Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Foundries In Minnesota
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for foundries in minnesota
In the ever-evolving global marketplace, Minnesota’s foundries stand out as a beacon of innovation and reliability for international B2B buyers. Renowned for their advanced manufacturing techniques and a diverse range of materials, these foundries cater to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The significance of Minnesota’s foundries lies not only in their capability to produce high-quality castings but also in their commitment to stringent quality control measures, ensuring that products meet the highest international standards.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of Minnesota’s foundries, detailing the various types of foundries available, the materials commonly used—including aluminum, zinc, and magnesium—and the manufacturing processes that define them. Additionally, it addresses critical factors such as supplier selection, cost considerations, and market dynamics, equipping buyers with essential knowledge to navigate their sourcing decisions confidently.
For international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in countries like Poland and France—this guide serves as a vital resource. It empowers you to make informed decisions by demystifying the complexities of sourcing from Minnesota’s foundries. By leveraging the insights within, you can enhance your procurement strategies, build robust supplier relationships, and ultimately drive your business’s success in the global arena.
Understanding foundries in minnesota Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting Foundries | Uses sand molds; versatile for complex shapes. | Automotive, aerospace, general manufacturing. | Pros: Cost-effective for low-volume production. Cons: Surface finish may require additional machining. |
| Die Casting Foundries | Employs high-pressure to force metal into molds. | Electronics, automotive components. | Pros: Excellent dimensional accuracy; suitable for high-volume production. Cons: Higher initial tooling costs. |
| Investment Casting Foundries | Utilizes wax patterns; provides intricate designs. | Medical devices, aerospace parts. | Pros: High precision and excellent surface finish. Cons: Longer lead times compared to other methods. |
| Permanent Mold Foundries | Uses reusable metal molds; ideal for aluminum and zinc. | Heavy machinery, automotive. | Pros: Good surface finish; efficient for large runs. Cons: Limited to simpler geometries. |
| Lost Foam Casting Foundries | Employs foam patterns that vaporize in the mold. | Construction, automotive parts. | Pros: Complex shapes without draft angles. Cons: Less common; may have limited supplier options. |
Sand Casting Foundries
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most versatile casting methods, where sand molds are used to create parts. This technique is particularly suitable for producing large and complex shapes, making it a popular choice in industries like automotive and aerospace. For B2B buyers, the key consideration is the cost-effectiveness for low-volume production runs, although it may require additional machining for a finer surface finish.
Die Casting Foundries
Die casting is characterized by injecting molten metal into steel molds under high pressure, resulting in parts with excellent dimensional accuracy. This method is ideal for high-volume production, especially in the electronics and automotive sectors. While die casting offers significant efficiency and precision, buyers should be prepared for higher initial tooling costs, which can impact overall project budgets.
Investment Casting Foundries
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is renowned for producing intricate designs with high precision. It is often used in industries requiring complex geometries, such as medical devices and aerospace components. Buyers should consider the longer lead times associated with this method, but the trade-off is a superior surface finish and accuracy, making it a preferred option for high-quality applications.
Permanent Mold Foundries
Permanent mold casting involves the use of reusable metal molds, typically for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and zinc. This method is efficient for larger production runs and provides a good surface finish. Buyers should note that while permanent mold casting is advantageous for producing consistent parts, it may be limited in terms of complex geometries compared to other casting methods.
Lost Foam Casting Foundries
Lost foam casting utilizes foam patterns that vaporize when molten metal is poured into the mold. This innovative method allows for the creation of complex shapes without the need for draft angles. It is suitable for various applications, including construction and automotive parts. However, due to its specialized nature, buyers may find fewer suppliers offering this technique, which could affect sourcing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of foundries in minnesota
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of foundries in Minnesota | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of engine components and transmission parts | Enhanced performance and durability of vehicles | Quality certifications, production capacity, lead times |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of lightweight, high-strength components | Improved fuel efficiency and safety in flight operations | Compliance with aerospace standards, material specifications |
| Energy | Creation of turbine components for renewable energy | Increased efficiency and reliability of energy systems | Custom design capabilities, material sourcing, testing |
| Construction | Fabrication of structural components and fittings | Cost-effective and durable solutions for projects | Material quality, production timelines, customization options |
| Medical Devices | Production of precision castings for medical tools | Enhanced accuracy and reliability in medical applications | Regulatory compliance, precision machining capabilities |
Automotive Industry
Foundries in Minnesota play a crucial role in the automotive sector by producing components such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission parts. These components are essential for improving the performance and durability of vehicles, which is vital in a competitive market. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should focus on suppliers that offer high-quality materials and have certifications to ensure compliance with automotive standards. Additionally, understanding the lead times for production can help in aligning with project timelines.
Aerospace Sector
In the aerospace industry, Minnesota foundries are known for manufacturing lightweight and high-strength components, including brackets and housings for aircraft systems. These components significantly contribute to fuel efficiency and safety in aviation, making them indispensable. Buyers from Europe, especially those in countries like Poland and France, should prioritize suppliers that meet stringent aerospace regulations and can provide detailed material specifications. Ensuring compliance with industry standards will mitigate risks associated with safety and performance.
Energy Sector
Foundries contribute to the energy sector by creating turbine components used in both traditional and renewable energy systems. The efficiency and reliability of these components are critical in optimizing energy production. International B2B buyers should consider sourcing from foundries that specialize in custom designs and have proven capabilities in handling diverse materials. Additionally, thorough testing and quality assurance processes are vital to ensure that the components meet operational demands.
Construction Industry
In the construction industry, Minnesota foundries fabricate structural components such as beams, columns, and fittings. These castings provide cost-effective and durable solutions for various construction projects. For buyers, especially those in the Middle East with large-scale developments, it is essential to evaluate the material quality and customization options available. Understanding production timelines is also crucial for project management and timely completion.
Medical Devices
Foundries in Minnesota also cater to the medical sector by producing precision castings for surgical instruments and diagnostic tools. The accuracy and reliability of these components are paramount in medical applications. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with regulatory standards specific to medical devices. Additionally, assessing the precision machining capabilities of foundries can help in sourcing high-quality products that meet stringent healthcare requirements.
Related Video: 10 Nifty Uses for Oscillating Multitool Saws
Strategic Material Selection Guide for foundries in minnesota
When selecting materials for foundries in Minnesota, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact product performance, cost, and compliance with industry standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in Minnesota foundries, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperature and pressure, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which extends the lifespan of cast components. However, it can be more expensive than some alternatives and may require specialized manufacturing processes, such as die casting, which can increase complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods applications due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and aesthetic appeal. It is compatible with various media, including fuels and lubricants.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B85 and EN 1706. Additionally, they should be aware of regional preferences for aluminum alloys, which can vary based on application requirements.
Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its high wear resistance and excellent machinability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of cast iron is its durability and ability to absorb vibrations, which is beneficial in machinery applications. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is widely used in automotive components, machinery parts, and construction applications. Its compatibility with high-temperature media makes it suitable for exhaust systems and engine blocks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with ASTM A48 and ISO 185. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for specific grades of cast iron can help ensure product suitability.
Zinc
Key Properties: Zinc die casting offers excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for intricate designs due to its fluidity during the casting process. It has a relatively low melting point, making it easier to work with.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of zinc is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing, which can lead to lower production costs. However, it is less durable than aluminum and iron, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Zinc is often used in automotive parts, hardware, and electronic enclosures. Its compatibility with various environments makes it a versatile choice for many applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B240 and ISO 3613. Additionally, awareness of local regulations regarding zinc content and environmental impact is crucial.
Magnesium
Key Properties: Magnesium is the lightest structural metal, offering excellent strength-to-weight ratios. It has good corrosion resistance, especially when treated, and performs well under high temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The significant advantage of magnesium is its lightweight nature, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to cast.
Impact on Application: Magnesium is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and electronic applications. Its lightweight properties make it suitable for components that require high performance without the added weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM B93 and EN 1753 is essential for international buyers. Additionally, understanding the specific alloy preferences in different regions can aid in selecting the right material.
| Material | Typical Use Case for foundries in Minnesota | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Iron | Machinery parts, engine blocks | High durability and wear resistance | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Zinc | Hardware, electronic enclosures | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Less durable than aluminum and iron | Low |
| Magnesium | Aerospace, automotive applications | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and challenging to cast | High |
This guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for foundries in Minnesota, helping them make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for foundries in minnesota
Manufacturing Processes in Minnesota Foundries
The manufacturing processes utilized by foundries in Minnesota are well-structured and adhere to high industry standards. This section provides an overview of the main stages involved in the manufacturing process, key techniques employed, and the quality assurance measures taken to ensure product integrity.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Raw Material Selection: Foundries typically use metals such as aluminum, zinc, and iron. The selection of materials is critical and often involves alloying to achieve specific properties.
– Melting: The chosen raw materials are melted in furnaces. Different furnaces, such as induction or electric arc furnaces, are used depending on the material type and desired properties.
– Pouring: Once molten, the metal is poured into molds. The mold design can vary, including sand casting, die casting, or investment casting, depending on the required precision and complexity of the part. -
Forming
– Casting: After pouring, the metal cools and solidifies in the mold. This stage is crucial as it determines the shape and initial properties of the component.
– Mold Removal: Once cooled, molds are removed, and the cast parts are inspected for defects. The efficiency of mold design can significantly impact production rates. -
Assembly
– Machining: This may involve processes such as milling, turning, or grinding to achieve the final dimensions and surface finish. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for precision.
– Joining Techniques: Components may require joining through welding, brazing, or adhesive bonding, depending on the application and material compatibility. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatments: Various techniques like shot blasting, polishing, or coating may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
– Final Inspection: Finished products undergo a thorough inspection to ensure they meet design specifications and quality standards before delivery.
Key Techniques Used
- Die Casting: This method is prevalent for high-volume production, especially with aluminum and zinc alloys. It offers superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Sand Casting: Ideal for both small and large parts, sand casting is versatile and cost-effective, making it suitable for low-volume production runs.
- Investment Casting: Known for its precision, this technique is used for complex geometries and is often employed in industries requiring high-quality components.
Quality Assurance in Minnesota Foundries
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process in foundries, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard focuses on quality management systems and is pivotal for foundries aiming to improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For foundries supplying to the oil and gas industry, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards is essential, ensuring products meet specific industry requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early. Techniques include visual inspections and measurements.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection phase verifies that finished products comply with specifications. This may involve testing for mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish.
Common Testing Methods
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and magnetic particle testing are employed to detect internal and surface defects without damaging the components.
- Destructive Testing: Tensile tests, impact tests, and hardness tests are conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of materials.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are some actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Request Quality Assurance Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation such as ISO certificates, test reports, and quality control plans to verify their adherence to standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to evaluate the supplier’s processes and products, providing an unbiased assessment of quality.
- Evaluate Past Performance: Review customer feedback, case studies, and references to gauge the supplier’s reliability and product quality.
QC Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When engaging with foundries in Minnesota, international buyers should be aware of certification nuances that may affect procurement:
- Understanding Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations and standards that may differ from your home country. This is particularly relevant for buyers from regions with stringent product standards.
- Language Barriers: Ensure that all quality documentation is available in a language you understand, as miscommunication can lead to quality issues.
- Cultural Differences: Be cognizant of cultural differences in business practices, which may impact communication and negotiation regarding quality expectations.
By leveraging these insights into manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing from Minnesota foundries, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for foundries in minnesota Sourcing
When sourcing from foundries in Minnesota, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure influenced by various factors. Understanding these components and their interplay will enable buyers to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant portion of the total expenses for foundries. Common materials include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Prices can fluctuate based on global market conditions, so it’s crucial to monitor these trends and factor them into your budget.
-
Labor: Labor costs in Minnesota tend to be higher than in some other regions due to the skilled workforce and labor regulations. This cost includes wages, benefits, and training. Buyers should consider the expertise level required for their specific casting needs, as complex projects may necessitate higher-skilled labor, impacting overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary significantly among foundries based on their operational efficiency and scale.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation of molds and dies specific to the buyer’s requirements. These can be substantial, particularly for custom components. Buyers should inquire about tooling amortization options to spread these costs over multiple production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential in the foundry industry to ensure product integrity and compliance with industry standards. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity of the inspection processes and certification requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are critical, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and packaging requirements can influence logistics costs. Buyers should explore different shipping options and Incoterms to optimize these expenses.
-
Margin: Foundries typically add a margin to cover profit, which can vary based on the complexity of the job, market demand, and competition. Understanding the average margins in the industry can provide a benchmark for negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often yield better per-unit pricing due to economies of scale. However, buyers should balance volume with actual project needs to avoid excess inventory costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized parts generally incur higher costs due to the additional engineering and tooling required. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected costs during production.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products meeting specific quality certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may command higher prices. Buyers should determine the necessary quality standards for their applications and factor these into their purchasing decisions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and reliability of a foundry can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms is crucial for budgeting and risk management in international transactions.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in proactive discussions with suppliers. Leverage volume commitments or long-term partnerships to negotiate better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider ongoing maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that may affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate exchange rate risks.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Utilize resources like Dun & Bradstreet or industry directories to compare pricing and services among different foundries. This information can provide valuable leverage during negotiations.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. It’s advisable for buyers to request detailed quotes tailored to their unique needs to ensure accurate budgeting.
Spotlight on Potential foundries in minnesota Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘foundries in minnesota’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for foundries in minnesota
Critical Technical Properties for Foundries in Minnesota
When engaging with foundries in Minnesota, international B2B buyers should be familiar with several key technical specifications that affect product quality, performance, and suitability for various applications. Understanding these properties can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of metals based on their properties, such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Common grades include ASTM A356 for aluminum castings and ASTM A536 for ductile iron. Knowing the appropriate material grade is essential for ensuring that the final product meets the specific requirements of your application, which can significantly impact durability and performance. -
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limits of variation in a dimension or physical property of the casting. It is crucial in ensuring that parts fit together correctly, especially in applications requiring precision engineering. Tighter tolerances often lead to higher production costs, so understanding your project’s needs can help in negotiating acceptable tolerances that balance quality and cost. -
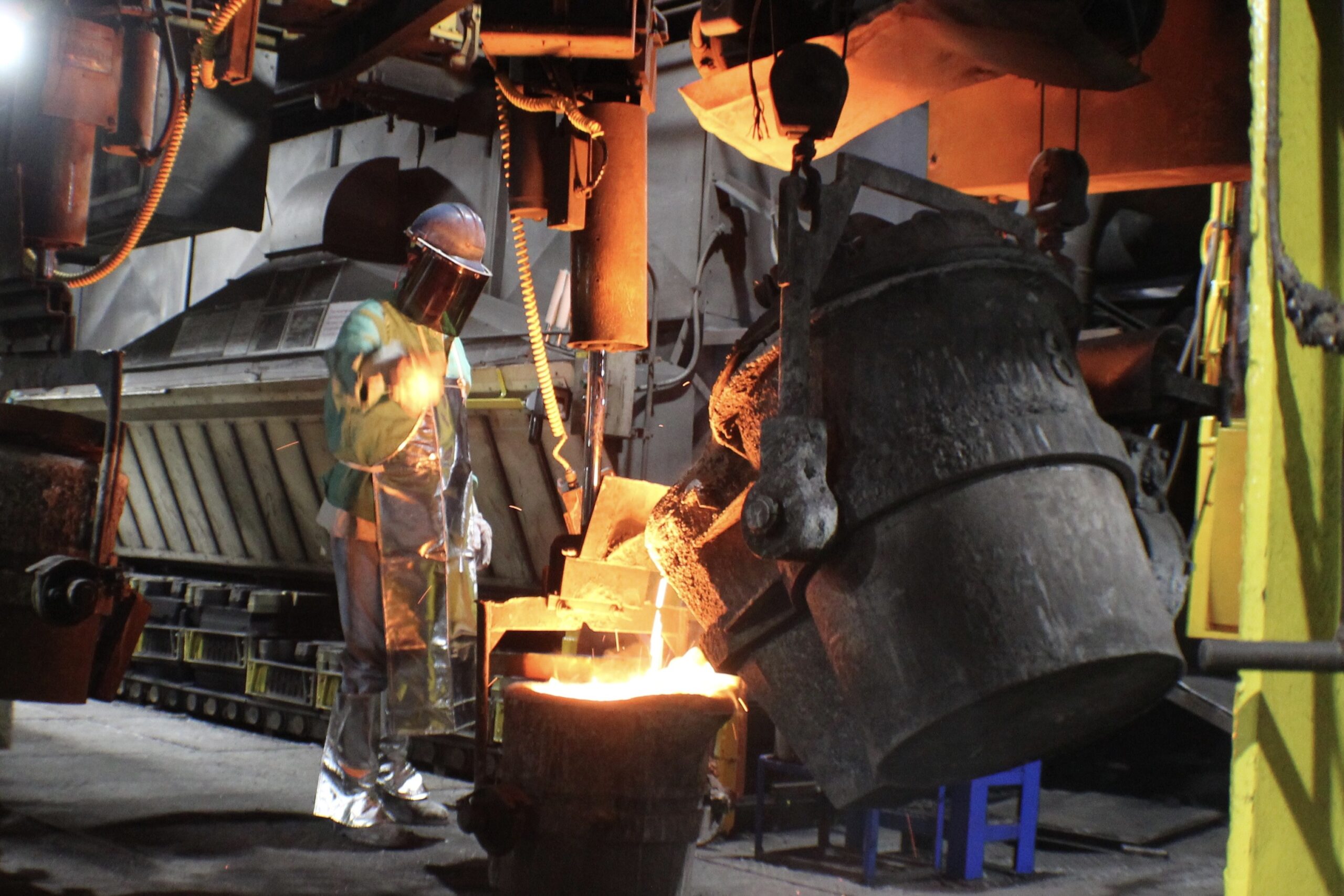
Casting Process
This encompasses the method used to create metal components, such as sand casting, die casting, or investment casting. Each process has distinct advantages and applications. For instance, die casting is ideal for high-volume production with intricate details, while sand casting is more versatile for various part sizes. Knowledge of the casting process can guide buyers in selecting the right foundry based on their project’s requirements.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Surface Finish
The surface finish is the texture of the casted part’s surface, which can affect its aesthetic appeal and functional properties, such as friction and wear resistance. Common surface finishes include as-cast, machined, and polished. Specifying the desired surface finish is important for both aesthetic considerations and functional performance in the final application. -
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as annealing or quenching, enhance the mechanical properties of cast metals, including strength and toughness. Understanding the heat treatment options available can help buyers select materials that are optimized for their intended use, particularly in demanding environments where material performance is critical.
Common Trade Terminology in the Foundry Industry
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication and negotiation processes between international buyers and Minnesota foundries. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is vital for buyers looking to procure components that fit within their existing systems or products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their orders effectively, ensuring they meet supplier requirements while avoiding excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and select the best option based on price, quality, and lead time. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers to understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. This is a critical consideration in supply chain management, as longer lead times can impact project timelines and overall business operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the foundry landscape in Minnesota more effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the foundries in minnesota Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The foundries sector in Minnesota is experiencing notable transformation driven by global market dynamics and technological advancements. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focusing on cost efficiency, quality, and speed in sourcing. Digitalization is reshaping the landscape, with technologies such as 3D printing and automation improving production processes and reducing lead times. The rise of Industry 4.0 principles is also encouraging foundries to adopt smart manufacturing practices, enabling real-time data analytics for better decision-making.
Emerging trends indicate a growing emphasis on customization and specialization. Buyers are looking for suppliers that can cater to specific industry needs, particularly in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Additionally, the demand for aluminum and zinc die castings is on the rise due to their lightweight properties and recyclability, which aligns with broader sustainability goals. As global supply chains become more interconnected, international buyers should prioritize partnerships with foundries that demonstrate agility and responsiveness to market changes.
The competitive landscape is further influenced by geopolitical factors, fluctuating raw material prices, and trade policies. Buyers from Europe, such as those in Poland and France, should remain vigilant about tariff implications and regulatory compliance when sourcing from Minnesota. Collaborating with local foundries can also present opportunities for innovation and joint ventures, leveraging Minnesota’s established manufacturing expertise.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies within the foundry sector. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adopt environmentally friendly practices. Foundries in Minnesota are responding by implementing energy-efficient technologies and reducing waste through recycling initiatives. The environmental impact of metal casting processes, particularly regarding emissions and resource consumption, necessitates a shift towards greener practices.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers seeking transparency in the supply chain. Foundries that can provide certifications for sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are more appealing to conscientious buyers. Additionally, the use of recycled materials not only reduces the ecological footprint but also aligns with the circular economy principles, which are increasingly important to stakeholders across various industries.
Buyers should evaluate potential partners based on their commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing. This includes assessing their supply chain practices, waste management strategies, and certifications. By prioritizing suppliers that uphold these values, international B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with environmental compliance and enhance their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Brief Evolution/History
The foundry industry in Minnesota has a rich history that dates back to the late 19th century, driven by the state’s abundant natural resources and skilled labor force. Initially focused on basic metal casting for local industries, the sector has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced technologies and methodologies over the decades. The introduction of die casting in the mid-20th century marked a pivotal shift, enabling manufacturers to produce more complex components with improved precision and efficiency.
Today, Minnesota’s foundries are recognized for their innovation and adaptability, catering to a diverse array of industries including aerospace, automotive, and machinery. As the sector continues to evolve, international B2B buyers can leverage this historical expertise to establish strong partnerships that drive both efficiency and sustainability in their supply chains.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of foundries in minnesota
-
What should I consider when vetting foundry suppliers in Minnesota?
When vetting foundry suppliers, focus on their industry experience, production capabilities, and certifications. Request references from previous clients, especially those in your industry, to gauge reliability. Verify their quality assurance processes and compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, assess their capacity to handle your specific needs, such as material types and production volume. A thorough supplier audit can help mitigate risks and ensure that you partner with a reputable foundry. -
Can Minnesota foundries accommodate customization requests?
Many foundries in Minnesota offer customization to meet specific client requirements. Engage in detailed discussions about your design needs, materials, and any technical specifications. Ensure the foundry has a robust engineering team capable of translating your concepts into workable designs. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate their capabilities. Establishing a clear communication channel will facilitate collaboration and help in achieving the desired outcomes in your custom orders. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for foundries?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times vary among foundries based on production capacity and complexity of the project. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times can also vary, typically from 4 to 12 weeks depending on the specifics of the order and current workload. Always discuss these aspects upfront to avoid surprises, and consider aligning your production schedules with the foundry’s capabilities. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted by Minnesota foundries?
Payment terms can differ significantly among foundries. Most will accept various payment methods, including wire transfers, letters of credit, and even credit terms for established relationships. It’s essential to clarify the payment schedule, including deposits and final payments, prior to initiating production. Establishing a clear agreement on payment terms can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother transaction process. -
How do Minnesota foundries ensure quality assurance and certifications?
Quality assurance in foundries typically involves rigorous testing and inspection processes. Most reputable foundries will possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which demonstrates adherence to international quality management standards. Inquire about their quality control measures, including material sourcing, in-process inspections, and final product testing. Request documentation of quality certifications to verify compliance and ensure that the foundry meets your quality expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing from Minnesota?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Understand the shipping options available, including freight forwarding and customs clearance processes. Discuss the foundry’s experience with international shipping and their ability to handle export documentation. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and duties when calculating total costs. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can help ensure timely and safe delivery of your orders. -
How can disputes with a Minnesota foundry be resolved effectively?
To minimize disputes, establish clear terms and conditions in your contract, including specifications, timelines, and payment terms. In the event of a disagreement, maintain open communication with the foundry to address issues promptly. Many foundries may have established dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration. Consider including a clause in your contract that outlines the steps for resolving disputes, which can help facilitate a smoother resolution process. -
What are the advantages of sourcing foundries in Minnesota for international buyers?
Minnesota boasts a strong manufacturing base with a reputation for high-quality foundry services. The state offers advanced technology, skilled labor, and a commitment to innovation, making it an attractive option for international buyers. Additionally, the proximity to major transportation networks can facilitate efficient shipping. Engaging with Minnesota foundries can provide access to specialized expertise and the ability to meet diverse casting needs, enhancing your supply chain reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for foundries in minnesota
The landscape of foundries in Minnesota presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking quality metal casting solutions. With a robust network of experienced foundries, Minnesota stands out for its commitment to precision, innovation, and sustainability. Key takeaways include the importance of leveraging local expertise to meet specific project requirements, and the potential for cost-effective sourcing through strategic partnerships with established foundries.
Strategic sourcing not only enhances supply chain efficiency but also facilitates access to advanced technologies and skilled labor. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can benefit from Minnesota’s diverse offerings, including aluminum and zinc die casting, which cater to a wide range of industries.
As global demand for high-quality castings continues to rise, Minnesota’s foundries are well-positioned to meet these needs. Engage with local suppliers to explore tailored solutions that can drive innovation and competitiveness in your operations. Embrace this opportunity to forge lasting relationships that will enhance your business’s capabilities and market reach.