Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Electronic Enclosures
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electronic enclosures
In an increasingly interconnected world, the demand for reliable and efficient electronic enclosures has surged across diverse industries. These enclosures are not merely protective casings; they are critical components that safeguard sensitive electronic systems from environmental hazards, electromagnetic interference, and physical damage. For B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of electronic enclosures is paramount for optimizing product performance and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of electronic enclosures, covering a wide range of topics that include various types of enclosures, materials selection, manufacturing quality control, and supplier evaluation. It also addresses cost considerations and market trends that can significantly impact purchasing decisions. With a focus on actionable insights, this resource empowers international buyers to make informed sourcing choices tailored to their specific operational needs.
By navigating the complexities of electronic enclosures, buyers will gain clarity on how to select the right products that enhance durability and functionality. Whether you’re in telecommunications, automotive, or consumer electronics, this guide serves as a strategic tool to streamline your procurement process and foster successful partnerships with suppliers worldwide.
Understanding electronic enclosures Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Electronic Enclosures | Compact design, low-voltage applications | Consumer electronics, key fobs, USB drives | Pros: Cost-effective, lightweight. Cons: Limited protection, not suitable for harsh environments. |
| Large Electronic Enclosures | Robust construction, suitable for harsh environments | Telecommunications, industrial machinery | Pros: High durability, excellent protection. Cons: Higher cost, may require more space. |
| Climate-Controlled Enclosures | Built-in cooling/heating systems, temperature regulation | Data centers, laboratory equipment | Pros: Optimal performance for sensitive electronics. Cons: More complex, higher maintenance. |
| Modular Enclosures | Customizable sections, scalable design | OEMs, telecommunications, and manufacturing | Pros: Flexibility for future upgrades. Cons: Initial design can be more time-consuming. |
| EMI/RFI Shielded Enclosures | Specialized coatings or materials to block interference | Aerospace, medical devices, telecommunications | Pros: Enhanced signal integrity, compliance with regulations. Cons: Typically more expensive, may require specific sourcing. |
Small Electronic Enclosures
Small electronic enclosures are ideal for low-voltage applications, such as consumer electronics and portable devices. Their compact design makes them suitable for products like key fobs and USB drives. When purchasing, buyers should consider material choices that provide adequate protection against dust and minor impacts while balancing cost. These enclosures are often less robust than larger options, which may limit their use in more demanding environments.
Large Electronic Enclosures
Large electronic enclosures are constructed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them essential in industries like telecommunications and manufacturing. They often feature robust materials to protect sensitive components from moisture, dust, and mechanical impacts. B2B buyers must assess the specific protection ratings needed for their applications, as these enclosures can be a significant investment but offer long-term reliability and durability.
Climate-Controlled Enclosures
Climate-controlled enclosures are designed to maintain a consistent internal temperature, making them ideal for sensitive electronic components found in data centers and laboratories. These enclosures often integrate cooling and heating systems to manage thermal conditions effectively. Buyers should evaluate the energy efficiency of these systems, as they can influence operational costs. While they provide superior protection for sensitive equipment, the complexity and maintenance requirements can be higher than standard enclosures.
Modular Enclosures
Modular enclosures offer a flexible design that allows for customization and scalability, making them particularly valuable for OEMs and manufacturing applications. These enclosures can be adapted as needs change, accommodating future upgrades or modifications without requiring a complete redesign. B2B buyers should consider the initial design time and costs, as creating a modular system may require more planning upfront. However, the long-term adaptability can lead to cost savings and enhanced functionality.
EMI/RFI Shielded Enclosures
EMI/RFI shielded enclosures are critical for applications where electromagnetic interference could compromise the performance of electronic devices, such as in aerospace or medical fields. These enclosures utilize specialized materials or coatings to prevent interference from affecting sensitive components. Buyers must ensure that these enclosures meet specific regulatory standards and consider the potential higher costs associated with advanced shielding technologies. While they provide essential protection, sourcing the right materials and manufacturers is crucial for maintaining compliance and performance.
Related Video: Transformer models and BERT model: Overview
Key Industrial Applications of electronic enclosures
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electronic Enclosures | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Housing telecommunications equipment like routers and switches | Protects sensitive electronics from environmental factors and ensures reliability | IP ratings for moisture and dust resistance, thermal management solutions |
| Manufacturing | Control panels for automated machinery | Enhances operational efficiency and protects machinery from damage | Material durability, ease of access for maintenance, and space optimization |
| Automotive | Electronic control units (ECUs) in vehicles | Safeguards critical components from vibrations and temperature fluctuations | EMI/RFI shielding, compatibility with vehicle design, and regulatory compliance |
| Medical Devices | Enclosures for diagnostic and monitoring equipment | Ensures patient safety and device reliability | Biocompatibility, stringent regulatory standards, and ease of cleaning |
| Renewable Energy | Enclosures for solar inverters and wind turbine controllers | Protects electronics from harsh environmental conditions, ensuring longevity | Weather resistance, thermal management, and mounting options for various installations |
Telecommunications
In the telecommunications sector, electronic enclosures are essential for housing equipment such as routers, switches, and base stations. These enclosures protect sensitive components from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures, which can otherwise lead to equipment failure. For international buyers, especially from regions with varying climates, sourcing enclosures with appropriate IP ratings for moisture and dust resistance, as well as thermal management solutions, is crucial to ensure equipment longevity and reliability.
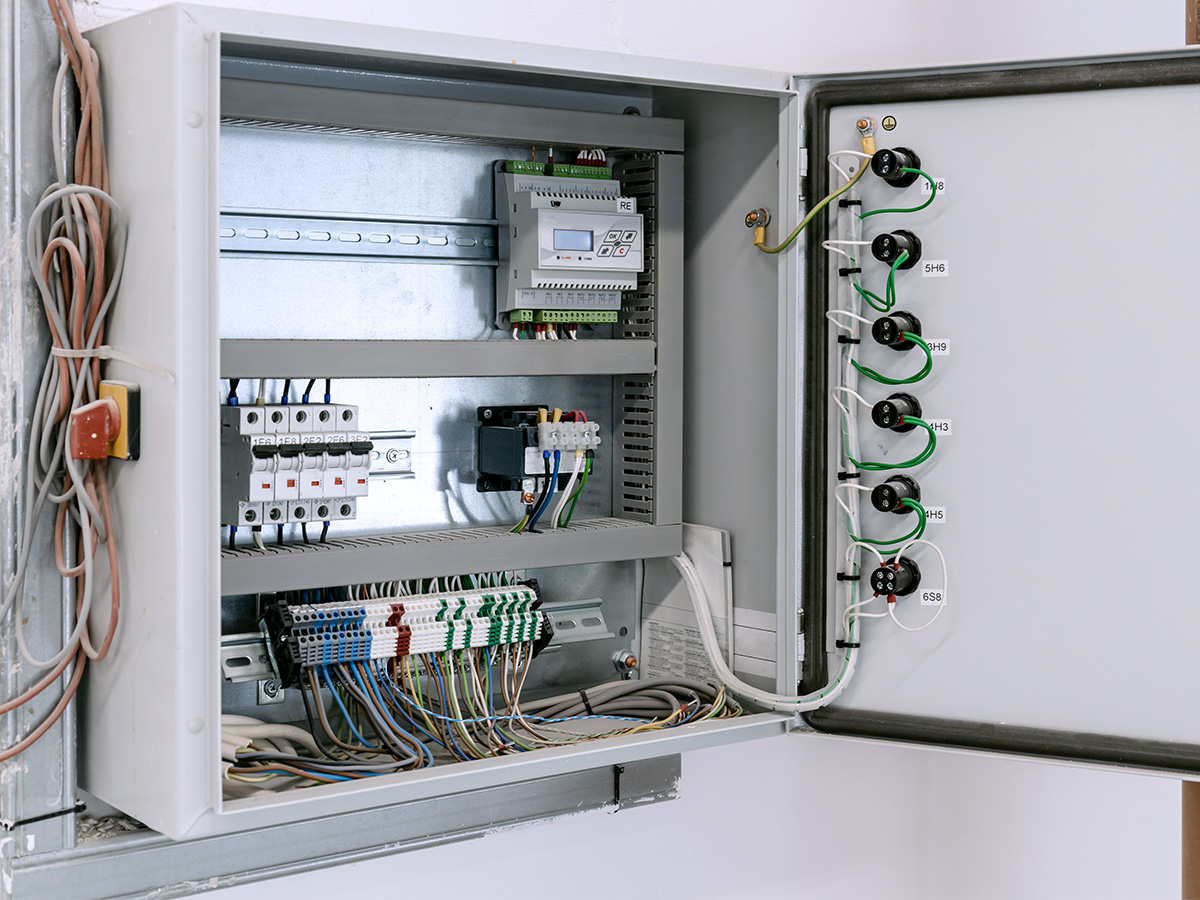

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments, electronic enclosures are commonly used for control panels that manage automated machinery. These enclosures protect electronic components from mechanical damage, dust, and vibrations, which are prevalent in industrial settings. For businesses, this translates to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime. Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that are durable and facilitate ease of access for maintenance while optimizing space to accommodate existing machinery layouts.
Automotive
Electronic enclosures play a vital role in the automotive industry, particularly in housing electronic control units (ECUs) that manage various vehicle functions. These enclosures must withstand vibrations and temperature fluctuations while protecting sensitive electronics. International buyers need to consider EMI/RFI shielding to prevent interference, as well as ensuring compatibility with vehicle designs. Additionally, compliance with automotive regulations is critical for successful integration.
Medical Devices
In the medical sector, electronic enclosures are designed to house diagnostic and monitoring equipment, ensuring patient safety and device reliability. These enclosures must meet stringent regulatory standards and be biocompatible, as they are often used in environments where cleanliness is paramount. Buyers should focus on sourcing enclosures that allow for easy cleaning and maintenance, as well as considering materials that can withstand sterilization processes.
Renewable Energy
For the renewable energy sector, electronic enclosures are crucial for protecting solar inverters and wind turbine controllers from harsh environmental conditions. These enclosures safeguard electronics from moisture, dust, and temperature extremes, ensuring operational efficiency and longevity. Buyers should prioritize sourcing enclosures with weather-resistant properties and effective thermal management solutions, as well as versatile mounting options suitable for various installation environments.
Related Video: Electronics Metal Enclosures Design Tips – Product Designers Must Know
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electronic enclosures
When selecting materials for electronic enclosures, B2B buyers must consider a variety of factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in electronic enclosures, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international markets.
Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and thermal conductivity. It is often used in applications requiring good heat dissipation.
- Key Properties: High corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, and lightweight.
- Pros: Durable and resistant to rust; easy to machine and fabricate; can be anodized for additional protection.
- Cons: Higher cost compared to plastics; may require additional coatings for extreme environments; can be less impact-resistant than steel.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for outdoor enclosures due to corrosion resistance; not ideal for high-impact applications without reinforcement.
- International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for aluminum alloys. In regions like Europe, adherence to REACH regulations is crucial.
Steel (Stainless and Carbon)
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is renowned for its strength and durability. It is commonly used in heavy-duty applications.
- Key Properties: High strength, good impact resistance, and excellent durability.
- Pros: Very robust and suitable for harsh environments; stainless steel offers corrosion resistance; can withstand significant mechanical stress.
- Cons: Heavier than aluminum and plastics; may require additional treatments to prevent rust; higher manufacturing complexity.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for industrial settings where mechanical protection is vital; can be used in environments with exposure to chemicals if properly coated.
- International Considerations: Compliance with DIN standards in Europe and ASTM standards in the U.S. is necessary. Buyers in the Middle East should consider local corrosion factors such as humidity and saline conditions.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass is a composite material made from glass fibers and resin, offering unique properties for specific applications.
- Key Properties: High chemical resistance, lightweight, and good electrical insulation.
- Pros: Excellent for corrosive environments; non-conductive; can be molded into complex shapes.
- Cons: Generally less durable than metals; may not withstand high impact; can be more expensive due to manufacturing processes.
- Impact on Application: Suitable for chemical processing industries; effective in environments where electrical insulation is crucial.
- International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with JIS standards in Japan and consider local regulations regarding chemical exposure in South America.
Plastic (Polycarbonate and ABS)
Plastic materials, such as polycarbonate and ABS, are widely used for electronic enclosures due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
- Key Properties: Lightweight, good impact resistance, and ease of fabrication.
- Pros: Cost-effective; available in various colors and finishes; resistant to UV light (in the case of polycarbonate).
- Cons: Limited temperature resistance; can warp under extreme conditions; less durable than metals.
- Impact on Application: Ideal for consumer electronics and indoor applications; not suitable for high-temperature environments.
- International Considerations: Compliance with ISO standards is essential, particularly in Europe. Buyers should also consider local preferences for recyclable materials in Africa and South America.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electronic enclosures | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Outdoor electronics, telecommunications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than plastics | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial control panels, outdoor cabinets | Very robust and impact-resistant | Heavier and may require rust protection | High |
| Fiberglass | Chemical processing, electrical insulation | Excellent chemical resistance | Less durable and higher manufacturing cost | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics, indoor applications | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for electronic enclosures, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electronic enclosures
Manufacturing Processes for Electronic Enclosures
The manufacturing process for electronic enclosures involves a series of critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary standards for durability, functionality, and safety. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection: Choosing the right material is fundamental. Common materials include aluminum, steel, fiberglass, and plastic. The choice depends on the required durability, environmental resistance, and cost considerations.
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut to size using techniques like laser cutting, CNC machining, or shearing. This step is crucial for ensuring precision and minimizing waste. -
Forming
– Bending and Stamping: Depending on the design, materials undergo bending or stamping processes to achieve the desired shape. Techniques like hydroforming may also be used for complex geometries.
– Welding and Joining: For metal enclosures, welding techniques such as MIG or TIG welding are often employed. Adhesives or rivets may be used for plastic enclosures. -
Assembly
– Component Installation: Once the enclosure is formed, internal components such as circuit boards and connectors are installed. This process may involve soldering and securing components with screws or fasteners.
– Integration of Accessories: Features like ventilation fans, locks, and cable management systems are added during assembly to enhance functionality. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: The finishing process includes treatments such as powder coating, anodizing, or painting, which enhance aesthetics and provide additional protection against corrosion and wear.
– Quality Check: Final inspections are performed to ensure that the enclosure meets design specifications and quality standards.
Quality Assurance in Electronic Enclosure Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing of electronic enclosures, ensuring that products are reliable and safe for end users. This involves adherence to international standards and specific industry regulations.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). It emphasizes a process-oriented approach and continuous improvement, ensuring that suppliers maintain high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
- CE Marking: In Europe, electronic enclosures must comply with CE marking requirements, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For enclosures used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary, ensuring suitability for harsh environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– This initial inspection checks the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. It ensures that materials meet specified standards and are free from defects. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During manufacturing, various checkpoints are established to monitor processes and ensure compliance with specifications. This may include measuring dimensions, verifying assembly, and checking for surface defects. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– After assembly and finishing, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing, environmental testing (e.g., IP ratings), and visual inspections to ensure the enclosure meets all design and safety standards.
Common Testing Methods
- Environmental Testing: Enclosures are subjected to tests for moisture, dust, and temperature extremes to ensure they perform under various conditions. IP and NEMA ratings are often verified through these tests.
- Mechanical Testing: Stress tests and vibration tests assess the enclosure’s durability and ability to protect internal components against physical impacts.
- Electrical Testing: If applicable, enclosures are tested for EMI/RFI shielding effectiveness to ensure that they protect sensitive electronics from electromagnetic interference.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess manufacturing practices, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards. This can help establish trust and ensure that the supplier follows stringent QA protocols.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation related to quality control processes, including inspection reports and testing results. This transparency can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Consider hiring independent inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing facilities and processes. This can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing electronic enclosures internationally, several nuances should be considered:
- Cultural Differences: Understand that manufacturing practices and quality standards may vary significantly across regions. Engage with suppliers to clarify expectations and compliance requirements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are aware of and compliant with local regulations, especially if the enclosures will be sold in specific markets. This may include certifications like UL or CSA for North America.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Consider the implications of international shipping on quality. Ensure that suppliers have robust logistics processes in place to prevent damage during transit.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality electronic enclosures.
Related Video: The Most Sophisticated Manufacturing Process In The World Inside The Fab | Intel
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electronic enclosures Sourcing
The cost structure and pricing for electronic enclosures involve several components that international B2B buyers must consider when sourcing. Understanding these elements can help buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Common materials include:
– Metal (Aluminum, Stainless Steel): Generally more expensive but offers durability and strength.
– Plastic (Polycarbonate, ABS): Typically less costly, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion but may not provide the same level of protection as metals. -
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the final pricing. Countries with lower labor costs can offer more competitive pricing, but this may come with trade-offs in quality or service.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with maintaining production facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can lead to lower overhead costs, impacting pricing positively.
-
Tooling: Custom enclosures often require specialized tooling, which can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider whether they need standard or custom solutions to balance initial investments with long-term needs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing and certification can add to costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications (like IP ratings) against their budget constraints.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and the Incoterms agreed upon. Understanding these can help buyers mitigate unexpected expenses.
- Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin that can range from 10% to 30%, depending on the complexity and demand for the product.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of electronic enclosures:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should assess their actual needs against potential enhancements.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality enclosures that meet stringent certifications (e.g., UL, CE) usually command higher prices. Buyers should consider whether these certifications are necessary for their market.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects who bears shipping costs and risks, which can influence overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing electronic enclosures, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate: Always engage in negotiations to explore price reductions, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Consider maintenance, potential downtime, and the longevity of the enclosure when evaluating costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and currency fluctuations, especially when dealing with suppliers in different countries. This knowledge can be crucial for budget planning.
-
Assess Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication can also facilitate smoother transactions.
Disclaimer
Prices for electronic enclosures can vary based on numerous factors including materials, specifications, and supplier conditions. The insights provided here are indicative and should be validated through direct engagement with suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential electronic enclosures Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electronic enclosures’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electronic enclosures
Understanding the technical specifications and trade terminology related to electronic enclosures is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right product but also facilitates better negotiations and procurement processes. Below are some essential specifications and common trade terms that every buyer should be familiar with.
Key Technical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type of material used in an enclosure, such as aluminum, steel, plastic, or fiberglass.
– Importance: The choice of material affects durability, weight, thermal conductivity, and resistance to environmental factors. For instance, aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for portable applications, while stainless steel offers superior strength for harsher environments. -
Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
– Definition: A standard that classifies and rates the degree of protection provided by an enclosure against the intrusion of foreign objects and moisture.
– Importance: Understanding IP ratings (e.g., IP65) helps buyers ensure that enclosures will perform adequately in specific conditions, such as dusty or wet environments, thus prolonging the lifespan of electronic components. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the enclosure.
– Importance: Tolerances are critical in ensuring that the enclosure fits the components correctly and operates without issues. Tight tolerances can prevent misalignments that may lead to performance failures. -
Thermal Management Features
– Definition: Design elements such as ventilation holes, heat sinks, or air conditioning systems incorporated to manage heat within the enclosure.
– Importance: Proper thermal management is vital to prevent overheating, which can damage sensitive electronic components. Buyers should assess whether the enclosure design adequately supports thermal dissipation for their specific applications. -
Protection Ratings (NEMA)
– Definition: Ratings that indicate the enclosure’s suitability for specific environmental conditions, primarily in the U.S. (e.g., NEMA 4 for water and dust resistance).
– Importance: Buyers must consider these ratings to ensure compliance with local regulations and standards, especially for outdoor or industrial applications. -
Modularity
– Definition: The capability of the enclosure to accommodate various configurations or components.
– Importance: A modular design allows for flexibility and scalability, enabling businesses to adapt their systems without needing a complete redesign, which can save time and costs.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to plan their purchases effectively and avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal request sent to suppliers to solicit pricing for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms, enabling informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact total costs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Relevance: Understanding lead times is crucial for planning project timelines and managing inventory effectively. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Compliance with industry standards such as ISO, CE, or UL that ensure product safety and reliability.
– Relevance: Buyers should verify that enclosures meet relevant certification standards to avoid regulatory issues and ensure product quality.
Equipping yourself with knowledge of these specifications and terminology will enhance your decision-making capabilities, ultimately leading to more efficient procurement processes and successful project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electronic enclosures Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electronic enclosures sector is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for protection of sensitive electronic components across various industries. Global drivers include the rise of IoT devices, advancements in telecommunications, and the expansion of renewable energy technologies. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evolve, there is a growing emphasis on durable and efficient enclosures that can withstand extreme environmental conditions while ensuring optimal performance.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Current B2B sourcing trends highlight a shift towards modular and customizable enclosure solutions. Manufacturers are increasingly offering products that can be tailored to specific applications, enabling buyers to optimize both functionality and cost. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies into enclosures is gaining traction, allowing for better monitoring and management of environmental conditions. This trend is particularly relevant for sectors like telecommunications and energy, where real-time data is crucial for operational efficiency.
Market dynamics indicate a rising focus on regulatory compliance and environmental standards. International buyers must navigate various certification requirements, such as IP and NEMA ratings, to ensure their enclosures meet local and international standards. Furthermore, as global supply chains adapt, buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who have established robust logistics capabilities to minimize lead times and reduce costs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming increasingly critical in the electronic enclosures market. The environmental impact of production processes and materials used in enclosures is under scrutiny, pushing manufacturers to adopt greener practices. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and utilizing eco-friendly materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. By choosing suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and sustainable sourcing methods, international B2B buyers can contribute to a more responsible industry. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS compliance for hazardous substances can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In terms of materials, there is a growing availability of ‘green’ alternatives for electronic enclosures. Biodegradable plastics, recycled metals, and eco-friendly coatings are gaining popularity, providing buyers with options that align with their sustainability goals. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly investing in technologies that reduce waste during production, further enhancing the appeal of eco-conscious sourcing.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electronic enclosures has been shaped by technological advancements and changing industry needs. Initially, enclosures were primarily designed for basic protection against dust and moisture. However, as electronic devices became more complex, the demand for enclosures that could provide thermal management, EMI shielding, and ergonomic design emerged.
Over the years, the materials used in enclosure manufacturing have diversified, transitioning from simple metals to advanced composites and plastics. This evolution reflects the need for lightweight, durable, and cost-effective solutions in a competitive market. Today, the focus on modular designs and smart technologies illustrates a significant shift towards enhancing user experience and operational efficiency, setting the stage for further innovations in the sector.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electronic enclosures
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of electronic enclosures?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, client testimonials, and production capabilities. Verify their certifications (like ISO 9001) for quality assurance. It’s also crucial to assess their compliance with international standards relevant to your region (e.g., NEMA for the U.S. or IP ratings in Europe). Request samples to evaluate material quality and craftsmanship. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales service and support to ensure they can address issues post-purchase. -
Can I customize electronic enclosures for my specific application?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electronic enclosures to meet specific requirements. Customization may include dimensions, materials, colors, and features such as cutouts for connectors or ventilation systems. Discuss your needs in detail with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and limitations. Be prepared to provide specifications and prototypes to facilitate the design process and ensure that the final product meets your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs for standard enclosures may range from 50 to 500 units, while custom designs might have higher MOQs. Lead times typically depend on production schedules and can range from a few weeks to several months, especially for customized products. Always clarify these details upfront to align your project timelines and budget. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international orders?
Payment terms for international orders often include options like advance payment, net 30/60/90 days, or letters of credit. Suppliers may require a deposit upfront, particularly for custom orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide you with sufficient protection, such as escrow services or payment upon delivery for larger orders. Always confirm the currency for transactions and consider any potential exchange rate fluctuations that may affect costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality management systems and certifications. Common certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management and IP ratings for environmental resistance. Ask for test reports or compliance certificates that confirm the enclosure meets industry standards. Additionally, consider conducting an on-site audit or third-party inspection if feasible, especially for large orders, to verify production practices and quality control measures. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing enclosures?
When importing electronic enclosures, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with the specific regulations in your destination country. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance, such as commercial invoices and packing lists. Factor in lead times for shipping and customs processing to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
Dispute resolution should be clearly outlined in your contract with suppliers. Establish terms for addressing issues such as quality discrepancies or delays in delivery. Common methods for resolution include negotiation, mediation, and arbitration. Ensure that both parties understand the process and agree on timelines for resolution. Maintaining open communication can help prevent misunderstandings and facilitate quicker resolutions. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with suppliers?
To foster a successful long-term relationship with suppliers, prioritize clear and consistent communication. Regularly share feedback on product quality and service experiences, and be open to discussing improvements. Establishing a partnership mentality can be beneficial; consider collaborating on product development or joint marketing efforts. Consistently meeting payment terms and honoring commitments will also strengthen trust and reliability, paving the way for future collaboration.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electronic enclosures
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronic enclosures, strategic sourcing has become an essential practice for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the significance of material selection, compliance with protection ratings, and the importance of thermal management can greatly enhance product reliability and performance. By prioritizing well-designed enclosures, businesses can safeguard sensitive components, ensure user accessibility, and optimize operational efficiency.
Key takeaways include the necessity of evaluating suppliers based on their ability to meet specific environmental requirements, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, and considering modular options for future scalability. Emphasizing these aspects not only mitigates risks but also drives innovation in product development.
Looking forward, the demand for customized, durable, and efficient electronic enclosures will continue to rise. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers that offer comprehensive support and a diverse range of products tailored to specific industry needs. By adopting a proactive sourcing strategy, businesses can position themselves advantageously in the global market, paving the way for sustainable growth and competitive differentiation.