Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Extrusion Plastic
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for extrusion plastic
In today’s interconnected world, plastic extrusion stands as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, driving innovations across various industries, from construction to consumer goods. As global demand for sustainable and efficient production methods increases, understanding the intricacies of extrusion plastic becomes paramount for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide aims to equip you with the essential knowledge to navigate the complexities of this market, enabling informed sourcing decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore the different types of extrusion processes, the various plastic materials used, and the critical aspects of manufacturing and quality control. We will also provide insights into selecting the right suppliers, understanding cost structures, and analyzing current market trends. Additionally, we will address frequently asked questions to clarify common concerns and enhance your decision-making capabilities.
By leveraging this guide, you will gain a deeper understanding of how to optimize your procurement strategies, ensuring that you select the best extrusion solutions tailored to your specific needs. This knowledge will not only streamline your supply chain but also enhance your competitive edge in the global marketplace. As you embark on your journey through the world of extrusion plastic, let us empower your sourcing decisions with actionable insights and expert guidance.
Understanding extrusion plastic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tubing Extrusion | Produces hollow profiles like tubes and pipes. | Plumbing, medical devices, automotive | Pros: Versatile for various applications; Cons: Higher energy requirements for hollow profiles. |
| Blown Film Extrusion | Creates thin plastic films by inflating a tube. | Packaging, agricultural films, trash bags | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes; Cons: Limited thickness control. |
| Sheet Extrusion | Produces flat sheets for further processing. | Construction, signage, packaging | Pros: Uniform thickness; Cons: Requires additional processing for complex shapes. |
| Co-extrusion | Combines multiple materials in a single profile. | Food packaging, electronics, automotive | Pros: Enhanced properties through layering; Cons: Complex machinery and processes. |
| Profile Extrusion | Creates complex shapes with precise dimensions. | Window frames, door profiles, furniture | Pros: High customization; Cons: Longer lead times for custom dies. |
Tubing Extrusion
Tubing extrusion is ideal for producing hollow profiles such as pipes and tubes. This method is particularly useful in industries requiring durable and lightweight materials, such as plumbing and medical devices. Buyers should consider the specific material requirements, as different plastics offer varying levels of strength and flexibility. Energy consumption is a crucial factor, as producing hollow sections can demand higher power, impacting overall costs.
Blown Film Extrusion
Blown film extrusion is widely used to create thin plastic films, commonly found in packaging applications like shopping bags and agricultural films. This process is highly efficient for producing large volumes at a lower cost. However, buyers must be aware of the limitations in controlling film thickness, which can affect product performance. Understanding the end-use application is vital for selecting the right material for desired durability and flexibility.
Sheet Extrusion
Sheet extrusion produces flat plastic sheets that can be further fabricated into various products. This method is prevalent in sectors such as construction and signage, where uniform thickness and surface quality are critical. Buyers should evaluate the need for additional processing, as complex shapes often require further machining or fabrication. Selecting the right polymer type is essential to ensure compatibility with the intended application.
Co-extrusion
Co-extrusion allows manufacturers to combine different materials into a single extrusion, enhancing the final product’s properties. This technique is especially beneficial in food packaging and electronics, where barrier properties or aesthetic qualities are paramount. Buyers must consider the complexity of co-extrusion machinery and the potential for higher initial costs due to specialized equipment. However, the benefits of improved performance may justify these investments.
Profile Extrusion
Profile extrusion is characterized by producing complex shapes with precise dimensions, making it suitable for applications like window frames and furniture. Customization is a significant advantage, allowing buyers to meet specific design requirements. However, this process often entails longer lead times due to the need for custom dies, which can affect project timelines. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential delays in production.
Related Video: Extrusion Blow Molding – Lesson 2 – Plastic Behavior during Blow Molding
Key Industrial Applications of extrusion plastic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of extrusion plastic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Window and door profiles | Enhances energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal in buildings. | Look for suppliers with expertise in weather-resistant materials and custom profiles. |
| Packaging | Blow film for flexible packaging | Cost-effective production of lightweight and durable packaging solutions. | Ensure supplier can provide sustainable materials and compliance with international packaging regulations. |
| Automotive | Interior and exterior trim components | Reduces vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency and performance. | Source from suppliers with advanced materials that meet safety and durability standards. |
| Medical Devices | Tubing for medical applications | Ensures reliability and safety in critical medical environments. | Verify certifications for biocompatibility and quality control processes. |
| Consumer Goods | Custom containers and housings | Offers tailored solutions that enhance product usability and market differentiation. | Assess suppliers’ capabilities in customization and rapid prototyping for unique designs. |
Construction
In the construction industry, extrusion plastic is prominently used for manufacturing window and door profiles. These profiles offer improved thermal insulation and weather resistance, which are crucial for energy efficiency in modern buildings. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who specialize in custom profiles that meet specific architectural requirements and can provide materials that withstand local climate conditions. Additionally, understanding local building codes and standards is vital for compliance.
Packaging
Extrusion plastic plays a significant role in the packaging sector, particularly through blow film processes that create flexible packaging materials. These materials are lightweight yet robust, making them ideal for various applications, from food packaging to retail bags. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers who can provide sustainable options, as environmental regulations are tightening globally. Ensuring compliance with international packaging standards is also essential for market access.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, extrusion plastic is extensively used for producing interior and exterior trim components. Utilizing lightweight plastics helps reduce the overall weight of vehicles, which in turn enhances fuel efficiency and performance. Buyers should seek suppliers with expertise in advanced materials that comply with safety and durability standards required in the automotive industry. Additionally, collaboration on design and engineering can lead to innovative solutions that meet specific automotive needs.
Medical Devices
The medical industry benefits greatly from extrusion plastic through the production of specialized tubing for medical applications. This tubing must meet stringent safety and reliability standards, as it is often used in critical medical environments. International buyers should ensure that suppliers hold relevant certifications for biocompatibility and quality control. Understanding the specific requirements for sterilization and material properties is crucial for maintaining product integrity in medical applications.
Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods sector, extrusion plastic is utilized for creating custom containers and housings that enhance product usability. This application allows businesses to differentiate their products in a competitive market. Buyers should assess suppliers for their capabilities in customization and rapid prototyping, which can significantly shorten time-to-market for new products. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s production capacity and lead times is essential for effective inventory management.
Related Video: Plastic Extrusion
Strategic Material Selection Guide for extrusion plastic
When selecting materials for plastic extrusion, international B2B buyers must consider various factors to ensure the chosen material aligns with their product requirements and market standards. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in plastic extrusion, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse regions.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties: PVC is known for its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and low thermal conductivity. It can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F) and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PVC is its cost-effectiveness and versatility, allowing it to be used in a wide range of applications from construction to medical devices. However, it can be less flexible than other materials and may require additives to improve its properties, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: PVC is often used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, and window frames. Its compatibility with water and various chemicals makes it a preferred choice in construction and plumbing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding PVC use, especially in construction. Standards such as ASTM D1784 and EN 13245 are relevant in many regions, including Europe and the Middle East.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Key Properties: HDPE boasts a high strength-to-density ratio, excellent impact resistance, and a melting point of around 120-180°C (248-356°F). It is also resistant to many solvents and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and resistance to impact make HDPE ideal for outdoor applications. However, it can be more expensive than other plastics and may require specific processing conditions, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: HDPE is commonly used for packaging, containers, and piping systems due to its strength and resistance to environmental stress. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for chemical storage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA regulations) if using HDPE for food packaging. European buyers should be aware of the EN 13432 standard for biodegradable plastics.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Key Properties: ABS is known for its toughness, impact resistance, and ability to withstand temperatures up to 80°C (176°F). It also has good chemical resistance, particularly against acids and bases.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of ABS is its excellent surface finish and ease of machining, making it suitable for high-quality aesthetic applications. However, it is less resistant to UV light, which can limit its use in outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: ABS is widely used in automotive parts, consumer goods, and electronic housings due to its aesthetic appeal and durability. Its compatibility with various finishes makes it a popular choice for products requiring a polished look.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ABS products meet relevant safety and quality standards, such as ISO 9001. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is essential for chemical safety.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties: Polypropylene has a high melting point of around 160-170°C (320-338°F) and excellent chemical resistance. It is also lightweight and has good fatigue resistance.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of PP include its low cost and versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, it can be prone to environmental stress cracking, which may limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: PP is commonly used in packaging, automotive components, and textiles due to its lightweight nature and resistance to moisture. Its compatibility with various chemicals enhances its application in industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with local standards such as ASTM D4101 and EN 13432 for biodegradable plastics. In regions like Africa and South America, understanding local recycling regulations is also crucial.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for extrusion plastic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Plumbing, electrical insulation | Cost-effective and versatile | Less flexible, requires additives | Low |
| HDPE | Packaging, chemical storage | High strength and impact resistance | More expensive, specific processing | Medium |
| ABS | Automotive parts, consumer goods | Excellent surface finish | Less UV resistance | Medium |
| PP | Packaging, automotive components | Lightweight and versatile | Prone to environmental stress cracking | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into common extrusion plastics, aiding in informed decision-making for their specific applications and compliance needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for extrusion plastic
The manufacturing process for plastic extrusion involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality plastic products. Understanding these stages, along with the associated quality assurance measures, is essential for B2B buyers aiming to source reliable plastic extrusion components. Below is a detailed breakdown of the typical manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols.
Manufacturing Process
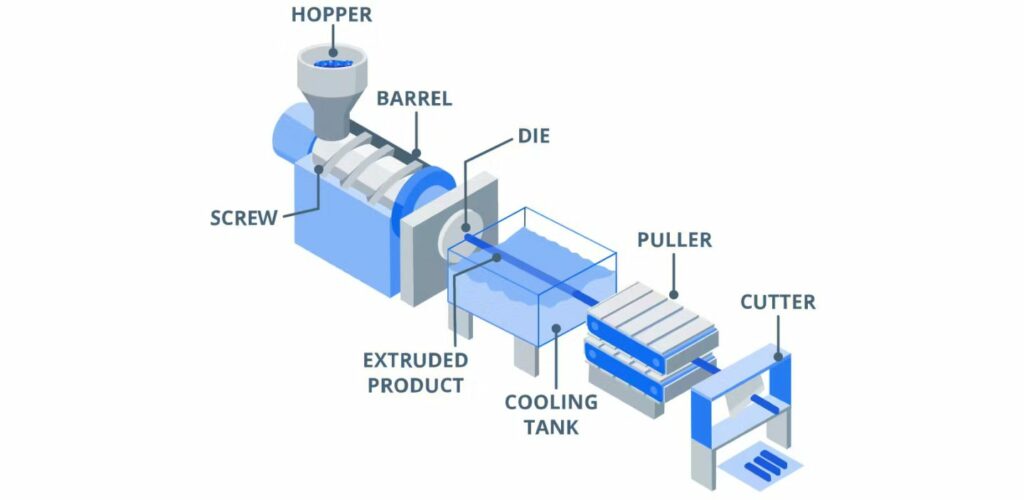
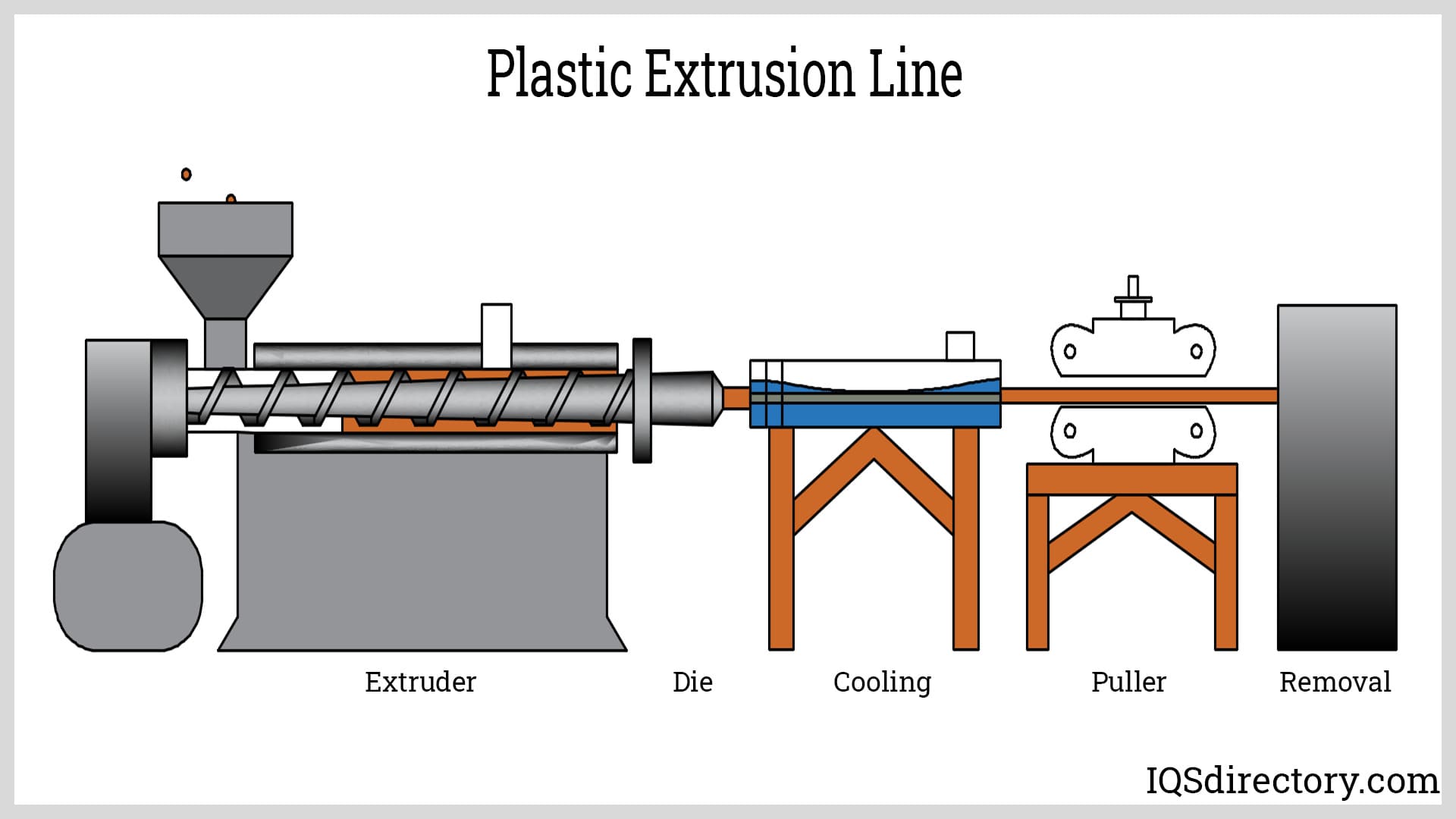
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the plastic extrusion process is material preparation, which involves selecting the appropriate type of plastic resin. Common materials include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The raw materials, typically in the form of pellets or granules, are stored in a hopper.
- Key Techniques:
- Drying: Some plastics may require drying to remove moisture, which can affect the quality of the final product.
- Blending: Different resins or additives may be blended to achieve specific properties, such as flexibility or UV resistance.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they are fed into the extruder, where they undergo a series of processes to be formed into the desired shape.
- Heating and Melting: The extruder features a heated barrel where the material is melted using a combination of heat and mechanical shear from a rotating screw.
- Extrusion through the Die: The molten plastic is forced through a die, which shapes it into a continuous profile (e.g., sheets, tubes, or custom shapes).
- Cooling: After exiting the die, the extruded plastic is cooled, typically using air or water cooling systems, to solidify the shape.
3. Assembly
In some cases, the extruded components may need to be assembled or combined with other parts. This could involve:
- Joining Techniques: Methods such as welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening to integrate different components.
- Secondary Operations: Processes like cutting, trimming, or machining to achieve precise dimensions.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes to enhance the product’s aesthetics or functionality.
- Surface Treatments: Techniques such as coating or polishing may be applied to improve appearance or resistance to environmental factors.
- Quality Check: Final inspections are performed to ensure compliance with specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the plastic extrusion process, ensuring that products meet international standards and specific customer requirements.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following quality standards relevant to plastic extrusion:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Applicable in industries like oil and gas, ensuring that products meet specific safety and quality criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To maintain high standards throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival for compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspections of finished products to verify they meet quality standards before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Quality control involves various testing methods to ensure product integrity:
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluating properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility.
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to ensure products meet specified dimensions.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, color consistency, and overall appearance.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps to conduct effective due diligence:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to assess manufacturing capabilities, equipment, and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports and certifications from suppliers to validate their compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspectors to perform unbiased assessments of the manufacturing process and final products.
- Sample Requests: Ask for samples or prototypes to evaluate the quality and consistency of extruded products before making bulk orders.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be mindful of specific nuances regarding quality assurance:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Be aware of different quality expectations and regulatory requirements across regions. For instance, European standards may be stricter compared to those in some African countries.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that communication regarding quality standards and specifications is clear and understood by both parties to avoid misinterpretations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Understand how logistics can impact quality. Delays and improper handling during transit can affect the integrity of plastic products.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in plastic extrusion, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality standards. This knowledge not only supports successful sourcing but also fosters long-term business relationships based on trust and quality.
Related Video: Plastic Extrusion Process Digital Work Instruction
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for extrusion plastic Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing for extrusion plastic sourcing is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will provide a comprehensive overview of the various cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for buyers.
Cost Components of Extrusion Plastic
-
Materials: The choice of plastic resin significantly impacts costs. Common materials include PVC, polyethylene, and polypropylene, each with varying price points based on market demand and availability. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally to reduce expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on geographical location and the complexity of the extrusion process. Regions with higher labor costs may necessitate a more extensive evaluation of supplier capabilities to ensure efficiency and productivity.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Understanding a supplier’s operational efficiency can help buyers gauge potential overhead costs embedded in pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often required for specific extrusion profiles. Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for bespoke designs, and should be factored into the total cost. Buyers are advised to clarify tooling responsibilities upfront.
-
Quality Control (QC): Effective QC processes ensure product consistency and compliance with specifications. While this adds to manufacturing costs, it is essential for minimizing defects and ensuring quality standards, especially in regulated industries.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling are critical components of total cost. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and freight rates can influence logistics costs. Buyers should evaluate Incoterms to determine who bears the risk and cost during transit.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin within their pricing structure. This margin can vary based on market competition, supplier reputation, and service levels provided. Understanding the competitive landscape is key for negotiation.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Order volume can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for buyers to negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized products usually incur higher costs due to the additional resources required for tooling and production. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the base price but also influences the overall performance and longevity of the product. Premium materials will increase initial costs but may offer better value over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) may charge more due to the assurance of higher standards. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Factors such as supplier reliability, experience, and geographical location can influence pricing. Suppliers in regions with lower operational costs may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for determining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect overall costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in open discussions about pricing structures and potential discounts based on order volume or long-term contracts. Effective negotiation can yield substantial savings.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront pricing. Evaluate factors like durability, maintenance, and disposal costs to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to economic conditions and market demand.
-
Research and Compare: Utilize industry networks, trade shows, and online platforms to gather quotes from multiple suppliers. This will provide a benchmark for pricing and help identify competitive offers.
Disclaimer
Pricing for extrusion plastic can vary widely based on numerous factors and is subject to change. This analysis provides indicative insights and should be complemented with direct supplier engagement for precise quotations.
Spotlight on Potential extrusion plastic Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘extrusion plastic’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for extrusion plastic
Critical Technical Properties of Extrusion Plastic
Understanding the essential technical properties of extrusion plastic is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the materials meet their project specifications and performance expectations. Here are some key properties to consider:
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Grade
Material grade defines the specific type of plastic being used, which can include options like PVC, HDPE, or ABS. Each grade has unique characteristics affecting durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance. For buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital as it influences product longevity and suitability for specific applications. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions during the extrusion process. This property is essential for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies. Buyers should emphasize tight tolerances for precision applications, as deviations can lead to functional failures and increased production costs. -
Melt Flow Index (MFI)
The Melt Flow Index is a measure of the viscosity of the plastic when molten. It indicates how easily the material can be processed during extrusion. A lower MFI means a thicker material, while a higher MFI indicates a more fluid material. Understanding MFI helps buyers select materials that will be manageable in their specific manufacturing processes. -
Impact Resistance
Impact resistance measures a material’s ability to withstand sudden forces or shocks without fracturing. This property is particularly important for products that will be subjected to rough handling or extreme conditions. Buyers should assess impact resistance to ensure that the final product can endure its intended use, particularly in industries like automotive or construction. -
Thermal Stability
Thermal stability refers to how well a material can maintain its properties under varying temperatures. This is critical for applications exposed to heat, as poor thermal stability can lead to deformation or failure. Buyers should verify the thermal stability of materials to ensure they will perform reliably in their operating environments.
Common Trade Terminology in Extrusion Plastic
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the extrusion plastic market. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is crucial for buyers sourcing components, as it relates to product quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers to consider when assessing costs and inventory needs. Understanding MOQs can help buyers optimize their purchasing strategies and manage cash flow effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It typically includes details such as quantity, specifications, and delivery terms. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to ensure they receive competitive pricing and terms that align with their project requirements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify logistics and responsibilities, reducing potential misunderstandings and disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and meeting customer demands. Buyers should confirm lead times with suppliers to ensure timely project execution.
By understanding these critical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline their procurement processes, and enhance their product offerings in the competitive landscape of extrusion plastic manufacturing.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the extrusion plastic Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global plastic extrusion market is influenced by several key drivers, including the growing demand for lightweight materials in automotive and construction sectors, advancements in extrusion technology, and the increasing application of plastics in various industries. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing decisions.
Currently, there is a notable trend towards automation and digitalization within the extrusion process. Advanced technologies such as Industry 4.0, IoT (Internet of Things), and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are being integrated into manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Buyers should seek suppliers who leverage these technologies to optimize production timelines and improve product quality.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a central theme in sourcing decisions. B2B buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers that prioritize environmentally friendly practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient machinery. In Europe, for instance, regulatory frameworks are pushing companies toward greener practices, which is also affecting sourcing strategies in other regions, including Africa and South America.
Emerging markets are witnessing a surge in demand for customized extrusion profiles, driven by local industries seeking tailored solutions. This shift opens opportunities for international buyers to collaborate with local suppliers who can provide specialized products that meet specific market needs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of plastic production and waste has made sustainability a critical concern for B2B buyers in the extrusion plastic sector. The industry is under pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and improve resource efficiency. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who implement sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled plastics and minimizing energy consumption during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers must consider the entire supply chain, from raw material extraction to product delivery. This involves assessing suppliers’ labor practices, environmental policies, and compliance with local and international regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for sustainable sourcing can guide buyers in selecting responsible partners.
Additionally, buyers should explore options for biodegradable plastics and bio-based materials, which are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional plastics. Engaging with suppliers who are committed to innovation in sustainable materials will not only enhance a company’s reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The plastic extrusion process has evolved significantly since its inception over a century ago. Initially limited to specific plastic types, modern advancements have enabled the processing of a diverse range of materials, allowing for greater flexibility in production. Innovations in machinery and technology have enhanced efficiency, enabling manufacturers to produce high-quality extruded products at lower costs.
Today, the extrusion process is integral to various industries, including automotive, construction, and packaging. The rise of customization in product offerings has further transformed the landscape, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements and supplier capabilities to remain competitive in the market.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of extrusion plastic
-
What should I consider when vetting a plastic extrusion supplier?
When vetting a plastic extrusion supplier, focus on their experience, reputation, and capabilities. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry, and verify their quality control measures, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, assess their production capacity to ensure they can meet your volume requirements. Visiting their facility, if possible, can provide valuable insights into their operations and commitment to quality. -
Can I customize my plastic extrusion orders?
Yes, most reputable suppliers offer customization options for plastic extrusion orders. You can specify dimensions, materials, colors, and any unique design requirements. Be clear about your specifications during the initial discussions. Suppliers with advanced tooling capabilities can accommodate complex designs, so ensure they have the necessary resources to meet your customization needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and project complexity. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times also depend on factors such as production capacity and the complexity of the order. It’s crucial to discuss these details upfront to align your expectations with the supplier’s capabilities and avoid delays in your supply chain. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications from suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO 9001. It’s essential to evaluate their testing procedures for the extrusion products, including material tests and dimensional checks. Asking for sample products or prototypes can also help you assess the quality before committing to larger orders. -
What should I know about logistics and shipping when sourcing extrusion plastics?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of your products. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight costs and delivery times to your location. Understand the supplier’s capabilities regarding international shipping, customs documentation, and insurance for your goods. It’s also wise to consider potential tariffs or import regulations in your country that could impact costs. -
How can I handle disputes or issues with my supplier?
To effectively handle disputes, establish clear communication channels from the beginning. Ensure all terms, including quality expectations, delivery schedules, and payment terms, are documented in a contract. In case of issues, address them promptly with the supplier, providing clear evidence of the problem. If necessary, consider mediation or legal routes based on the contract terms to resolve disputes amicably. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for plastic extrusion?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront deposits (20-50%), followed by the balance upon delivery or after inspection. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit both parties, considering options like letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
Are there sustainability considerations I should ask about?
Yes, sustainability is increasingly important in the plastic industry. Inquire about the supplier’s commitment to eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials or adopting energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Understanding their waste management and recycling programs can also help you align with your company’s sustainability goals, making your procurement more responsible and ethical.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for extrusion plastic
As the landscape of plastic extrusion continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains a cornerstone for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricacies of the extrusion process, from material selection to supplier capabilities, is essential for achieving high-quality outputs. Buyers must prioritize suppliers with proven expertise, robust quality assurance practices, and the flexibility to customize solutions based on specific project needs.
Key Takeaways:
– Define clear project requirements to facilitate effective supplier evaluation.
– Assess supplier capabilities and quality certifications to ensure they align with your standards.
– Engage in transparent negotiations regarding pricing and lead times to optimize cost efficiency.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable and innovative plastic solutions is set to rise, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage global partnerships and technological advancements to stay competitive. By fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers and embracing best practices in sourcing, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of the extrusion plastic industry.
Act now: Evaluate your sourcing strategy and explore new partnerships that can propel your business forward in this dynamic market.