Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Electrostatic Precipitator
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrostatic precipitator suppliers
Navigating the global market for electrostatic precipitator (ESP) suppliers is essential for businesses seeking effective air pollution control solutions. As industries worldwide face stringent environmental regulations and rising operational costs, the importance of reliable ESP systems cannot be overstated. These advanced devices not only enhance air quality but also ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks, such as the Clean Air Act, thereby safeguarding organizations against potential fines and enhancing their corporate reputation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted landscape of electrostatic precipitator suppliers, offering international B2B buyers—from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Poland and Kenya)—valuable insights to inform their sourcing decisions. Readers will explore various types of ESPs, the materials used in their manufacturing, and the quality control measures that ensure their reliability. Additionally, the guide outlines key suppliers, expected costs, and market trends, equipping buyers with the knowledge needed to select the right technology for their specific needs.
Whether you are a procurement officer in a cement plant or an environmental compliance manager in a chemical processing facility, this guide empowers you to make informed choices. By understanding the intricacies of the ESP market, you can streamline your purchasing process, optimize your operational efficiency, and contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment.
Understanding electrostatic precipitator suppliers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet Electrostatic Precipitators (WESPs) | Operate with a liquid medium, enhancing particle removal efficiency. | Power generation, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing. | Pros: High efficiency for sticky and fine particles. Cons: Higher maintenance due to water management. |
| Dry Electrostatic Precipitators (DESPs) | Use dry collection methods without liquid, suitable for high dust loads. | Cement manufacturing, steel production, and incineration. | Pros: Lower operating costs and energy efficiency. Cons: Less effective for sticky particles. |
| Industrial Electrostatic Precipitators | Designed for large-scale industrial applications with robust construction. | Heavy industries, automotive, and mining sectors. | Pros: High durability and capacity. Cons: Higher upfront investment. |
| Modular Electrostatic Precipitators | Flexible designs that can be easily expanded or modified. | Pharmaceutical, food processing, and small manufacturing units. | Pros: Scalability and adaptability. Cons: Potentially higher cost per unit area. |
| Electrostatic Precipitator Systems with Smart Technology | Incorporate IoT and AI for real-time monitoring and optimization. | Various industries focusing on sustainability and efficiency. | Pros: Enhanced performance tracking and predictive maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment and complexity. |
Wet Electrostatic Precipitators (WESPs)
Wet Electrostatic Precipitators utilize a liquid medium to improve the efficiency of particulate removal. This type is particularly suited for applications involving sticky or hygroscopic particles, making them ideal for power generation and wastewater treatment. When considering WESPs, buyers should evaluate the water management systems, as maintenance can be more intensive due to the need for consistent liquid flow and potential corrosion issues.
Dry Electrostatic Precipitators (DESPs)
Dry Electrostatic Precipitators are designed to handle high dust loads without the use of water. This makes them a popular choice in industries such as cement manufacturing and steel production. Buyers should consider the type of particulate matter in their processes, as DESPs may struggle with sticky particles. However, they offer lower operating costs and energy efficiency, making them appealing for large-scale operations.
Industrial Electrostatic Precipitators
These precipitators are built for heavy-duty applications, featuring robust construction to withstand harsh industrial environments. Commonly used in sectors like automotive and mining, they provide high durability and capacity. Buyers should weigh the upfront investment against the long-term benefits of reduced emissions and compliance with environmental regulations.
Modular Electrostatic Precipitators
Modular designs allow for easy expansion and modification, making them suitable for smaller manufacturing units and industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. Their flexibility is a significant advantage, but potential buyers should consider the cost implications of scalability. This type is particularly beneficial for businesses anticipating growth or changes in production capacity.
Electrostatic Precipitator Systems with Smart Technology
Incorporating IoT and AI technologies, these systems enable real-time monitoring and optimization of performance. They are increasingly sought after by industries prioritizing sustainability and operational efficiency. While they offer enhanced functionality and predictive maintenance capabilities, buyers must also consider the higher initial investment and complexity associated with implementing smart technologies.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of electrostatic precipitator suppliers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electrostatic Precipitator Suppliers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Emission control for coal-fired power plants | Achieves regulatory compliance and reduces environmental impact | Ensure ESPs meet local emission standards and are energy-efficient |
| Cement Manufacturing | Dust control in clinker production | Minimizes air pollution and enhances product quality | Consider durability under high temperatures and corrosive conditions |
| Steel Production | Particulate removal from blast furnaces | Improves air quality and operational efficiency | Look for customizable solutions for varying dust loads |
| Chemical Processing | Air purification in chemical plants | Protects worker health and maintains product integrity | Evaluate compatibility with specific chemical processes |
| Waste Incineration | Capture of fly ash and hazardous materials | Reduces landfill waste and enhances recycling opportunities | Assess the ability to handle varying waste compositions |
Power Generation
In the power generation sector, electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are crucial for controlling emissions from coal-fired power plants. These systems efficiently remove particulate matter, such as fly ash, from exhaust gases, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations. For international buyers, especially in regions with strict air quality mandates, selecting ESPs that meet local standards and optimize energy consumption is vital. Additionally, suppliers should provide robust service options for maintenance and support.
Cement Manufacturing
Cement manufacturing involves high levels of airborne dust during clinker production. Electrostatic precipitators are employed to capture this dust, significantly reducing air pollution. This not only helps cement producers comply with environmental regulations but also improves the quality of the final product by minimizing contamination. Buyers in Africa and South America should focus on sourcing durable ESPs that can withstand the harsh conditions typical in cement facilities, including high temperatures and abrasive materials.
Steel Production
In steel production, ESPs play a pivotal role in removing particulate matter generated during processes like blast furnace operations. By enhancing air quality, these systems contribute to a healthier work environment and improve overall operational efficiency. International buyers should consider the adaptability of ESPs to different production scales and dust load variations, ensuring that the selected equipment can handle specific operational demands effectively.
Chemical Processing
Chemical processing plants utilize electrostatic precipitators to purify air and manage emissions. These systems are essential for protecting worker health and maintaining the integrity of chemical products by preventing contamination from airborne particles. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers that offer ESPs with customizable features to suit specific chemical environments, including resistance to corrosive substances and varying humidity levels.
Waste Incineration
In waste incineration, electrostatic precipitators are vital for capturing fly ash and hazardous materials from exhaust gases. This not only minimizes landfill waste but also enhances recycling opportunities for incinerated materials. For B2B buyers, especially in regions with increasing waste management regulations, sourcing ESPs that can adapt to diverse waste compositions and provide efficient ash removal is crucial for compliance and operational success.
Related Video: How does an Electrostatic Precipitator installed
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrostatic precipitator suppliers
Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are critical for industries aiming to control air pollution effectively. The selection of materials used in their construction significantly impacts performance, durability, and overall system efficiency. Here, we analyze four common materials utilized in manufacturing ESPs, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength. It can withstand extreme conditions, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and long lifespan, which reduces maintenance costs over time. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which can impact initial project budgets. Additionally, manufacturing processes for stainless steel can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is particularly effective in environments with high humidity or corrosive gases, such as chemical processing plants. Its resistance to oxidation ensures that it maintains structural integrity over time.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. It’s important to consider local availability and pricing fluctuations, which can vary significantly.
2. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is characterized by its high strength and toughness. While it is less resistant to corrosion than stainless steel, it can be treated with coatings to enhance its durability.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of carbon steel is its lower cost compared to stainless steel, making it a budget-friendly option for many applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can lead to shorter lifespans if not properly maintained or coated.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is suitable for dry environments where corrosion is minimal. It is often used in less demanding applications, such as in power generation facilities.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings and regular maintenance to prevent rust and degradation. Compliance with local standards, such as ASTM A36, is also crucial for ensuring product quality.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It performs well in moderate temperature ranges and is often used in applications requiring reduced weight.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can reduce installation and transportation costs. However, it has a lower melting point than steel, making it less suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is ideal for applications with lower particulate loads and where weight is a critical factor, such as in mobile or temporary installations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider the environmental impact of aluminum production and ensure compliance with recycling standards. Additionally, understanding local market conditions can help in sourcing aluminum competitively.
4. Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
Key Properties:
FRP is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. It can withstand a wide range of chemical exposures, making it suitable for aggressive environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of FRP is its resistance to corrosion, which extends the life of the equipment in harsh environments. However, it may not have the same mechanical strength as metals, which can limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application:
FRP is particularly beneficial in chemical processing and waste management industries where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the FRP meets local standards for chemical resistance and durability. Understanding the specific chemical environment in which the ESP will operate is crucial for selecting the right grade of FRP.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electrostatic precipitator suppliers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, high-humidity environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Carbon Steel | Power generation, less demanding applications | Lower cost | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Mobile or temporary installations | Lightweight, reduces transport costs | Lower melting point | Medium |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic | Chemical processing, waste management | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide offers valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrostatic precipitator suppliers
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are critical for ensuring that these air pollution control devices meet the rigorous demands of various industries. For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can lead to better purchasing decisions and enhanced compliance with environmental regulations.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of electrostatic precipitators involves several distinct stages, each crucial for delivering a reliable and efficient product.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, typically including stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum. The choice of material is essential for ensuring durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall performance. Manufacturers often employ advanced material testing methods to verify the properties of the materials, ensuring they can withstand the operational conditions of the intended application.
2. Forming
In this phase, the prepared materials undergo various forming techniques such as cutting, bending, and welding. Precision machining is often utilized to create the intricate components that comprise an ESP, including discharge electrodes, collector plates, and hoppers. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines may be employed to enhance accuracy and reduce waste during fabrication.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are fabricated, they are assembled into the complete ESP system. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended. The assembly process often includes the installation of electrical systems, such as high-voltage power supplies, which are critical for the operation of the electrostatic charging mechanism.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves applying surface treatments to enhance the durability and performance of the ESP. Techniques such as galvanizing, powder coating, or applying anti-corrosion linings are common. These treatments not only protect the equipment from environmental factors but also contribute to its longevity and efficiency.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of electrostatic precipitators, ensuring that they meet international standards and customer specifications.
Relevant International Standards
Internationally recognized standards, such as ISO 9001, govern quality management systems and are essential for manufacturers aiming to enhance their operational effectiveness. Specific certifications that may also be relevant include:
– CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– API Standards: Relevant for industries such as oil and gas, ensuring equipment meets specific safety and quality benchmarks.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the manufacturing process, checking for adherence to design specifications and operational parameters during production.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts comprehensive testing on completed units before shipment to verify performance and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the functionality and reliability of ESPs, including:
– Electrical Testing: Verifying the performance of high-voltage components.
– Pressure Drop Testing: Ensuring the system operates efficiently with minimal energy loss.
– Performance Testing: Assessing the effectiveness of particulate removal under simulated operational conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions with varying regulatory landscapes, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is crucial. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. Buyers should consider both scheduled and random audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from testing and inspections. These reports should be easily accessible and transparent.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can help verify that suppliers meet industry standards and deliver products that align with contractual specifications. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with less stringent local regulations.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
When navigating the global market, B2B buyers must consider the nuances of quality control and certification that may differ by region. For instance:
-
Africa: Buyers should be aware of local environmental regulations that may differ significantly from international standards. Understanding regional compliance requirements is essential for ensuring that ESPs will be accepted by local authorities.
-
South America: Countries may have unique certifications that must be considered, such as INMETRO in Brazil, which focuses on product quality and safety.
-
Middle East: Many countries in this region are adopting international standards, but local requirements may still vary, requiring buyers to perform due diligence.
-
Europe (e.g., Poland): The EU has stringent regulations regarding air pollution control, making compliance with CE marking and other European standards imperative for manufacturers.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electrostatic precipitators. Prioritizing quality and compliance will not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to achieving environmental sustainability goals.
Related Video: What Is An Electrostatic Precipitator And How Does It Work?
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrostatic precipitator suppliers Sourcing
The cost structure for sourcing electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is multifaceted, comprising various components that influence the final pricing. Understanding these components can empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in ESP manufacturing include high-grade metals such as stainless steel and aluminum, which are essential for durability and corrosion resistance. The quality and type of materials can significantly impact costs, particularly in regions where raw material prices fluctuate.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and expertise required for manufacturing. Skilled labor is essential for precision fabrication and assembly, thus affecting overall pricing. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but could compromise on quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overheads, which can be reflected in more favorable pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tools and equipment necessary for the production of ESPs can be substantial. These costs are often amortized over production runs, influencing the price per unit.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent quality control measures ensure product reliability and compliance with environmental standards. Investment in QC can lead to higher initial costs but can result in lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to reduced failure rates.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs significantly affect pricing, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distances, customs duties, and local taxes can add to the overall expense.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary widely depending on market competition, demand, and the supplier’s positioning.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often yields better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Tailored solutions may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential increase in price.
-
Materials: Selecting higher-quality materials will elevate costs but can enhance longevity and efficiency, impacting TCO positively.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers offering certified products that meet international standards may command higher prices. However, these certifications can be crucial for regulatory compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge a premium. Conversely, newer or less-known suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market entry, but this comes with risk.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping can influence costs. Buyers should be clear on whether prices include shipping, insurance, and duties, as these can significantly affect the final invoice.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage your position as a buyer by negotiating terms, especially for larger orders. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality ESPs may yield long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances: Buyers from different regions should be aware of local market conditions that can affect pricing. For instance, tariffs and import taxes in Africa or South America may influence total costs, necessitating careful calculation.
-
Research Suppliers: Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Verify their credentials, quality assurance practices, and customer feedback to ensure you’re getting value for your investment.
Disclaimer
Prices for electrostatic precipitators can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. This analysis provides a general overview and should not be construed as indicative of specific prices. Always consult with suppliers for tailored quotes based on your requirements.
Spotlight on Potential electrostatic precipitator suppliers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electrostatic precipitator suppliers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrostatic precipitator suppliers
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge enables effective decision-making and fosters better communication with suppliers. Below are essential specifications and commonly used terms in the industry.
Key Technical Properties of Electrostatic Precipitators
-
Material Grade
The materials used in manufacturing ESPs significantly impact their durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum. High-grade materials resist corrosion and withstand extreme temperatures, which is essential in industries like power generation and waste incineration. Choosing the right material grade can reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of the equipment. -
Collection Efficiency
This specification indicates the percentage of particulate matter that the ESP can capture from the gas stream. High collection efficiency (often above 99%) is critical for compliance with environmental regulations. Buyers should assess the efficiency ratings to ensure that the equipment meets their specific air quality standards and operational requirements.
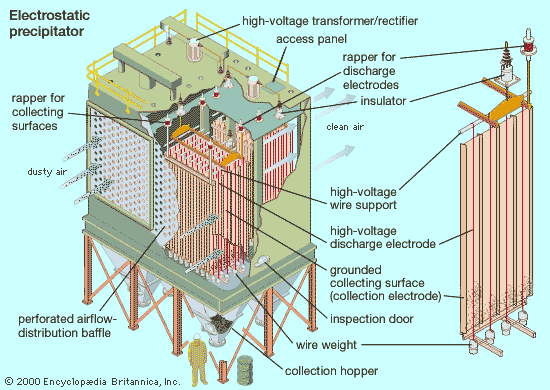
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Voltage Rating
ESPs operate using high-voltage power supplies to create the electrical field necessary for particle charging. Voltage ratings can range from tens to hundreds of kilovolts. Understanding the voltage requirements is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems and optimizing operational safety. -
Gas Flow Rate
The gas flow rate, typically measured in cubic meters per hour (m³/h), indicates the volume of gas that can pass through the ESP. This specification helps in sizing the equipment appropriately for different industrial applications. A mismatch in gas flow rate can lead to inefficient operation and increased emissions. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in dimensions or performance specifications. It is crucial for ensuring that the ESP components fit together correctly and operate as intended. Tight tolerances can enhance the overall reliability and effectiveness of the system, reducing the risk of operational failures.
Common Trade Terms in the Electrostatic Precipitator Industry
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce equipment that may be marketed by another company under its brand. For buyers, working with OEMs can assure quality and compatibility, as they often provide tailored solutions and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to ensure they can meet procurement needs without incurring excess costs or inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process through which buyers request price estimates from suppliers for specific products or services. This process helps buyers compare options and make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and costs associated with the delivery of ESPs. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their operations effectively and manage their supply chain efficiently.
- After-Sales Support
This term encompasses the services provided by suppliers after the sale is complete, including installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Reliable after-sales support can significantly impact the operational success of ESPs and should be a key consideration for buyers.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the most suitable electrostatic precipitator solutions for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electrostatic precipitator suppliers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and a rising focus on air quality management. Industries such as power generation, cement manufacturing, and steel production are pivotal in this trend, as they generate substantial particulate emissions. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, stringent compliance with environmental standards, such as the EU’s Industrial Emissions Directive, is compelling companies to invest in advanced air pollution control technologies.
Emerging technologies, including digital monitoring and predictive maintenance, are transforming the sourcing landscape for B2B buyers. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in ESP systems allows for real-time monitoring of particulate emissions and operational efficiency. This tech-driven approach not only enhances compliance but also reduces operational costs by minimizing downtime and maintenance needs. Additionally, the rise of modular ESP designs offers buyers flexibility in scaling operations based on demand, which is particularly advantageous for emerging markets.
Furthermore, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate innovation in their product offerings, such as ESPs that are designed for high efficiency at low energy consumption. The global shift towards sustainable practices is also shaping procurement strategies, with many companies favoring suppliers who employ eco-friendly materials and processes. For international B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is essential to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the procurement of electrostatic precipitators. The environmental impact of industrial operations is under scrutiny, and companies are expected to adopt greener technologies that minimize emissions. For B2B buyers, selecting suppliers who prioritize sustainability is essential not only for compliance but also for enhancing corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles.
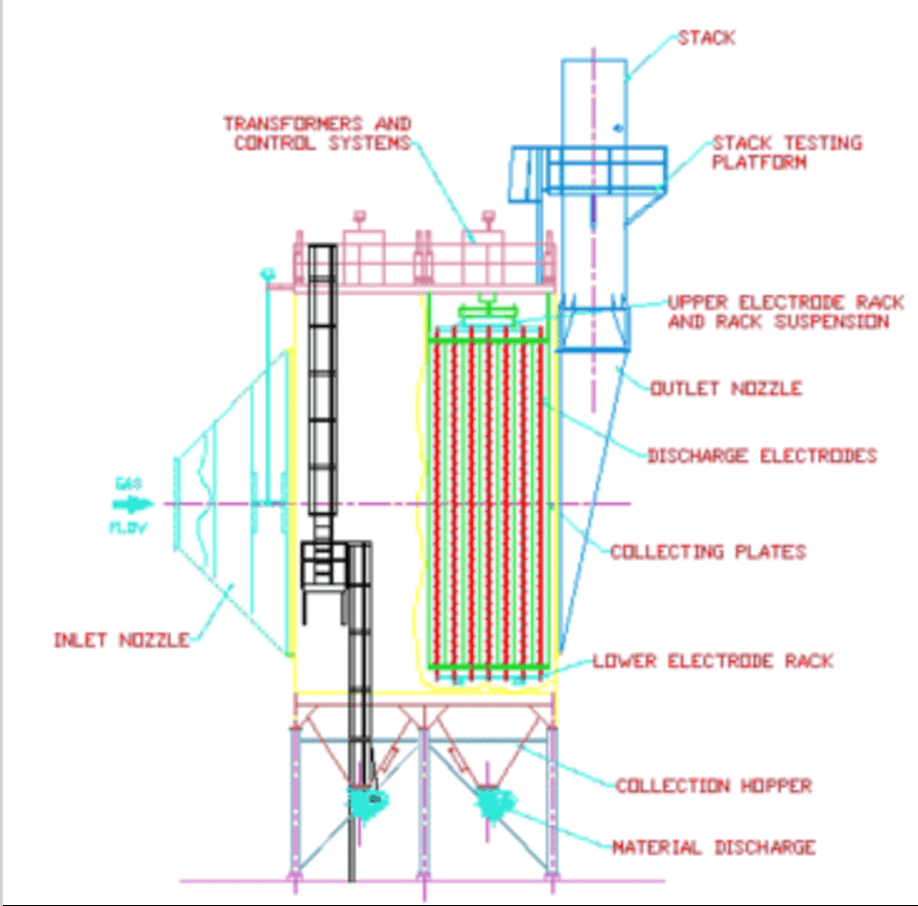
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
An essential aspect of sustainability in the ESP sector is ethical sourcing. Buyers should look for suppliers that implement transparent supply chain practices, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly. This includes the use of recycled or sustainable materials in manufacturing ESP components, which not only reduces environmental impact but also meets the growing demand for eco-friendly products.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Green Seal can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices. Additionally, choosing suppliers that utilize low-emission materials and technologies will significantly contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of industrial processes. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international B2B buyers can ensure compliance with regulations while fostering a positive brand image in their respective markets.
Brief Evolution/History
The development of electrostatic precipitators dates back to the early 20th century, with their initial use in the control of industrial smoke and dust emissions. Over the decades, advancements in electrical engineering and materials science have greatly enhanced the efficiency and effectiveness of ESPs. The introduction of high-voltage power supplies and improved designs has enabled these systems to capture even the smallest particulate matter, making them indispensable in industries that are heavy pollutants.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the regulatory landscape began to shift significantly, with governments worldwide imposing stricter emissions standards. This evolution has driven innovation in ESP technology, pushing suppliers to develop more advanced systems that not only comply with regulations but also offer improved energy efficiency and lower operational costs. As global awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, the evolution of electrostatic precipitators remains closely tied to the quest for cleaner air and sustainable industrial practices.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrostatic precipitator suppliers
-
How should I vet suppliers of electrostatic precipitators?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications, and customer references. Look for suppliers that comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Request case studies or references from similar projects, especially in your industry. It’s also prudent to assess their financial stability and reputation in the market. Engaging in site visits or virtual tours can also provide insights into their manufacturing capabilities and operational processes. -
Can electrostatic precipitators be customized for specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific operational requirements. This may include adjustments to the size, capacity, and materials used in the electrostatic precipitator. When discussing customization, provide detailed information about your operational parameters, such as gas composition, temperature, and particulate characteristics. Ensure that the supplier can demonstrate previous successful custom implementations, which can indicate their capability to meet your unique specifications. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electrostatic precipitators?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the complexity of the equipment and the customization required. Typical MOQs range from one unit to several units for large-scale projects. Lead times may also vary; expect anywhere from a few weeks to several months depending on the supplier’s production capacity and the complexity of your order. Always clarify these terms upfront to align your project timelines effectively. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering electrostatic precipitators?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and may include options such as upfront deposits, progress payments, or payment upon delivery. Common arrangements are 30% down payment with the balance due upon completion or delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide you with sufficient protection, such as payment milestones tied to specific project deliverables. Ensure that all terms are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings later. -
What quality assurance processes should suppliers have in place?
Reputable suppliers should have robust quality assurance protocols that adhere to international standards. Look for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates commitment to quality management. Ask about their testing procedures for electrostatic precipitators, including factory acceptance tests (FAT) and site acceptance tests (SAT). Additionally, inquire about their post-installation support and maintenance services, which are crucial for ensuring long-term operational efficiency. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international orders of electrostatic precipitators?
Logistics for international orders involve several factors, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Discuss with your supplier their experience in handling international shipments and any partnerships they have with logistics companies. Ensure that the supplier provides clear information regarding shipping costs, insurance, and liability during transit. It’s also beneficial to understand local regulations regarding import duties and compliance to avoid delays at customs. -
What should I do in case of disputes with the supplier?
In the event of a dispute, the first step is to refer to the contract terms regarding dispute resolution. Many suppliers will have specific procedures in place, such as mediation or arbitration, which can help resolve issues amicably. Maintain open communication with your supplier to discuss any concerns as they arise. Document all interactions related to the dispute, as this information can be valuable if the issue escalates and requires formal resolution. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for in electrostatic precipitator suppliers?
Yes, certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and regulatory compliance. Look for ISO certifications, especially ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, suppliers may hold certifications relevant to specific industries, such as compliance with the Clean Air Act or other local environmental regulations. These certifications not only assure quality but also demonstrate the supplier’s adherence to international best practices in environmental responsibility.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrostatic precipitator suppliers
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their air quality management and comply with environmental regulations. By selecting reliable suppliers who offer tailored solutions, organizations in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce emissions.
Key takeaways include the importance of understanding the specific needs of your industry, such as particulate characteristics and environmental compliance standards. Engaging with manufacturers who utilize advanced engineering and rigorous quality assurance processes will ensure the procurement of high-performing ESPs.
As the global market evolves, buyers should remain vigilant about technological advancements in ESP systems, which promise increased efficiency and lower energy consumption.
Now is the time to act. As environmental regulations tighten worldwide, proactively investing in effective air pollution control technologies will position your business as a leader in sustainability. Leverage strategic sourcing to establish partnerships with reputable suppliers and drive your operational success in a competitive landscape.