in the automotive, telecommunications, or consumer electronics sector, understanding how to select the right EMI filter can significantly impact your product’s success and compliance with international standards.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to navigate the complex landscape of EMI filters. We delve into various types of filters, including passive and active options, and explore the raw materials used in their manufacturing, such as conductive polymers and metal composites.
Moreover, we examine manufacturing and quality control processes, ensuring that buyers are well-informed about the standards and certifications that guarantee product reliability. The guide also provides insights into market trends, pricing strategies, and a curated list of reputable suppliers to facilitate informed sourcing decisions.
With a dedicated FAQ section addressing common concerns and queries, this resource aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make strategic purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and product quality in the global market.
Understanding electromagnetic interference filter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC Filters | Combines inductors (L) and capacitors (C) to filter EMI. | Telecommunications, Consumer Electronics | Pros: Effective for a wide frequency range. Cons: Can be bulky; may require tuning. |
| RC Filters | Utilizes resistors (R) and capacitors (C) for noise suppression. | Automotive, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Simple design; cost-effective. Cons: Limited frequency response; can introduce signal distortion. |
| Active Filters | Employs amplifiers to enhance signal quality and filter EMI. | Medical Devices, Data Acquisition Systems | Pros: High performance; adjustable parameters. Cons: More complex and expensive. |
| Ferrite Beads | Passive components that suppress high-frequency noise. | Power Supplies, Communication Lines | Pros: Compact size; easy to integrate. Cons: Limited effectiveness at lower frequencies. |
| Shielded Cables | Cables with a conductive shield to prevent EMI ingress/egress. | Data Transmission, Sensitive Electronics | Pros: Excellent protection against interference. Cons: Higher cost; less flexibility. |
LC Filters
LC filters leverage inductors and capacitors to achieve effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression across a broad frequency spectrum. They are ideal for applications in telecommunications and consumer electronics where high-frequency noise can disrupt signal integrity. When considering LC filters, B2B buyers should evaluate the physical size and potential need for tuning, as these filters can be larger and may require adjustments for optimal performance in specific applications.
RC Filters
RC filters are straightforward designs that use resistors and capacitors to mitigate EMI. Their simplicity makes them a cost-effective solution for applications in automotive and industrial equipment. However, buyers should be aware of their limited frequency response, which may not suffice for all applications, and the potential for signal distortion that can occur if not properly designed.
Active Filters
Active filters incorporate amplifiers to enhance signal quality while filtering out EMI, making them suitable for high-performance applications such as medical devices and data acquisition systems. These filters offer high adaptability and performance, but their complexity and higher cost can be a barrier for some B2B buyers. It is crucial to consider the specific performance requirements and budget constraints when selecting active filters.
Ferrite Beads
Ferrite beads are passive components that effectively suppress high-frequency noise in electronic circuits. They are particularly useful in power supplies and communication lines where compactness and ease of integration are essential. While they provide excellent noise suppression, buyers should note that ferrite beads may not be as effective at lower frequencies, necessitating a comprehensive assessment of the frequency range in their application.
Shielded Cables
Shielded cables are designed with a conductive layer that protects against EMI by preventing interference from entering or exiting the cable. These cables are widely used in data transmission and sensitive electronics where signal integrity is paramount. While they offer superior protection, the higher cost and reduced flexibility can be drawbacks. Buyers should evaluate the trade-offs between cost and the need for robust EMI protection in their applications.
Key Industrial Applications of electromagnetic interference filter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electromagnetic Interference Filter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Filtering signals in mobile base stations | Enhances signal clarity, reduces interference | Compliance with international standards, durability, and performance metrics |
| Automotive | EMI filtering in electric vehicles | Protects sensitive electronic systems | Temperature resistance, size constraints, and integration capabilities |
| Healthcare | Shielding medical devices | Ensures reliability and safety of devices | Biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, and customization options |
| Aerospace & Defense | EMI protection in avionics systems | Increases safety and operational reliability | High-performance materials, weight considerations, and certification requirements |
| Consumer Electronics | EMI filtering in smart devices | Improves device functionality and user experience | Cost-effectiveness, aesthetic design compatibility, and rapid prototyping capabilities |
Telecommunications
In the telecommunications sector, electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters are crucial for ensuring clear signal transmission in mobile base stations. These filters mitigate unwanted electromagnetic noise that can disrupt signal integrity, leading to dropped calls or data loss. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that comply with regional standards and demonstrate the durability and performance of their filters under various environmental conditions.
Automotive
The automotive industry increasingly relies on EMI filters to protect the sensitive electronic systems found in electric vehicles (EVs). These filters shield components from electromagnetic noise generated by other systems, ensuring reliable operation of crucial features like navigation and safety systems. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider factors such as temperature resistance and size constraints, which are vital for integration within compact automotive designs.
Healthcare
In healthcare, EMI filters play a vital role in shielding medical devices, such as MRI machines and patient monitoring systems, from electromagnetic interference. This protection is essential for maintaining the reliability and safety of these devices, which can directly impact patient outcomes. Buyers must focus on sourcing filters that are biocompatible and comply with stringent regulatory standards, ensuring that they meet safety requirements in their respective markets.
Aerospace & Defense
The aerospace and defense sectors utilize EMI filters in avionics systems to enhance safety and operational reliability. These filters protect critical electronic components from the high levels of electromagnetic interference typical in aviation environments. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the materials used in these filters are high-performance and meet strict certification requirements, particularly for mission-critical applications.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, EMI filters are essential for improving the functionality of smart devices, such as smartphones and tablets. These filters help reduce interference from other electronic devices, enhancing user experience through clearer audio and video signals. For international B2B buyers, sourcing filters that are cost-effective while also offering aesthetic design compatibility and rapid prototyping capabilities is crucial for maintaining competitive advantages in the fast-paced electronics market.
Related Video: Introduction to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Filter or Power Line Filter!
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electromagnetic interference filter
When selecting materials for electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the material’s properties, application suitability, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in EMI filters, providing insights tailored for international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Conductive Polymers
Key Properties:
Conductive polymers are lightweight materials that exhibit good conductivity and flexibility. They can operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 85°C and are resistant to moisture, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of conductive polymers is their cost-effectiveness and ease of processing, which allows for rapid production and customization. However, they may not be as durable as metals and can degrade under extreme environmental conditions, limiting their application in harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
These materials are particularly effective in consumer electronics and automotive applications where weight reduction is crucial. However, they may not perform well in high-frequency applications compared to metals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D257 for resistivity and consider the specific environmental conditions of their regions, which may affect material performance.
2. Metal Foils (Copper and Aluminum)
Key Properties:
Metal foils, particularly copper and aluminum, offer excellent conductivity and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. They typically have a corrosion resistance that varies based on surface treatment.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of metal foils is their superior shielding effectiveness against EMI, making them ideal for high-performance applications. However, they can be more expensive and heavier than polymer options, and their manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring precise handling.
Impact on Application:
Metal foils are widely used in telecommunications and aerospace applications where high-frequency interference is a concern. Their robustness makes them suitable for outdoor applications, although they may require additional treatments to prevent corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must verify compliance with international standards such as DIN 4102 for fire behavior and ASTM B193 for electrical conductivity. Additionally, understanding local corrosion risks is crucial for ensuring long-term performance.
3. Ferrite Materials
Key Properties:
Ferrites are ceramic compounds that exhibit magnetic properties and can effectively absorb electromagnetic waves. They operate well at high temperatures (up to 300°C) and have good chemical stability.
Pros & Cons:
Ferrites are excellent for high-frequency applications due to their ability to attenuate EMI. However, they can be brittle, which may complicate manufacturing and handling. Their cost can also be higher than traditional materials.
Impact on Application:
Ferrites are commonly used in power electronics and RF applications where high-frequency noise suppression is essential. Their performance can be significantly affected by the frequency of operation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the specific frequency ranges of their applications and ensure compliance with standards such as IEC 61000-4-3 for electromagnetic compatibility.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often combining metals with polymers or ceramics, offer tailored properties such as enhanced strength, reduced weight, and improved EMI shielding effectiveness.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage is their versatility, allowing for customization to meet specific application needs. However, they can be expensive to produce and may require complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Composites are suitable for aerospace and automotive applications where weight and performance are critical. Their adaptability makes them ideal for innovative designs but may lead to longer lead times for production.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific manufacturing capabilities in their regions and ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management.
| Material | Typical Use Case for electromagnetic interference filter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive Polymers | Consumer electronics, automotive | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable in harsh environments | Low |
| Metal Foils | Telecommunications, aerospace | Superior shielding effectiveness | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Med |
| Ferrite Materials | Power electronics, RF applications | Excellent for high-frequency applications | Brittle and higher cost | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, automotive | Versatile and customizable | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions regarding EMI filter materials, ensuring compliance and suitability for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electromagnetic interference filter
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters play a vital role in ensuring the functionality and reliability of electronic devices across various industries. To make informed procurement decisions, B2B buyers must understand the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with these filters. This section outlines the key stages in manufacturing EMI filters, the quality control (QC) measures employed, and how international buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products.
Manufacturing Processes for EMI Filters
The manufacturing of EMI filters involves several critical stages, each requiring specific techniques and expertise. Understanding these stages can help buyers assess potential suppliers more effectively.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing EMI filters is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include:
- Conductive materials: Metals such as copper and aluminum are frequently used for their excellent conductivity.
- Dielectric materials: Ceramics and polymers that provide insulation and structural integrity.
- Composite materials: Innovations in materials science have led to the development of composites that combine the benefits of multiple materials, enhancing performance.
During material preparation, suppliers must ensure that the materials meet specific performance criteria, such as conductivity and dielectric strength. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of these materials and any certifications that ensure quality.
2. Forming
Forming involves shaping the prepared materials into components of the EMI filter. Key techniques include:
- Stamping: Used to create metal parts with precise dimensions.
- Injection molding: Ideal for producing complex shapes from plastic or composite materials.
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing): An emerging technology that allows for complex geometries and customization, particularly beneficial for prototyping and low-volume production.
Buyers should assess suppliers’ capabilities in these forming techniques, particularly if they require customized designs or specific tolerances.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage brings together the various components of the EMI filter. This may involve:
- Soldering: For electrical connections, ensuring that joints are reliable and meet electrical standards.
- Mechanical fastening: Using screws or clips to secure components together.
- Encapsulation: Protecting the filter from environmental factors, enhancing durability.
During this stage, the precision of assembly is crucial. Buyers should request information on assembly techniques and the qualifications of personnel involved in the process.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the performance and aesthetic of the EMI filters. Common techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and enhance conductivity.
- Polishing: Improving surface finish to reduce signal loss and enhance performance.
- Testing and calibration: Ensuring that the final product meets specified performance criteria.
Buyers should inquire about the finishing processes employed by suppliers, as these can significantly affect product performance.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of EMI filters, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards
Several international standards govern the quality of EMI filters:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Required in Europe, indicating compliance with safety and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for filters used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring reliability under extreme conditions.
Understanding these standards is critical for buyers, as compliance can affect market access and product performance.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing to identify and rectify issues immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to verify performance against specifications.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers about their QC processes and the frequency of inspections.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is an integral part of ensuring product quality. Common methods include:
- Electrical testing: Measuring conductivity, impedance, and other electrical properties.
- Environmental testing: Assessing performance under various environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.).
- Life cycle testing: Evaluating durability and long-term performance.
Suppliers should provide detailed reports on testing outcomes, and buyers should verify these results against industry standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, especially from diverse regions, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential. Here are effective strategies:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities to assess adherence to quality standards.
- Documentation: Request detailed quality assurance documentation, including test reports and compliance certificates.
- Third-party inspections: Engage independent inspectors to verify product quality before shipment, ensuring an unbiased assessment.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing EMI filters internationally, buyers must be aware of potential nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regulatory differences: Different regions may have varying compliance requirements. For instance, products sold in Europe must comply with CE standards, while those in the Middle East may need to meet local certifications.
- Cultural considerations: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can help in negotiating terms and ensuring quality expectations are met.
In summary, by understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place for EMI filters, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also fosters long-term partnerships based on trust and reliability.
Related Video: The Most Sophisticated Manufacturing Process In The World Inside The Fab | Intel
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electromagnetic interference filter Sourcing
In the realm of electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The following analysis outlines the key components that influence costs and pricing, along with actionable tips for buyers.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor in the overall pricing of EMI filters. Common materials include metals, ceramics, and advanced composites. The choice of materials affects not only the price but also the filter’s performance characteristics, such as shielding effectiveness and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the expertise required for manufacturing EMI filters. Skilled labor is essential for quality assurance, particularly in custom manufacturing settings where precision and knowledge of EMI principles are vital.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Companies with advanced manufacturing capabilities, such as additive manufacturing, may have higher overheads due to the sophisticated technology and processes involved.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom EMI filters. This involves the creation of molds and fixtures necessary for production. For low-volume orders, these costs can disproportionately impact the price per unit.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that EMI filters meet specific standards requires investment in quality control processes. This includes testing and certification to comply with international standards, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, particularly for international transactions, must be factored into the total cost. This includes customs duties, insurance, and transportation fees, which can vary widely depending on the destination.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s position in the market, their operational costs, and the competitive landscape.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly influence pricing. Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts, which can lead to substantial cost savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications often lead to higher prices due to the increased complexity and resource requirements. Buyers should balance the need for customization with the associated costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts not only the price but also the performance and longevity of the EMI filters. Higher-quality materials may command higher prices but offer better performance and durability.
-
Quality/Certifications: Filters that meet higher quality standards or possess specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may be priced higher. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium for their products.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect total costs. Buyers should be aware of which party is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly for larger orders. Negotiating terms such as payment schedules or delivery timelines can also lead to better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, shipping, installation, and maintenance costs. Sometimes, a higher upfront cost can lead to lower long-term expenses if the product is more durable and efficient.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, suppliers in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America, impacting the final price. Understanding these nuances can help in making informed sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for EMI filters can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential electromagnetic interference filter Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electromagnetic interference filter’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electromagnetic interference filter
Critical Specifications for Electromagnetic Interference Filters
When selecting electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters, understanding key specifications is crucial for ensuring product efficacy and compliance with international standards. Below are essential technical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in EMI filters significantly influences their performance. Common materials include ferrite, conductive polymers, and metal composites. Each material has unique properties affecting conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures optimal shielding effectiveness against electromagnetic radiation. -
Attenuation Level
This specification measures how much electromagnetic energy is reduced when passing through the filter. It is usually expressed in decibels (dB). A higher attenuation level indicates better performance in blocking unwanted frequencies. For B2B buyers, choosing filters with appropriate attenuation levels is critical to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive equipment.
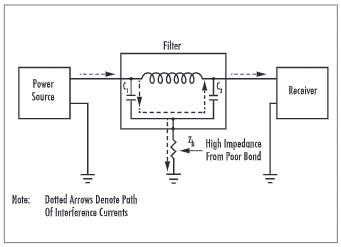
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Frequency Range
EMI filters are designed to operate within specific frequency ranges. Buyers must ensure that the filter’s frequency range aligns with the operational frequencies of their electronic devices. This alignment is essential to prevent signal degradation and ensure compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. -
Insertion Loss
Insertion loss quantifies the amount of signal power lost when the filter is inserted into a circuit. It is a vital metric that affects the overall efficiency of the electronic system. Buyers should look for filters with low insertion loss to maintain the integrity and performance of their systems. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the acceptable range of deviation from the specified values in the filter’s performance. High tolerance levels can lead to variability in product performance, which may affect system reliability. Buyers should prioritize filters with tight tolerances to ensure consistent operation in critical applications. -
Operating Temperature Range
The operational environment can greatly affect filter performance. EMI filters must withstand specific temperature ranges to maintain functionality. Understanding the operating temperature range helps buyers select filters that will perform reliably in their intended environments, particularly in regions with extreme climates.
Common Trade Terminology in EMI Filter Procurement
Navigating the procurement process for EMI filters requires familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing EMI filters, it’s essential to identify the OEM to ensure product quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers manage inventory and costs, particularly when dealing with specialized EMI filters that may have limited availability. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for EMI filters allows for comparison of options and negotiation of favorable terms. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with these terms is vital for international transactions, as they clarify costs, risks, and logistics involved in the procurement of EMI filters. -
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
EMC refers to the ability of electronic devices to operate in their intended environment without causing or experiencing electromagnetic interference. Understanding EMC is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and the effective operation of their products.
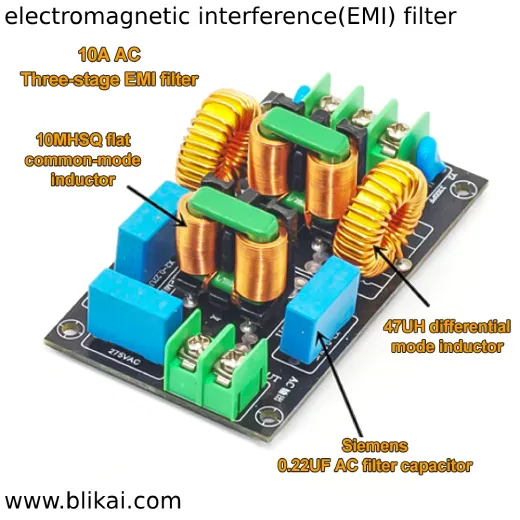
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In the context of EMI filters, shorter lead times can significantly impact project timelines. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of critical components.
By comprehending these technical specifications and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and ensure compliance with relevant standards in their respective markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electromagnetic interference filter Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) filter sector is experiencing dynamic growth influenced by several global drivers. The increasing integration of electronic devices across industries, from automotive to telecommunications, necessitates robust EMI solutions to ensure operational reliability. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where rapid urbanization and technological adoption are driving the need for advanced electronic systems.
Emerging trends in sourcing indicate a shift towards additive manufacturing (AM) techniques, which offer customization and flexibility in design. AM allows for the production of lightweight, efficient, and multifunctional EMI filters, catering to the miniaturization of electronic components. Furthermore, the rise of smart technologies is prompting B2B buyers to seek filters that not only mitigate interference but also enhance performance across various applications.
As international buyers navigate this market, understanding local regulations and compliance standards is crucial. For instance, European markets are increasingly focused on sustainability and eco-design principles, which influence purchasing decisions. Buyers from Africa and South America should also consider partnerships with local manufacturers to enhance supply chain efficiency and reduce lead times. Overall, the EMI filter market is characterized by a blend of technological innovation and evolving buyer preferences, making it imperative for international B2B buyers to stay informed and agile.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the electromagnetic interference filter sector. The environmental impact of electronic waste and the production processes associated with EMI filters cannot be overlooked. As a result, international B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ethical supply chains are essential for fostering trust and long-term partnerships. Buyers should seek manufacturers who employ eco-friendly materials and processes, ensuring that their products align with sustainability goals. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials, such as bioplastics or recycled metals, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with EMI filter production. Buyers should actively inquire about the sourcing of raw materials and the lifecycle of products to ensure that they are making responsible choices. By integrating sustainability into their procurement processes, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electromagnetic interference filters has been closely tied to advancements in electronics. Initially developed in the mid-20th century, these filters were primarily used in military and aerospace applications to shield sensitive equipment from interference. As consumer electronics proliferated in the late 20th century, the demand for EMI filtering solutions expanded significantly.
With the advent of new technologies, such as wireless communication and the Internet of Things (IoT), the complexity of EMI challenges has increased, prompting innovations in filter design and manufacturing. The introduction of additive manufacturing techniques in recent years has revolutionized the sector, allowing for the creation of customized filters that meet specific application requirements. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards greater efficiency and performance in electronic systems, positioning the EMI filter sector as a critical component in the future of technology.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electromagnetic interference filter
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of electromagnetic interference filters?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their experience in the industry, production capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Request references and case studies to assess their past performance. Evaluate their quality assurance processes, including certifications such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider their technological capabilities, especially in customization, which can be crucial for specific application needs. -
Can I customize electromagnetic interference filters to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electromagnetic interference filters. Discuss your specific application needs, such as size, shape, and material requirements, with potential suppliers. Ensure that the supplier has the necessary technology, such as additive manufacturing, to provide tailored solutions. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate their ability to meet your specifications before committing to a larger order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electromagnetic interference filters?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the filters. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times can also differ; standard production may take 4-6 weeks, while custom orders might extend to 8-12 weeks. Always confirm these details during negotiations to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What payment options are typically available for international B2B transactions?
Payment options can include wire transfers, letters of credit, or escrow services, depending on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. It’s advisable to establish clear payment terms in the contract, including deposits and payment upon delivery. Be cautious of suppliers that demand full payment upfront, especially if you are working with them for the first time. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from my supplier?
Expect suppliers to have robust quality assurance measures in place, such as regular testing and inspection protocols throughout the production process. Inquire about certifications like ISO 9001 or specific industry standards relevant to electromagnetic interference filters. Request documentation of test results and quality reports to ensure the products meet your requirements. -
How should I handle logistics and shipping for international orders?
Logistics should be planned in advance, considering the shipping method, customs regulations, and potential delays. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight forwarders who specialize in your region. Ensure that all necessary documentation is prepared for customs clearance to avoid delays. Consider using Incoterms to clearly define responsibilities for shipping and handling. -
What steps should I take if there is a dispute with a supplier?
Start by reviewing your contract and understanding the terms regarding disputes. Communicate directly with the supplier to address the issue, documenting all correspondence. If resolution is not reached, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your agreement. Engage legal counsel if necessary, especially if significant financial stakes are involved. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for when sourcing electromagnetic interference filters?
Yes, look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals). Depending on your industry, other certifications may be relevant, such as MIL-STD for military applications or IEC standards for electronics. These certifications indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and regulatory compliance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electromagnetic interference filter
The strategic sourcing of electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters is essential for international buyers looking to enhance the performance and reliability of their electronic products. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing methods, such as additive manufacturing, which offer customization and flexibility to meet specific application requirements. By investing in strategic sourcing, companies can not only improve their product quality but also reduce the risks associated with EMI issues, which can lead to costly operational disruptions.
The value of strategic sourcing lies in its ability to foster partnerships with suppliers who are at the forefront of technological advancements. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to innovation and customization, ensuring they have access to the latest EMI shielding solutions.
As the demand for compact and efficient electronic devices continues to grow, the future outlook for EMI filters is promising. International buyers are encouraged to engage proactively with suppliers, leveraging their expertise to tailor solutions that not only comply with regional standards but also drive competitive advantage in their markets. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategies and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving electronics landscape.